-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Human Resource Management Research
p-ISSN: 2169-9607 e-ISSN: 2169-9666
2013; 3(4): 124-149
doi:10.5923/j.hrmr.20130304.02
Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior among Store Executives
Shruti Mathur 1, Padmakumari 2
1Department of Psychology,Christ University Bangalore, India
2Assistant Professor Christ University
Correspondence to: Shruti Mathur , Department of Psychology,Christ University Bangalore, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The purpose of the study was to find out the employee perceptions’ of Organizational Justice or perceived fairness levels of employees and whether these positive perceptions would lead to citizenship behaviours and specifically, aimed at finding out if a certain notion of justice affects extra role behaviours more than the other among 72 store executives of a single retail chain in Bangalore. The researcher also aimed to find out if there were gender differences in justice perceptions. The measures used to assess the two variables were Organizational Justice Scale by Colquitt (2001) and Organizational Citizenship Behavior by Jain & Sharma (2010). The data was analysed using Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation, a linear regression analysis and a t-test. A significant relation was found between Organization Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors. It was also found that employees perceived interactional justice to be the most important in influencing extra-role behaviors and significant differences in overall as well as interactional justice perceptions were found among males and females.
Keywords: Organizational Justice, Organizational Citizenship Behaviors, Store Executives, Gender Differences and Indian Retail Industry
Cite this paper: Shruti Mathur , Padmakumari , Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior among Store Executives, Human Resource Management Research, Vol. 3 No. 4, 2013, pp. 124-149. doi: 10.5923/j.hrmr.20130304.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
 The above quotes highlight the importance of the justice construct among people in every aspect of their living. In today’s world where awareness levels and communication have reached new heights, fair treatment is something that all employees expect from an organization, considering the time and effort they invest. If this is not given, the employees tend to seek these out in different ways - like absenteeism, turnover, counter-productive behaviors etc. In other words, they will not do justice to their work responsibilities. The quote below highlights this fact.
The above quotes highlight the importance of the justice construct among people in every aspect of their living. In today’s world where awareness levels and communication have reached new heights, fair treatment is something that all employees expect from an organization, considering the time and effort they invest. If this is not given, the employees tend to seek these out in different ways - like absenteeism, turnover, counter-productive behaviors etc. In other words, they will not do justice to their work responsibilities. The quote below highlights this fact. Thus, we see employees not only want a lot of benefits and perks but also want something additional or extra that will make them ‘stick’ to the organization longer. The theme of Organizational Justice is the ‘glue’ that allows them to work together effectively and is the essence of Industrial relations in an organization.Organizational justice refers to an employee’s perception of whether an event or situation is morally right, which is defined by the ethics, religion, equity, fairness or law. It is thus a subjective concept, where one is less concerned with what is just and rather more concerned with what people think or believe is just. Researchers have adopted a descriptive paradigm to study and understand why employees might view certain situations or events to be labeled just or unjust. It is regarded as a personal evaluation about organizational conduct and moral standing. (Cropanzano et al., 2007) In today’s competitive world, organizations are constantly trying their utmost limit to retain the best talent and outdo their competitors by doing the same things differently. Employees have become more aware of their rights and value the employer’s sense of justice and further expect and them to be fair or just at all times. Thus, fairness has become a prime aspect for organizations to take a deep look into - as it directly affects workplace attitudes and behavior. Thus, the construct of Organizational Justice is receiving a great deal of attention currently. The succeeding chapters go on to explain the concepts of Organizational Justice with respect to the Retail Industry in India.
Thus, we see employees not only want a lot of benefits and perks but also want something additional or extra that will make them ‘stick’ to the organization longer. The theme of Organizational Justice is the ‘glue’ that allows them to work together effectively and is the essence of Industrial relations in an organization.Organizational justice refers to an employee’s perception of whether an event or situation is morally right, which is defined by the ethics, religion, equity, fairness or law. It is thus a subjective concept, where one is less concerned with what is just and rather more concerned with what people think or believe is just. Researchers have adopted a descriptive paradigm to study and understand why employees might view certain situations or events to be labeled just or unjust. It is regarded as a personal evaluation about organizational conduct and moral standing. (Cropanzano et al., 2007) In today’s competitive world, organizations are constantly trying their utmost limit to retain the best talent and outdo their competitors by doing the same things differently. Employees have become more aware of their rights and value the employer’s sense of justice and further expect and them to be fair or just at all times. Thus, fairness has become a prime aspect for organizations to take a deep look into - as it directly affects workplace attitudes and behavior. Thus, the construct of Organizational Justice is receiving a great deal of attention currently. The succeeding chapters go on to explain the concepts of Organizational Justice with respect to the Retail Industry in India.1.1. The Indian Retail Industry
- The India Retail Industry is one of the largest among all the industries in the country. It accounts for the largest component of the services sector in terms of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) and around 8 per cent of the total employment. The Retail Industry in India has come forth as one of the most dynamic and fast paced industries with several players entering the market.The retail industry has evolved over a period of time in India. It is basically divided into the unorganized and the organized sector. The unorganized sector comprises of the small and more localized shops, like ‘kirana’ stores, owner operated general stores (fondly called the ‘mom & pop stores’ in technical parlance), convenience stores, hand carts, pavement vendors etc. On the other hand India also boasts an organized form of the retail sector. It refers to trading activities undertaken by licensed retailers. These include corporate backed hypermarkets and retail chains as well as privately owned large retail businesses.Unorganized retailing is by far the more prevalent form of retailing in India but a survey in 2007 by A.T. Kearney revealed that India is probably the most sought after retail investment destination and will be the world’s largest consumer market by 2025.Until 2011, the Indian Government denied Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in multi-brand Indian retail, forbidding foreign groups from any ownership in supermarkets, convenience stores or any retail outlets, or to sell multiple products from different brands directly to the Indian consumers. However, in the year 2012, the government led by Dr. Manmohan Singh, Prime Minister, announced that India would allow foreign groups to own up to 51 per cent in “Multi-Brand Retail ” groups and also, allow a foreign company to start a fully owned “Single-Brand” retail business in India. The opening of retail industry to global competition is expected to generate an additional 10 million new jobs by 2014. With this development it is important for the organizations to consider providing effective HR policies and a conducive environment to work in.In any retail organization, the employees deal with the customers on a one-to-one basis and thus, are the brand ambassadors of the organization and making it imperative for every organization to have a system wherein, employees are managed, developed, rewarded and retained in an appropriate manner.The present situation for retailers is that they experience high employee turnover, though industry experts point out that there is no lack of labour in the country. But training and developing an employee involves huge costs and time. One measure of increasing productivity, customer satisfaction and sales as an end outcome could be to look at employee perceptions of the organization. An often-overlooked construct is Organizational Justice. Tapping into these perceptions could help organizations formulate policies in a manner, which best suits, the organization as well as the employees.
1.2. Organizational Justice and its Components
- Organizational justice refers to the perceptions employees hold about the organization as being fair or unfair. These perceptions on justice have been linked to critical processes such as commitment, citizenship behaviors, satisfaction, and performance. (Colquitt, 2001) It has been recognized as a major component to get an insight into the attitudes of employees in an organization.Employee reactions can be grouped into three different notions of fairness. These came about in three different waves, or time periods or intellectual themes.• The Distributive justice wave• The Procedural justice wave• The Interactional justice waveThe Distributive Justice wave spanned from the 1950’s through the 1970’s, focusing on the distribution of resources.The Procedural Justice wave shifted the focus on fairness in procedures rather than allocation of resources. It gained momentum around the mid 1970’s and continued through the mid 1990’s.The third wave, known as the Interactional Justice wave has its beginnings in the mid 1980’s and continues even today, concentrating more on the interpersonal aspects of justice.Today in the 21st century, academicians have come up with another field of thought known as the “Integrative Wave” which emphasizes the integration of all the three notions of justice into one larger concept, called Organizational Justice.Distributive justice refers to the appropriateness of outcomes. It has to do with outcomes and allocations that some get and some don’t because of the inherent nature of employees to imagine that they are not treated alike. Outcomes such as pay/salary, benefits, satisfying supervision, job status and a variety of the formally and informally sanctioned pre-requisites are compared to the individual attributes like effort, education intelligence, experience skills, seniority, age, sex, ethnic backgrounds and social status (Adams, 1965). It concerns itself with:ο Equity: Rewarding employees based on their contributions.ο Equality: Providing employees of one level roughly the same compensation.ο Need: Providing a benefit based on an employees’ individual requirement.The above three rules also map out Aristotle’s famous dictum that all men wish to be treated like all other people (equality), like some other people (equity) and like no other person (need). (Cropanzano et al., 2007)Adams in 1965 conceptualized the equity theory stating that employees look at how much they get (outcomes) relative to how much they contribute (inputs). (Cropanzano et al., 2007) This ratio is compared to that of other co-workers and the ratio then helps to decide whether the employees feel the organization has been or not been fair. When these ratios are out of alignment, it results in employees becoming uneasy and balancing out the inequity. Due to its focus on outcomes, distributive justice is predicted to be mainly related to the cognitive, affective and behavioral reactions of particular outcomes. (Cohen-Charash & Spector, 2001)For example, if an employee feels that he is being paid lesser (perceived injustice), it affects his emotions i.e., anger, guilt, jealousy as well as his cognitions (cognitively distort input and output by comparing himself with his co-worker for doing the same work) and ultimately his performance drops due to perceived injustice, which is the behavioral aspect.In contrast, Procedural justice focuses on the means through which decision making or outcomes are allocated. In other words, how the outcome was, decided carried considerable significance even when the outcome was not in accordance to one’s expectations. (Cropanzano et al., 2007)Leventhal (1980) defined procedural rules as an individual’s belief that allocative procedures, which satisfied certain criteria, were fair and appropriate. He had given specific criteria that define the rule of fair procedures as:ο Consistency- Procedures to be the same across time and kinds of people.ο Bias Suppression- Procedures not to be affected by preconceptions.ο Accuracy Correctability-Procedures to be based on valid and accurate information.ο Representativeness- Procedures must reflect the basic concerns, values and outlooks of all stakeholders being impacted by the allocation.ο Ethicality- Procedure must be consistent with the fundamental moral and ethical guidelines of all stakeholders.According to Tyler and Blader (2000), procedural justice affects what employees think about the entire organization as a whole. If the process is perceived as just, employees show greater loyalty & willingness to go out of their way to perform. They are also unlikely to betray the organization.The third notion of justice known as Interactional justice deals with the interpersonal factors that govern procedures. (Cropanzano et al., 2007) In other words, it simply refers to how one person treats another. If a person shares information and avoids any kind of negativity, the interaction is regarded as just.It is regarded as the human side of organizational practices or the way the management deals with the recipient of Justice. (Cohen-Charash et al., 2001)Accordingly, Colquitt (2001), Bies and Maog (1986) defined interactional justice as being sensitive to the quality of interpersonal treatment one receives during the enactment of organizational procedures. Interactional justice is divided into two aspects: ο Interpersonal justice- Treating employees with dignity, courtesy and respect.ο Informational justice- Sharing relevant information with employees. (Cropanzano et al & Colquitt, 2001)Bies and Maog (1986) drew up a list of four rules governing the fairness of interpersonal treatment or the four antecedents of fair treatment. They are as follows:ο Truthfulness: Managers should be open, honest and straightforward in their conversations and should avoid playing with their words at all cost.ο Justification: Managers should provide appropriate and timely reasoning or explanations for all the decisions taken.ο Respect: Managers should treat everyone with dignity and should refrain from discriminating employees on any grounds.ο Propriety: Managers should refrain from asking inappropriate questions or making discomforting statements.The fourth intellectual theme or wave known as the Integrative waveseeks to explain Organizational Justice in terms of theoretical models to explain the multi-dimensional aspect of justice. The conceptualization of justice theories began in the 21st century but it was Folger in 1986 who called for a more integrative approach to justice, which led to the beginning of this phase.
1.3. Theoretical Framework of Organizational Justice
- Scholars have come up with three kinds of approaches:
1.3.1. Counterfactual Conceptualizations
- a) Referent Cognitions Theoryb) Fairness Theory
1.3.2. Group Oriented Conceptualizations
- a) The Relational Modelb) The Group Engagement model
1.3.3. Heuristic Conceptualizations- Fairness Heuristic theory
- Counterfactual Conceptualizationsa)Folger in 1986 suggested that it would be worthwhile in explicitly dwelling over the cognitive and affective aspects of how injustice leads to dissatisfaction. Unlike Adams (1965), who focused on a sense of distress in the equity theory, Referent Cognitions theory (RCT) focuses on a deprivation framework. It elaborates on how employees compare an existing reality to a more desired or favorable state and how feelings of anger and resentment can stem out of this relative deprivation.The (RCT) theory purports that such feelings are heightened under three mental stimulations:• When Referent Outcomes are high, i.e., when employees imagine a better and different or alternative state as compared to where they are right now. Employees become more aware of alternatives when they perceive others around them getting rewards different from them and think about ‘what might have been’.• When the perceived likelihood of amelioration is low, i.e., when employees have little hope that the future rewards or outcomes will be better, the more they are dissatisfied.• When outcomes are not justifiable, i.e., an appropriate and a convincing rationale are not provided, dissatisfaction increases.Referent outcomes not only reflect distributive concerns but also procedural concerns (Justification) as well. They also explain the tenets of Interactional justice. Thus (RCT) explains how employees’ make comparisons between existing and imagined states and how this eventually leads to feelings of injustice. (Williams, Pitre & Zainuba, 2002)b)Folger and Cropanzano (2001) reflected on the (RCT) and shifted the focus from “if-only” or imagined alternatives to appraising the situations in a manner which takes into account extenuating events which might be responsible for a negative outcome or situation. For something to be regarded as Injustice, the theory purport’s that blame will be placed only when three questions are answered in the affirmative. The questions are:• Would I have been better off if a different Outcome or procedure had occurred? In other words, have I experienced some injury?• Could the authority have behaved differently? In other words, were there other feasible courses of action?• Should the authority have behaved differently? In other words, were moral and ethical standards violated?This theory captures all three notions of fairness; Distributive in the sense of end outcomes, Procedural concerns in the actions taken as well as Interpersonal justice concerns like bias or lack of ethicality. (Colquitt, 2001)Group Oriented ConceptualizationsThese conceptualizations stress the importance of Social Identity and social acceptance in a group. a) Tyler and Lind (1992), drew attention towards the organization by conceptualizing what authorities need to do to function effectively? The relational model of authority in groups’ focus is to determine the legitimacy of authorities, keeping in mind Tyler’s three factors. Tyler and Lind (1992) concluded after many studies that, “ a good relationship with the authorities promotes feelings of procedural fairness and that this, in turn, leads one to feel values by the group”. The group value model and relational model are similar and have been used interchangeably in justice literature. (Colquitt, 2001)b)This model also focuses on an organization with the fundamental question here being “What causes employees to perform behaviors which help the group reach its goals?” In other words, what makes employees engaged in their work in the group they belong to? Tyler and Blader (2000) suggest that justice is a major intrinsic motivation factor and task and citizenship forms of performance. Unlike the group value and relational models, which focus on distributive justice as a factor to influence identity judgments, the group engagement model focuses on procedural and interactional justice coming from the authority figures in the organization. They believed that engagement influences identity judgments i.e., employees cooperate with the group if the identity information flows through the group and this identity information in turns proceeds justice evaluations in the group.This model is new and is yet to be fully tested but the little research done so far supports and highlights the fact that it fills up existing gaps in the literature. (Colquitt, 2001)Heuristic ConceptualizationsHeuristics are simple, efficient and faster rules that have been proposed to explain how people make decisions, judgments, solve problems etc. Scholars have recently focused on mental shortcuts to explain psychological judgments of fairness.The Fairness Heuristic Theory (FHT) was formed out of tests done on the relational model, which suggested justice as a key indicator of the legitimacy of authority figures. Scholars supporting (FTH) argue that employees rely on heuristics or a psychological shortcut to make judgments and decide whether or not to accept or reject directives from supervisors or other authority figures in an organization.There are two concepts in this theory, primacy effect and trust as a proxy.Primacy Effect refers the extent to which employees make use of information that is readily available or presented to them first. The theory asserts that information presented first will have more impact on the fairness judgment than information presented later. This proposition has been widely supported in many studies.The second concept is that fairness heuristics are used as a proxy for trust. It was found that trust in authorities is critical in organizations but is much more difficult to judge than fairness. Studies revealed that when positive or negative trust information was presented, the effects of procedural justice on satisfaction and fairness ratings were neutralized. Thus, employees form fairness heuristics on the first few encounters with authority and then rely on them only to serve as proxies of trust in decision-making. (Colquitt, 2001)
1.4. Organizational Justice and its Outcomes: Organizational Citizenship Behavior
- Empirical evidence has supported that organizational justice is associated with a variety of positive work attitudes and behaviors (Konovsky & Cropanzano-1991, Barling & Philips-1993, Brockner & Wiesenfeld-1996). Thus, justice should become a core value of management practices to build a competitive edge. (Cropanzano et al)The Employees contribution is critical to any business and with increasing competition and rapidly changing market dynamics, employers also expect employees to go that extra mile and display initiative, collaboration, accountability, high quality in their workplace behaviors. Studies by (McFarlin and Sweeny, 1992), have found that positive justice perceptions could be linked to important individual as well as organizational outcomes. Greenberg, 1993 also found that organizations violate the norms of fair treatment receive negative reactions.Justice perceptions, in the author’s opinion, though individual and subjective in nature, act collectively to influence employees’ behaviour. Citizenship behaviour’s are reflected in customer interactions in the retail industry to a very high level and they in turn, enhance the image of the store in the minds of the consumers, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and eventually benefitting the store.Thus, positive justice perceptions have shown to foster what is known as employee Organizational Citizenship Behaviors (OCB’s) or behaviors that go beyond the call of duty (Organ, 1988). In other words, it is individual behavior that is discretionary not directly or explicitly recognized by the formal reward system and that in the aggregate promotes the effective functioning of the organization. (Organ, 1988)Organ (1988) postulated five specific categories of discretionary behavior and the contribution of each to efficiency.ο Altruism is directed towards other individuals, but contributes to group efficiency by enhancing an individual’s performance; thus participants help colleagues.ο Conscientiousness is the thoughtful use of time to enhance the efficiency of both individuals and the group; participants give more time to the organization and exert effort beyond the formal requirements.ο Sportsmanship increases the amount of time spent on organizational endeavors; participants decrease time spent on whining, complaining and carping.ο Courtesy prevents problem and facilitates constructive use of time; participants give advance notices, timely reminders and appropriate information.ο Civic Virtue promotes the interests of the organization broadly; participants voluntarily serve on committees and attend functions.Several studies have found that justly-treated employees are more likely to comply with workplace policies, show extra conscientiousness, and behave altruistically toward others (Cohen-Charash & Spector, 2001). In-deed, workers tend to tailor their citizenship behaviors carefully, doling them out to those groups or individuals who have treated them justly and withholding them from those who have not.Justice-inspired employees exhibit OCBs, such as behaving altruistically toward others, these also sound much like employee customer service–oriented behaviors, such as helping others and listening carefully to their needs. Building on this, Bowen, Gilliland and Folger (1999) suggested that just treatment of employees would lead to OCBs that “spill over” to customers (Cropanzano et al., 2007). This results in customers feeling appropriately treated, thereby yielding customer satisfaction and loyalty. Employee’s perception of organizational justice was found to be positively correlated to extra-role behaviors towards the organization as well as the customer. (Lichtenstein, D. et. al, 2008)Organizational Citizenship Behavior is one of the most widely linked outcomes of Organizational Justice. It refers to, organizationally beneficial behaviors that can neither be reinforced on the basis of formal role obligations nor can they be elicited by contractual guarantee of recompense. (Cohen-Charash et al., 2001) OCB thus consists of informal contributions that employees’ might choose to give or not give. Recent studies have highlighted that procedural and interactional justice are predictors of OCB but the role and importance of distributive justice cannot be declined.Organ (1990) has proposed that distributive-justice concerns may influence citizenship according to predictions derived from equity theory (Adams, 1965). If employees perceive unfair compensation, then they may be less likely to perform OCB because such behaviors are discretionary & falling outside an employee’s formal role requirements. Failure to perform OCB is less likely than failure to perform a duty in the job description that may result in official sanctions or in the sacrifice of incremental rewards provided by the formal reward system. As a response to perceived inequity, an employee may withhold voluntary behaviors to adjust his or her input portion of the equity ratio calculation. (Williams, Pitre & Zainuba, 2002)Organ (1990) suggested that perceived procedural unfairness alters an employee’s relationship with the organization. Employees who perceive their relationship with the organization as one of social, rather than economic, exchange may be more likely to exhibit OCB because a social contract is more ambiguous than an economic contract and because extra role behaviors may be less likely to be perceived as exploitation or submission. (Williams et al., 2002)Moorman (1991) suggested that procedural justice involves the fairness of the procedures to determine the outcomes for employees. According to Moorman, procedural justice is concerned with both the organization’s formal procedures and the employees’ interaction with or involvement in the decision-making process. Perceived interactional fairness demonstrated to employees that the supervisor considered them valuable and important as individuals, whereas perceived formal procedural fairness focused on the organization as a whole. From an employee’s perspective, fair procedures may be in place, but the practice of fairness by supervisors demonstrates that justice actually occurs. (Williams et al., 2002)Meta analysis by Cohen-Charash et al., 2001 suggests that all three justices are predictors of OCB but this may also vary due to cultural aspects, industry dynamics etc.
1.5. The Need and Rationale for the Study
- As we know, employees are just not automatons fulfilling the needs of the organization in its march forward. Whether the employer immediately recognizes this fact or not, each employee with the organization is there to fulfill a personal goal too, whether it is monetary or social, or both. Over the years, just as organizational systems have grown, so has employee maturity. An employee today needs to feel that he is receiving justice from the organization that wants him to behave as if he is a part of the system and reciprocate accordingly.Therefore, of the fact that Organizational Justice is the need of the hour, there can be no doubt. Over the years as organizations have grown and moved towards globalization, the importance of suitably trained and experienced employees has grown manifold. It is the employee who finally provides the impetus and drives the organization, much as the owners and the management steer it towards a pre-determined goal.This puts a tremendous amount of pressure on the organization to ensure that the employee gets the justice he deserves and perceives this input of justice as equitably reasonable in his personal case. Finally, it is the employee satisfaction level that brings down attrition and gives to the organization the much-needed doses of suitable behaviors. This study also brings out in detail the many kinds of justices that may be perceived by an employee, his possible reactions and the outcome of each in relation to the advantages to be gleaned by the organization. As the possible scope for this study is huge and is as varied as the myriad different kinds of organizations that employ people, this study limits its scope to the emerging ‘Retail Sector in India’. This study, therefore,aims to find out which kind of justices influence citizenship behavior of the employee to the maximum possible extent in the retail sector in India only. Most of the earlier studies on organizational justice so far have focused on different industries in already developed countries. India is a developing nation and the organized retail sector is in its nascent stage with competition from national and international players. It requires a more focused approach to understand employees and further carve out policies in a way that will help improve performance and overall organizational effectiveness to bring us on par and possibly outstrip the developed nations in the just treatment of employees. It is now crucial that a deep study on Organizational Behavior and the resulting Organizational Citizenship Behaviors of the employees be done keeping these focused goals in mind.
1.6. Statement of the Problem
- The study aimed to find out the Employee perceptions of Organizational Justice and its influence on Organization Citizenship Behavior in the retail sector.
1.7. Objectives of the Study
- The study analyzed the influence of store executives’ perceptions of Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior.1. To find out if there is a relationship between Organizational Justice and Organization Citizenship Behavior.a) To find out if Distributive justice influences Organization Citizenship Behavior.b) To find out if Procedural justice influences Organization Citizenship Behavior.c) To find out if Interactional justice influences Organization Citizenship Behavior.2. To find out if there is gender differences in the perceptions’ of Organization Justice.
1.8. Hypotheses
- I. H1: There is a significant relationship between Organization Justice and Organization Citizenship Behavior.a): There is no significant relationship between Distributive justice and Organization Citizenship Behavior.b) There is a significant relationship between Procedural justice and Organization Citizenship Behavior.c) There is a significant relationship between Interactional justice and Organization Citizenship Behavior.II. H2: There are gender differences in the perceptions’ of Organization Justice.Resume of the Following ChaptersThe following chapters discuss and highlight the related literature. The methodology is explicitly explained and the analysis and results are discussed.
2. Review of Literature
- This chapter highlights the review of related literature and studies. The relationship between the Dependent and Independent Variables is considered and revolves around the key concepts of the problem. It is also the intention of the researcher to find out the research gap in this area and focus on the areas that have achieved little attention.
2.1. Studies on Organizational Justice
- Lee and Farh (1999) aimed to study the moderating effect of gender on the justice and organizational outcomes. The researchers hypothesized a stronger positive relationship between distributive justice and organizational outcomes among males than females and a stronger positive relationship between procedural justice and organizational outcomes among females than males. The study was conducted in two phases or research settings. In the first setting 354 employees of a consumer products company were asked to participate and employees attitudes towards a new pay plan implemented in the company were examined. In the second setting the data set of prominent researcher Folger and Konovsky were used and 217 employees were given questionnaire measuring distributive and procedural justices , pay satisfaction, trust in supervisor, organizational commitment and negative affectivity were measured. The results of this study contradicted the hypothesis and it was concluded that women concentrated more on distributive issues rather than procedural issues in order to address past pay discrepancies. This shows that gender did not effect organizational outcomes. These results indicate a work value of similarity and narrowing of gender differences in the recent times.Mc Farlin and Sweeney (1992) conducted a study to find out the perceptions of distributive and procedural justice as predictors of job satisfaction, pay satisfaction, organizational commitment and subordinate’s evaluation of supervisor among 675 bank employees. The results showed that both distributive and procedural justice have an impact on work outcomes but distributive justice tended to be a stronger predictor of personal outcomes like pay. Procedural justice on the other hand was a better predictor of organizational outcomes like job commitment.Mc Farlin and Sweeney (1997) examined the gender differences in men and women for the two notions of justice i.e., distributive and procedural. The data came from another study done by the Federal office of Personnel Management in 1980. Surveys were mailed to civilian employees and 13862 mails came back in return. The survey-included details like employment data, attitudes towards work, supervisor and co-workers. Participants also provided information such as gender, race, pay level, tenure in the organization. Indexes for each distributive and procedural justice were constructed. Job satisfaction, intentions to stay and supervisor evaluations were made. It was found that procedural justice and its relation with organizational variables was stronger in women and stronger in men for distributive justice and organizational outcomes. Hence, managers must adopt different strategies for men and women to create an overall environment of fairness.Colquitt, Conlon, Porter and Ng(2001) did a meta analysis of Justice literature. 183 justice studies were examined and concluded that organizational justice has evolved as a construct over time with different notions of justice coming into existence. It was also noted that justice is a moderate to high indicator of fairness perceptions and related to organizational outcomes like Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment, Trust, Turnover Intentions, Organizational Citizenship Behaviors, performance, withdrawal. A literature search was done using PsychINFO database starting fro the year 1975 to 1999. It was found that the three constructs of justice are theoretically distinct and that a three way interaction exists among thejustice constructs. The study also called for more research to be done on Interactional Justice as it was still an emerging concept.Colquitt (2001) explored the construct of justice and provided a new measure for assessment. Items were constructed based on the previous literature. The measure was validated in two different settings, first in an university setting and secondly in an automobile manufacturing setting. This justice measure is an indirect one that is it does not ask how fair something is instead it assesses fairness criteria like bias, consistency ,explanation etc. Factor analysis showed four different constructs of justice i.e., distributive, procedural, informational and interpersonal. The nature of the measure being indirect makes it a better predictor of organizational outcomes than direct measures.
2.2. Studies on Organizational Citizenship Behavior
- Posdakoff and MacKenzie (1994) studied the impact of OCB’s on a sales performance unit and evaluate this effect on managerial evaluations of employees. This was done by evaluating the effect of OCB on overall performance of a unit with a sample of 987 insurance agents and then by evaluating the effect an agent’s performance on the overall organizational effectiveness. The results of these studies were then compared to find out the extent of weightage managers give to OCB when evaluating employees. Results revealed that managers gave lot of importance to OCB as a factor to evaluate a sales employee ‘s performance. However, it was also found that OCB do not increase overall unit performance always, rather some OCB behaviors enhance performance while some hinder it.Van Dyne, Graham and Dienesch (1994) conceptualized OCB and proposed a network of antecedents and a new measure to assess OCB. A sample of 950 employees and 169 subordinates was taken. The new construct measured Obedience, Loyalty and Participation. The other measures used were Commitment, Satisfaction, Cynicism, workplace values and job characteristics. Results showed loyalty to be the strongest mediating factor for OCB and its antecedents. The measure had a high validity.Konovsky and Organ (1996) conducted a study on 402 professional and administrative employees to see if dispositional factors like Agreeableness, Conscientiousness and Equity Sensitivity could account for OCB. Questionnaires were given out to assess OCB, agreeableness and conscientiousness, perceived fairness, equity sensitivity, supervisor satisfaction. The results indicated that OCB were neither effected by satisfaction, fairness perceptions, equity sensitivity nor Agreeableness but Conscientiousness played a significant role predicting OCB behaviors.Organ (1997) reexamined the construct of organizational citizenship behavior after his first book called ‘Good Soldier Syndrome’. This paper aimed at developing a more precise definition of OCB. The author reviewed other studies done after his work in 1988 and reaffirmed some of the earlier meaning of concepts in his OCB construct. The author also suggested to look at OCB in the lines of Borman and Motowildo’s work in 1993 called contextual performance.Roberts, Coulson and Chonko (1999) researched salespersons’ perceptions of equity and justice affected their commitment levels and turnover intentions. The study was conducted among 1000 salespersons across eight industries. A total of 249 questionnaires were usable and measures to assess turnover intent, commitment and internal and external equity to measure fairness perceptions, internal distributive and internal procedural justice were used. Results showed perceptions of equity and justice are good predictors of affective and behavioral dimensions of commitment. Perceptions of internal and external equity were positively correlated to commitment. Contrary to earlier studies, it was found that distributive justice also played a salient role as compared to procedural justice.Chaitanya and Tripathi (2001) explored the dimensions of Organizational Citizenship Behaviors and its relation with Organizational Commitment. The study was undertaken with 100 public-sector employees in India. The measure used to assess OCB had six dimensions to it : Altruism, Civic Sense, Courtesy, Sportsmanship and Perception of Organization towards OCB. Factor analysis showed that Perception of Organization towards OCB, Sportsmanship, Altruism are significantly predicted commitment.Maxham and Netemeyer (2003) proposed a theoretical model wherein they proposed employees perceptions of shared values and organizational justice trigger and stimulate customer directed extra role behaviors when handling complaints. They further elaborated that customers’ perception of justice could lead to favorable customer outcomes. The sample for this study consisted of online customers making complaints about the electronic equipment purchased from a retailer. 320 survey sheets were completed and assessed customer related extra role behavior, distributive justice, procedural and interactional justice, overall firm satisfaction and purchase intent and likelihood of spreading a positive word of mouth using different scales. This study helps bridge the gap between theory and practicality by measuring both employee and customer perceptions in a complaint-handling situation. The study found that customer directed behaviors were a result of all the three kinds of justice being perceived as appropriate. This resulted in the customer justice being high in turn affecting customer outcomes like increased loyalty to the firm, spreading a good word about the product and the company.Borman (2004) described the construct of citizenship behavior and summarized research done. It also addressed topics like the weightage managers give while making evaluations, personality factors impacting OCB, links between OCB and Organizational effectiveness and relation between Justice and OCB.Gadot (2007) gave the construct of OCB a new dimension, wherein he proposed that OCB might emerge from external pressures rather than goodwill as proposed by Organ and the others.The author challenges the view OCB’s are voluntary and asserts that they may even stem out of managerial strategies or coercive social pressure. He proposes the concept of CCB or Compulsory Citizenship behavior, which unlike OCB has a more destructive side to it. A sample of 28 teachers from 13 Isareli schools was taken and questionnaires on CCB, job stress, innovation, organizational politics, job satisfaction, intentions to leave, negligent behavior, burnout and group level OCB, OCB and in- role performance were administered. The findings confirmed that CCB existed in the system with no rewards offered for an employee’s efforts. The paper explored new boundaries of extra-role behavior.Lin, Hung and Chiu (2008) explored service oriented OCB’s(loyalty, service delivery and participation) which are hypothetically influenced by personal cooperativeness, social approval, task interdependence and outcome interdependence. This proposed model was tested on 227 employees of the top five financial holding companies in Taiwan. The results showed that OCB was significantly related to loyalty, service delivery, participation, social network ties and organizational commitment. This research consistent with earlier research also shows that fairness perceptions go a long way in showing service oriented OCB’s.
2.3. Studies on Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior
- Niehoff and Moorman (1993) studied the relationship among three methods of leader monitoring, employee perceptions of workplace justice, and employee citizenship behavior. The basic premise for the study was that strict or close monitoring would negatively affect citizenship behavior and keep employees from performing duties seen as extra and perhaps not leading to rewards. The researchers also hypothesized that monitoring through unobtrusive methods like informal meetings, observation, formal meetings helps in gathering unbiased information and avoids the managers in making attribution errors. Thus, the researcher’s tested the premise that if employees feel that monitoring methods were justified and appropriate, employees’ perceptions and outcomes would also be positive towards the organization.Mauborgne and Kim (1996) developed a theory on how procedural justice affects managers' in-role and extra-role behavior in a business scenario. They did so by studying the direct and indirect effects of procedural justice judgments on the in-role and extra-role behavior of multinationals' subsidiary top management in the context of the global resource allocation decision process. This paper tested a theory, which predicted that the attitude of commitment to support decisions provided a bridge between procedural justice and extra-role behavior. 119 subsidiary top managers were given three questionnaires one on perceptions of procedural justice, second on the reflections after annual global resource allocation and lastly reflections on satisfaction with outcomes. The results suggested that procedural justice inspires managers to go beyond the call of duty and engage in innovative actions, spontaneous cooperation, and creative behavior on behalf of the organization in their execution of decisions.Moorman and Blakely (1998) studied how procedural justice influences organizational citizenship behaviors by influencing perceived organizational support. Three questionnaires were given to a sample of 450 civilian subordinates of a military hospital out of which 255 were usable. Results suggested that procedural justice is an antecedent of perceived organizational support that in turn promotes citizenship behaviors.Moorman and Blakely (1998) did a study to test how procedural justice may effect organizational citizenship behavior and how perceived organizational support may mediate this relationship. The study was conducted on 157 supervisors and their subordinates of a large military hospital. The results indicated that fairness in procedures is an antecedent to the perception of organizational support and influence organizational citizenship behaviors in an organization.Fields, Pang and Chiu, (2000) studied the extent to which distributive and procedural justices predicted work outcomes like intention to stay, job satisfaction and evaluation of supervisors. The major focus of the study was to find out if cultural differences play any role in work outcomes being different. The researchers had conducted this study on the notion that no study had been conducted in Hong Kong, which examined the differences in justice levels and resulting organizational outcomes unlike in the United States. 783 workers were given questionnaires to measure the two kinds of justice, satisfaction, and turnover intent. The results indicated both kinds of justice influenced work outcomes like Job Satisfaction, Intention to stay in Hong Kong. It was also found that perceptions of justice did not effect evaluations of supervisors. It was also seen that justice perceptions differ between the two nations and this could be due to cultural factors such as power distance, individualism- collectivism.Cohen-Charash & Spector (2001) examined the three kinds of justice in a meta-analysis study. The study clearly established or validated the three forms of justice to be distinct and unique as well as interacting with each other to form the overall notion of justice. It was found that satisfaction measures were mostly related to types of justice, whereas, OCB was related to distributive as well as procedural justice. Other outcomes of Justice such as Commitment, Trust, performance and counter-productive behavior were related to Procedural justice.Aryee , Budhwar and Chen (2002) did a study on an Indian public sector organization to test a social exchange model of work attitudes and behavior. The researchers hypothesized that the three dimensions of justice were also related to the trust employees put in their supervisor and this would influence work attitudes like turnover intentions, organizational citizenship behavior, organizational commitment, task performance and job satisfaction of employees. The sample constituted of 179 supervisor-subordinate dyads that were given different questionnaires. The results indicated that distributive justice correlated to turnover intentions, organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior. Procedural justice correlated to Job satisfaction, turnover intentions and organizational commitment, whereas Interactional justice correlated to all the dimensions. Trust in the organization was a mediating factor for organizational outcomes like satisfaction, commitment, turnover intent and trust in supervisor helped in increasing organizational citizenship behavior and task performance.Viswesvaran &Ones (2002) did a meta- analytic study both electronically and manually using Psych Info Database and psychological abstracts to examine the organizational justice construct and its influence on work attitudes and behavior. Correlation studies showed that both distributive and procedural justice had a high and positive correlation with organizational commitment, job satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior. In conclusion the authors note that procedural justice was a better predictor of workplace behaviors.Williams, Pitre & Zainuba (2002) conducted a study across industries (like manufacturing, banking, IT, financial services and others), organizations and job positions to show that positive relationships with supervisors led to OCB intentions and not fair rewards and procedures. Questionnaires on Historical OCB, OCB Intentions and Organizational justice were given to 144 employees out of which 114 completed the questionnaires. The aim of the study was to find out if Interactional justice impacted OCB intentions and it was found that the present study supported early researchers perspective that it was fair treatment or employees who’s supervisor supported and treated them fairly were more likely to exhibit citizenship behavior.Tepper and Taylor (2003) conducted a study among 373 military supervisor-subordinates dyads. The researchers hypothesized that supervisor’s mentoring behavior and role definitions would mediate the subordinates procedural justice perceptions and thus, organizational citizenship behavior. The results suggest that the hypothesized relationship was true.Harvey, S and Haines, V (2005), studied the three notions of organizational justice during a crisis situation through a telephonic interview to 366 working individuals of ice-storm affected households. The researchers hypothesized that procedural and interactional justices play an important role in influencing an employee’s perceptions. Justice was measured with a telephonic interview and commitment through a questionnaire. Results indicated that work attitudes like satisfaction and commitment were predicted by policies and procedures adopted at the time of a disaster. An interaction between distributive and procedural justice was found to predict job satisfaction.Zinta (2005), did a study on 150 employees studied and the relationship between Organizational Justice and Organizational Politics, Turnover Intentions, Citizenship Behaviors and Performance. The results indicated that procedural justice played a significant role for employees to display OCB but did not seem to influence organizational politics much.Blakely, Moorman & Andrews (2005), did a study on equity sensitivity as an explanation of individual differences in Organizational Citizenship Behaviors in response to the perceptions of organizational justice. Questionnaires were given to 150 MBA students for the three variables- equity sensitivity, Organizational Citizenship Behavior and Organizational justice. Results indicated that as the positive perceptions of justice increase so does the level of OCB. It suggests that a fair working environment promotes the performance of OCB’s. The study also found that contrary to their expectations sensitivity did not vary OCB’s according to justice perceptions.Messer and White (2006) did a study to find the influence of employees’ mood and fairness perceptions on Organizational Citizenship Behavior. The study was undertaken in five large service organizations among 138 employees’. The study suggested that employees’ perception of fairness affected their likelihood to perform organizational citizenship behavior. Also, a positive mood influences extra-role behaviors. Chiaburu & Lim (2008) conducted a study to find out the antecedents of Organizational Citizenship Behavior as Manager Trustworthiness or Interactional Justice. 120 supervisor dyads were asked to participate and were administered questionnaires for manager trustworthiness and interactional justice. The results indicated that both factors influenced OCB and also, found that manager trustworthiness can act like a substitute by lending support for the importance of trustworthiness over and above interactional justice.Najafi et al. (2011) conducted a study to determine the causal relations between organizational justice, psychological empowerment, organizational commitment, job satisfaction and OCB, by investigating the mediating role of job satisfaction and organizational commitment. A sample of 280 educational experts from universities participated in the study. Questionnaires were administered to assess the five variables. The study produced a number of findings: Organizational justice directly influences job satisfaction and psychological empowerment and turnover intentions. Also psychological empowerment directly and positively influences job satisfaction and psychological empowerment. Job satisfaction positively influences organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior. Organizational commitment directly influences organizational citizenship behavior. Also organizational justice and psychological empowerment positively and indirectly influences organizational citizenship behavior. The researchers concluded that if there is organizational justice and psychological empowerment within an organization, employees' job satisfaction and organizational commitment will increase and these will in turn improve organizational citizenship behavior.
2.4. Conclusions
- The studies on Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship behavior show that justice is an antecedent of citizenship behavior. Though many studies have been done of find out which kind of justice influences citizenship behavior the most is not very clear. Cohen- Charash et al. (2001) called for more studies to be done.The studies done in the past concentrate on other sectors and not specifically on the retail sector in India i.e., among store employees. Some studies have been done on Salespersons but a store comprises of other personnel also apart from the customer representatives.According to Mc Farlin and Sweeney (1997) differences among employee perceptions on justice vary among the two genders. This study aims to identify if men and women give more importance to a certain kind of justice or not.
3. Methodology
- This chapter discusses procedures adopted to evaluate the research. The terms and concepts used in the chapters have been operationally defined. The sampling technique, tools for data collection and statistical techniques used are also stated. The purpose of the research was to find out the justice perceptions of Store Executives and how these perceptions influence Organization Citizenship Behavior.
3.1. Variables under Investigation
- Independent Variable: Organizational JusticeDependent Variable: Organization Citizenship Behavior
3.2. Operational Definitions
- • Organizational Justice- Employee’s perception of the fairness of treatment received from organizations. (Cropanzano & Greenberg, 1997). It refers to the extent to which employees are treated fairly in the organization.• Organizational Citizenship Behavior- Individual behavior that is discretionary not directly or explicitly recognized by the formal reward system and that in the aggregate promotes the effective functioning of the organization. (Organ, 1988)• Store Executives – Employees working in a store including customer executives, cashiering, inventory executives and managers.
3.3. Research Design
- The research method adopted for the present study was a quantitative paradigm, to study Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior among store executives.
3.4. Sample
3.4.1. Brand / Organization
- The international brand offers Apparel, Footwear and Accessories at affordable prices in an excellent shopping environment for its customers with a unique concept of delivering international fashion & value to the discerning shopper. The brand has more than 65 stores operating all over India.
3.4.2. Location
- Bangalore, India
3.4.3. Size
- A sample of 72 store executives for the study was drawn from a Single Retail chain In Bangalore having eleven stores in the region.
3.4.4. Positions / Job Roles
- The sample comprised of Customer Relationship Executives, Department Managers, Cashiering Executives, Inventory Executives and the Store manager.
3.4.5. Sampling Method
- Purposive Sampling
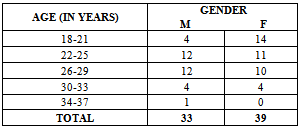
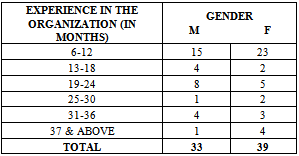
3.4.6. Profile of the Sample
|
|
3.4.7. Inclusion Criteria
- 1. Both male and female respondents were included in the sample.2. Participants were required to have a minimum of six months experience in the organization and maximum of five-year experience.3. The participant’s age should have been a minimum of 18 years.4. Participants were only chosen from stores in the Bangalore region.An Inclusion criterion of employees’ with a minimum of six months experience was chosen as, the retail sector has a high attrition rate and six months is enough time for an employee to form fairness perceptions.
3.4.8. Exclusion Criteria
- 1. Participants without a minimum of six months experience in the organization were not included.2. Participants below 18 shall not be included in the sample.3. Participants were not chosen from stores in different cities.
3.5. Measures Used
- 1. Organizational Justice Scale (Colquitt, 2001) was used to measure Organizational justice. The scale is a 5-point scale consisting of a total of 20 items: four items measuring Distributive Justice, seven items measuring Procedural Justice and nine items measuring Interactional Justice. The cronbach’s alpha is 0.96.2. Organization Citizenship Behavior scale (Jain, S & Sharma, V, 2010) was developed to measure Organization Citizenship Behavior. The scale consists of 36 items. The items are on a 5point scale and sum of all scores would reflect OCB score. The reliability of the scale was determined by split half- method on a sample of 260 subjects and the reliability coefficient was found to be 0.89. The Validity was found to be 0.94. The norms were established on 260 respondents working in the manufacturing industry in India.
3.6. Procedure
- The organization’s permission was taken to administer the study. The researcher met the participants to established rapport. Participants were informed about the purpose of the study and the consent form was signed. Questionnaires were distributed to the participants in their duty hours. The researcher was present while participants’ responded to the questionnaires, so that any doubts could be clarified. Each questionnaire set took about 15-20 minutes for completion.
3.7. Data Analysis
- • Correlation analysis was done using Pearson’s Product Moment correlation to find out the relationship between the Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior. • A simple linear Regression Analysis was done to find out the variance. • t-test was used to find out the gender differences in Organizational Justice.
3.8. Ethical Considerations
- • The anonymity of the subjects and the confidentiality of the responses were maintained. • The subjects were asked to sign the consent form and were not coerced to participate. They were informed that they were free to withdraw from the survey at any time should they felt the need to do so. • It was also clearly stated that the data collected from the study would be used for academic purposes only.
4. Results and Discussion
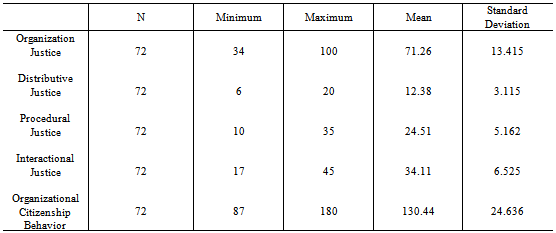
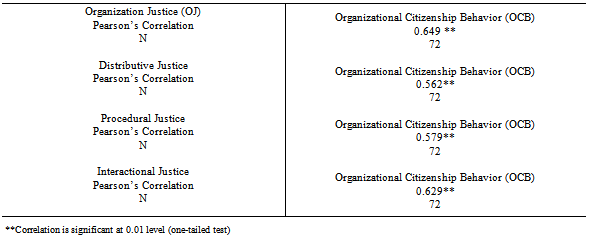
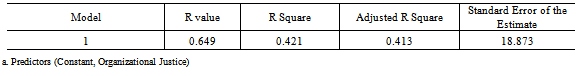
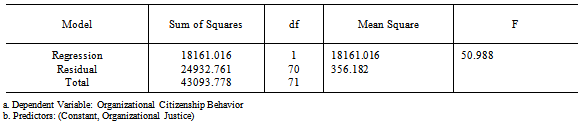
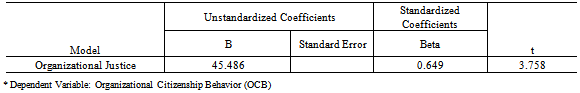
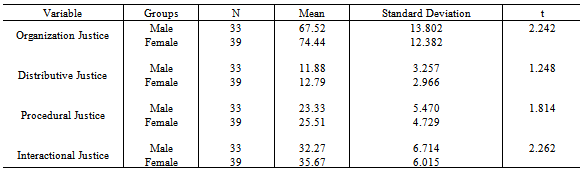
- The present chapter gives an overview and interpretation of data.The data has been carefully processed, systematically classified and tabulated, scientifically analyzed, interpreted and concluded. The study aimed to find out the Employee perceptions of Organizational Justice and its influence on Organization Citizenship Behavior and if there were any gender differences in these perceptions, among retail sector employees. The sample chosen for the study were store executives from a single retail chain in Bangalore, having a minimum of six months of work experience in the organization and involved customer, inventory, cashiering executives and managers of the stores. Prior permission from the organization was taken and questionnaires to measure the Independent and Dependent Variables were administered. The different sections of this chapter have been organized under the following sections:1. Descriptive statistics2. Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation- Correlation Analysis3. Regression Analysis4. T-test5. DiscussionThe hypotheses generated after reviewing prior literature were:
|
|
|
|
|
5. Summary and Conclusions
5.1. Summary
- The study aimed to bridge the gap between employers and employees by giving an insight into how employees perceive the organization and it’s functioning. This study particularly targeted if employees felt they were being treated fairly or not and how this impacted their work performance outcomes. With employees evolving to a more mature state of mind, organizations must treat providing justice as an input to be able to receive the desired output. This study enlightens employers on what their employees value and how modifying certain principles and procedures could lead to lowering attrition and increasing satisfaction and eventually going beyond from what their job description requires.The study was carried out in the retail sector, which is one of the fastest growing sectors in India. The sample was taken from a leading apparel brand, which had stores in Bangalore. Two separate questionnaires were administered to measure the Independent Variable-Organization Justice and Dependent Variable-Organizational Citizenship Behavior. A total sample of 72 was analyzed using SPSS version 20.0.The results signal towards a positive significant relationship between Organization Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior. The study also pointed out that employees value the construct of organizational justice itself. The three components of justice work in tandem with each other. Interactional Justice has emerged as one of the most important factors to be kept in mind if organizations want exceptional performance. There were significant gender differences found in the overall justice perceptions as well as in the interactional justice notion.
5.2. Conclusions
- The study examined the extent to which Organizational Justice predicts Organizational Citizenship behaviors in a store setting. According to the results, employees not only engage in citizenship behaviors when they perceive the rewards and outcomes to be sufficiently fair but also laid importance to the procedures that led to the allocation and distributions of the outcomes. Most importantly, the study also emphasizes how the role of the supervisors and the organization interpersonal relationships can inspire citizenship behaviors among employees. A gender difference among justice perceptions was also noticed.
5.3. Implications
- The below mentioned implications are relevant to the entire managerial cadre of the organization and need to be stressed by the Human Resource Department.With recent developments in the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Policy, doors are now open to International players bringing in not only a variety of products and services but also newer business models which focus on human resources as the most vital asset an organization can possess. Human Resource managers will be required to create, develop and maintain a competitive advantage, aligned to the organization’s competitive strategy in a volatile environment.The construct of Organizational justice thus, can help in providing this much needed competitive strategy by ensuring not only the smooth functioning of an organization but also create an organizational climate for service.The results of the study show that Interactional justice which is the human side of organizational practices and the communication between the source and the recipient of justice was found to be the most influential in promoting citizenship behaviors, closely followed by procedural and distributive justice. Thus, employers looking for exceptional performance in terms of efficiency and effectiveness should treat employees fairly and appropriately, which will in turn result in transcending the demands of a formal job requirements to extra-role behaviors.
5.4. Limitations of the Study
- Although the study provided interesting insights, the study also has shortcomings.Firstly, the measures used in the study are self-report measures, which typically suffer the problem of a social desirability effect. Many a times, participants choose an ideal alternative instead of the truth.Secondly, this study is restricted to the retail sector and the findings are provisional and cannot be generalized to other organizations in the same sector as well as to other sectors. Thus, the external validity of the study is low.Thirdly, future researchers may also wish to develop their own set of questionnaires, as the Organizational Justice scale in the current study was adopted from a Western setting, which included certain words that may have implied a different meaning from what the question intended to measure.
5.5. Directions for Future Research
- Future research can replicate the methodology adopted in the present study to other sectors. Secondly, since Organizational Justice is one of the factors that influences Organizational Citizenship Behavior, the other influencing factors can be explored.The present study does not investigate the antecedents of organizational justice. Literature reviews shows that trust, organizational support, organizational politics have a significant impact on justice perceptions. A future initiative can therefore, explore these aspects.Thirdly, another project that can be carried out is to find out the extent to which Organizational Citizenship Behavior influences Organizational Justice Perceptions.Fourthly, the development of scientific and practical tools and techniques to implement the above findings can be a future initiative.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Many people have played an important role in the compilation of the present research work, either directly or indirectly.My sincere gratitude goes to the large Retail Chain organization who allowed me to conduct this research and assisted my efforts with immense understandingI would like to thank all the researchers who contributed to the field and the number of people for their assistance with this work. My gratitude goes to all of those who have filled my questionnaires within such a short period of time. Without their help my research would have been incomplete.I would also like to thank Dr. Tony Sam George, Head of the Department of Psychology, Christ University, Bangalore for giving me the opportunity to do this research.I further extend my deepest gratitude to Dr. Padmakumari, Assistant Professor- Department of Psychology, for her help in my research.Without her encouragement and support, this study would not have been possible. Her regular patient guidance and suggestions helped me to resolve and compile the myriad issues involved in my research.Lastly, I would like to extend a heartfelt gratitude to my family and friends who have been a constant source of support and encouragement.
Appendix A
- Informed Consent FormTitle of the study: A study on theOrganizational Justice And Organizational Citizenship Behavior among Store Executives.Name of the Researcher:Shruti MathurCost/Compensation:There are no costs or compensation for participating in this study.Confidentiality: The participant will not be identified by name in any report using information from the results of questionnaire responses. Confidentiality of the participant in this study will remain secure. Any subsequent uses of information or data in this study will be subjected to ethical considerations that protect the anonymity of the participants and institutions. Voluntary Participation: Participation in this study is voluntary. Participants have the right to withdraw or discontinue participation at any time without penalty.I, _______ have voluntarily given my consent to participating in a psychological study conducted by Shruti Mathur, for her research on A study on theOrganizational Justice And Organizational Citizenship Behavior among Store Executives.I have received a clear and complete explanation of the general nature and purpose of the study and the specific reason(s) as to why I am being examined. I understand that I will be provided with the name and contact details of the researcher should I have questions about the research. I also understand that I will retain a copy of this form for my personal records.Date: ________ Signature of the participant: ________Signature of the Researcher: ________Shruti MathurEmail Id: shrutimathur16@gmail.comMobile: 07259222060
Appendix B
- DEMOGRAPHIC SHEET:Name:Age:Sex:Name of the Organization:Work Experience in the Organization:Contact Number:Signature:Date:
Appendix C
- ORGANIZATIONAL JUSTICE QUESTIONNAIRE, COLQUITT (2001)Kindly tick the most appropriate answer for the following questions. Please do not leave any questions unanswered. The questions are on a 5 ponit rating scale, where 1 indicates the smallest degree of extent and 5 indicates the largest degree of extent.

Appendix D
References
| [1] | Adams, J. S. (1965). Inequity in social exchange. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 2, pp. 267–299). New York: Academic Press. |
| [2] | Ambrose, L. M. & Schminke, M. (2009). The results of overall Justice Judgments in Organizational Justice Research: A test of Mediation. Journal of Applied Psychology. Vol. 94, No. 2, pp. 491-500. Published by American Psychological Association. Retrieved July 30, 2012. doi : 10.1037/a0013203 |
| [3] | Ando, N. &Matsuda, S. (2010). How Employees See Their Roles: The Effect of Interactional Justice and Gender. Journal of Service and Science and Management. Retrieved on September 15, 2012. doi:10.4236/jssm.2010.32034 |
| [4] | Arnold, T. & Spell, S. C. (2006). The Relationship between Justice and Benefits Satisfaction. Journal of Business and Psychology, Vol. 20, No. 4, pp. 599-620. Published by: Springer . Retrieved on June 15, 2012 from,http://www.jstor.org/stable/25092960 |
| [5] | Aryee, S., Budhwar, S. P. & Chen, X. Z. (2002). Trust as a mediator of the relationship between organizational justice and work outcomes: Test of a social exchange model. Journal of Organizational Behavior. Vol. 23, pp. 267-285. Wiley Interscience. Retrieved on June 26, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/4093804 |
| [6] | Bettencourt, L. A. &Brown, W.S. (1997). Contact Employees: Relationships among Workplace Fairness, Job Satisfaction and Prosocial Behaviors,” Journal of Retailing, 73(1), 39-61. |
| [7] | Blakely, L. G., Andrews, C. M. & Moorman, H. R. (2005). The Moderating Effects of Equity Sensitivity on the Relationship between Organizational Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors. Journal of Business and Psychology, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp. 259-273. Retrieved on June 26, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/25092936. |
| [8] | Borman, C. W. (2004). The Concept of Organizational Citizenship. Current Directions in Psychological Science, Vol. 13, No. 6 pp. 238-241 Published by: Sage Publications, Inc. on behalf of Association for Psychological Science. Retrieved on June 15, 2012 fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/20182965 |
| [9] | Brief, P. A. & Motowidlo, J. S. (1986). Prosocial Organizational Behaviors. The Academy of Management Review, Vol. 11, No. 4 (Oct., 1986), pp. 710-725. |
| [10] | Brockner , J. (2002). Making Sense of Procedural Fairness: How High Procedural Fairness Can Reduce or Heighten the Influence of Outcome Favorability . The Academy of Management Review, Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 58-76. |
| [11] | Burton, J., Sablynski, J.C. & Sekiguchi, T. (2008). Linking Justice, Performance, and Citizenship via Leader-Member Exchange. Journal of Business and Psychology, Vol. 23, No. 1/2 (Sep., 2008), pp. 51-61. Retrieved on June 26, 2012 fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/27753888 |
| [12] | Chaitanya, K. S. & Tripathi, N. (2001). Dimensions of Organisational Citizenship Behaviour. Indian Journal of Industrial Relations, Vol. 37, No. 2 (Oct., 2001), pp. 217-230. Retrieved on September 3, 2012 fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/27767778 . |
| [13] | Chen, J. Y., Lin, C. C., Tung, C. Y. & Ko, T. Y. (2008).Associations of organizational Justice and Ingratiation with organizational citizenship Behavior: the Beneficiary perspective. Social Behavior and Personality, VOL. 36(3), pp. 289-302. |
| [14] | Chiaburu, S. D. & Audrey S. (2008). ManagerTrustworthiness or Interactional Justice? Predicting Organizational Citizenship Behaviors. Journal of Business Ethics, Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 453-467. Retrieved on June 26, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/25482389 |
| [15] | Cohen-Charash. Y., & Spector, P. E. (2001). The role of justice in organizations: A meta-analysis. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, Vol. 86, 278- 321. Doi:10.1006/obhd.2001.2958 |
| [16] | Colquitt J. A., Conlon, D. E., Wesson, M. J. & Porter O. H. (2001). “Justice at the millennium: a meta-analytic review of 25 years of organizational justice research”. Journal of Applied Psychology .pp. 86(3): 425-45. Doi:10.1037/ /00219010.86.3.425 |
| [17] | Colquitt JA (2001). On the dimensionality of organizational justice: A construct validation of a measure. Journal of Applied Psychology, pp. 86: 386-400. Doi:10.1037//00219010.86.3.386. |
| [18] | Cropanzano, R., Bowen, E.D. & Gilliland, W.S. (2007). The Management of Organizational Justice. Academy of Management Perspectives. Pp.34-48. |
| [19] | Donavan, D. T., Brown, J. T. & Mowen , C. J. (2004). Internal Benefits of Service-Worker Customer Orientation: Job Satisfaction, Commitment, and OrganizationalCitizenship Behaviors . Journal of Marketing, Vol. 68, No. 1 (Jan., 2004), pp. 128-146. American Marketing Association. |
| [20] | Dyne, V. L. Graham, J. & Dienesch, M. R. (1994). Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Construct Redefinition, Measurement, and Validation. The Academy of Management Journal, Vol. 37, No. 4, pp. 765-802. |
| [21] | Fields, D., Pang, M. &Chiu, C. (2000). Distributive and Procedural Justice as Predictors of Employee Outcomes in Hong Kong. Journal of Organizational Behavior, Vol. 21, No. 5 (Aug., 2000), pp. 547-562. Wiley-Blackwell.Retrieved on June 26, 2012 fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/3100448 |
| [22] | Folger , R. & Husted, W. B. (2004). Fairness and Transaction Costs: The Contribution of Organizational Justice Theory to an Integrative Model of Economic Organization . Organization Science, Vol. 15, No. 6, pp. 719-729. Published by: INFORMS. Retrieved on September 3, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/30034772. |
| [23] | Gadot, V.E. (2007). Redrawing the boundaries of OCB? An empirical example of extra-role behavior in the workplace. Journal of Business and Psychology. Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 377-405. Springer.Retrieved on September 3, 2012 fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/30221744 |
| [24] | Gilson, L. L., Fedor. B. D & Roth. L. J. (2005). What is Fair and to Whom? Fairness Evaluations of Socio-sexual Behavior. Journal of Managerial Issues, Vol. 17, No. 3, pp. 293-309. Pittsburg State University. |
| [25] | Guruswamy, M., Sharma, K., Mohanty. P. J & Korah. J.T.(2005). FDI in India's Retail Sector: More Bad than Good? . Economic and Political Weekly, Vol. 40, No. 7. pg. 619-623. Retrieved from:http://www.jstor.org/stable/44161 |
| [26] | Henle, A. C. (2005). Predicting Workplace Deviance from the Interaction between Organizational Justice and Personality. Journal of Managerial Issues, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 247-263. Published by: Pittsburg State University. Retrieved on June 15, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/40604498 |
| [27] | J. A. -M. Coyle-Shapiro. (2002). Psychological Contract Perspective on Organizational Citizenship Behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior, Vol. 23, No. 8 (Dec., 2002), pp. 927-946. Wiley-Blackwell.Retrieved on September 3, 2012 fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/4093678 |
| [28] | Kuvaas, B. (2008). An exploration of how the Employee - Organization Relationship affects the linkage between Perception of Developmental Human Resource Practices and Employee Outcomes. Journal of Management Studies. Published by : Blackwell Publishing.i doi:10.1111/j.1467-6486.2007.00710.x |
| [29] | Lee, C. & Farh, J. The Effects of Gender in Organizational Justice Perception. Journal of Organizational Behavior, Vol. 20, No. 1 (Jan., 1999), pp. 133-143 Published by: John Wiley & Sons. Retrieved fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/3100208 . |
| [30] | Lichtenstein, D., Netemeyer, G. R. & Maxham, G. J. (2008). The Retail Value Chain: Linking Employee Perceptions to Employee Performance, Customer Evaluations, and Store Performance. Marketing Science, Vol 27, No. 2, pp. 147-167. |
| [31] | Lin, P. C., Hung, T.W. & Chiu, K. C. (2008). Being Good Citizens: Understanding a Mediating Mechanism of Organizational Commitment and Social Network Ties in OCBs . Journal of Business Ethics, Vol. 81, No. 3 (Sep., 2008), pp. 561-578. Springer. |
| [32] | Mauborgne , A. R. & Kim, C. H. (1996). Procedural Justice and Managers' In-Role and Extra-Role Behavior: The Case of the Multinational. Management Science, Vol. 42, No. 4 (Apr., 1996), pp. 499-515. Retrieved fromhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/2634384 |
| [33] | Mary A. Konovsky, A. M. & Organ. W. D. (1996). Dispositional and Contextual Determinants of Organizational Citizenship Behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior, Vol. 17, No. 3 (May, 1996), pp. 253-266. Published by: John Wiley & Sons. Retrieved on July16, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/2488572. |
| [34] | McFarlin, D. B., & Sweeney, P. D. (1992). Distributive and procedural justice as predictors of satisfaction with personal and organizational outcomes. Academy of Management Journal, 35, 626–637. |
| [35] | McFarlin, D. B., & Sweeney, P. D. (1997). Process and Outcome: Gender Differences in the Assessment of Justice. Journal of Organizational Behavior, Vol. 18, No. 1 (Jan., 1997), pp. 83-98 Published by: Wiley-Blackwell . Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/3100277 . |
| [36] | Messer, A. E. B. and White, A.F. (2006). Employees' Mood, Perceptions of Fairness, and Organizational Citizenship Behavior. Journal of Business and Psychology, Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 65-82. |
| [37] | Moorman, H. R., Blakely, L. G. &Niehoff , P. B. (1998). Does Perceived Organizational Support Mediate the Relationship between Procedural Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior? The Academy of Management Journal, Vol. 41, No. 3 pp. 351-357. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/256913 . |
| [38] | Najafi, S. , Noruzy, A. , Azar, K. H. , Sajad Nazari-Shirkouhi, N. S. & Dalvand, R. M. (2011). Investigating the relationship between organizational justice, psychological empowerment, job satisfaction, organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior: An empirical model. African Journal of Business Management Vol.5 (13), pp. 5241-5248, DOI: 10.5897/AJBM10.1505 |
| [39] | Netemeyer, G. R. & Maxham, G. J. (2003). Firms reap what they sow: The effects of Shared Values and Perceived Organizational Justice on Customer’s Evaluations of Complaint Handling. Journal of Marketing. Vol. 67, No. 1, pp. 46-62. American Marketing Association.Retrieved on September 3,2012 formhttp://www.jstor.org/stable/30040510. |
| [40] | Niehoff, P.B & Moorman, H. R. (1993). Justice as a Mediator of the Relationship between Methods of Monitoring and Organizational Citizenship Behavior. The Academy of Management Journal, Vol. 36, No. 3, pp. 527-556. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/256591. |
| [41] | Organ, D. W. (1997). Organization Citizenship Behavior: It’s construct clean-up time. Human Performance, 10 (2), pp.85-97. |
| [42] | Organ, D.W. (1988). Organizational citizenship behavior: The good soldier syndrome. Lexington, MA: Lexington Books. |
| [43] | Peelle, E. H. (2007). Reciprocating Perceived Organizational Support through Citizenship Behaviors. Journal of Managerial Issues, Vol. 19, No. 4 pp. 554-575. Pittsburg State University. |
| [44] | Posdakoff, M. P. & MacKenzie, B. S. (1994). Organizational Citizenship Behaviors and Sales Unit Effectiveness. Journal of Marketing Research, Vol. 31, No. 3 (Aug., 1994), pp. 351-363. American Marketing Management. |
| [45] | Randall, L.M., Cropanzano, R., Bormann, A.C. & Birjulin, A. (1999). Organizational Politics and Organizational Support as Predictors of Work Attitudes, Job Performance, and Organizational Citizenship Behavior. Journal ofOrganizational Behavior, Vol. 20, No. 2 (Mar., 1999), pp. 159-174. John Wiley & Sons. |
| [46] | Roberts, A. J., Coulson, R. K. & Chonko, B. L. (1999). Salesperson Perceptions of Equity and Justice and Their Impact on Organizational Commitment and Intent to Turnover . Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 1-16 . Sales and Sales Management. Published by: M.E. Sharpe, Inc. Retrieved on June 15,2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/40469943. |
| [47] | Singh, D. B., Mishra, S. (2008). Indian Retail Sector- HR Challenges & Measures for Improvement. Indian Journal of Industrial Relations, Vol. 44, No. 1 (Jul., 2008), pp. 99-111. Retrieved from:http://www.jstor.org/stable/27768175 |
| [48] | Stecher, D. M. & Rosse, G. R. (2005). The Distributive Side of Interactional Justice: The Effects of Interpersonal Treatment on Emotional Arousal . Journal of Managerial Issues, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 229-246. Published by: Pittsburg State University. Retrieved on September 3, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/40604497. |
| [49] | Steve Harvey, S. & Haines, Y. H. (2005). Employer Treatment of Employees during a Community Crisis: The Role of Procedural and Distributive Justice. Journal of Business and Psychology, Vol. 20, No. 1, pp. 53-68. Published by: Springer. Retrieved on June 15, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/25092924. |
| [50] | Tepper, J. B. & Taylor, C. E. (2003). Relationships among Supervisors' and Subordinates' Procedural Justice Perceptions and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors . The Academy of Management Journal, Vol. 46, No. 1, pp. 97-105. |
| [51] | Umphress, E. E., Labianca, G., Brass, J. D., Kass, E. & Scholten, L. (2003). The Role of Instrumental andExpressive Social Ties in Employees' Perceptions of Organizational Justice. Organization Science, Vol. 14, No. 6, pp. 738-753. Published by: INFORMS . Retrieved on June 15, 2012 from http://www.jstor.org/stable/4135131 |
| [52] | Viswesvaran, C., Deniz, S. (2002). Examining the Construct of Organizational Justice: A Meta-Analytic Evaluation of Relations with Work Attitudes and Behaviors. Journal of Business Ethics, Vol. 38, No. 3 (Jul., 2002), pp. 193-203. |
| [53] | Williams, S., Pitre, R., Zainuba, M. (2002). Justice and Organizational Citizenship Behavior Intentions: Fair Rewards Versus Fair Treatment. The Journal of Social Psychology, Vol.142 (1), Pg. 33–44. |
| [54] | Zinta, S. B. (2005). Fairness Reduces the Negative Effects of Organizational Politics on Turnover Intentions, Citizenship Behavior and Job Performance. Journal of Business and Psychology, Vol. 20, No. 2 (Winter, 2005), pp. 175-200. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML