-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Health Sciences
2012; 2(4): 38-42
doi: 10.5923/j.health.20120204.04
In Vitro Antibacterial Activity and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Zinc Oxide and Nano-particle Zinc oxide Against Pathogenic Strains
Jehad M. Yousef , Enas N. Danial
Biochemistry Department, Sciences Faculty for Girls, King Abdulaziz University, P. O. Box 51459, Jeddah- 21453, Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: Enas N. Danial , Biochemistry Department, Sciences Faculty for Girls, King Abdulaziz University, P. O. Box 51459, Jeddah- 21453, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In the emerging issue of increased multi-resistant properties in food borne pathogens, zinc oxide (ZnO) and nano-particle zinc oxide (nano-ZnO) are being used increasingly as antimicrobial agents. Thus, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of nano-ZnO towards pathogens microbes Bacillus subtilus NRRL B-543, Bacillus megaterium ATCC 25848, Staphylococcus aureus; NRRL B-313, Sarcina lutea ATCC27853, Escherichia coli; NRRL B-210, Pseudomonas aeruginosa NRRL B23 27853, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 27736, proteus vulgaris NRRL B-123, Candida albicans NRRL Y-477 and Aspergillus niger NRRL-3 were examined in this study. The results obtained suggested that nano-Zno exhibit a good bacteriostatic effect but poor bactericidal effect towards all pathogens tested. Nano-ZnO can be a potential antimicrobial agent due to its low cost of production and high effectiveness in antimicrobial properties, which may find wide applications in various industries to address safety issues.
Keywords: Nano Particles, Antimicrobial Activity Zinc Oxide Nano-Zinc Oxide
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Nanotechnology offers unique approaches to control a wide variety of biological and medical processes that occur at nanometer length and it is believed to have a successful impact on biology and medicine (1 -2). By controlling the structure precisely at nano scale dimensions, one can control and modify their surface layer for enhanced aqueous solubility, biocompatibility or bio-conjugation Nano- particles exhibit attractive properties like high stability and the ability to modify their surface characteristics easily. The basic necessities for drug targeting are that the carrier should be capable of extended circulation in the blood stream; it must be small enough to gain access to target tissues and target cells (3). Nowadays, research efforts are being concentrated on integrating nano-particles with biology. It has been reported that antibiotics often disturb the bacterial flora of digestive tract which may develop multiple drug-resistant isolates, hence novel ways of formulating biocide materials is an upcoming field of attraction (4-7). For this reason, there is a need for the use of an agent which does not generate resistance and presents a good bactericidal property. The field of nanotechnology is one of the most active areas of research in modern materials science.Nano-particles exhibit completely new or improved properties based on specific characteristics such as size, distribution and morphology. New applications of nano-particles and nano-materials are emerging rapidly. Nano crystalline particles have found tremendous applications in the field of high sensitivity biomolecular detection and diagnostics, antimicrobials and therapeutics, Catalysis and microelectronics (8). The commonly proposed pathogenic mechanisms initiated by nano particles (NPs) are dominated by inflammation- driven effects, including fibrosis, oxidative stress, and DNA damage, making inflammation a target for toxicological testing (9). Inflammation is a complex, concerted group of responses that, although defensive against infection, is harmful when induced chronically by environmental stimuli such as inhaled particles (10). The type, harmfulness, and outcome of inflammation vary depending on the nature of the stimulus initiating the inflammation; the affected tissue; the nature of the cellular exudates; its chronicity, severity, and potential to resolve; and the genetic susceptibility of the individual.There are some reports (11) on the considerable antibacterial activity of CaO, MgO and ZnO, which is attributed to the generation of reactive oxygen species on the surface of these oxides. The advantage of using these inorganic oxides as antimicrobial agents is that they contain environmentally safe mineral elements essential to humans and exhibit strong activity even when administered in small amount. The activity is quantitatively evaluated by studying the growth medium caused by the bacterial metabolism (12). Many researchers have attempted to correlate the biological activity of inorganic antibacterial agents with the size of the constituent particles (13-14). The advantages of inorganic antibacterial materials over organic antibacterial materials are that the former show superior durability, less toxicity, greater selectivity and heat resistance. Nagarajan and Rajagopalan 2008 (15) reported that the activity was affected by particle size, which is controlled by processing parameters.ZnO has recently achieved special attention regarding potential electronic application due to its unique optical, electrical and chemical properties (16). The use of antimicrobial agents in them later on promoted to the emergence of resistance in micro-organism (17-18). Therefore, the resistant bacteria can certainly infect the humans via the food (19). The emergence and the development of antimicrobial resistance in pathogens with its scattering nature therefore turned into a global public health concern. Research has been intensively done in antibacterial material containing various natural and inorganic substances to overcome this problem (20). Among them, ZnO and nano-ZnO has known to have strong inhibitory and antibacterial effects as well as a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activities. The availability of a wide range of nanostructures makes ZnO an ideal material for nanoscale optoelectronics (21) and piezoelectric nanogenerators (22) as well as an efficient material for biotechnology (23). Furthermore, ZnO appears to be strongly resisted to microorganisms , and nano-ZnO are now widely used as antibacterial (24).At present, ZnO and nano-ZnO have emerged as a viable treatment option for antimicrobial activities and then we determined the minimum inhibitory concentrations of the pathogenic strains which showed low resistant against ZnO and nano-ZnO.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms
- The organisms used were: Gram positive bacteria namely Bacillus subtilus NRRL B-543, Bacillus megaterium ATCC 25848, Staphylococcus aureus; NRRL B-313 and Sarcina lutea ATCC27853, Gram negative bacteria Escherichia coli; NRRL B-210, Pseudomonas aeruginosa NRRL B23 27853, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 27736 and proteus vulgaris NRRL B-123, pathogenic yeast Candida albicans NRRL Y-477 and fungi Aspergillus niger NRRL-3. These microorganisms were obtained from Natural Research center, Department of Chemistry of Natural and Microbial product Cairo Egypt.
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
- ZnO and nano-ZnO were tested in vitro for their antimicrobial activities against strains by the agar diffusion technique (25). The tested samples were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to prepare chemicals of stock solutions of 20 μg/ml. The pathogenic bacteria and fungi were maintained on nutrient agar and Czapek’s-Dox agar media, respectively in Petri dishes with an inner diameter 9 cm to provide thin agar plates after solidification of thickness 3.4-3.5 mm. After solidification, hollows of 10 millimetre diameter wells were cut from the agar using a sterile cork-borer, and 0.1 ml of each of the tested solutions were poured into the wells. The Petri dishes were incubated at 5-8°C for 2-3 h to permit good diffusion and then incubated for 24 h at 30°C in case of bacteria and 48 h at 28°C in case of yeast and fungi. After incubation the diameter of inhibition zone (mm) was measured. amoxycillin and chloramphenicol, were purchased from Egyptian market and used in a concentration of 20 μg/ml as standard antibacterial and antifungal references.
2.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
- The antimicrobial activities of the samples were evaluated through the determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) by the micro dilution method in culture broth. For both the antibacterial and the antifungal assays, the compounds were dissolved in DMSO (20 mg/ml). Further dilutions were prepared at the required quantities of 20, 10, 5 1 and 0.5 μg/ml concentrations. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values were determined using the method of twofold serial dilutions (26). The Nutrient Broth, which contained tested samples and controls, were inoculated with approximately 5×105cfu/ml of actively dividing bacterial and fungal cells or spores. The cultures were incubated for 24 h and 48 h at 30°C on a metabolic rotary shaker (220 rev/min), and the growth was monitored visually and spectrophotometerically (at 540 nm). In order to ensure that the solvent had no effect on bacterial growth, a control test was also performed containing inoculated broth supplemented with only DMSO at the same dilutions used in our experiments and found inactive in culture medium. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration required to arrest the growth of the bacteria at the end of 24 h of incubation. The MBC was determined by sub culturing a 0. 1-ml volume of the medium drawn from the culture tubes after 48 h on Nutrient Agar and incubated further for bacterial growth. The growth was scored for relative numbers of the bacterial colonies. The lowest concentration of the antimicrobial agent causing negative growth (fewer than three colonies) was considered the MBC. Since the MIC and MBC were virtually the same, we generally reported only the MBC in the results.
3. Results and Desiccations
- A wide variety of synthetic compounds exert antibacterial effect, but just some of them can be used as biocides to develop drugs or coatings. The primary impediment for their use is their toxicity compared with their bactericidal effect; some of them are so toxic for eukaryotic cells that cannot be proposed as antibiotics. Among these materials, ZnO and nano-ZnO compounds raise as potent antimicrobial agents. The advantage of using these inorganic oxides as antimicrobial agents is that they contain environmentally safe mineral elements essential to humans and exhibit strong activity even when administered in small amount In order to study ZnO and nano-ZnO as novel antimicrobial agents. The antimicrobial activity of ZnO and nano-ZnO were determined against Bacillus subtilus NRRL B-543, Bacillus megaterium ATCC 25848, Staphylococcus aureus; NRRL B-313, Sarcina lutea ATCC27853, Escherichia coli; NRRL B-210, Pseudomonas aeruginosa NRRL B23 27853, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 27736, proteus vulgaris NRRL B-123, Candida albicans NRRL Y-477 and Aspergillus niger NRRL-3 as a pathogenic strains.
3.1. Agar Diffusion Technique
- Antimicrobial activities of ZnO and nano-ZnO tested against pathogenic microorganisms using agar diffusion technique. The results represented in Fig (1) showed that the best zone of inhibition against Bacillus subtilus (24mm), Escherichia coli (24mm) Staphylococcus aureus (22mm) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (22mm) for oxide zinc nano-partials. The date also refer that ZnO has moderated effect on Bacillus megaterium (20mm), Sarcina lutea (18mm), Candida albicans (18mm), Klebsiella pneumoniae (16mm) proteus vulgaris (14mm), and Aspergillus niger (14mm). On the other hand the uses of ZnO appeared the lowest effect on all tested microorganisms as shown in Fig (1). The antimicrobial ability of nano-ZnO might be referred to their small size which is 250 times smaller than a bacterium. This makes them easier to adhere with the cell wall of the microorganisms causing its destruction and leads to the death of the cell. Also, metal nano-particles are harmful to bacteria and fungi (26). Nano-ZnO stimulate biofilm production and aggregate within this bio-film. They bind closely to the surface of microorganisms causing visible damage to the cells, and demonstrating good self assembling ability. Nano-ZnO possess well-developed surface chemistry, chemical stability which make them easier to interact with the microorganisms (27). Also, the particles interact with the building elements of the outer membrane and might cause structural changes, degradation and finally cell death.
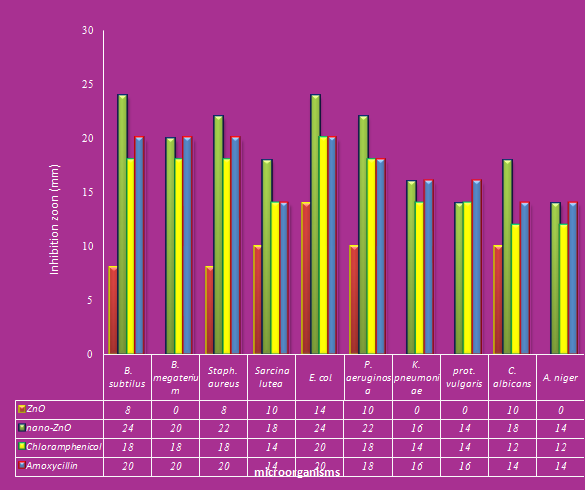 | Figure 1. Antimicrobial activity of ZnO and nano –ZnO against pathogenic microorganisms |
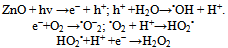 Since, the hydroxyl radicals and superoxide are negatively charged particles, they cannot penetrate into the cell membrane and must remain in direct contact with the outer surface of the bacteria cell of the bacteria; however, H2O2 canpenetrateinto the cell (30).Concerning, the effect of the amoxycillin as antibiotic or chloromphenicol in combination ZnO and nano-ZnO were studied. It indicated that the best results were against Escherichia coli with zone of inhibition equal (20 and 20mm), respectively followed by Bacillus megaterium (20 and 18mm), Bacillus subtilus (20 and 18 mm), Staphylococcus aureus (20 and 18 mm), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (18 and 18 mm), Klebsiella pneumoniae (16 and 14 mm), proteus vulgaris (16 and 14 mm), Sarcina lutea, (14 and 14 mm) Candida albicans (14 and 12 and Aspergillus niger (14 and 12 mm), as shown in Figure (1). This results will be agreement with the results obtains by (31).
Since, the hydroxyl radicals and superoxide are negatively charged particles, they cannot penetrate into the cell membrane and must remain in direct contact with the outer surface of the bacteria cell of the bacteria; however, H2O2 canpenetrateinto the cell (30).Concerning, the effect of the amoxycillin as antibiotic or chloromphenicol in combination ZnO and nano-ZnO were studied. It indicated that the best results were against Escherichia coli with zone of inhibition equal (20 and 20mm), respectively followed by Bacillus megaterium (20 and 18mm), Bacillus subtilus (20 and 18 mm), Staphylococcus aureus (20 and 18 mm), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (18 and 18 mm), Klebsiella pneumoniae (16 and 14 mm), proteus vulgaris (16 and 14 mm), Sarcina lutea, (14 and 14 mm) Candida albicans (14 and 12 and Aspergillus niger (14 and 12 mm), as shown in Figure (1). This results will be agreement with the results obtains by (31).3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
References
| [1] | West J.L. and Halas N.J. (2000): Applications of nanotechnology to biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 11: 215. |
| [2] | Zandonella C. (2003): Cell nanotechnology: The tiny toolkit. Nature; 423: 10-12. |
| [3] | Tom R.T., Suryanarayanan V., Ganapati Reddy P. Baskaran, S. and Pradeep T. (2004): Ciprofloxacin-Protected Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir; 20:1909-1914. |
| [4] | Jarvinen H., Tenovuo, J. and Huovinen P. (1993): In vitro susceptibility of Streptococcus mutans to chlorhexidine and six other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother; 37(5): 1158–1159 |
| [5] | Concannon S.P., Crowe T.D., Abercrombie J.J., Molina, C.M., Hou, P. and Sukumaran D.K. (2003): Susceptibility of oral bacteria to an antimicrobial decapeptide. J Med. Microbiol. 52:1083–1093. |
| [6] | Altman H., Steinberg D., Porat Y., Mor A., Fridman D. and Friedman M. (2006): In vitro assessment of antimicrobial peptides. J Antimicrob Chemother; 58:198–201. |
| [7] | Daglia M., Papetti A., Grisoli P., Aceti C., Dacarro, C. and Gazzani G. (2007): Antibacterial activity of red and white wine against oral streptococci. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55: 5038– 5042. |
| [8] | Jain D., Kumar Daima H., Kachhwaha S. and Kothari S. L.(2009): Synthesis of Plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using papaya fruit extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. A. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures: 4, 557 – 563. |
| [9] | Lu S, Duffin R, Poland C, Daly P, Murphy F, Drost E, MacNee M, Stone V and Donaldson K. (2009). Efficacy of simple short-term in vitro assays for predicting the potential of metal oxide nanoparticles to cause pulmonary inflammation. Environ Health Perspect 117:241–247. |
| [10] | Donaldson K, Aitken R, Tran L, Stone V, Duffin R, Forrest G and Alexander A. (2006): Carbon nanotubes: a review of their properties in relation to pulmonary toxicology and workplace safety. Toxicol Sci 92(1):5–22. |
| [11] | Sawai J. and Yoshikawa T. (2004): Quantitative Evaluation of Antifungal Activity of Metallic Oxide Powders (MgO, CaO and ZnO) By an Indirect Conductimetric Assay, J. Appl. Microbiol. 96, 803. |
| [12] | Sawai J., Doi R., Maekawa Y., Yoshikawa T., and Kojima H. ( 2002): Short Communication Indirect Conductimetric Assay of Antibacterial Activities,” J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotech. 29: 296. |
| [13] | Stoimenov P. K., Klinger R.L., Marchin G.L, and Klabunde K.J, (2002): Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Bactericidal Agents, Langmuir 18, 6679. |
| [14] | Brayner R., Ferrari-lliou R., Brivois N., Djediat S., Benedetti M. F., and Fievet F. (2006): Toxicological Effect of ZnO Nanoparticles Based on Bacteria,” Nano Lett. 6: 866 |
| [15] | Nagarajan P. and Rajagopalan V. (2008): Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nano-particles—an antimicrobial study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 9 (035004), 7-15 |
| [16] | Baxter J. B. and Aydil E.S. ( 2005): Nanowire based dye sensitized solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 53114, 2005. |
| [17] | Asai T., Kojima A., Harada K., Ishihara K., Takahashi T. and Tamura Y. (2005): Correlation between the usage volume of veterinary therapeutic antimicrobials and resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from the feces of food-producing animals in Japan. Journal of Infectious Diseases 58: 369-372 |
| [18] | Olofsson S.K. (2006): Relation between drug exposure and selection of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Uppsala, Sweden: Uppsala University, Faculty of Medicine, Dissertation |
| [19] | Phillips I., Casewe M., Cox T., Groot D.B., Friis C., Jones R., Nightingale C., Preston R. and Waddell J. (2004): Does the use of antimicrobials in food animals pose a risk to human health? Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 53, 28-52. |
| [20] | Kim J.S., Kuk E., Yu K.N., Kim J.H., Park S.J., Lee H.J., Kim S.H., Park Y.K., Park Y.H., Hwang C.Y., Kim Y.K., Lee Y.S., Jeong D.H. and Cho M.H.(2007): Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Nanomedicine 3(1): 95-101. |
| [21] | Sawai J., Igarashi H., Hashimoto A., Kokugan,c T. and Shimizu M. (1996): Antibacterial Characteristics of Magnesium Oxide Powder. J. Chem. Eng. Japan 29, 556 |
| [22] | Wang Z.L. (2004): Functional Oxides Nanobelts Materials, Properties and Potential Applications in Nanosystems and Biotechnology, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 55(159): 1656-1662 |
| [23] | Song J., Zhou J., and Wang Z.L. (2006): Piezoelectric and Semi conducting Coupled Power Generating Process of a Single ZnO Belt/Wire. A Technology for Harvesting Electricity from the Environment. Nano, Lett. 6: 1656. |
| [24] | Huang M.H., Mao S., Feick H., Yan H.Q., Wu Y., Kind H., Weber E., Russo R, and Yang P.(2001): ZnO Microrods Photodeposited with Au–Ag Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Application, In Sers. Science 292: 1897 |
| [25] | Perez C., Pauli M. and Bazevque P. (1990) An antibiotic assay by the agar well diffusion method. Acta Biologiae et Medicine Experimentalis 15, 113-115 |
| [26] | Chwalibog A., Sawosz E., Hotowy A., Szeliga J., Mitura S., Mitura K., Grodzik M., Orlowski P. and Sokolowska, A. (2010): Visualization of interaction between inorganic nano-particles and bacteria or fungi. International Journal of Nanomedicine; 5, 1085–1094. |
| [27] | Nirmala G. A. and Pandian K. (2007): Antibacterial efficacy of aminoglycosidic antibiotics protected gold nano-particles a brief study. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 297: 63–70. |
| [28] | Sunada K., Kikuchi Y., Hashimoto K. and Fujshima A. (1998): Bactericidal and detoxification effects of TiO2 thin film photocatalysts. Environ.Sci.Technol. 32 (5), 726–728. |
| [29] | Fang M., Chen J. H., Xu X. L., Yang P. H. and Hildebr H. F. (2006): Antibacterial activities of inorganic agents on six bacteria associated with oral infections by two susceptibility tests Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 27, 513-517 |
| [30] | Blake M. D., Maness P., Huang Z., Wolfrum E. J., Huang J. and Jacoby W. A. (1999): Application of the photo catalytic chemistry of titanium dioxide to disinfection and the killing of cancer cells. Sep. Purif. Methods 28 (1)1-50 |
| [31] | Zawrah M. F. and Abd El-Moez S. I. (2011): Antimicrobial Activities of Gold Nanoparticles against Major Foodborne Pathogens Life Science Journal. 8(4) 37-44 |
| [32] | Avanzato C. P., Folliri J. M. and Banerjee I. A. (2009): Bio mimetic Synthesis and Antibacterial Characteristics of Magnesium Oxide–Germanium dioxide Nano-composite Powders Journal of composite materials, 43 (8), 897-910 |
| [33] | Nawaz H. R., Solangi B. A., Zehra B. and Nadeem U. (2011): Preparation of Nano Zinc Oxide and its Application in Leather as a Retaining and Antibacterial Agent. Canadian Journal on Scientific and Industrial Research. 2 (4): 164-170 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML