-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Human Resource Management Research
p-ISSN: 2169-9607 e-ISSN: 2169-9666
2015; 5(1): 1-11
doi:10.5923/j.hrmr.20150501.01
Non-Traditional Expatriate Assignments in the Asia-Pacific: Characteristics & Challenges
Noorziah Mohd Salleh1, Alan Nankervis2
1Faculty of Business Management, Universiti Teknologi Mara, Sabah, Malaysia
2School of Management, Curtin Business School, Curtin University
Correspondence to: Noorziah Mohd Salleh, Faculty of Business Management, Universiti Teknologi Mara, Sabah, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Despite reported increases in the number of non-traditional international assignments and assertions that it is an alternate way of undertaking international assignments, few researchers have conducted empirical studies of the phenomenon. Further, the success or failure of non-traditional expatriates can be as significant as that of traditional expatriates. Although their failure may not be as costly that for traditional expatriates, unsuccessful non-traditional expatriates can be rather expensive and the cumulative cost of their failure could become as high as the cost of traditional expatriate failure. In addition, the detrimental effects in terms of costs, diminished expatriates’ morale, and missed business opportunities, could cause considerable damage to their organisations. As such, understanding the new expatriate assignments, particularly the reasons for undertaking the assignments, is crucial. This paper discusses the reasons for using non-traditional expatriate assignments and associated knowledge transfer from a sample of such managerial employees. This study used a convergent interview technique to obtain authentic responses.
Keywords: Non-traditional expatriates, International assignments, Short-term expatriates, International staffing
Cite this paper: Noorziah Mohd Salleh, Alan Nankervis, Non-Traditional Expatriate Assignments in the Asia-Pacific: Characteristics & Challenges, Human Resource Management Research, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2015, pp. 1-11. doi: 10.5923/j.hrmr.20150501.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The rapid pace of internationalisation and competition among international organisations has led to growing emphasis on expatriate assignments across the world. One of the consequences of the global economic growth has been an increase in expatriate assignments (KPMG, 2010). It is claimed that expatriates are important in organisations and the costs associated with sending them overseas are very high (Fenwick, 2004). KPMG reports that 80 percent of 1000 organisations studied have recently undertaken overseas assignments for shorter periods, due to the failure of long-term assignments (Petrovic, Harris, & Brewster, 2000). Tahvanainen, Welch and Welch (2005) suggest that short-term expatriate assignments are an effective alternative to more traditional approaches. Many different types of short-term assignment are introduced in the literature such as ‘short-term’ (Bharadwaj, 2000), ‘non-standard’ and ‘international commuter’ (Minbaeva & Michailova, 2004; Tahvanainen et al., 2005), ‘flexpatriate’ (Collings, Scullion, & Morley, 2007; Mayerhofer, Hartmann, Michelitsch-Riedl, & Kollinger, 2004), ‘international business traveller’ (Mayerhofer, Hartmann, & Herbert, 2004; McKenna & Richardson, 2007) or ‘frequent flyer’ (Welch, Welch, & Worm, 2007) 2007), and ‘boundary spanner’ (Collings et al., 2007) These terms have a range of definitions which have raised questions about the purposes of short-term assignments and the issues surrounding them, notably knowledge transfer. To date, few studies have been undertaken on these issues, some of which were not empirical studies but merely collections of literature. The findings gathered from interviews in this study indicate that organisations usually do not have specific terms for expatriates who undertake temporary international assignments. It appears that, to date there is no universal term for the short term expatriates. In fact, one research study found that 32 percent of its respondents did not record the number of their personnel who had undertaken short-term assignments (Petrovic et al., 2000). Although there was no rationale given in the study, it can be assumed that the reason is possibly due to the informal procedures used for selecting short-term expatriates (Tahvanainen et al., 2005). A rigorous literature review reveals that time is the key factor distinguishing short-term from long-term assignments. Therefore, the duration of an assignment can be used as the key factor to define the assignments. Using duration as a decisive factor, most of the non-traditional assignments such as short-term, international assignments, and international business travellers have one thing in common: they are undertaken in less than one year. The purposes of the assignments are described as troubleshooting, controlling, and management development, and they involve durations of 1 to 12 months, unaccompanied by family, and the selection procedures are mostly informal - minimal bureaucracy or training (Tahvanainen et al., 2005). To differentiate short-term and long-term assignments, this paper uses the term ‘traditional assignment’ to refer to long-term assignments that are undertaken for more than one year, and the term ‘non-traditional assignment’ to describe assignments that are undertaken in less than one year.
2. Problem Statement
- Non-traditional assignments are reported to have emerged in the late 1980s and 2000s (Dowling & Welch, 1988; Petrovic et al., 2000). A number of studies show that companies have been utilising these new ways of doing international business (Harris, 2002; Mayerhofer, Hartmann, & Herbert, 2004). Therefore, understanding the reasons for using these types of assignments is crucial. Further, the success or failure of non-traditional expatriate assignments can be as significant as for traditional assignments. Although non-traditional expatriate assignments may not be as costly as traditional assignments, the cumulative costs of their failure could be similar to the costs of traditional assignments. Additionally, the detrimental effects, diminished employee morale, and missed business opportunities could add overall damage to organisations. Evidence shows that one of the roles of expatriates is as knowledge transferror (Bonache, Brewster, & Suutari, 2007; Bonache & Zarraga-Oberty, 2008; Harzing, 2001b; Riusala & Suutari, 2004), and the knowledge being transferred is varied, including management, marketing, technology, company policy and know-how, and corporate image (Bonache & Zarraga-Oberty, 2008; Hocking, Brown, & Harzing, 2007; Mayerhofer, Hartmann, & Herbert, 2004; Minbaeva & Michailova, 2004; Riusala & Suutari, 2004), however, a study by Harzing (2001b) shows that only technical knowledge is being transferred. This is clearly not comprehensive. Thus, there is an urgent need to study the knowledge transfer characteristics. Next, a different perspective of knowledge presented by Hocking, Brown and Harzing (2007) shows that knowledge is a generic intent of all strategic expatriate assignments and that only the type of knowledge involved and its means of transfer vary from one assignment purpose to another. Therefore, the clarification of the type of knowledge transferred is significant to depict not just the assignments but also the ways it is being conveyed.There is also a need to identify the knowledge transfer direction since the current literature explains that the direction of knowledge being transferred was merely between headquarters and subsidiaries (Harzing, 2001b). Measurement used by Mudambi & Navarra (2004) was taken to identify the directions involved. There are four direction identified in knowledge transfer process. The first direction involves providing knowledge and skills to the subsidiary. The second direction involves providing knowledge and skills to the parent corporation. The third direction involves receiving knowledge and skills from the parent corporation. The fourth direction involves receiving knowledge and skills from the subsidiary (Mudambi & Navarra, 2004). Previous studies merely studied the direction between headquarters and subsidiaries.
3. Purpose of Study
- This paper reports the reasons for using non-traditional expatriate assignments from the perspective of those engaged in the phenomenon. The differences between the reasons for using traditional and non-traditional assignments could aid the choice between the uses of those assignments. It may also assist in the development of a more comprehensive instrument to measure non-traditional expatriate performance. The aims of this study are, firstly, to identify the reasons for using non-traditional assignments by gathering and analysing the perspectives of those who are engaged; and secondly, to investigate the relationships between the perceived importance of their assignments with their backgrounds. Thirdly, discussing the differences between the use of traditional and non-traditional assignments, and fourthly, suggesting the selection criteria to select non-traditional expatriates. Finally, to identify knowledge characteristics and the directions involved in transferring the knowledge.
4. Methodology
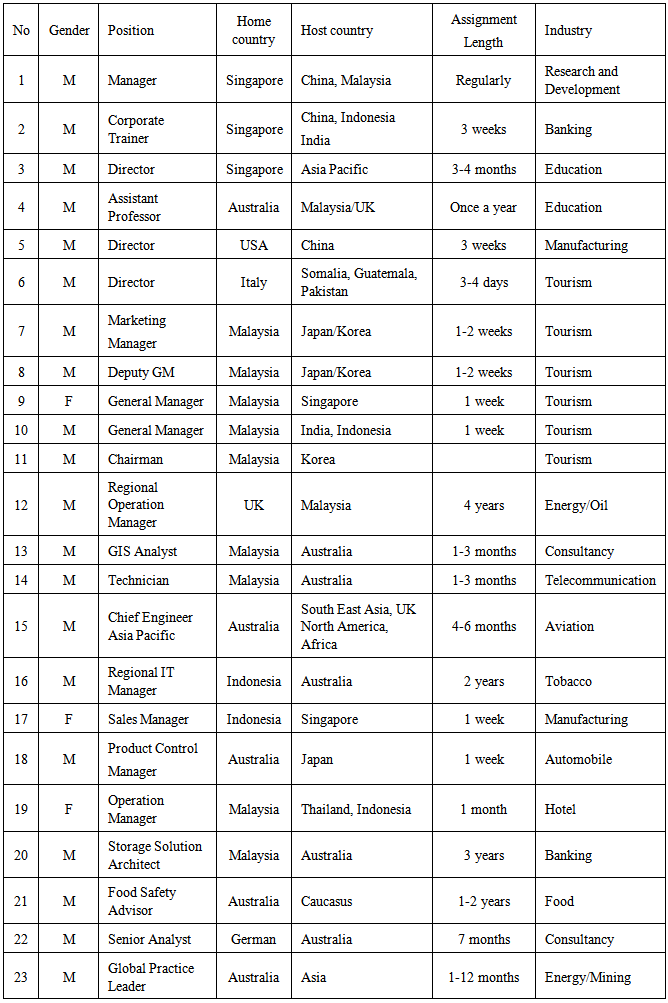
- A series of face-to-face interviews with non-traditional expatriates was conducted to obtain a broad overview of issues followed by an online survey. The interviewees were chosen on the following criteria: 1) an international manager who has undertaken non-traditional assignments, or 2) an international manager who has knowledge about the assignments or has been engaged in allocating and managing non-traditional expatriates. Twenty-three international managers were identified and selected as interviewees. The managerial levels of the interviewees were obtained from their organisational charts which were available online or in their offices. There was an open ended-question in the questionnaire that aimed to obtain information about the reasons for using non-traditional assignments. Convergent and thematic analyses were conducted in the effort to obtain data. Likert scales of 1 to 5 were used to obtain respondents’ perceived of their assignment importance. The assignment criteria used in questionnaire were generated from the literature and interview sessions conducted in this study.
5. Research Findings
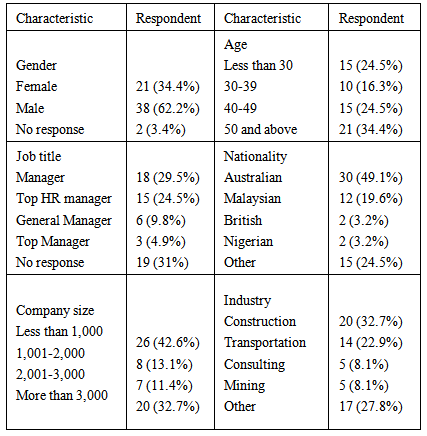
- Survey respondentsAn online survey was undertaken in order to obtain rich data. There were 1121 identified managers who have undertaken non-traditional assignments. They were identified based on their online profiles and also from a human resource database which was available for purchase. In total 157 managers responded to the survey, but only 61 responses were deemed useable.
|
|
|
6. Discussion and Conclusions
- This study found the four main reasons for using non-traditional expatriate assignments are: implementing specific assignments and knowledge transfer, maintaining relationships, troubleshooting or problem-solving, and gaining international experience. The assignments were mainly undertaken for short periods for different purposes such as training, meetings, or projects. Skills transfer is related to this assignment since the assignees must possess skills in particular fields. When an assignment requires a short period to complete and does not warrant a traditional expatriate assignment, organisations use non-traditional assignments. Traditional assignments, on the other hand, are more complex and time-consuming. They involve tasks such as position-filling that may involve assignments for a period of at least three years. The assignment requires adaptation and an understanding of foreign culture, which needs a long period to adapt. As such, the differences indicate that non-traditional expatriate assignments cannot be replaced by traditional expatriate assignments.The knowledge transfer directions were found to be mostly from subsidiaries. They provide knowledge and skills to the parent corporation, receive knowledge and skills from subsidiaries and receive knowledge and skills from the parent corporation. This study confirms that non-traditional assignees, although travelling mostly for short-term periods, dispersed and received knowledge as well.The second main role the interviewees frequently mentioned was that of maintaining relationships. One non-traditional assignee had undertaken a few assignments before he returned home. He undertook a series of assignments, and carried out the same assignments on a regular basis. His assignments included global business meetings, technical meetings, and safety meetings. The several purposes of his series of trips took him between 4-6 months to complete. Therefore, this non-traditional assignee has multi-purpose assignments and makes a series of trips. In a narrow sense, assignees are possibly able to build and maintain relationships with clients or local managers by meeting them a few times for substantial periods.High quality relationships can be developed through face-to-face meetings and are very important in some countries. In a country where trust, integrity, and personal contacts are major priorities in business negotiations, a manager has to meet and build a good rapport with customers or business partners to start or build a relationship (Haake, Schummer, & Haake, 2003). The interviewees stated that usually this relationship is built by socialising with them. Socialising includes taking business partners and customers out for dinner or drinks, providing funds for promotional purposes, giving gifts, and entertaining clients’ children. Almost all of the respondents stated that information communication technology (ICT) tools could be used to facilitate communication. However, they also believed that these tools were not equivalent to face-to-face meetings, especially in terms of developing a relationship between business partners, customers, or host country employees. One respondent was sent to a subsidiary specifically to socialise with the local managers. Therefore, building relationships is another important reason for sending managers on non-traditional expatriate assignments.The third reason for using the assignment is for management development. This assignment is aimed at exposing young managers to international assignments and, thus, they may be able to use it for their career development. Middle managers mostly perceived this assignment as being very important to them. Unlike senior managers, skills transfer is their main purpose for a non-traditional expatriate assignment. Problem solving or troubleshooting is confirmed as another main aim of the non-traditional expatriate assignment. Managers are selected based on the problems which have been identified at the headquarter level and then the organisation sends someone who is capable of solving the problems. These assignees serve different purposes concurrently: 1) they undertake the assignments for the stated reasons and 2) they expose themselves to international environments. As such, they gain international experience, which can be used at head offices or at branches. For career development purposes, a junior manager might be attracted to international assignments. This may provide organisations with a pool of available managers.The reasons for using non-traditional expatriate assignments have been discussed and the selection is now proposed based on our research. This selection is expected to facilitate practitioners in making decisions, particularly when designing selection or compensation packages for non-traditional expatriate managers. Referring to the well-developed model by Tahvanainen, Welch and Worm (2005), this study has added to the reasons for using non-traditional expatriate assignments by providing detailed descriptions of non-traditional expatriate assignments. The assignment purposes identified may possibly assist practitioners to find and select suitable candidates for the assignments. This study found that technical and managerial skills are important in the implementation of assignments. Therefore, these skills are significant indicators to use when selecting a suitable candidate. Additionally, most of the assignments undertaken by the participants in this study were for training, meetings, and projects. The training assignment, in particular, requires a manager that has knowledge about the training content. Apart from that, other criteria such as personality, good communication skills, and open-mindedness are some important characteristics for the assignments. It is even more important when the selected assignees have to deal with local clients or managers. Since the most important item in the non-traditional expatriate assignments is skills, a candidate should possess the skills required to undertake the intended assignment and selection can be made from available sources. Organisations are currently facing a shortage of assignees (Sparrow, Brewster, & Harris, 2004) so they should widen their choice to obtain assignees from their closest affiliates worldwide. Position filling is the reason applicable for both traditional and non-traditional expatriate assignments. Apparently, in non-traditional assignments, a position is filled by a manager for only a temporary basis. In traditional expatriate assignments, the manager who is sent to fill a position stays in the foreign country for a longer period. For management development purposes, both types of expatriate assignments are planned to provide managers with international exposure and to train them. However, in traditional assignments, the assignment takes longer to achieve its aims due to the socialisation process, which requires the managers to adapt to local cultures and to learn local behaviours. Controlling purposes appear to be carried out in both assignments as well. However, a greater importance on control is emphasised in traditional expatriate assignments. This is since the ‘control by socialisation’ suggested by Edstrom and Galbraith (1977) and Harzing (2001a) seems to be undertaken over a longer period. Clearly, non-traditional expatriate assignments are not designed to achieve this aim. Therefore, this study questions the assertion made previously by some authors that traditional expatriate assignments are in retreat. Since the two types of assignments serve different purposes, the one cannot replace the other. Additionally, a few reasons such as controlling and position filling cannot be achieved by using non-traditional expatriate assignments. Some positive effects have resulted from the emergence of non-traditional assignments. First, companies have alternatives to execute their international assignments. Second, the strategic implementation of international assignments can be undertaken within a short period and, thus, may be able to contribute immediate results. It is speculated that, overall, the traditional expatriate has some ‘unique’ competitive advantage such as the experience he or she gains during long-term assignments. The skills and experience gained are the most valuable experiences and can be used to enhance value to organisations and to the expatriates as well. Thus, it may be the reason why companies continue to utilise the traditional assignment (Black, Gregersen, & Mendenhall, 1992) despite its somewhat adverse image. Therefore, both assignments serve different purposes and have different aims. Organisations are using them in different situations and different countries depending on their business operations’ needs. Interestingly, non-traditional expatriate assignments are undertaken by skilled and specialised expatriates regardless of their age, gender, or managerial level. This can be seen from a range of managers’ ages who participated in and have undertaken non-traditional expatriate assignments in this study. For example, a young interviewee mentioned that he was chosen from a pool of candidates from different subsidiaries in a region due to his knowledge about his organisation products. Any available and skilful managers, regardless of their background factors, can be selected to undertake non-traditional expatriate assignments. Therefore, the headquarters does not ‘headhunt’ for someone in a high managerial position but, instead, look for someone who is skilful, mobile, and suitable for the identified assignments.Some of the interviewees mentioned that the aim of non-traditional assignment was not necessarily to cut costs. Investigation on the background of the interviewees was carried out to obtain clearer explanation. The investigation revealed that the managers who said that non-traditional expatriate assignments were not necessarily used to cut costs were from large companies. One interviewee stated that ‘my organisation is not being restricted on travel or cost.’ This interviewee worked for a large aviation company that operates worldwide. The interviewee was needed in different locations to serve different specific assignments such as meetings, training, and discussion and to undertake his work as an aviation engineer. The manager was transferred from one location to another location to serve different organisational needs. In order to serve or fulfil these needs, his organisation paid for travel allowance, insurance, and airline tickets. Therefore, we can conclude that an organisation has to bear related costs to serve their international business operational needs and that the completion of a non-traditional expatriate assignment is more important than the costs involved. However, a manager who worked for a bank said that non-traditional expatriate assignments were for cutting costs. In his statement he clearly said that training should be undertaken briefly and quickly since the competition was stiff, particularly in the banking industry. An examination of his background revealed that he worked for one of the major banks in Singapore. Since both of these managers worked in large organisations, this matter merits further investigation. Influential factors such as an organisation’s profit, size, goals, and industry need to be examined in order to obtain more evidence so that a conclusion can be made. Therefore, based on the statements of the professional managers, cutting cost is not necessarily the primary reason why organisations use non-traditional expatriate assignments. Instead, it appears that they use them primarily to complete a specific aim. Additional empirical studies need to be conducted to achieve a more conclusive finding. In conclusion cutting cost appears to become a major purpose, however only in a particular situation or if the situation permits the organisation to do so. Recently, it has been suggested that the increasing shortage of international managers has become an increasing problem for international organisations and has been a significant constraint on the implementation of global strategies (Scullion & Dowling, 2011). To overcome this situation, organisations are recruiting younger international managers by sending them on non-traditional expatriate assignments. Further, one report says that selecting non-traditional assignees is mostly informal (Tahvanainen et al., 2005) and may become an attractive option to organisations. Traditional expatriate assignments, on the other hand, have been known as problematic assignments and, thus, this may have prompted organisations to choose non-traditional expatriate assignments. Since international organisations are competing for talent, the competition has become global (Sparrow et al., 2004), retaining experienced employees and managing repatriates has become difficult, and organisations have had to recruit more talented young expatriates to serve their international operations’ needs. As such, organisations use non-traditional expatriate assignments to expose younger managers to international environments to gain experience and to train them to become skilled and knowledgeable managers. This study has several limitations. Firstly, it was the aim of the researchers to obtain data from a broad range of industries so that broader generalisations might be made. Due to the small responses gathered this aim was unachievable. Secondly, a partial mixed methodology was employed, but quantitative analysis proved difficult for the latter reason. Thirdly, the Asia-Pacific context of the study restricts the findings to the region rather than more generally.Future researchers might aim to attract larger samples, more comprehensive industry representation, or to conduct comparative global studies, in order to contribute to our aggregated knowledge of the characteristics of non-traditional expatriate assignments.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML