-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Human Resource Management Research
p-ISSN: 2169-9607 e-ISSN: 2169-9666
2014; 4(2): 13-18
doi:10.5923/j.hrmr.20140402.01
The Influence of Mapalus Culture via Hospital-based Human Resources Behavior on Maternal and Child Health toward Millenium Development Goals (Case Study of RSUP Kandou Manado)
Heiskar Ririmasse1, 2, Edi Widjajanto3, 4, Jack Roebijoso5, Soemarno1, 5
1Environmental Science and Technology Graduate Program, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
2General Services Agency of Prof. dr. R.D Kandou Manado Hospital, North Sulawesi, Indonesia
3Department of Biomedical Science, Faculty of Medicine, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
4Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
5Department of Soil Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Heiskar Ririmasse, Environmental Science and Technology Graduate Program, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Mapalus is a traditional form of shared community work. It is assumed that Mapalus culture can improve all hospital performances. The objective of this research is to assess the influence of Mapalus culture application through human resource behavior on the improvement of Millenium Development Goals (MDGs) 4 and 5. Sampling method used simple random sampling. The model used a functional equation in simultaneous model of Structural Equation Modeling. The sample includes 100 respondents. Research variables are classified into two types, i.e. exogenous variable of Mapalus culture (X1); endogenous variables of hospital human resource behavior (Y1) and the improvement of MDGs (Y2). Data are collected using questionnaire and converted in Likert Scale. Primary data were obtained with survey and questionnaire list which are directly delivered to respondents at obstetric patient in wards of RSUP Kandou. The analyzed data of Mapalus culture include shared help, openness, group discipline, collectivity, and versatility. Related to human resource behavior, the analyzed data include the behavior of doctor, nurse and non-medical worker. In relative with the improvement of MDGs 4 and 5, the analyzed data involve the reduction of mortality rate of baby and toddlers, and the improvement of maternal health. Results indicate that Mapalus culture is influencing the improvement of MDGs through human resource behavior in hospital and Mapalus culture has been depleted.
Keywords: Mapalus Culture, Human Resources Behavior, Millenium Development Goals 4 and 5
Cite this paper: Heiskar Ririmasse, Edi Widjajanto, Jack Roebijoso, Soemarno, The Influence of Mapalus Culture via Hospital-based Human Resources Behavior on Maternal and Child Health toward Millenium Development Goals (Case Study of RSUP Kandou Manado), Human Resource Management Research, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 13-18. doi: 10.5923/j.hrmr.20140402.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Application of the mutual help principle can be seen with the pillars of affection, which is implied in public health insurance and childbirth insurance as government programs to help poor patients. Application of the openness principles were implied in the open information about the rate or cost of the hospital for community. Application of the group discipline principle is indicated by justice on the equal division of work schedule (shift) – sharing the equal schedule routine. Furthermore, principles of togetherness were implied from the tolerance of employees every Friday before worship. Christians and Muslims is held community service in Kandou Hospital environments. Application of efficiency and effectiveness principle then viewed in the obstetric post health efforts to implement efficient and effective manner with a focus on supporting the delivery, i.e. prevention of infant mortality and maternal health healing. The efforts were carried out in a harmonious and integrated manner to improve and implement prevention and referral.Hospital changed becomes more institutional business need a philosophy to be ethically justifiable. A crucial goal in hospitals change is an increase in efficiency and the guarantee for the poor to obtain hospital services. Public participation is a necessary condition for success, sustainable and independence of development in all aspects, including health development. Health care financing implement health funds from public funds collection which based on health mutual assistance and familial joint venture that has been known for a long time. Social organization in society is mutual cooperation and discussion. Mutual aid at the present time has been changed. It is threatened by new ways of interacting and social gatherings that have recently emerged.Mapalus is a traditional form of mutual assistance (inherited from ancestors from ancient time that remains today). Further analyze found that Mapalus is a system, procedures, methods or techniques of working together for common interests. Mapalus life principles are the principle of mutual help, openness, group discipline, togetherness, efficiency and effectiveness (Turang, 1983).Lund (2003) provides a definition of corporate or organizational culture as a shared system of values and beliefs that interact with the people, structures and systems of an organization to produce behavior norms (the way things are done). To provide the same view of human resources within the organization, firmness is a necessary requirement for organizations in the form of a work culture that reflects the specification, which in turn affects the behavior of all the individual layers that exist within the company. Work culture is what ultimately establishes a corporate culture, which if understood and implemented by all employees, will guide the achievement of the work performance (Susanto, 1997).General health workers are an integral force which consists of medical personnel, maintenance personnel, non-paramedics and non-medical personnel. Of all categories of health personnel who work in hospitals, nursing personnel is the most recruited human resources with most contact with patients, so that they have a crucial role in determining the quality of health services in hospitals (Simmons et al., 2001).Organizations really need competent human resources to support the successful performance of the job. Competence may include aspects of knowledge, skills, attitudes and behaviors of employees. Managerially, resource development as the capital should continuously develop to contribute to the achievement of organizational goals. "Only if the employee is placed in right position and received training, equipment, structures, incentives and accountability to work effectively, it is very likely that the organization will be successful" (U.S. Office of Personnel Management, 1999).One of the competencies that should be possessed by a hospital worker is the ability to manage (management), both in nursing and cooperate in carrying out the functions of coordination with other areas as part of integrated service (Santoso, 2003). Siddique (2007) also explained that there are two basic competencies that need to be owned by human resources of an organization, i.e. social competence and personal competence. In personal competence, there are two key elements that are important, i.e. self-awareness and self-management, while the principal components of the social competences are social awareness and relationship management. According to Spencer et al. (2009), characteristics of competencies required of a person in order to do a good job based on predetermined criteria, including motive, traits, self-concept, knowledge and skills. Competence is a complex set of behaviors that build the components of knowledge, psychomotor, effectiveness, as a competent individual (Carraccio et al., 2002).The attitude of a good nurse is the manner in which the nurse would do the job without being overwhelmed by some internal conflict in completing the assigned tasks. This attitude will influence the behavior of the nurses in facing the patient, while one's attitude in responding to problems is influenced by one's personality. Personality is formed from birth and growing until adulthood (Gibson et al., 1996). Gibson et al. (1996) also explained performance of individual employees affected by motivation, ability and work environment. Motivational factors have a direct connection with the performance of individual employees, while the ability of individual factors and work environment has indirect relationship with performance. Both factors will affect the existence of employee’s motivation. Because of the position and relation, it is strategic if the development of individual performance starts by improvement of the employee’s work motivation. Nurses as health care in hospitals are expected to always be friendly, soft temper, trustworthy, skilled, competent, and have good moral responsibilities (Suhaemi, 2003). Millennium development goals targeted to be achieved by 2015 can be used as a booster and the spirit to do a better effort in handling issues related to the fulfillment of basic human needs. In the current millennium, the prime program of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) became the main theme of national development. Particularly in the areas of health, MDGs, have certain targets, which aim to accelerate the pace of growth and development achievements of public health rate. Common targets that span the hierarchy of MDGs include reducing child mortality and improving maternal health (Sudayasa, 2010).The infant mortality rate is a sensitive indicator to determine the health status of a country even to measure the level of progress of a nation. In obstetric care services, besides Maternal Mortality, Prenatal Mortality can also be used as parameters for services success. Childbirth insurance (Jampersal) is an effort to achieve MDGs 4 and 5. Childbirth insurance is an insurance of childbirth service that includes prenatal care, delivery assistance, and postpartum care including family planning services. Postpartum and newborn care is performed by health workers at health facilities. Delivery assurance is intended to eliminate financial barriers for pregnant women to get the facilities and support they need. Basically childbirth insurance is an extension of society’s health insurance membership and includes not only poor people (Ministry of Health, 2011).National strategy for efforts to reduce infant and child mortality is family empowerment, community empowerment, enhancing cooperation and coordination across sectors, and improving health care coverage and comprehensive child quality. National development programs for these efforts to reduce infant and child mortality is one of the priorities in health development (Bappenas, 2003). Indonesia as one of the countries that signed the MDGs, also committed to realize the eight goals as the embodiment of human resource development and quality of a better life. Nationally, the commitments outlined in national planning documents, including the National Medium Term Development Plan (RPJMN) 2004-2009. Then, emphasized on RPJMN 2010 - 2014 and Presidential Decree No. 3 of 2010 regarding equitable development programs (UNICEF, 2000).Legislation with the enactment of Law no. 23 of 2002 on the protection of children, the opportunity of Indonesian children to live healthy, grow, and develop optimally become increasingly open. The law states that every child has the right to obtain medical care and social security in accordance with the needs of physical, mental, spiritual, and social. National programs for children in Indonesia are referring to the general development of national health policies. Efforts to reduce infant and child mortality are an important part of the National Program for Indonesian Children (PNBAI) which outlined in 2015 Vision towards Indonesian healthy children (Department of Health, 2009).Reduction of child mortality needs togetherness to improve the health of mother and child because the child is the successor of the nation so that we needs to nurture. Performed work together is more easily than if only done by one party alone. Nielson et al. (2001) found that prenatal care is influenced by the level of education, number of births, previous pregnancy history, and access distance to health services. Generally more intensive prenatal care is done by educated mothers compared with uneducated mothers. Besides, these examinations are performed routinely in the first or second births, and become decreasing in the next birth. The results of previous studies by Tarigan (2005) stated that Mapalus institutional workforce in Minahasa community provides an overview of the Mapalus culture that is very famous and prominent. The results show there has been a three-phase social change in Mapalus social institutions.Widaryanto (2005) analyzed the factors that influence the behavior of services and their effects on organizational performance in Kariadi hospitals Semarang. Research showed that leadership, communication, and system control have a positive and significant effect on the behavior of the service. Sintaasih (2009) stated the role of Knowledge Management and human resources as a strategic partner in planning the organization's strategy (study at a hospital in Bali). These results indicate that important organization leaders continuously maintain and enhance its capabilities for knowledge management and human resources executives as crucial strategic partner to actively engage in the formulation, implementation, evaluation and control of strategic decisions.Sedyaningsih (2012) also studied the concern of neonatal mortality rate that tends to stagnate. Infection factors and nutritional problems are very influential on child survival. RISKESDAS (2007) showed the cause of 36% of infant mortality are neonatal problems (asphyxia, Low Birth Weight (LBW) and infection), 17,2% due to diarrhea and 13,2% by pneumonia. Indonesian Basic Health Survey - IDHS (2007) showed 228 mortalities per 100,000 live births. Based on linear regression analysis of IDHS data 1994-2007, the projected mortality of 2015 was 161 per 100,000 live births. Then we required breakthroughs and support of all parties to overcome these problems.The objective of this research aimed to assess the influence of Mapalus culture through human behavior and the improvement of the MDGs 4 and 5 within the department of Kandou Manado hospital. Offered solution based on the description and the theory above, this study proposed a hypothesis as follows: Mapalus culture affects the increase in MDGs 4 and 5 through the behavior of the human resources of Kandou Hospital, Manado.
2. Materials and Methods
- This research was conducted in the hospital of Prof. dr. R.D Kandou Manado. The sample was randomly selected (Solimun, 2002), with a total 100 patients in Kandou Manado Hospital who are inpatients. The sampling method in this study is simple random sampling method. Variables were classified into two types, i.e. exogenous variables of Mapalus culture (X1); endogenous variable behavior of hospital human resources (Y1) and Improved MDGs 4 and 5 (Y2). Data collection in this study was conducted by survey method using a questionnaire that was submitted directly to the respondents. Questionnaires were given to obstetric inpatient of Kandou Manado Hospital. Indicators are arranged in the questions to elicit responses as expected by the time of study for April to May 2013. Secondary data collection was done by the documentation of the service-IRINA D Hospital to obtain data on the amount of data delivery and prenatal.
2.1. Data Analysis
- This study performed analysis of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), to see the causal relationship between exogenous and endogenous variables. Analysed variables are Mapalus culture as exogenous variables (X1), behaviour of hospital human resources (Y1) and increase in MDGs 4 and 5 that the endogenous (Y2). The form of causal relationship in this research is between the exogenous variables are variables Mapalus culture. We performed analysis of a causal relationship or series relationships that have mutual dependencies among variables. We used technical multivariate analysis to explain simultaneous causal relationship by SEM. The reason for using SEM in this study is the exogenous variable that is linked to the endogenous variables simultaneously. Mapalus cultural variables (X1) are: shared help (X1.1), openness (X1.2), groups discipline (X1.3), togetherness (X1.4), efficiency and effectiveness (X1.5). Behaviour of hospital human resources are: doctor (Y1.1), nurses (Y1.2) and non-medical personnel (Y1.3). Increased MDGs 4 and 5 are: reduce the number of infant-toddler deaths (Y2.1), improve the maternal health (Y2.2). Scores determination of categories on respondents using four levels, i.e. average of 1,00-1,80 categorized as very low, average of 1,81-2,60 categorized as low, average of 2,61-3,40 categorized as high, and the average of 3,41-4,00 categorized as very high (Sugiyono, 2011).
3. Results and Discussion
- Cooperation need in completing a job. From this cooperation it began to create a sense of mutual respect, cherish and love each other in the form of internal groups that live in harmony. “Torang samua bersaudara” is a Minahasa idiom to describe prioritizing actions and attitudes of mutual interest, which manifest in action and real hope (Montori, 2012). Potter and Perry (2005) also explained that a nurse must implement a professional attitude in providing services to patients in accordance with the applicable standard of nursing care.Aspects of collaboration include the attitudes of nurses to do a good cooperation with the patient and patient's family. In addition, cooperation or cohesiveness among health care workers must be maintained due to it being crucial to smooth the health care to patients. Hospital performance is strongly influenced by the values, norms and the applicable standard of the profession, and patients. Public will be satisfied if the hospital performance can provide services in accordance with the norms and standards (Sastrohardiwiryo, 2005).
3.1. Mapalus Culture
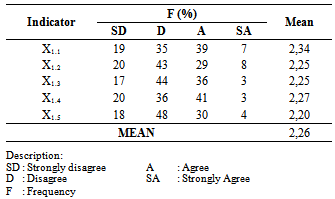
- Mapalus culture existence in the hospital and human resources affect the implementation that supports the management of hospital performance. Data implied that Mapalus culture variables measured from five indicators is that shared help (X1.1), openness (X1.2), groups discipline (X1.3), togetherness (X1.4), efficiency and effectiveness (X1.5). The following Table 1 presents a description of the variables include the frequency, percentages, and the average of each indicator.
|
3.2. Human Resources Behaviour
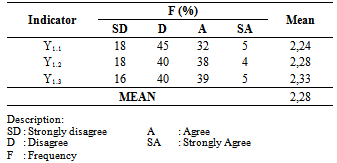
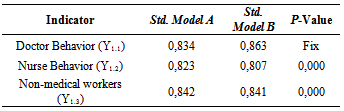
- Behavior of Human Resources variable is measured by three indicators: Doctors Behavior (Y1.1), Nurse Behavior (Y1.2) and Non - Medical Workers Behavior (Y1.3). Majority (45 respondents) of respondents answered disagree on Doctor Behavior indicators (Y1.1). Average score of 2,28 indicates that respondents assess the behavior of hospital’s human resources are low (Table 2).
|
3.3. MDGs Improvement
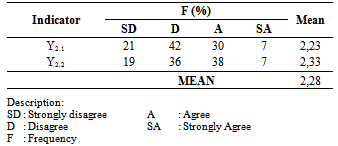
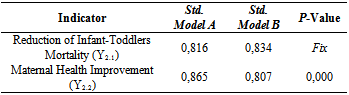
- Improved on MDGs 4 and 5 variable were indicated by two indicators: reducing infant and toddlers mortality (Y2.1); and improve the maternal health (Y2.2). Majority (42 respondents - 42%) of respondents answered disagree on the Reduction of Infant-Toddler Mortality indicator (Y2.1). Average score of 2,23 of reduction on Infant-Toddler Mortality indicating a very low category.
|
3.4. Measurement Model
3.4.1. Mapalus Culture
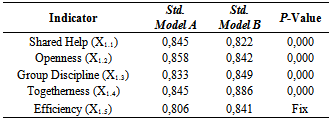
- Second indicator - Openness (X1.2) with standardize coefficient or factor loading 0,858 and 0,842 (p-value of 0.000> 0.05), is significant to Mapalus Culture variable (X1). The higher the Openness then the higher Mapalus Culture variables will also be. Openness indicator is the strongest indicator for measuring Mapalus Culture variable. So Mapalus Culture is primarily seen because of the openness (Table 4).
|
3.4.2. Human Resource Behavior
- Based on Table 5, non-medical workers behavior (Y1.3) standardize coefficient or factor loading are 0,842 and 0,841 (p-value of 0.000 <0.005). So it can be concluded that this indicators is significant to human resources behavior variables (Y1). The higher value of non-medical workers behavior (Y1.3), the results of measurements of human resource behavior variables will also be higher. Non-medical workers behavior (Y1.3) is the strongest indicator on human resources behavior. Therefore, human resources behavior that is primarily seen is non-medical workers behavior.
|
3.4.3. MDGs Improvement
- Table 6 shows that Infant-Toddler Mortality Reduction (Y2.1), has standardize coefficient or factor loading 0,816 and 0,834. It indicates that this indicator is significant to measure the MDGs Improvement (Y2) variable (Table 6). The higher value of Infant-Toddlers Mortality Reduction, the measurement results of MDGs Improvement will also higher.
|
3.5. Structural Equation Model of Kandou Manado Hospital
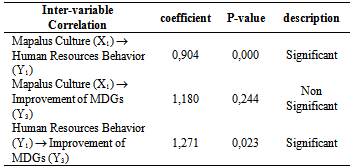
- There is a significant influence of Mapalus Culture on the Human Resources Behavior (Table 7). The positive coefficient is indicating both unidirectional relations, which mean that the higher value of Mapalus Culture resulting the higher value of Human Resources Behavior. There is no significant influence of Mapalus Culture on the Improvement of MDGs. It implied that the value of Mapalus Culture will not affect the value of MDGs Improvement.There is a significant effect of human resources behavior on the Improvement of MDGs. The positive coefficient indicates that both has unidirectional relations, means that the higher the value of human resources behavior, then the higher value of MDGs Improvement.
|
4. Conclusions
- The higher value of Mapalus Culture result the higher value of Human Resources Behavior. Mapalus culture will not affect the value of MDGs Improvement. The higher value of Human Resources Behavior result the higher value of MDGs Improvement. There are correlations of Mapalus culture through the implementation of human resources behavior towards the improvement of the Millennium Development Goals 4 and 5 in the hospital.
5. Suggestion
- Community togetherness (family) is crucial in an effort to improve and child maternal health to achieve the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). Childbirth insurance (Jampersal) and dissemination of communication, information and education to the community would not too late: too late for decisions making and recognize the risk, late referred, and the delay in medical treatment. One of the efforts to prevent such risk factors is by assistance of health personnel in health care facilities.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML