-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Health Science
p-ISSN: 2166-5966 e-ISSN: 2166-5990
2021; 11(1): 17-21
doi:10.5923/j.health.20211101.02
Received: Aug. 1, 2021; Accepted: Aug. 20, 2021; Published: Aug. 25, 2021

A Perspective Study on Repeated Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Linking with Congenital Heart Diseases
Md. Shahariar Khan1, Md. Rahimullah Miah1, Manjur Hossain2, Mashreky Md Isha1, Tania Hussain1, Mohammad Basir Uddin1, Sultana Begum1, Syed Moosa M. A. Quaium1
1North East Medical College & Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh
2Directorate General of Family Planning, Dhaka, Government of Peoples Republic of Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Md. Shahariar Khan, North East Medical College & Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Respiratory Tract Infections (RTIs) are the most important causes of mortality and morbidity in children. There are so many children suffering from repeated lower respiratory infections (RLRIs). A huge number of congenital heart diseases (CHDs) are responsible for RLRIs but these could not be identified due to deficiencies of proper checkup, diagnostic availabilities, routinely follow-up and much awareness. The aim of the study is to assess the relationship between the repeated Lower Respiratory Tract Infection and CHD. Methodology: The method of the study was prospective observational studies completed at the Department of Paediatrics in Private Medical College Hospital within 6 months from 1st January 2021 to 30th June 2021. Total 100 cases of RLRIs were selected and data were taken from history, clinical and laboratory study observations. Results: Out of them 43% of cases were recognized as CHD which are linked to RLRI and residual 57% cases were exclusively RLRI with no CHD. Conclusion: From the study, there are a significant number of correlations between the congenital heart disease and repeated lower respiratory infection. So, the repeated lung infections can be prevented by early identification and adequate treatment of CHD, which is a significant cause of RLRI. The study explores future research trajectories for development of physical condition in children for correct diagnosis and prevention of frequent attack by ideal management.
Keywords: Congenital Heart Disease, Repeated, Lower Respiratory Tract Infection, Relationship
Cite this paper: Md. Shahariar Khan, Md. Rahimullah Miah, Manjur Hossain, Mashreky Md Isha, Tania Hussain, Mohammad Basir Uddin, Sultana Begum, Syed Moosa M. A. Quaium, A Perspective Study on Repeated Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Linking with Congenital Heart Diseases, Journal of Health Science, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 17-21. doi: 10.5923/j.health.20211101.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In the present situation, child mortality is high worldwide [1]. About 6.3 billion children of fewer than 5 years die in each year globally [2]. RTIs are the primer causes of childhood morbidity and mortality all over the world [3]. This is yet more frequent in under-five age in developing countries. Approximately 16% of deaths of children under this age happen in order to respiratory infections which are near about 50,000 in every year and about 80,000 children less than five years are admitted to hospital with this sickness in each year [4]. The general acute lower respiratory infection includes bronchiolitis, pneumonia, acute bronchitis, influenza and whooping cough etc. which are the major causes of death in children all over the world [5]. In the majority of the cases, there occurred repeated lower respiratory infections (RLRI), which also known as recurrent respiratory infection can be defined as 3 or more annual events of respiratory infections that may merit further investigation for an underlying etiology [6].Lower respiratory infection (LRI) is very common caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi and others [7]. There are many causative factors for RLRI like severe malnutrition, congenital and acquired immunodeficiency states, CHD etc. [8]. Major clinical features include dry cough, fever and dyspnea in children [9]. Nowadays, the most frequent type of congenital defect in children is CHD worldwide [10]. The main reasons for CHD among maximum children are unidentified, but mother’s relevant situations such as pre-existing obesity and diabetes are also linked to congenital defects in children [11]; [12]. Some CHD causes pulmonary blood flow which is widespread risk factors for pneumonia in children [13]. Atrial septal defect, Ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus and atrioventricular septal defect are usual acyanotic CHD in children that are prone to develop RRI [14]. In acyanotic congenital heart diseases because of left to right shunting of blood, via a septal defect or the arterial duct, there happens more pulmonary circulation and pulmonary oedema tends to develop congestive cardiac failure (CCF) and become a source of infection for the lower respiratory infections. So RLRI and the CCF may be the first clinical features of an underlying CHD. Earlier studies have shown that CHD is an underlying factor of repeated RTI. So, the co-existence of RLRI and CHD may amplify the mortality in children. The age of beginning and the severity of symptoms in children with CHD are depending on the size of the lesions [15]. The study is to establish a connection between RLRI and CHD.
2. Materials and Methods
- The research was a prospective observational that was done in the department of Paediatrics in Northeast Medical College Hospital (NEMCH), Sylhet between the months of January, 2021 to June, 2021 over a period of 6 months. The selected sample number was hundred (100) in amount. Primary data collected from the NEMCH in Bangladesh pertaining to RLRI in children from the existing ward and outpatient department. Meanwhile, secondary data was collected from diverse sources like ICDDRB, NEMCH central library, books, Journals, daily news, different web pages and relevant update sources. Informal discussion is integrated with the patient’s guardian like parents, grandmother, and other close relatives at Northeast Medical College Hospital. Some hospital data was accumulated through informal counseling with them to monitor patient’s problems. This discussion process was also used to awaken them to get well from this illness. Age group under 5 years, recurrent cough and cold, fever, respiratory distress, cyanosis, anemia, respiratory rate, heart rate, normal and abnormal breath sound and heart sound, hepatosplenomegaly, body weight, Percent saturation of Oxygen, The exclusion criteria are associated with other diseases, viral fever, congenital anomalies other than heart. All general information regarding RRI, its history, clinical examination, investigation and diagnosis were accommodated according to research objectives. Compiled data were integrated for study, analysis and interpretation as findings using standard data analysis software like SPSS version 27, MS Excel 2019 and R programming version 3.6. Ethical consideration is ignored due to questionnaire based surveys.
3. Results
3.1. Age Prevalence
- From study at NEMCH, the prevalence of the disease is more within one year and secondly between 1 to 2 year but low in between 3 to 4 year of age which as shown in Figure 1.
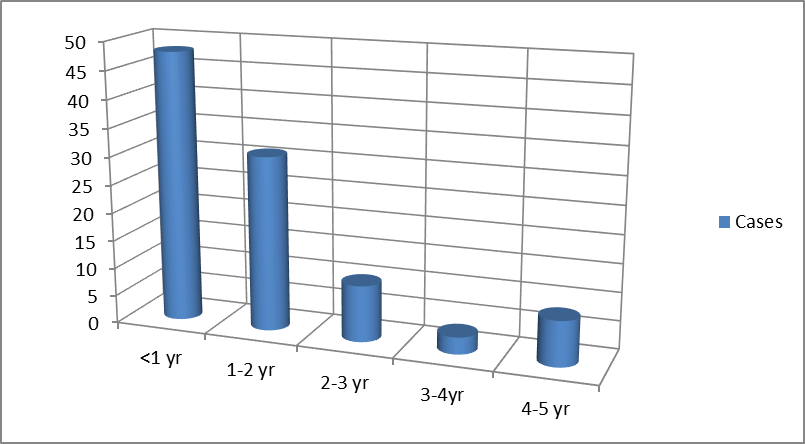 | Figure 1. Prevalence of disease in different years at Department of Paediatrics of NEMCH |
3.2. Sex Variations
- From the patient record of NEMCH, the total numbers of male children are 63 and female children are 37 in number at the Department of Paediatrics from 1st January to 31st July, 2020. So, the disease happening, male is more predominant than females, which as shown in Figure 2.
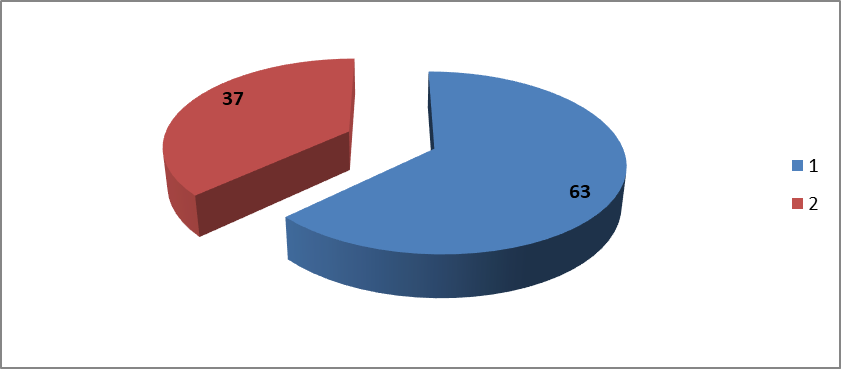 | Figure 2. Sex variation status of multiple Patients at Department of Paediatrics of NEMCH |
3.3. State of Heart Sound and Added Sound in Heart
- From the survey, it has been shown that the rate of abnormal heart sounds of those children is very minimal which is only 8%, otherwise the rate of normal heart sound is 92%. The added sound present in the heart is 42% and absent in 58% cases which as shown in Figure 3.
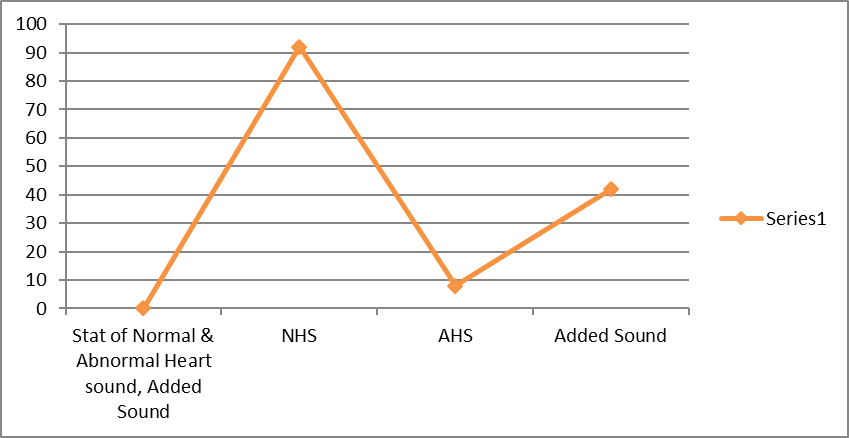 | Figure 3. The percentage of normal and abnormal heart sound and also presence of added sound in the heart |
3.4. Percentage of Oxygen Saturation in Patient
- From a field survey, the majority of patients remain in between the saturation level of 90 to 94%.
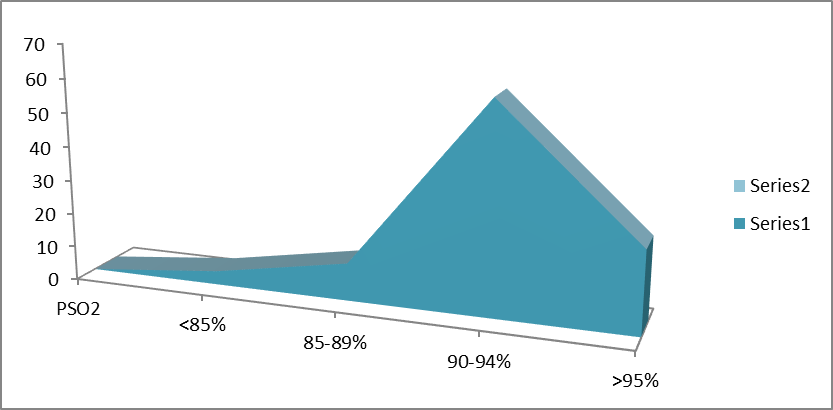 | Figure 4. The percent saturation of Oxygen in different children admitted in Paediatric ward |
3.5. X-ray Finding of Heart in Total Patients
- From assessment at NEMCH, out of the 100 patients, cardiomegaly was found in 31% of children and among them male was 20%, female was 11%. On the other hand, Heart was normal in size in 69% of children and among them male was 43% and female 26%.
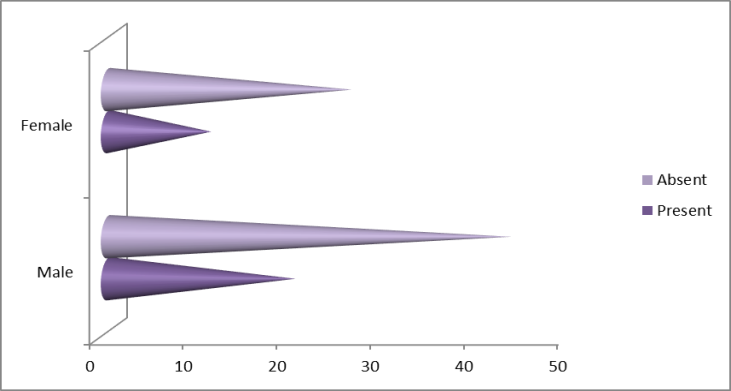 | Figure 5. Radiological finding of heart in all Children |
3.6. ECG Abnormalities
- From observation, ECG abnormalities were found in 16% of children and among them Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) were 10%, Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) were 6%, which as shown in Figure 6.
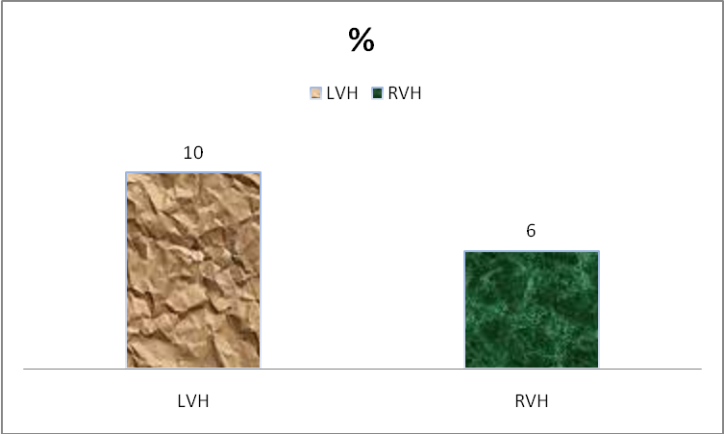 | Figure 6. ECG Findings |
3.7. Existence of CHD in Echocardiography
- In 43% cases, CHD was diagnosed by echocardiography and in 57% cases, CHD was not found. In both cases there was male predominance than female, which as shown in Figure 7.
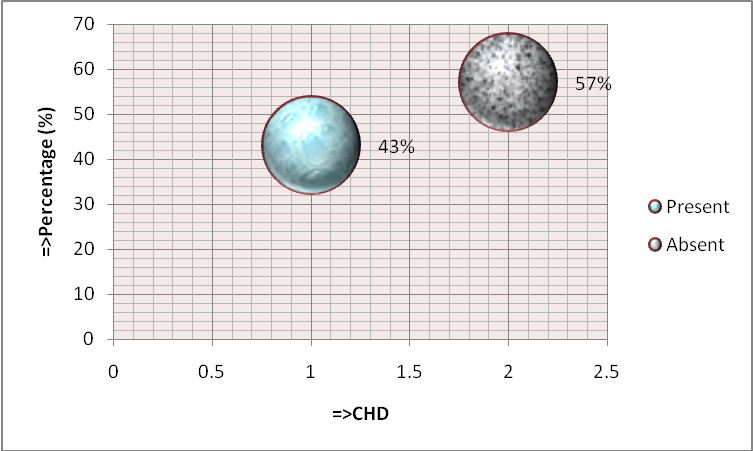 | Figure 7. Proportion of CHD and non-CHD in echocardiography |
4. Discussion
- The study illustrated patients' status with RLRI at the Department of Paediatrics in Northeast Medical College Hospital over a period of 6 months. During this study, hundred patients were included. Samples were listed in respect to history, physical examinations & investigations. The outcomes were analyzed as follows: among them, the prevalence of the disease is more within one year and next between 1 to 2 years but minimum between 3 to 4 years. The incidence is more among males than females. The result of exposure to the abnormal heart sound of those children is very low, which is only 8%; otherwise the normal heart sound is 92%. The added sound present in the heart is 42%. From the field survey, the percentage of Oxygen saturation in the greater part of patients remains in between the saturation level of 90 to 94%. Cardiomegaly was present in 31% of children and CHD was diagnosed in 43% of cases on echocardiography. Over the last 30 years there has been an increasing alertness regarding the importance of early referral of newborn with heart disease to special centers [16]. Most CHD remains asymptomatic and diagnosed during routine neonatal checkup [17]. As it is so common among major congenital defects, puts a major economic burden and emotional impact on affected families and treatment is costly, it is very important to discover its pattern among children [18]. In the western countries pattern of CHD is well known, but has not been studied countrywide in Bangladesh as in other western and neighboring countries [19]. It is not a standing situation; changes take place all through a patient's life end-of-life care [20]. Constant advances in technology and training in Paediatric cardiology has improved long term benefit and promised better quality of life [21].If CHD is left untreated it is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in children, therefore early recognition and proper intervention is most important [22]. As the frequency of CHD is increasing in Bangladesh, the magnitude of the problem is progressively becoming alarming in the country [19]. The current number of experienced personnel for pediatric cardiology is not enough [23]. The aim of this study was to survey all the children with repeated RTI both indoor and outdoor to identify the congenital heart disease that remains behind them. Early detection of CHD is very important for proper management purposes and so perfect clinical examination and skilled echocardiography is considered a gold standard for the diagnosis of CHD [24]. Colour doppler three-dimensional echocardiography is also essential for the diagnosis and a special cardiac center should be established in our region in order to manage the patient successfully without delay that may affect the out- come of the disease [25]. With the advanced treatment, children associated with CHD will live longer and lead a healthy life [10]. However, the special importance needs to provide for the children below 2 years to recover from congenital defects in heart.
5. Conclusions
- The study concludes the case of children with RLRI; congenital heart disease is a significant cause behind it. Through proper management of CHD, RLRI can be prevented more. Parents counseling is very essential to understand the evaluation of this condition. In that way, we can reduce the infant and childhood mortality in our country and correlate the existing national policy in connection with Sustainable Development Goals 2030 [26]. So, it should be remembered that every child with RLRI will check correctly to search for any CHD present or not.
Disclosure
- Data Availability The data are being used to support the findings of this research work are available from the corresponding author upon request. Competing Interests The authors declare no potential conflict of interests in this research work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledged the authority of NEMCH, Sylhet, Bangladesh for kind support.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML