-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Health Science
p-ISSN: 2166-5966 e-ISSN: 2166-5990
2013; 3(2): 21-24
doi:10.5923/j.health.20130302.03
Syphilis and Associated Risk Factors among Homeless in Khartoum State
Eltayib Hassan Ahmad-Abakur, Hasnaa Abdelrahim Khogali Ahmed, Mohamed Ahmed Abrahim-Holi
Dept. of Microbiology & Immunology, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Science,Alzaiem Alazhari University, P. O. Box 1432, Khartoum Bahri 13311, Sudan
Correspondence to: Eltayib Hassan Ahmad-Abakur, Dept. of Microbiology & Immunology, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Science,Alzaiem Alazhari University, P. O. Box 1432, Khartoum Bahri 13311, Sudan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
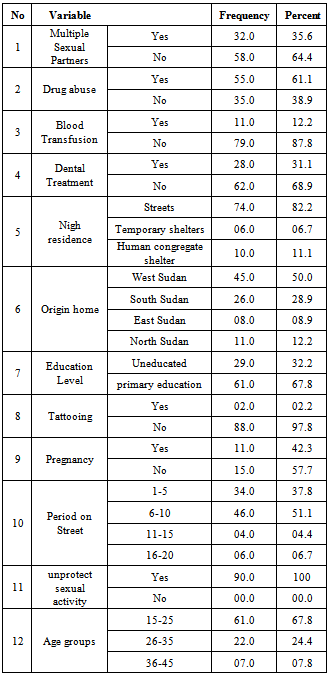
The present study aimed to determine the prevalence and risk factors associated with syphilis among homeless people in Khartoum state, Sudan.Ninety mature homeless were participates in this study, the blood samples were tested for IgG anti-treponemapallidum using RPR and ELISA techniques. The risk factors such as sexual behavior, unprotected sexual activity, pregnancy, period on streets, tattooing and level of education were collected via direct interview. 64(71.1%) of study population were male, 26(28.9%) were female, 11(42.3%) of the female had previous pregnancy, 45 (50 %) from west Sudan. 74 (82.2%) of study populationspent their day on street, 55(61.1%) had a history of drug abuse. Treponemapallidum was detected in 50 (55.6%) and 38(42.2%) of study population using RPR and ELISA techniques respectively. The results indicated significant relations (P value < 0.05) between syphilis infection and multiple sexual partner and pregnancy.
Keywords: ELISA Technique, RBR, Sensitivity, Specificity
Cite this paper: Eltayib Hassan Ahmad-Abakur, Hasnaa Abdelrahim Khogali Ahmed, Mohamed Ahmed Abrahim-Holi, Syphilis and Associated Risk Factors among Homeless in Khartoum State, Journal of Health Science, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 21-24. doi: 10.5923/j.health.20130302.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The world health organization estimates that there are about 12 million new cases of syphilis worldwide each year, with greater than 90% of cases in the developing world[1]. Syphilis is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. It transmitted primarily by sexual contact or during pregnancy from a mother to her fetus; the spirochete is able to pass through intact mucous membranes or compromised skin. It could be transmissible by kissing, oral, vaginal, and anal sex[2, 3]. Syphilis increases the risk of HIV transmission by two to five times and co-infection is common[4].T. pallidum organisms may be able to evade the acquired immune response by antigenic variation of bacterial surface proteins, consistent with the resistance to phagocytosis of those select treponemes that survive bacterial clearance of the primary lesion[5, 6]. Several factor place the homeless people at high risk of acquiring sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as syphilis, this factor includes drug consumption, shared use of injecting drugs, sexual promiscuity, extreme poverty, city life, risky behavior, economic reasons, family disruption, family abuse and low educational level place[7,8]. Homelessness populations are people who have no adequate, fixed residence in the night period. Using or living in shelters, institutions and private or public locations not designated or used as regular accommodation to sleep is also considered homeless condition[9]. In Sudan, homelessness is becoming an increasing phenomenon due to many factors that includes civil war, drought and poverty. Most of Sudanese homeless were born in Khartoum state but the origins of the majority of them are the western and southern Sudan[8]. The numbers of homeless on the streets of Khartoum have started to increase rapidly ever since the early 1980s, when many families moved to escape the war in southern Sudan and the drought afflicting the western regions of Kordofan and Darfur. Available data on child labor and street children in Sudan suggests that the number of street children in northern Sudan was around 70000 by the end of the year 2002, with 73% of these living in the streets of Khartoum. Boys make up around 86% of those on the streets, and girls 14%[10]. There are two types of street people in Khartoum; Working street people are those who spend most of their days working on the street but usually sleep at home while full-time homeless people are those who generally spend both day and night on the street[8]. The present study was undertaken to determine the syphilis infection and associated risk factors among homeless peoples in Khartoum State, Sudan.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Area
- Descriptive cross sectional study, conducted in Khartoum State, Sudan in a period from January to March2012.
2.2. Study Subjects
- Mature homeless who did not show psychiatric disturbances and live in close distance to central area of Khartoum stat were considered eligible to be enrolled in this study.
2.3. Sample Size
- It was challenging to persuade homeless to participate in scientific research. However, several approaches were used such as health education program and financial support in order to convince the homeless to contribute in this study; unfortunately few of them were interested.A total of 90 homeless were agreed to participate in this study as well the approval for this study was obtained from ministry of social care, Khartoum State,Sudan.
2.4. Data Collection
- Information related to study was collected using structural questionnaire covering factors associated with the transmission of STIssuch as age, multiple sexual partners, unprotect sexual activity, drug abuse, history of blood transfusion, dental treatment, original home, night residence, pregnancy, tattooing, education level and period on streets.
2.5. Sample Collection
- Sterile disposable vacutainer tube was used to collect 5 ml of blood from the anticubital vein under aseptic conditions, the blood samples were allowed to clot at room temperature. The clotted samples were centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 minutes in order to separate the sera; the obtained sera were frozen at -20ºC until used.
2.6. Detection Treponemapallidum
- Sera samples were tested for the presence of cardiolipin antibody and IgG antibodies of treponemapallidum using plasma regain RPR (SPINREACT) and ELISA (Biorex) respectively. The tests were performed according to the instructions of the manufacturers.
2.7. Sensitivityand Specificity of RPR
- The sensitivity and specificity of RPRwere calculated according to the following equations considering ELISA technique as golden method:Sensitivity= total number of positive results/total number of infected patients×100Specificity= total number of negative results/total number of uninfected patients×100
2.8. Method of Data Analysis
- Analysis of results was carried out by means of the statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS). A descriptive statistic frequencyand Chi-square were used to compare the variables with sero-positive results.
3. Results
- Ninety mature homeless were participates in this study, 64(71.1%) were male, 26(28.9%) were female, 11(42.3%) of the female had previous pregnancy. All participants fall in age range from 15 to 45 years old, the mean age was 24 years, 45 (50%) from west Sudan and 74 (82.2%) of study population entirely spent their day on street, 55 (61.1%) had a history of drug abuse and 66(73.3%) were smokers (table1).
|
|
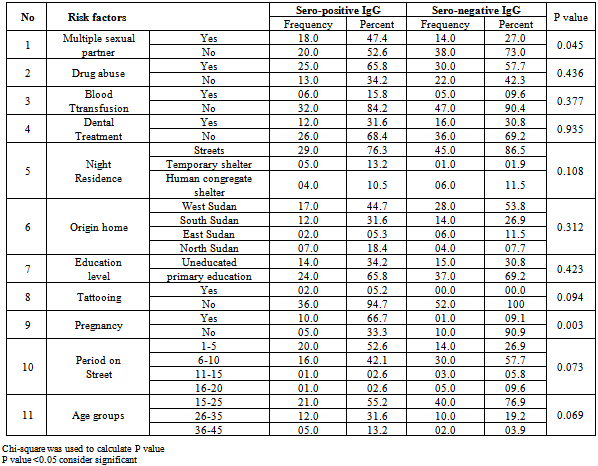
- The T. pallidum was detected in 50(55.6%) of the subject population as indicated by RPR while ELISA technique showed 38(42.2%) sero-positive. Four samples showed negative result when using the RPR technique, simultaneously these sample showed positive reaction when applied ELISA technique. Sixteen samples displayed positive reaction when RPR technique was applied, the same sample give negative reaction when ELISA technique was applied. RPR sensitivity and specificity was found to be 89% and 69% respectively. 23(36%) of male and 15(57.7%) of female were positive for syphilis respectively.Table 2 showed statistical relation of T. pallidum sero-diagnosis and its risk factors among homeless using ELISA technique. The results indicated significant relations (p value < 0.05) between syphilis infections and multiple sexual partners (p value 0.045) and previous pregnancy (p value 0.003).
4. Discussion
- Homeless people suffer from a wide range of health and social problems and have a high rate of mortality and morbidity; numerous infectious and noninfectious diseases are detected among this group of people. However, the present study was undertaken to screen STIs namely Syphilis and its associated risk factors among this group.Two different sero-diagnostic techniques were used in this study to detect the T. pallidum; RPR technique displayed 50 (55.6%) seropositive while ELISA technique showed 38(42.2%). These results were relatively high in comparison to the prevalent of syphilis among homeless in Tehran(0.5%) [7] and in Brazil (5.7%)[9]. The prevalence of the syphilis among the other communities was significant less than that on homeless community; it was 8.9% in Pakistan[11], 16.5% among prisoners in Ghana[12], and 13.5% in China[13]. This difference might be attributing to the influences of risk factors among different communities and disease controlling plans in special societies. RPR technique showed relatively low sensitivity and specificity, this result was in agreement with that reported by Castro et al.[14]. However, RPR is non-treponemal tests, its widely available, cheap, rabid and easily to perform, convenient to perform on large numbers of specimens. The limitations of the non-treponemal serologic tests include their lack of sensitivity in early and late syphilis and produce false negative reactions in the presence of high titers of antibody, and with co-infection. Screening with RPR test alone may also `yield false positive reactions in various acute and chronic conditions in the absence of syphilis[14, 15,16]. ELISA IgG antibody tests had 100% sensitivities in all stage of syphilis and 100% specificities in patient without history of syphilis. The limitations of the ELISAs are time and cost when small numbers of samples are to be processed, also cannot be used to monitor treatment[15, 16, 17]. Therefore and for precious results ELISA technique was applied simultaneously with RPR in this study.Multiple sexual partners were critical factors affecting the prevalence of syphilis[13,18], the present study showed statistically relation between seropositive syphilis and multiple sexual partners. However, the homeless at Khartoum state had low level of education and did not familiar with the proper sexual behavior. In alignment to these finding several authors were reported that the syphilis was strongly related to unprotected sexual activity and low level of education[13,18]. Significant correlation was also observed between T. pallidumsero-positive and history of pregnancy; this finding was in arrangement with other study carried out to estimate the sero-prevalence of Syphilis among pregnant women in the Tri-capital Khartoum[19].The present study showed that the positive rate of IgG against treponemapallidum was higher in female (57.7%) than in male (36%). This result was similar to study carried by Maity et al. who studied the Syphilis sero-prevalence among patients attending a sexually transmitted disease clinic in west Bengal[20].
5. Conclusions
- The present study showed noticeable occurrence of syphilis among homeless with significant association between infection and sexual behavioramong homeless in Sudanparticularly multiple sexual partners and history of pregnancy.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML