-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Health Science
p-ISSN: 2166-5966 e-ISSN: 2166-5990
2015; 5(3): 47-51
doi:10.5923/j.health.20150503.01
The Prevalence of Malaria in Children between the Ages 2-15 Visiting Gwarinpa General Hospital Life-Camp, Abuja, Nigeria
Nmadu P. M., Peter E., Alexander P., Koggie A. Z., Maikenti J. I.
Department of Biological Sciences, Bingham University karu, Nasarawa State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Peter E., Department of Biological Sciences, Bingham University karu, Nasarawa State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Malaria is a major cause of illness and death especially among children under 5 years and pregnant women. It is estimated that more than one million children living in Africa especially in remote areas with poor access to health services die annually from direct and indirect effects of malaria. Fatally affected children often die within less than 72hrs after developing the symptoms. In Nigeria, malaria consistently ranks among the five most common causes of death in children. As a result of increased mortality and morbidity there is need for proper understanding of the epidemiology of the disease among the most at risk groups. Two milliliters venous blood was collected from each of the 200 children and stored in an anticoagulant specimen bottle. Thick and thin films were prepared, stained and examined for malaria parasite under the microscope using the oil immersion objective. Malaria infection was found to be most prevalent among 2-5years old, (29%) while ages 6-10 and 11-15yrs both had 17.5% infection. There was no significant difference in prevalence among the male and female children, with 67 and 61%,respectively. The most prominent specie in the community is Plasmodium falciparum (62.5). There is need for mothers to protect their children from mosquito bite by ensuring that they sleep under Insecticide Treated Net.
Keywords: Epidemiology, Plasmodium,Falciparum, Gwarinpa, Hypoendermic, Karimo, Idu, Gwagwa
Cite this paper: Nmadu P. M., Peter E., Alexander P., Koggie A. Z., Maikenti J. I., The Prevalence of Malaria in Children between the Ages 2-15 Visiting Gwarinpa General Hospital Life-Camp, Abuja, Nigeria, Journal of Health Science, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 47-51. doi: 10.5923/j.health.20150503.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Malaria is a major public health problem and cause of suffering and premature death in tropical and subtropical countries (Cheesbrough, 2003). This preventable disease has reached epidemic proportions in many regions of the world and continues to spread unchecked (WHO, 2010). African children under five years and pregnant women are most at risk of malaria. Fatally afflicted children often die less than 72 hours after developing symptoms. In those children who survive, malaria drains vital nutrients from them impairing their physical and intellectual development (WHO, 2000).It is estimated that more than one million children living in Africa die yearly from direct and indirect effects of malaria infection (Fawole & Onadeko, 2001). Malaria is a parasitic disease caused by single celled protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium belonging to the apicomplexan phylum (Krief et al., 2009). Malaria parasites, (Plasmodium species) are spread from one person to another through the bites of haematogenous female adults of mosquitoes belonging to the insect genus Anopheles. These adult female Anopheles mosquitoes are, hence said to be carriers of malaria parasites. These mosquitoes primarily inhabit the tropical and subtropical parts of the world (MMWR, 1999 and Epidi et al., 2008).The four known species of Plasmodium genus that cause human malaria are Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae and they contribute to majority of human health problem in malaria endemic regions of the world (Mohan et al, 2007).The major vectors of human malaria are Anopheles gambiae, Anopheles funestus, Anopheles arabiensis and Anopheles melas. A.arabiensis is most dominant in the savannah areas and cities. A. gambiae are found in highly dense forest areas, A funestus has an uneven distribution while A. melas is a salt water species (Federal Ministry of Health, 1990). Anopheles mosquitoes can adapt to urban breeding sites over time e.g., in India, Anopheles Stephensi has developed into urban species and is found in much higher numbers in many cities in India than in the surrounding country side (WHO,2000). There is evidence that Anopheles mosquitoes are likewise becoming better adapted to the breeding site of Accra (Benneh et al, 1993).Transmission of malaria is intense and stable in Nigeria because the intensity of attack remains constant throughout the year or from year to year. In Nigeria, malaria is holoendemic in the rural areas and mesoendemic in the urban areas. In the southern part of the country the transmission rate is approximately uniform throughout the year. In the far North there is a marked difference between the high transmission rate in the short wet season and low transmission rate in the long dry season (Lucas & Gilles, 1998).Man and Malaria seem to have evolved together. It is believed that most, if not all, of today's populations of human malaria may have had their origin in West Africa (P. falciparum) and Central Africa (P. vivax) on the basis of the presence of homozygous alleles for hemoglobin C and RBC Duffy negativity that confer protection against P. falciparum and P. vivax respectively (Peter et al., 2009). Recent molecular studies have found evidence that human malaria parasites probably jumped onto humans from the great apes, probably through the bites of vector mosquitoes (Krief et al., 2010).WHO (1951), reported that the degree of endemicity of malaria is measured based on the spleen rate in children aged 2-9 years in their order of severity. Hypoendemic malaria occurs when spleen rate in children is less than 10%. Mesoendemic malaria occurs when spleen rate in children is 11- 50%. Hyperendemic malaria occurs when spleen rate is 75% in children and> 25% in adults. Holoendemic malaria occurs when spleen rate is >75% in children but very low in adults. WHO (1998a) reported a prevalence of 58% malaria parasite among children in Banjul the capital of Gambia. Umar (2006) reported 94% prevalence of malaria parasite among children in Gombe metropolis. The prevalence of infection recorded for wet season in Udi Enugu State, was 59.8% according to Eneanya, 1998.Mbanugo and Ejims (2000) in a study conducted in three hospitals and a Nursery School in Awka on prevalence of Plasmodium infections in children, discovered that out of 400 children, 233(58%) were positive and only Plasmodium falciparum were found. Matur et al. (2001), in a prevalence study reported 61% recorded in Abuja. Krogstad (1996), reported that Plasmodium infection was more prevalent in young children because of their relatively less developed immune system.Malaria infections represent substantial social costs due to school absenteeism and reduced economic productivity. Malaria costs Africa up to US $12billion annually. A poor family living in malaria affected area may spend up to 25% or more of its annual income on prevention and treatment of malaria. (WHO, 2000).The Plasmodium species responsible for malaria infections in Nigeria are Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale. Over 80% of malaria infections are caused by P. falciparum while up to 15% are caused by P malariae and less than 5% are caused by P.ovale infections. Mixed infections with P. falciparum are common (Federal Ministry of Health 1990, Orajaka, 1996). Although P. vivax and P. malariae had achieved the widest global distribution, today P. malariae has lost its predominance and P. vivax and P. falciparum are the most commonly encountered malaria parasites. Almost 85% of the nearly 500 million annual malaria cases occur in sub-Saharan Africa and about 85% of cases in Africa are caused by P. falciparum with the remaining cases being caused by the other three strains. P. vivax is now the most geographically widespread of the human malarias, estimated to account for 100-300 million clinical cases across much of Asia, Central and South America, the Middle East, where 70–90% of the malaria burden is of this species and the rest due to P. falciparum ( Lock et. al, 1997).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Size
- The study was conducted on a sample size of two hundred (200) children, within the age range of 2 – 15 attending Gwarinpa general hospital, Abuja Nigeria. The hospital serves people from Gwarinpa Estate, Jabi, Life-Camp and some suburbs of the city such as Karimo, Gwagwa and Idu industrial area.
2.2. Sample Collection
- The blood samples were collected into EDTA bottles/containers which were labelled with information such as Name of the Patient, Investigation, Date, Sex, Age, Laboratory and Hospital Numbers and screened for the presence of malaria parasites within the months of June and July 2014.
2.3. Staining Technique
- The laboratory method employed for staining and identification of malaria parasites in collected blood samples was as described by (Cheesbrough, 2003).
2.4. Smear Preparation
- During this research, both thick and thin films smear were prepared. The thin film slide was flooded with Leishman stain for few minutes, two drops of buffered distil water of pH 6.8 was added and left for further 10 minutes, the slide was washed thoroughly under tap water to differentiate (the colour should be salmon pink), the slide was left to dry and the back of the slide were cleaned with cotton wool. The thick film were flooded with Giemsa stain and allowed to stand for 30minutes. The slides were then washed using clean water and the back of the slides were wiped with cotton wool and placed in a draining rack to air dry.
2.5. Microscopic Examination
- The stained slides were examined for malaria parasites. Immersion oil was spread to cover about 10mm in diameter in the areas of the film. Both the thick and thin smears prepared were examined microscopically under oil immersion with the (x100) objective.
3. Results
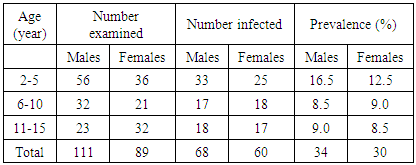
- Table 1 shows the distribution of malaria in relation to age and sex. In ages 2-5, 56males and 36 females were tested of which 33 and 25 were infected respectively. These represents 16.5% and 12.5% respectively. While in ages 6-10, 32males and 21females were examined out of which 17were positive for males and 18 for females representing 8.5% and 9% respectively. In the same vein, within the ages of 11-15, 23males and 32 females were tested out of which 18 and 17 were positive respectively representing 9% and 8.5%. In all, a total of 111males and 89 females were tested. Among these 68 (34%) male were infected and 60(30%) for females.
|
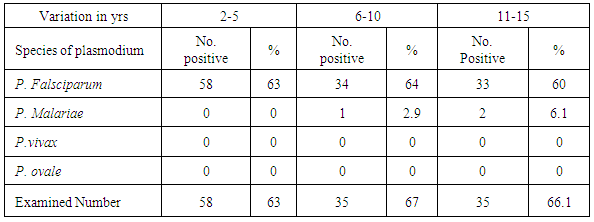
 Table 2 shows that generally 58 children (2-5yrs) old, 34 children (6-10yrs old) and 33 children (11-15yrs) totalling 125 (62.5%) of the children sampled were infected with P. falciparium. Among those 6-10yrs, 1 child (2.9%) and 11-15yrs, 2 children (6.1%) had P. malariae. P. vivax and P. ovale however were not identified in any of the groups examined.
Table 2 shows that generally 58 children (2-5yrs) old, 34 children (6-10yrs old) and 33 children (11-15yrs) totalling 125 (62.5%) of the children sampled were infected with P. falciparium. Among those 6-10yrs, 1 child (2.9%) and 11-15yrs, 2 children (6.1%) had P. malariae. P. vivax and P. ovale however were not identified in any of the groups examined.
|
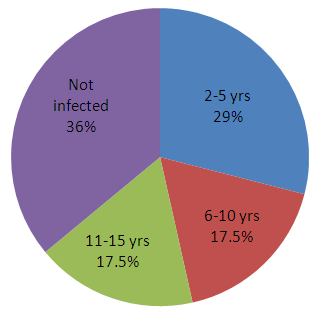 | Pie-chart showing percentage distribution of both infected and non infected children. |
4. Discussion
- In this study, it was observed that children between the ages of 2 - 5 years had the highest prevalence of Plasmodium infections (table 1) compared with the other age groups. This may be due to the fact that at that age, their immunity to parasitic infections has not been fully developed. Although it has been established that residual immunity derived from mothers could be very effective in younger children but environmental conditions and inability of children of this age in the study area to ward-off environmentally induced mosquito attacks predisposed them to malaria attack. The prevalence of Plasmodium infections has been found to reduce with other ages (6-10 and 11-15 years) this could be attributed to the fact that children of this age have developed immunity against Plasmodium parasite (Brown, 1980). The prevalence of parasitic infections among the different age groups in the present study was not significant (P< 0.05) indicating that the occurrences of these infections on these age groups were the same (table 1).The present study has shown that Plasmodium infections were more common in the male than in the female subjects (Table 2). The present result conforms with the recorded higher prevalence of Plasmodium infection in males than in females in the hospital. However, studies have shown that females have better immunity to parasitic diseases and this was attributed to genetic and hormonal factors (Krogstad, 1996).
5. Conclusions
- From the result of this research, of the 200 children (2-15yrs) sample size, 128 children (64%) were infected with malaria parasite, out of which children between the age of 2-5 were observed to have the highest percentage (29%) of the infection followed by 6-10 and 11-15 years respectively as shown in Table 2, with P. falciparum having the highest prevalence among the causative agents as shown in Table 2. The following recommendations were therefore made:● Public health education campaign for mothers and health care givers given to create awareness that may lead to reduction of vectors of malaria infection and control of the disease especially in young children.● Free or subsidized Insecticide Treated Nets (ITN) should be made available to mothers so that the infection of malaria could be controlled in children.● Mothers and other caregivers need to be empowered to treat malaria infection at home.● Governments should train more health workers that will go into the rural areas to enlighten them about malaria (prevention and control). ● Children should be treated with antimalaria drugs every three months to prevent malaria and to kill (if any) the early stage of malaria parasite.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML