-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Health Science
p-ISSN: 2166-5966 e-ISSN: 2166-5990
2017; 7(3): 50-56
doi:10.5923/j.health.20170703.03

Linkage Analysis of Retinitis Pigmentosa in Families of North Waziristan Agency
Muhammad Rafi1, Jabbar Khan1, Dost Muhammad Khan2, Ehsan Ullah Khan1, Farman Ullah1, Muhammad Ismail1, Atta Ur Rehman1
1Department of Biological Sciences, Gomal University, Dera Ismail Khan, Pakistan
2Bannu Medical College, Bannu, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Jabbar Khan, Department of Biological Sciences, Gomal University, Dera Ismail Khan, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) is a heterogeneous group of genetic diseases characterized by progressive loss of photoreceptor. In Pakistan, autosomal recessive RP is the most prevalent. We here address the issue of RP in families of very remote area of KPK, the North Waziristan Agency to molecularly characterize through linkage analysis for known loci in gene PDE6B. We collected blood samples of all the members the families having at least 2 affected individuals by RP. DNA was isolated by nonorganic method and master plate and replica plates were prepared accordingly. Amplification of microsatellite markers for reported loci was done through touch down PCR for any possible linkage analysis. Forward primer was labeled with one of the fluorescent dyes; FAM, VIC, HEX or NED. Only 4 families, PKRP398, PKRP399, PKRP400 and PKRP401 were included in this study. All the families belonged to Pashtun ethnic group. Family PKRP398 contained 4 affected individuals with their ages in the range of 12 to 27 years. No linkage was found in the family for the above-mentioned loci. Family PKRP399 consisted of 5 affected individuals and 6 normal individuals in three loops. All the affected and normal individuals were homozygous for markers D8S1110, D8S1737, D8S509, D8S2332 and D8S182, thus no linkage was seen in the family. Family PKRP401 comprised of 4 affected and 4 normal individuals but again no linkage was found. Family PKRP400 had two effected individuals in a loop and 4 normal individuals. The affected individuals had lost their vision in progressive fashion. Haplotype analysis of affected individuals showed linkage to PDE6B markers and their parents were heterozygous carriers of the diseased allele. Hence the knowledge of the disease causing genes seems to be the main element in better understanding of the disease, its diagnostics and novel therapies to combat the incidence of vision impairment.
Keywords: Heterogeneous, Vision, Linkage, Microsatellite markers, Touchdown PCR
Cite this paper: Muhammad Rafi, Jabbar Khan, Dost Muhammad Khan, Ehsan Ullah Khan, Farman Ullah, Muhammad Ismail, Atta Ur Rehman, Linkage Analysis of Retinitis Pigmentosa in Families of North Waziristan Agency, Journal of Health Science, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 50-56. doi: 10.5923/j.health.20170703.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Retinitis Pigmentosa is a heterogeneous group of genetic diseases characterized by progressive loss of photoreceptor [1, 2]. To date, more than 400 syndromes are known to be involved in RP [3]. In this disorder, degeneration of the retina usually begins in the mid-periphery that progress toward the macula and fovea. The main symptoms of RP are night blindness followed by decrease in visual fields [4]. Here the rod cells are mainly affected. In later stages of the disease, con photoreceptor cells also affected that ends with complete blindness [5]. RP is one of the commonest inherited forms of the blindness with a worldwide ratio of 1 in 3,000 to 1 in 5,000 individuals [4], affecting approximately 1.5 million people [6, 7]. The gene affected may remain and prevail in cases while there is strong custom of cousin marriages [8]. In Pakistan, autosomal recessive RP is the most prevalent [9]. Molecular diagnosis can be significant to set up any relationship between genotypic and phenotypic markers and for better comparison of the affected individuals as well. Moreover, diagnosis on molecular level may also be very much helpful for accurate prognosis. [10] About 50% to 60% of RP cases are autosomal recessive, more than 35% cases are autosomal dominant, and 10% to 15% are X linked, with rare cases of digenic or mitochondrial modes of inheritance [4, 11]. Majority of RP patients lack family history or consanguinity and thus, are difficult to know about the inheritance pattern [12]. The mode of inheritance plays a key role in determining the prognosis of the disease. But in many cases, knowing about the exact genetic mode of inheritance is not possible [11, 13]. The molecular basis of RP is not so simple and that a clear genotype-phenotype correlation has not been mapped so far. Moreover, complexity of mutations is also very vital. There are many examples where certain abnormalities may be caused by genetic changes in the same gene, symptoms of different diseases may overlap to each other and a significant complexity in the clinical phenotypes do exist even among individuals possessing the same mutation in the same gene [13]. Autosomal recessive RP (arRP) is the most frequently inherited type of RP. It accounts for approximately 50-60% of all cases [4]. PDE6A and PDE6B genes encode phosphodiesterase-6 protein that takes part in visual transduction process by rod photoreceptors. Mutations in PDE6B cause RP, night blindness, and autosomal dominant disease [14]. About 8% of all diagnosed arRP cases are because of defect in PDE6 complex [2, 15]. We thus address the issue of RP in families of very remote area of KPK, the North Waziristan Agency (NWA) to molecularly characterize through linkage analysis for known loci in gene PDE6B. We collected blood samples of all the members the families having at least 2 affected individuals by RP. DNA was isolated and accordingly master plate and replica plates were prepared. Amplification of microsatellite markers for reported loci was done through touch down PCR for any possible linkage.
2. Materials and Methods
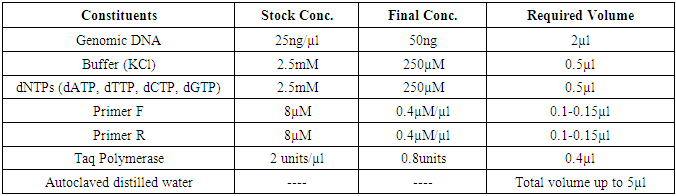
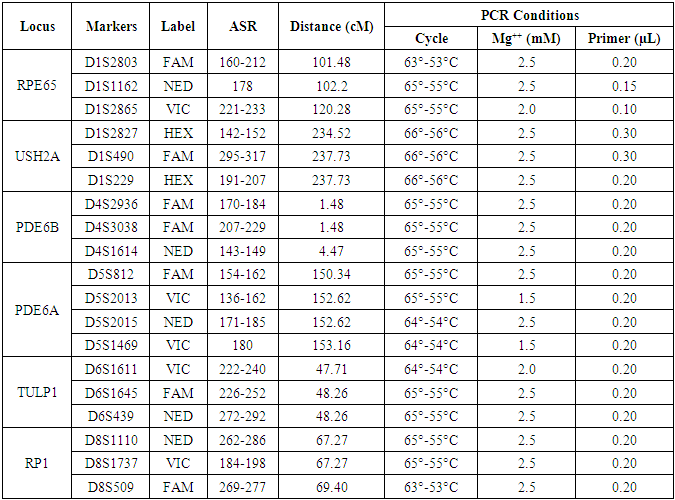
- The families having at least two affected individuals were selected for this study in NWA of KPK, Pakistan. Pedigree of each family was drawn and 5ml blood sample of each individual was collected in EDTA. Detailed informations of each family were recorded on studydesigned performa. Total 4 families were selected for further characterization. DNA was extracted by a nonorganic method [16]. Five ml of whole blood was washed with T.E (10 mM Tris HCl pH 8.0, 2 mM EDTA) after thawing. The pellet was resuspended in 4 ml buffer containing 10 mM Tris HCl of pH 8.3, 2mM EDTA and 450 mM NaCl. 250µg protienase K and 100 µl of 10% SDS were added for digesting protein. It was then incubated overnight at 37°C. Proteins were precipitated with 0.6 ml of 6M NaCl by shaking vigorously for 50 seconds and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 minutes. The supernatant was transferred to another 15 ml tube and DNA was precipitated with equal volume of isopropanol [16]. After washing with 70% ethanol, DNA was dissolved in 0.4 ml TE and heated at 70°C for 2 hours. DNA was quantitatively measured with NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific NanoDrop 2000).Preparation of Master Plate and Replica PlatesTo carry out linkage analysis in families affected with RP, a 96-well master plate map was designed in which, each sample was pipetted in triplicate. Both the parents and normal individuals were included in this study alongwith affected individuals. Linkage Analysis and amplificationThe DNA of selected families was amplified through touchdown PCR to see any possible linkage to already reported RP loci (Table 1). Linkage analysis was carried out, using microsatellite markers for each locus (Table 1). Forward primer was labeled with one of the fluorescent dyes (FAM, VIC, HEX or NED) (Table 2).
|
|
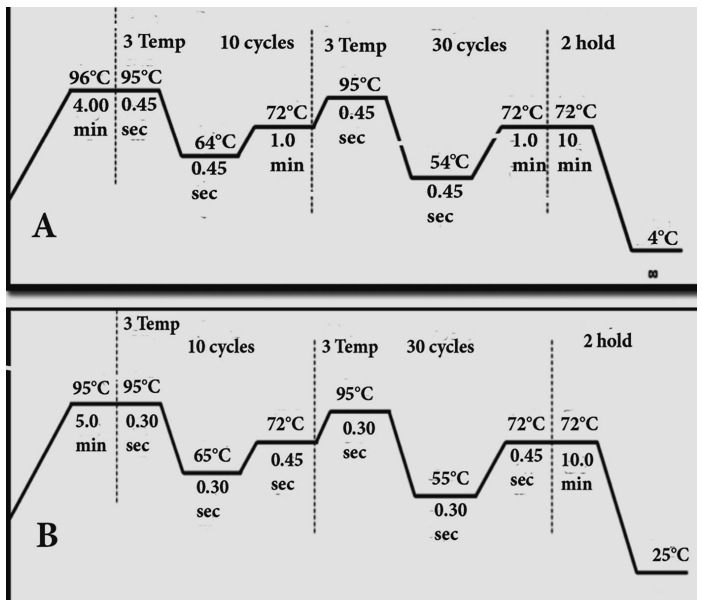 | Figure 1. Touchdown PCR, A. 64-54°C and B. 65-55°C program |
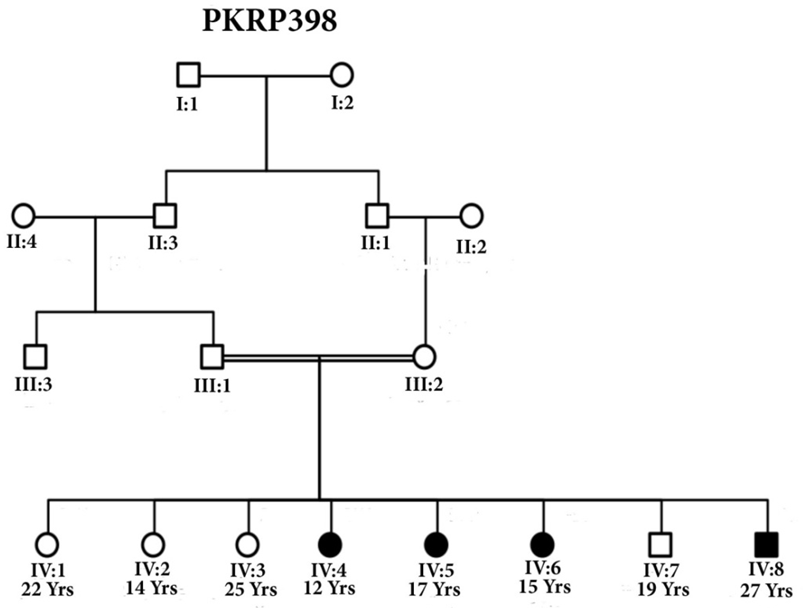 | Figure 2. Pedigree of family PKRP398 with squares representing males while circles are females. Filled symbols show patients of RP and double lines between individuals show consanguinity |
3. Results
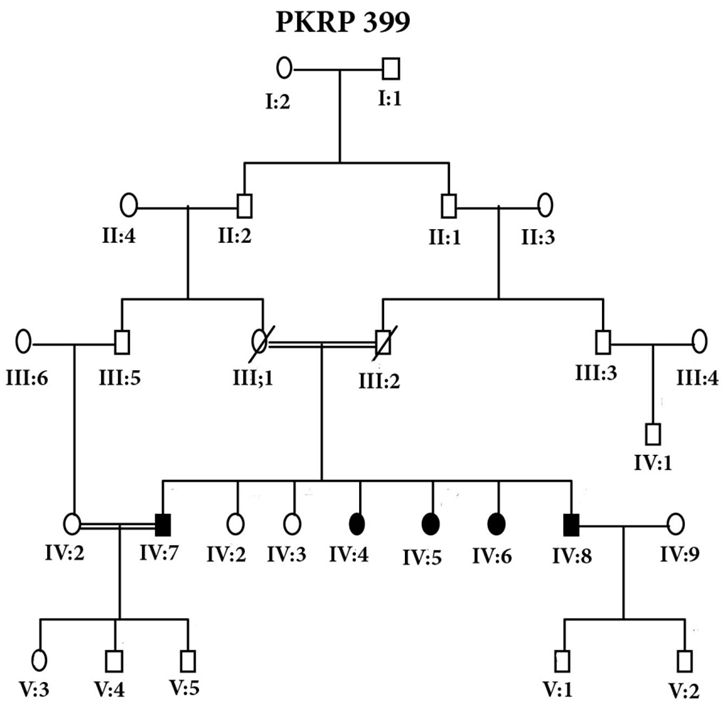
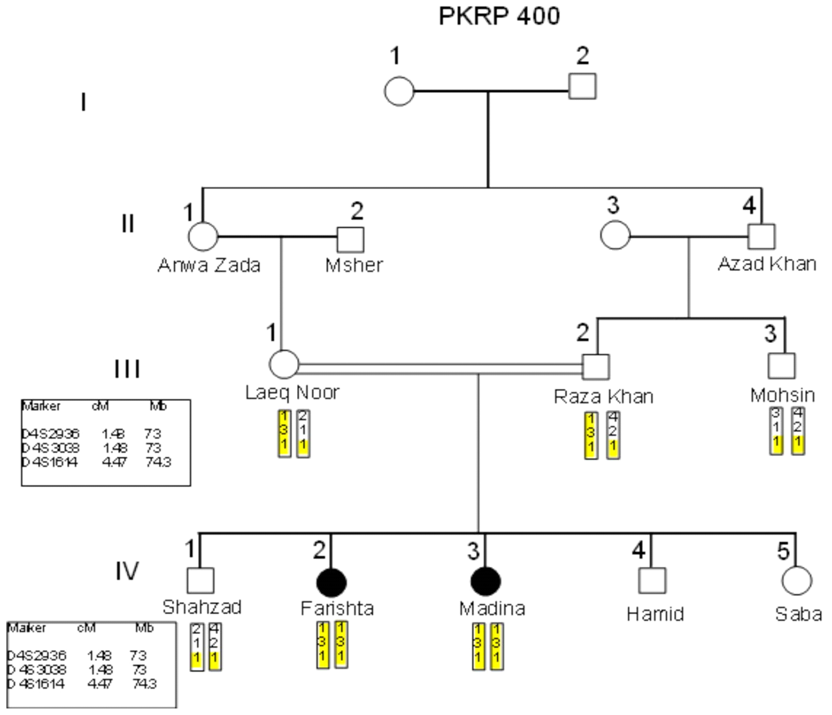
- Blood samples of 6 families were collected, based on having at least two effected individuals of RP in a family, but only 4 families were characterized for linkage analysis in PDE6B gene. The families were named as PKRP398, PKRP399, PKRP400 and PKRP401. All the families belonged to Pashtun ethnic group. The genes and loci were RPE65, USH2A, PDE6A, PDE6B, TULP1, and RP1. Linkage was found in family PKRP400 in locus PDE6B, showing autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa.Family PKRP398In this family 4 effected individuals were found in a single loop. Blood samples were collected from all the family members. Ages of all the brothers and sisters were in the range of 12 to 27 years while their parents were of age 50 to 55 years at the time of sample collection. No linkage was found in the family for the above-mentioned loci.Family PKRP399This family consisted of 5 affected individuals and 6 normal in three loops. Affected individuals had poor night vision. The disease was severe and progressive in this family, showing clear signs of RP. No clinical record of the family was found. Linkage analysis was performed with already reported regions of autosomal recessive RP by using at least 3 fully informative polymorphic markers flanking the known gene/loci. During screening of this family, all the affected and normal individuals were homozygous for markers D8S1110, D8S1737, D8S509, D8S2332 and D8S182, thus no linkage was seen in the family.Family PKRP401This consanguineous family comprised of 4 affected individuals (IV: 4, IV: 5, IV: 6 and IV: 7) in two loops and four normal individuals (Fig. 3). All the affected individuals had lost their night vision, showing signs of retinal degeneration. The disease in all the affected individuals progressed from loss of night vision completely. Linkage analysis showed that all the affected and normal individuals were homozygous for markers D8S1110, D8S1737, D8S509, D8S2332 and D8S182, showing no linkage in the family.
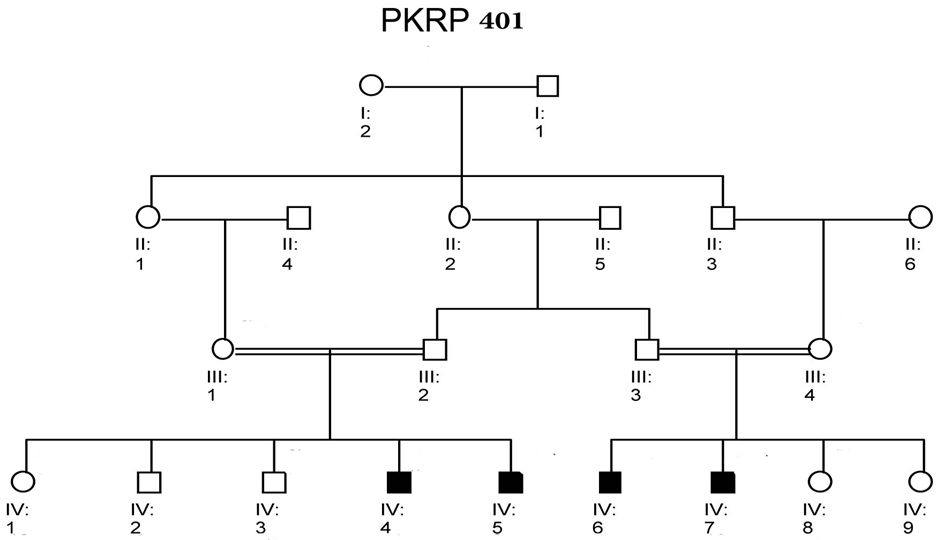 | Figure 4. Family PKRP401. Squares and circles males and females respectively. Filled symbols represent individuals of retinitis pigmentosa. Double lines between individuals show consanguinity |
4. Discussion
- Retinitis pigmentosa is a recessive inherited disorder, accounting for more than 25% of all retinitis cases [17]. Consanguinity is one of the major factors in the increased ratio of this disorder [7]. In Pakistan, because of consanguinity, the affected Pakistani families can play an important role in identifying genetic defects through homozygosity mapping [18-20]. The core objective of the study was to find out the chromosomal regions that have been mutated to cause arRP. Due to consanguinity it is possible to identify carriers and to offer genetic counselling so as to reduce the incidence and establish platform for hereditary RP in NWA population. Whenever mutation occurs in PDE6 gene, it causes the production of non-functional PDE and thus cGMP accumulates. Cells possessing non-functional PDE6B enzymes leads to excessive accumulation of cGMP that result in death of photoreceptor cell. The second most common cause of arRP is the mutations found in PDE6A and PDE6B genes [21-23]. Photoreceptor rescue has been achieved by subretinal transformation of b-PDE that resulted in delayed photoreceptor degeneration [24, 25]. The knowledge of the disease causing genes seems to be the main element in better understanding of the disease, its diagnostics and novel therapies to combat the incidence of vision impairment. Hope is there as recent studies show that gene therapy can play an important role in treating retinal diseases. Exploring the causative genes of RP and molecular mechanisms of onset of disease can help in better understanding of gene, its expression and remedies to disorder. Knowing the hereditary basis can also help in establishing future diagnostic. We tried to explore the genetic basis through linkage analysis and haplotyping in the 4 families of NWA, KPK, Pakistan for the known loci of PDE6B. We did not find linkage in families PKRP398, PKRP399 and PKRP401 to the known loci while a linkage to the gene PDE6B was found in family PKRP400 in which female twins were affected. Carrier diagnosis can be offered to the individuals whose family members are known to be associated with any RP gene. It can also permit a more accurate genetic counselling to affected families to reduce the incidence of hereditary RP in our population. Genetic counselling helps the affected individuals and their families to make medical and personal decisions more carefully. Continued research in pathogenesis of RP has significantly improved our understanding of the disease and identification of novel genes and mutations that may lead to better understanding of vision mechanisms at molecular level. It is possible that the unlinked families may have environmental factors for the disease rather than genetic defect and hence, further work needs to be done not only on the unlinked families but on the linked families as well.
5. Conclusions
- Mutations in the PDE6B are one of the main causative agents of aRP.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We are very much thankful for the kind cooperation and hospitality of the families from whom we collected blood samples.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML