-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Human Resource Management Research
p-ISSN: 2169-9607 e-ISSN: 2169-9666
2015; 5(4): 103-107
doi:10.5923/j.hrmr.20150504.03
Human Resource Management in MTR
Zhu Hanwen
Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai, China
Correspondence to: Zhu Hanwen, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This paper analysis some practical application of the human resource management and compares the difference between the homes and the abroad enterprises. Besides this, this paper takes the Mass Transit Railway Corporation Limited (MTR) as an example, and pays more attentions on the period of selection and training in MTR’s human resource management. After that, this paper concluded some advice from the MTR and aims to help the other companies, especially the urban railway transportation enterprises to have successful experiences to go by.
Keywords: Human Resource management, Selection, Training, the MTR
Cite this paper: Zhu Hanwen, Human Resource Management in MTR, Human Resource Management Research, Vol. 5 No. 4, 2015, pp. 103-107. doi: 10.5923/j.hrmr.20150504.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Attracted by the Chinese huge market, a lot of international enterprises chose china as their target market and swarm into it. They bring the latest technologies and the advantage management concepts, at the same time, they also desire human resource and consider the people as their great asset to the company. On this condition, international human resource management has been paid more attention by the international enterprises and the organizations.As an important management approach, the Human Resource Management has a great effect on employees’ behavior, attitudes, and performance. In the process of the Human Resource Management, selection and training play a vital role in the acquisition and preparation of human resources. So, a well selection can not only help the company to decide who will or will not enter the organization, but also will help the employee to fit the requirements of the job.
2. The Human Resource Management in Home and Abroad
- As Human resource plays an important role in society and economic life, human resource management becomes a practice which popular in foreign countries. With the rapid development of economic, more and more companies in our country realize the vital of the human resource management. So, study the history and the practice of HRM in home and abroad will have a positive effect in companies’ management.
2.1. The Human Resource Management in Foreign Countries
- Europe, cradle of the human resource management, has plays an important role in the management. There are a lot of theories and experience can others learning from.
2.1.1. The Human Resource Management in Britain
- The origins of human resource management in Britain can be traced to the nineteenth century, where its theories, experiences and early forms are clearly to be found, and its evolution can be traced through a number of phases over the past 100 or so years (John Berridge, 1992). Like the other countries, the human resource management in Britain has been formed by a complex interaction of forces, such as: economic, technological, social and legal. While HRM cannot be said to be firmly rooted in British business and industrial culture, it certainly is still in a state of change in terms of the status of the function, including its patterns of activity, and the orientations of its practitioners and managers, etc. The evolution of HRM in Britain has been a haphazard process, occurring in an uneven, unplanned, almost random fashion, and owing more to the environmental forces in industry, business and society than to rational, logical or central development. Until the 1970s (Berridge and Goodman,1998), across administrations of varying political complexions, the state's preferred role was to "hold the ring" rather than to intervene in terms of either institutions or substantive outcomes. Employers showed a reluctance to combine across all sectors of economic activity until 1965, when the first truly national body (the Confederation of British Industry) was formed: its personnel and industrial relations role has been muted, being largely representative in public relations forums.
2.1.2. The Human Resource Management in France
- The cultural context is the main characteristics of human resource management in France. Impact of Descartes and his method of analytical selection, when France people make analysis and thinking, they always separate out information in order to understand and manage others; use classification and ranking to take the qualitative dimension into account; and maintain a hierarchical distance to guarantee an apparent integration. All these characteristics are reflected in French management thinking and methods.Thus, HRM is permanently confronted by contradictory tendencies and this is one of its difficulties. Descartes' rigid approach (Ingrid Brunstein, 1992), which emphasized the importance of quantitative methods, has eroded social sensitivity towards the individual, yet employees are at the same time searching for a deeper comprehension of their personal and professional problems. In other respects, the same employees demonstrate an attitude towards authority which is in itself quite inconsistent.So, the France people do not submit easily to authority and find as many ways as possible to disobey the rules, and it has become obvious to them that authority is indispensable for collective action, which would only be hampered by deviating individualistic initiatives.
2.1.3. The Human Resource Management in Italy
- In recent years in Italy, as in the rest of Europe, new and profound changes have occurred both in institutions and in the economic and political world as a whole. (Carlo Alessandro Sirianni, 1992) In particular, assuming the competitiveness of the organization, a change in the model of human resource management becomes indispensable, above all for large companies.According to applied management theories, the personnel function in Italy has moved from an administrative role, such as: staff accountancy, legal and social security concerns to an auxiliary role, such as: the personnel office helping the other functions, then to a specialized functional role, and to a strategic role. Thus it is in a transitional phase from personnel management towards human resource management.
2.2. The Human Resource Management in Our Country
- With the rapid development in economic, more and more companies in our country realize the important role of the human resource management (Zeng Qing, 2007). The human resource management in our country experience four phases (Fang Guojun, 2013), including: the awareness phase of the human resource management; the forming phase of the human resource management; the develop phases of the human resource management and the strategic phrases of the human resource management.(1) The awareness period There are about 14 million people in our country, during a long period, we never worry about the use of the human resource. With the rapid development of the market, the government and the companies start to realize the importance of the human resource. But during this period, we just stay in the thinking stage and we still don’t know how to do that. (2) The forming periodAt the beginning, the human resource managers learn the theory from books and get the experience from foreign companies’ cases. After the study, some companies began to form their own system, which including: recruiting, selecting, training, performance management, etc. The beginning of the forming phase show we should from learning to use. (3) The develop period After the forming phases, with the further study and the experience in own companies, the human resource management become more and more matured. Quality, rather than quantity, becomes the new purpose which pursuit by the companies. During this period, the human resource manager began to pay more attention on the performance of the employees and establish a new salary system to meet the need of the company. After the job analysis and job descriptions, the manager will select more suitable people. With the revaluation of the salary system, the employee’s ability and performance will be improved and the company will become more efficient. (4) The strategic periodThe high degree of environmental instability, the rising level of competition, and the progressive globalization of economies and markets, all those make the companies pay more attention on human resource management. During the strategic period, human resource management will not only focus on itself, but also should fit the organization structure and meet the enterprise strategies. All those make the human resource management become a core element in the company’s competitiveness.
2.3. The Difference between the Home and Abroad Human Resource Management
- After the study of the home and abroad human resource management, we can easily find the human resource management was flourished by the economic boom. Compared with the long history of the foreign countries, our human resource management just stays in the beginning period. But at the same time, we are learning the advance management and formatting a system which suits us. Besides this, with the development of the globalization, our human resource management will not limited in Chinese market, the international human resource management will also become a key element in our future management.
3. Human Resource Management in MTR
3.1. Introduction of MTR
- Mass Transit Railway Corporation Limited (MTR) is the railway transportation operation systems in Hong Kong. The MTR operated by MTR Corporation Limited and has been providing a safe, reliable and efficient way to get around Hong Kong since 1979. In December 2007, the operations of MTR and Kowloon-Canton Railway Corporation have been merged to form one of the most efficient and far-reaching railway networks in Asia. The newly expanded system extends all the way from the heart of Central and Causeway Bay to the New Territories and Lantau Island.Today, the entire system stretches 218.2km and has 84 stations and 68 Light Rail stops. MTR operates nine main commuter lines serving Hong Kong Island, Kowloon and the New Territories. Among them, the East Rail Line connects to the boundary at Lo Wu and Lok Ma Chau stations for travel between Hong Kong and Shenzhen. In addition, a Light Rail network serves the local communities in the North West New Territories, while a fleet of buses provides convenient feeder services. The MTR also operates the Airport Express, a dedicated express rail link providing the fastest connections to Hong Kong International Airport and Asia World-Expo. Passengers can also travel with ease to Guangdong province, Beijing and Shanghai in the mainland of China using the MTR's intercity railway services. MTR Corporation is widely recognized as the provider of a world-class public transport service that consistently achieves the highest international standards in reliability, safety and efficiency. With passengers consistently arriving at their destinations on time 99% of the time, more than ever, passengers are counting on the MTR to provide fast and convenient connections to most locations in Hong Kong and beyond.
3.2. Human Resource Management in MTR
- Faced with the shortage of human resource, the MTR find two ways to solve this problem: the external sources and the internal sources. Those two ways all have advantages and disadvantages and the MTR analysis them as follow:(1) The external sourcesThe advantage managers and skilful employees come from advantage countries, such as Germany, Great Britain, Unite States of America, etc are the main external sources in the MTR. Those external employees sources have advantages such as the employees who come from advanced countries will bring latest and advanced technology and knowledge to the MTR, but at the same time, the external sources also have some disadvantages such as they always need expensive costs and there will have the communicate problems between the foreign employees and the local employees.(2) The internal sourcesThe main internal source of the MTR is to provide enough training programs to its employees. After the study and training, the employees will obtain advantage skills and high technologies. No doubt, the internal sources have the advantage such as the lower costs, the employees have relatively knowledge about the MTR and they will know the real need of the job, etc. But the MTR also find there are disadvantages in the internal sources, such as the training always need more times and sometimes the technologies will out of date.Considering the advantages and disadvantages of those two ways, the MTR decided to combine those two ways with their advantages and minimizes the disadvantages, for example, at the beginning of the company and some vital positions, the MTR will invite advantaged foreign employees, and with their helps, the MTR will find the ways which most suit themselves and finally improve the employees overall qualities and promote the development in an all-round ways.
3.3. The Training Resources and Projects in MTR’s Human Resource Management
- The MTR invest abundant training resources to cater for its employees professional and technical development needs. The MTR’s comprehensive staff development programmers, innovative Learning Organization, and self-paced multimedia learning facilities are highly valued by their staff, and a fast-track career path is open to high-fliers through the MTR’s Leadership Pipeline. There are many training and development programmers as follow:(1) The Graduate Trainee (GT) ProgrammeThe Graduate Trainee (GT) Programme is part of our Integrated Leadership Pipeline which aims at developing programme participants along the general management path under an accelerated 2-year programme. GTs will have intensive cross-functional job rotations in 3-4 core functions (with a typical duration of 6 months each) to gain in-depth knowledge and hands-on experience.From the 3rd year onwards, The Graduate Trainee will take up placement with senior supervisory responsibilities in a business function. The Graduate Trainee with academic qualifications recognized by the Hong Kong Institute of Engineers (HKIE) may undergo HKIE accredited Scheme 'A' Training in pursuit of chartered engineer status. After that, the Graduate Trainee may have job rotations in, but are not limited to, the following functions: Operations; Projects; Property; China & International Business; Commercial & Marketing; Corporate Relations.Customized development initiatives in the Graduate Trainee Programme are structured and comprehensive, including: Intensive induction programme; Experiential team-building workshop; Cross functional rotations; Management and leadership training workshops; Action learning projects; Mentoring; Study trips; Participations in corporate events; Outward Bound Training; Executive sharing sessions; Community services/volunteering work.
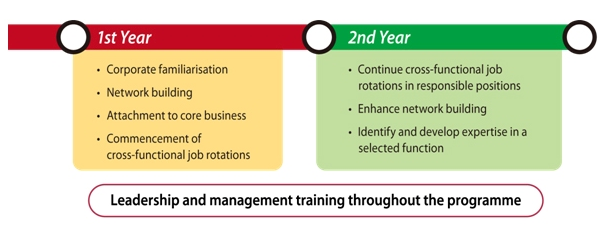 | Figure 1. The leadership and management training throughout the programme |
3.4. Selection in MTR
- There are many position vacations in the MTR, this paper use the Graduate Trainee Programme as an example to explain the selection process in MTR.After the study of MTR and its selection process, this paper found the MTR always decide the person who will or will not enter the organization by some steps such as: (1) explore the job vacation on home web sites; (2) make a career talk in colleges or universities; (3) ask the applicants to finish a testing paper; (4) take an interview; (5) invite the applicants to take part in the cognitive ability tests; (6) have a phone call interview; (7) give you the offer.(1) Explore the job vacation on home web sitesAt the MTR’s web sites, you will easily to find the job vacations. If you take the Graduate Trainee Programme as an example, you will find this position need the final year students or recent graduates from engineering, transportation, business and related disciplines with excellent academic results and the following qualities, such as: strong leadership potential and interpersonal skills; good commercial acumen; strong problem solving skills; Strong adaptability and flexibility; passion and commitment; high mobility to travel and work in the Mainland of China/overseas; strong alignment with MTR Values; excellent command of English and Chinese (including Putonghua). If you meet those requirements, you can go to the MTR’s career talk site and make an application. (2) Make a career talk in colleges or universitiesOn every October or November, the MTR will make some career talk in colleges or universities. When it arrived in Shanghai, it always choose Shanghai Jiao Tong University and TongJi University as the site for its’ career talk. During the talk, the MTR will not only introduce their company, but also share some information of the Graduate Trainee Programme. At the same time, the career talk also is a good opportunity for the applicants to learn more information about the MTR. (3) Ask the applicants to finish a testing paperAfter the career talk, the MTR will ask the applicants to finish a testing paper. This test paper will lasting 45-50minutes and including logic; mathematics; error detection and correction; translate passages; situation speech, etc. The aim of the testing is to learn the applicants’ abilities in language capacity; logic capacity and problem solving capacity. (4) Take an interviewThough the interview, the MTR will get some information about the applicants, including the learning experiences, work experiences, etc. At the same time, the MTR will also learn the applicants’ ability in foreign language and whether he/she will have a good communicate with each other.(5) Invite the applicants to take part in the cognitive ability testsThe cognitive ability tests including: verbal comprehension; quantitative ability; reasoning ability. The MTR will ask the third-part assessment, such as the SHL to help them invite the applicants to finish the cognitive ability tests. The cognitive ability tests including verbal reasoning test; numerical reasoning test; inductive reasoning test; personality, etc. (6) Have a phone call interview Once the applicants pass the interview and the tests, he/she will have a phone call interview. The interviewer will be the manager of the MTR and this interview always will be the final interview.(7) Give you the offer At the final of the selecting, the MTR will send the applicants an offer, which including the job analysis and salary.
4. Conclusions
- “Caring for life’s journeys” is the core concept in the MTR. This company not only applies it during their passenger service, but also uses it on their employee’s career planning. In the human resource management in the MTR, there are two ways we can learn from it:(1) Provide variety kinds of training program in training periodAs mentioned above, the MTR invest abundant training resources for its employees, including: the Graduate Trainee Programme, the Apprentice Training Scheme, etc. All these trainings met the different employees’ professional and technical development needs. Each employee can choose their suitable training program to improve their ability and pursuit their more bright career future. (2) Introduce the professional third - party evaluators in selection periodDiffer from some tradition companies, the MTR as an international company, they always introduce the professional third-party to evaluates their candidates. This method can help the company select their future employees more effective and fair. Therefore, it’s a feasible way for us to learn from. As an advanced company in urban railway transportation, The MTR has provided a great deal of experiences in human resource management. With the rapid development in Chinese urban railway transportation, we need to learn the MTR’s referential methods and experiences. Only in this way, can we discover some application value and improve our mainland urban railway transportation enterprises.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML