-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Health Science
p-ISSN: 2166-5966 e-ISSN: 2166-5990
2013; 3(1): 5-11
doi:10.5923/j.health.20130301.02
Validity and Reliability of the Social Skill Scale (SSS) as an Index of Social Competence for Preschool Children
Anme T.1, Shinohara R.2, Sugisawa Y.1, Tanaka E.1, Watanabe T.1, Hoshino T.3
1Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Ibaragi, Japan
2Yamanash University, Yamanashi, Japan
3Universiy of Nagoya, Aichi, Japan
Correspondence to: Anme T., Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Ibaragi, Japan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Thepurpose of this study was to validate the Social Skill Scale (SSS) as an evidence-based practical index of social competence. In total, 30,993 preschool children participated in the study. Childcare professionals evaluated participants with the SSS. Results indicated a highly rigid structure of 3 factors corresponding to social competence. Cronbach’s alpha coefficients ranged from 0.91 to 0.93 across the sampled age groups. These factors also positively correlated with theChild DevelopmentScale. The SSS is able to measure social competence with high validity and reliability. Thus, the SSS is a helpful tool for understanding the development of social competence.
Keywords: Social competence,Children, Evaluation, Scale
Cite this paper: Anme T., Shinohara R., Sugisawa Y., Tanaka E., Watanabe T., Hoshino T., Validity and Reliability of the Social Skill Scale (SSS) as an Index of Social Competence for Preschool Children, Journal of Health Science, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 5-11. doi: 10.5923/j.health.20130301.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Social competence has been an area of research interest in the field of child development[1]. This growing interest stems from studies observing thateffective social skill development confers a wide rangeof interpersonal, academic, and mental health benefits for children[2][3]. Given thesebenefits, center-based social skill training has become an increasingly common component ofchildren’s preschoolexperience[4][5].Social competence is determined by complex interactions between the individual, home and school environments, peer relationships, and the larger sociocultural context[6]. Given the increased number of children displaying impulsive behaviors and social maladjustment, societal preparedness for appropriate education and environments to foster pro-social behaviors among these children are needed. Social competence is defined by how well an individual functions inrelation to other people, particularly with respect togetting along with others and forming close relationships[7].From early dyadic relationships with caregivers, and play and social interactions with peers during thepreschool years, to the formation of peer networks and close friends, socialcompetence is viewed as a primary component ofhealthy functioning and development[8][9].Social relationships established through interactions are a major source of security and a sense of belonging[10]. Social competence is also viewed as the ability to understand others in the context of a social interaction and engage in smooth communication with others. Thus, social competence should be evaluated by the interaction between a person and their social environment[11]. However, methodologies that consider people in conjunction with their social environment across developmental stages have not been well developed.Assessments of early interactions have focused on measuring the quality of a child’s home environment and parenting, based on the theory that an early child-rearing environment greatly influences child development. Two instruments, namely the Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment (HOME)[12] and the Index of Child Care Environment (ICCE)[13], are often used in research on child development.The Interaction Rating Scale (IRS) was developed to measure a child’s social skills and a caregiver’s childrearing skills through observations of caregiver-child interactions, which is based on the HOME[12], SSRS (Social Skills Rating Systems)[14], and NCAST (Nursing Child Assessment Satellite Training) teaching scales[15]. The IRS contains 70 items for computing a behavioral score and 11 items for computing an impression score; these items are grouped into the following 10 subscales (the first 5 focus on a child’s social skills while the latter 5 assess a caregiver’s parenting skills): autonomy, responsiveness, empathy, motor regulation, emotional regulation, respect for autonomy development, respect for responsiveness development, respect for empathy development, respect for cognitive development, and respect for social-emotional development. This measure is used to evaluate, in less than 5 min, an observation appropriate for the assessment of interactions between caregivers and children from birth to 8 years of age. The reliability of the IRS is 0.91, and the IRS’s validity with the NCAST is, r =.89[16-18]. Even though these studies enhance the methods of evaluating social competence, it is useful to develop a scale via a questionnaire. We developed the Social Skill Scale for Preschool Children (SSS: see Appendix) as a questionnaire measure of social competence. The SSS is able to evaluate children’s social competence in a short period of time during daily situations. Several studies assessing social competence have included common factors related to “empathy/cooperation,” “self-control,” and “assertion.” These 3 factors have been found to be stable between the ages of 1 and 6 among Japanese children in a longitudinal study[18].It is essential to develop methods to evaluate social skills relevant to peer relationships among children in order to promote healthy development.No other study has done similar research as developing a practical index of social competence which is structurally valid over six age groups.The purpose of this study was to clarify the constructive validity and reliability of the SSS as an evidence-based practical index of social competence.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
- Participants were children enrolled in a longitudinal study of social development (“Japan Child CareCohort”) from 58 government authorized childcare centers all over Japan from 2000 to 2009. Data were obtained from 30,993 children (1-year-olds: 4,012, 2-year-olds: 5,758, 3-year-olds: 5,758, 4-year-olds: 5,762,5-year-olds: 5,682, and 6-year-olds: 4,021), and usable data were obtained from29,617 children(those whose social skills could be measured).In order to comply with ethical standards prior to conducting the research, all parents signed informed consent forms and were made aware that they had the right to withdraw from the experiment at any time. A personal ID system was used to maintain confidentiality of personal information. Furthermore, all data were stored on a disk, which was password protected; only researchers who were granted permission had access to the data.The ethics committee of the University of Tsukuba approved this study.
2.2. Measures
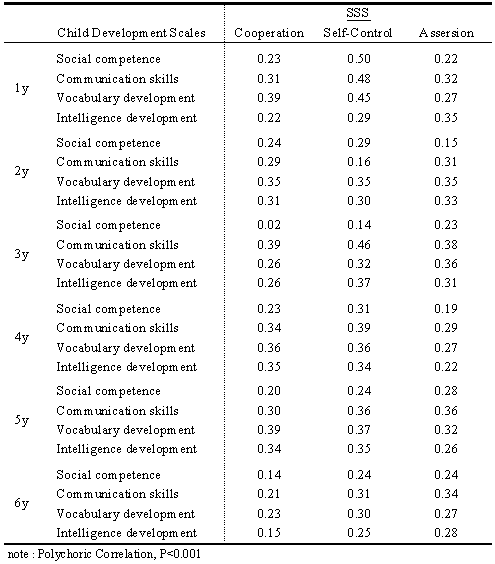
- The SSS was used to assess children’s social competence. It was developed as a questionnaire version of the IRS[16-18], which evaluates child-caregiver interactions by observations available for children under the age of 8. The SSS measures social competence through 24 questions. The evaluator completes the checklist composed of 24 items focusing on a child’s behavior in the class (e.g., “Cheers up and comforts a person who is missing someone”).Each item within the subscales is assessed in a Yes or No (1 = Yes, 0 = No or not sure) format, and the sum of all items in the subscale provides the overall score.A higher score indicates a higher level of social competence.In previous studies, social competence from infancy to adolescence had been classified into 3 core dimensions[14, 19, and 20], which are cooperation, self-control, and assertion. The SSS consists of 3 subscales that measure cooperation (8 items), self-control (8 items), and assertion (8 items). Scores for all SSS subscales are derived from professionals who carefor children in childcare centers. We also referred to the Interaction Rating Scale between Children (IRSC)[21], which evaluates children’s peer interactions by observations available for children between 3- and 18-years-old. The Child Development Scale[22], which is widely used among government authorized center-based care centers across Japan, was used to investigate relationships with the SSS.The Child Development Scale is constructed from 4 subscales: social competence, communication skills, vocabulary development, and intelligence development.
2.3. Analysis
- Factor analysis usinga maximum-likelihoodoblique rotation methodwas conducted to assess the factor structure of the SSS over our 6 age groups. Statistical Analysis System software (SAS version 9.1) was used for data analysis.
3. Results
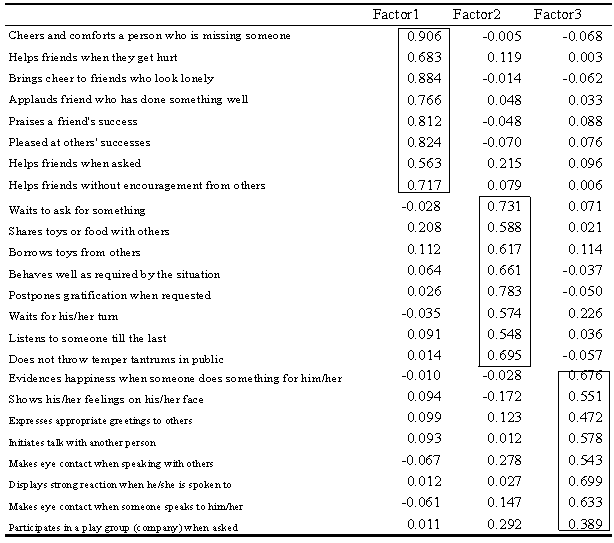
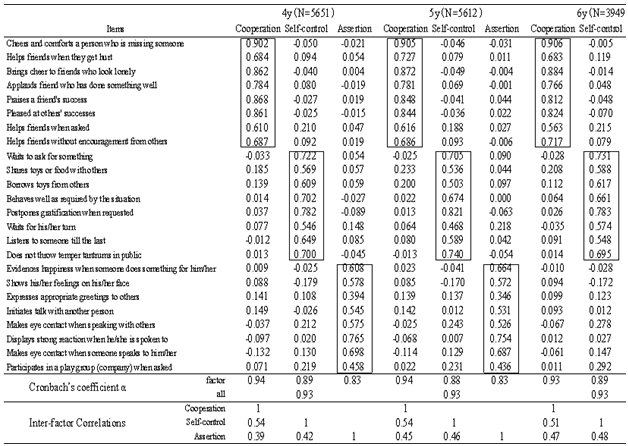
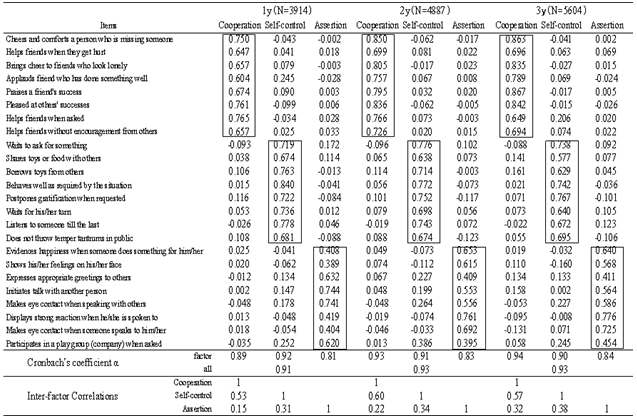
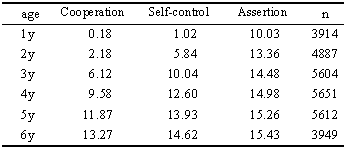
- Table 1 showsstandardized regression coefficientsof the factor pattern matrix of the SSS. The 3dimensionsextracted were consistent with those of previous studies on social competence (i.e., cooperation, self-control, and assertion).Table 2indicates that factor loadingsof the SSS were consistentacross the 1–6-year-old age range.The Cronbach's alpha coefficients ranged from 0.91 to 0.93 across the 6 age groups (1-year-olds: 0.91, 2-year-olds: 0.93, 3-year-olds: 0.93, 4-year-olds: 0.93, 5-year-olds: 0.93, and 6-year-olds: 0.93).Table 3and Figure1 show mean scores on the SSS for each age group. The scoreson each subscale increasedwith increasing age.Table 4 shows significant, positive correlations between the SSS subscales (cooperation, self-control, and assertion) and the Child Development Scale (social competence, communication skills, vocabulary development, and intelligence development).
4. Discussion
- Consistent with a main principle of developmental task theory[23], results of thisstudy demonstrate continuity within domains of social skills assessed by developmentally appropriate indices across time.Our analysis revealed a highly rigid structure of 3 factors, which were valid, universal components of social competence. However, it is importantto keep in mind that this finding is equally consistentwith the possibility that effective social competencewith peers is affected by general child development[24]. Nevertheless, our results suggest that the SSS is a reliable and valid measure of social competence in young children. The social competence scale for child-caregiver interactions (IRS), and for adult interactions, referred to as the Interaction Rating Scale Advanced (IRSA), have previously been found to be reliable, valid, feasible, and practical tools for assessing social interactions over time[16-18, 21]. Three strengths of the SSS, which is derived from the IRS, are described below.First, we used a large number of participants to clarify the stability of the SSS factors. This helps validate the ease of using this measure in practice; the SSS is highly adaptable because the subscale framework can be used across several age groups. Second, the SSS can be used for comparative studies across international samples given that the measure is based on a universal framework of social competence. The subscales are based on several categories, which have been widely used in research assessing social competence indicators. Third, we have evidence that the SSS has adequate construct and concurrent validity given the positive correlations observed between the SSS and the Child Development Scale.However, limitations of this study should be noted.First, the SSS subscales might not cover all the dimensions of social competence, even though we used some of the most common frameworks of social competence to develop this scale. Second, while the SSS uses the same scoring standard as a standardized tool, different developmental features of certain items across developmental stages might need further assessment. Third, the present study focused on observed social skills.The social skill strategies that would beeffective for coping with others are not necessarily the same strategies that would best allowchildren to cope with themselves[25]. Future research should examine strategiesfor regulating social skills, such as anger andfear. Overall, our findings suggest that reframing an upsetting outcome,whether by reappraising its importance or outcome,is an effective approach for evaluating social skill development across childhood.
|
|
|
|
|
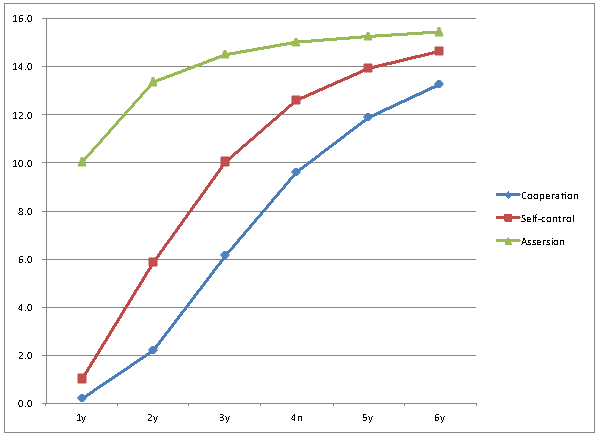 | Figure 1. Means of score by age |
5. Conclusions
- This studyprovides evidence of a simple measure that is able to validly and reliably assess children’s social competence. The SSS can be considered as an established, valid screening instrument that reflects attributes of social competence. This measure helps provide further evidence of the development of social competence, whichenhances our knowledge of the practicality of the SSS for practitioners and caregivers.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (23330174, 24653134).
Appendix: Social Skill Scale (SSS)
- 1. Cooperation: children’s cooperative and empathetic behaviors(1) Cheers up and comforts a person who is missing someone(2) Brings cheer to friends who look lonely(3) Praises a friend's success(4) Applauds a friend who has done something well(5) Pleased at others’ successes(6) Helps friends without encouragement from others(7) Helps friends when friends get hurt(8) Helps friends when asked2. Self-Control: children’s behaviors that emerge in conflict situations (1) Postpones gratification when requested(2) Behaves well as required by the situation(3) Waits to ask for something(4) Does not interrupt another’s speech(5) Borrows toys from others(6) Shares toys or food with others(7) Does not throw temper tantrums in public(8) Waits for his/her turn3. Assertion: children’s initiating behaviors(1) Displays strong reactions when he/she is spoken to(2) Evidences happiness when someone does something for him/her(3) Makes eye contact when someone speaks to him/her(4) Shows his/her feelings on his/her face(5) Initiates talk with another person(6) Makes eye contact when speaking with others(7) Participates in a play group (company) when asked(8) Expresses appropriate greetings to others
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML