-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Geosciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1697 e-ISSN: 2163-1719
2019; 9(2): 57-68
doi:10.5923/j.geo.20190902.03

Petrophysics and Geochemical Evaluation of the Lacustrine Chang 7 Member’s Shale Oil Reservoir in Ordos Basin, China
Mohamed Awad Sayid , Zhi Gang Yao
School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
Correspondence to: Zhi Gang Yao , School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Using well Logs, organic geochemical data, core and rock cutting samples, X-ray diffraction and QEMSCAN analysis, this study is an attempt to comprehensively evaluate the geological and geochemical characteristics of lacustrine shale oil reservoir in Chang 7 Member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation, with emphasis on hydrocarbon generation conditions and hydrocarbon retention characteristics, reservoir conditions, hydrocarbon-bearing properties, lithofacies characteristics, and mineralogical association. The organic geochemical characteristics show that the Chang 7 oil shale is characterized by a good hydrocarbon generation potential which is reflected in the abundance of organic matter (an average total organic carbon of 13.14%), of type I–II1, moderately mature kerogen, which is mostly at the beginning of oil window (Vitrinite reflectance = 0.9% to 1.03%). The pyrolysis parameters S1 and chloroform asphalt (A), and the measured oil saturation collectively elucidate that the Chang 7 shale has a good hydrocarbons retention characteristic. The mineral compositions of Chang 7 oil shale in the study area contains a high content of brittle minerals represented in quartz and feldspars. The main mineral constituent of the shale by average is (42.5%) clay minerals, (26%) quartz, (22%) feldspars, and (9.5%) iron oxides and siderite collectively. Carbonate minerals are virtually absent. Based on the organic matter content and the mineral association of the shale, Chang 7 oil shale can be classified as argillite rock with high- moderate content of organic matter. The porosity of the Chang 7 Member shale oil reservoir emphatically associates with TOC, which indicates the reservoiring space is mainly the porosity within the organic matter (Intra organic matter pores). According to the shale oil reservoir evaluation criteria adopted in this study, the Chang 7 Member shale oil reservoir is promising for the exploration and exploitation of shale oil resources.
Keywords: Oil shale, Hydrocarbon retention, Hydrocarbon generation potential, Reservoiring space, Brittle minerals
Cite this paper: Mohamed Awad Sayid , Zhi Gang Yao , Petrophysics and Geochemical Evaluation of the Lacustrine Chang 7 Member’s Shale Oil Reservoir in Ordos Basin, China, Geosciences, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 57-68. doi: 10.5923/j.geo.20190902.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Unconventional oil and gas development from shales has reshaped the world energy landscape with a progression of breakthroughs. As the conventional oil and gas production declines worldwide Unconventional resources have become more feasible supplement for the conventional energy sources. Oil shale as an important unconventional oil resource with its giant large resources and rich comprehensive utilization value has now turned into a plausible increment for conventional energy sources and drawn countries attention all over the world. China, the world’s second-largest economy and major energy consumer, is likewise prosperous in shale oil resources in its well developed and widely distributed lacustrine shale successions in the Meso-Cenozoic basins (Yang et al., 2013). These oil-prone sequences are characterized by high organic content, huge thickness, shallow burial depth, and low maturity, demonstrating an enormous shale oil potential. Ordos Basin contains multiple layers of oil shale deposits longitudinally distributed in the Permian Shanxi group (P1s), Triassic Yanchang Formation (T3y), Jurassic Yan'an Formation (J1y) and Anding Group (J2a). The most prospective production horizon of oil shale in the basin is the Triassic Yanchang Formation. However Chang 9, Chang 7 and Chang 4 + 5 members of the Triassic Yanchang Formation are predominantly composed of dark shale and mudstone. Among them the organic‐rich shale of Chang 7 member is regarded to have the greatest potential for shale oil exploration in Ordos Basin. However, the Chang 7 Member shale was deposited in a lacustrine environment and consequently it is fundamentally not quite the same as marine shales as far as kerogen type, maturity of organic matters, and mineral compositions. Furthermore, the precise and effective assessment and classification criteria for the shale oil reservoirs have not been well established. Consequently, the assessment of the reservoir and their Geochemical and geological controlling factors will help comprehend the mechanism of reservoir formation and hydrocarbon occurrence and accumulation in the Chang 7 Member’s organic-rich shale, thereby effectively guiding the exploration and development and appraisal of unconventional shale oil reservoirs the Ordos Basin. In addition, the understanding of rock mineralogy is vital factor for developing improved models for the exploration and exploitation of shale oil resources. The present work aims to comprehensively evaluate the unconventional oil shale reservoir of Chang 7 member in Ordos Basin and explored the geological significance with emphasis on rock mineralogy and lithofacies characteristics, hydrocarbon generation conditions and hydrocarbon retention characteristics, reservoir conditions, and hydrocarbon-bearing properties.
2. Geological Setting
2.1. Tectonics
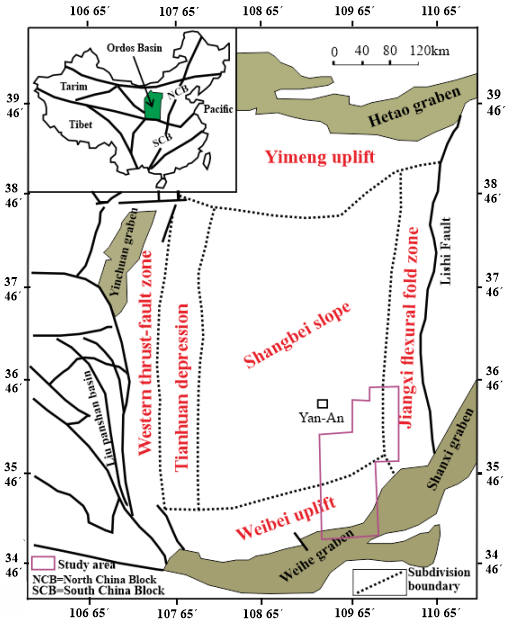
- Located in central China and extending from Yinshan in the north, reaches the Qinling Mountains in the south, and arrives in Tengger Desert in the west desert, east to Luliang Mountain, across the north of China, the Ordos Basin is a Mesozoic superimposed basin that developed in the west-central part of the North China platform, covering an area of about 2.5×105 Km2. The North China platform is bounded on the south by the North Qin ling (Tsinling) fold system, on the southwest by the Qilian (Nanshan) fold sytem, on the west by the Alaskan stable block, on the north by the Neimeng-Daxinganling (Inner Mongolian Great Khingan) fold system and the Ji-Hei (Kirin-Heilungkiang) fold system, and on the east by the Yangzi (Yangtze) platform (Huang et al., 1980). However, the basement rocks of the North China platform comprise the pre-Sinian metamorphic rocks, overlain by the Sinian, Cambrian, and Early and Middle Ordovician sedimentary covers, and then intruded by igneous rocks. The formation and development of the basin were controlled by regional geodynamics particularly Indo-Chinese movement in late Paleozoic. The basin has accomplished a principal transformation from the marine phase to the transitional phase to the intracontinental foreland basin. According to (Yang et al., 2005) the development of the Ordos basin during the Paleozoic–Mesozoic can be divided into three stages: Cambrian–Early Ordovician cratonic basin with divergent margins; Middle Ordovician–Middle Triassic cratonic basin with convergent margins; and Late Triassic–Early Cretaceous intraplate remnant cratonic basin. Throughout its complex development history, the Ordos basin subsidence and uplift alternately many times. The interior of the basin can be divided into six primary structural units (Figure 1): Yimeng Slope, Weibei Uplift, Jinxi Flexural-Fold Belt, Western Fold-Thrust Belt, Tianhuan depression, and Shanbei Slope, among which the Shanbei Slope is the major petroliferous unit, providing about 66% of the total oil and gas resources of the whole basin (Duan et al., 2008 and Tang et al., 2012). A set of three graben systems surrounds the interior of the basin namely Hetao Graben in the north, Fenwei Graben system in the southeast, and Yinchuan Basin in the west (Figure 1).
2.2. Stratigraphy
- The stratigraphy of the Ordos basin includes the Late Carboniferous, Permian, and Mesozoic sedimentary sequences. Based on palaeontologic studies, the Mesozoic stratigraphy of the Ordos basin consists of continental sequences of Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous sedimentary rocks (institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1980). However, petroleum deposits mainly occur in the Triassic Tongchuan and Yanchang Formations and in the Jurassic Fuxian, Yanan and Zhiluo Formations. The oil shale deposits in the basin are mainly developed in the third section of the Triassic Yanchang Formation and much more importantly in Chang 7 Member which is dominated by deep-semi-deep lake facies. Therefore, the stratigraphic section of this paper is concentrated on the Triassic Yanchang Formation as discussed below. The development and evolution of the Triassic Yanchang group objectively recorded a complete history of large freshwater lake basin from the occurrence and development to extinction. Earlier studies subdivided the Late Triassic Yanchang Formation into the lower, middle, and upper members. However, the later studies subdivided Yanchang Formation based on litholofacies characteristics into ten members from top to bottom Chang1 to Chang10 respectively (Figure 2). The Chang 9, Chang 7 and Chang 4 + 5 are composed predominantly of dark shale and mudstone, and the other intervals of the Yanchang Formation, particularly the Chang 8 and Chang 6, are composed of delta plain, delta front and fluvial sandstones and silt sandstone predominantly interbedded with greyish-green mudstones (Zou et al., 2013) (Figure 2). Lithologically the ten members of Yanchang Formation consist of mudstones, shales and sandstones, among which Chang 9, Chang 7 and Chang 4+5 are composed predominantly of dark shale, while the other members particularly the Chang 8 and Chang 6 are made out of sandstones and silty sandstone predominantly interbedded with greyish-green mudstones representing the delta plain, delta front and fluvial depositional environments (Chen, 2004; Zhang, 2006; Zou et al., 2013). The Chang 7 can be further subdivided into three oil reservoirs from the bottom to top Chang 73, Chang 72 and Chang 71 oil reservoirs respectively.
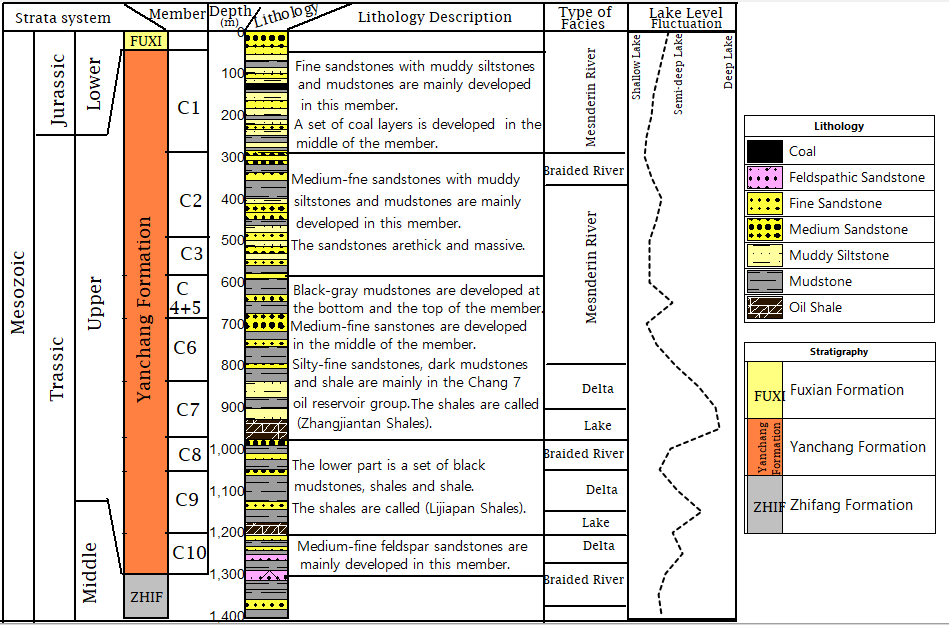 | Figure 2. Comprehensive stratigraphic column of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin (modified after Xu et al., 2017) |
3. Materials and Methods
- In order to understand the geological and geochemical characteristics of the Chang 7 shale oil reservoirs in a more systematic and comprehensive way, a variety of test and analysis methods were carried out on the collected data which includes well logs, geochemistry, cores and rock cuttings etc. The geochemical survey was based on the analysis of 23 sample were obtained from 17 wells cores of the Yanchang Formation from depths ranging from 573.45 m to 2290.35 m. All samples were experimentally examined and tested for TOC content measurements, Vitrinite reflectance (Ro) analysis, rock-eval pyrolysis parameters, QEMSCAN analysis, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. The geochemical assessment was attempted to evaluate TOC content, thermal maturity level, kerogen type, and the nature of generated and retained hydrocarbons.The mineralogical assessment is not commonly associated with geochemical studies, however; it appears to be a significant factor for oil shale assessment as the exploitation of this kind of reservoir is completely different from other conventional oil sources. For unconventional oil production, the assessment of reservoir homogeneity and brittleness the mineralogical association, clay type, quartz and carbonate percentages are very important parameters for shale oil production. Therefore, thin-section investigation, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and QEMSCAN technology were used to investigate the mineral composition of shale cores and cuttings. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used for whole‐rock (bulk) and clay fraction (<2 μm) mineralogy. QEMSCAN technology was used to map the sample surface and identification of the background minerals thus providing quantitative analyses of rock mineralogy. Physical properties including porosity permeability, and oil saturation were measured on samples collected from three different wells namely Fuxi71, Wan91, and Zheng426. Thereby, a comprehensive evaluation of distribution characteristics, mineral petrology and organic geochemistry of Chang 7 oil shale reservoir is provided.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrocarbon Generation Potential and Oil Content of Shale
- The organic matter type, organic matter abundance, and maturity are not only the key parameters for oil shale qualitative evaluation but also important pointers for reserves estimation. They are also the basis for the study of shale oil occurrence and formation mechanism. The organic matter content determines the amount of shale oil. Under the condition of similar organic matter type and maturity, the higher content of organic carbon in shale implies greater hydrocarbon generation potential, which can bring about increasingly more residual hydrocarbon. In short, higher TOC leads to higher oil content in shale.
4.1.1. Quantity of Organic Matter
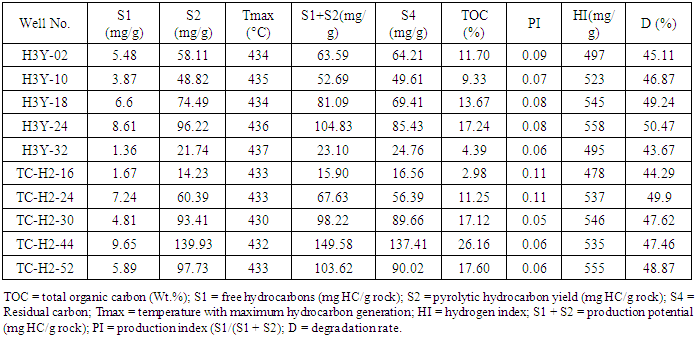
- The organic carbon test results show that the Chang 7 shale layer is rich in organic matter and contain a high – very high residual organic carbon. The statistical results show that the residual organic carbon content is mostly above 9%, with the highest TOC contents being 26%, and the average total organic carbon content is 13.14% (Table 1). The organic geochemical data of the Chang 7 shale oil reservoir showed that the content of chloroform bitumen “A” and “S1” have a good positive correlation with TOC (Figure 3) which indicates the high oil content of shale.
|
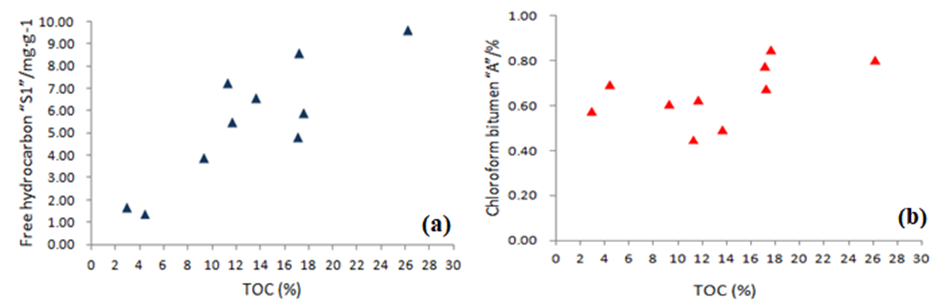 | Figure 3. Relationship between oil content and TOC of oil shale in the Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation; (a) free hydrocarbons versus TOC, (b) chloroform bitumen versus TOC. |
4.1.2. Quality of Organic Matter
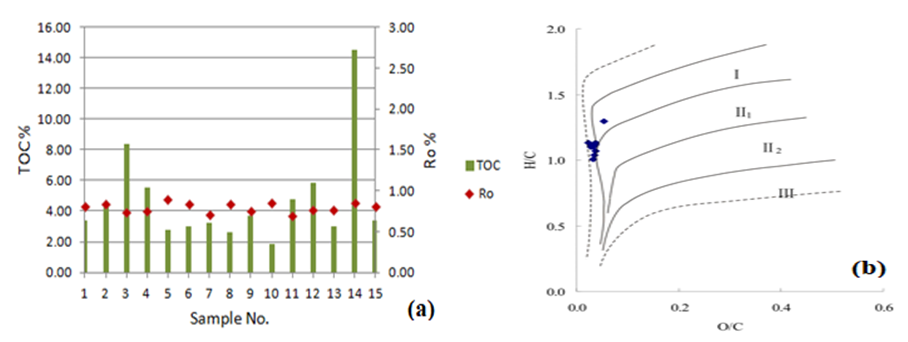
- Kerogen type determination is a fundamental key to anticipate the kerogen behavior throughout the maturation and conversion of organic matter. Organic matter type is mainly determined by original biological types and their combination, which is controlled by the dominant biological living environments during the deposition (Deng, H. W. el. 1993). The studied samples of Chang 7 lacustrine shale layer are characterized by a high hydrogen index (mainly distributed in the range of 497- 558mg/g) and a low oxygen index (mostly less than 20mg/g) (Table 1), representing type I-II1 kerogen, which is an oil prone kerogen (Figure 4). The terrestrial organic components such as vitrinite indicate that the parent material is mainly low-lying organisms (algae), which is good for oil production. However, kerogen type II1 is dominated by yellow to brown structureless organic matter (Figure 5).
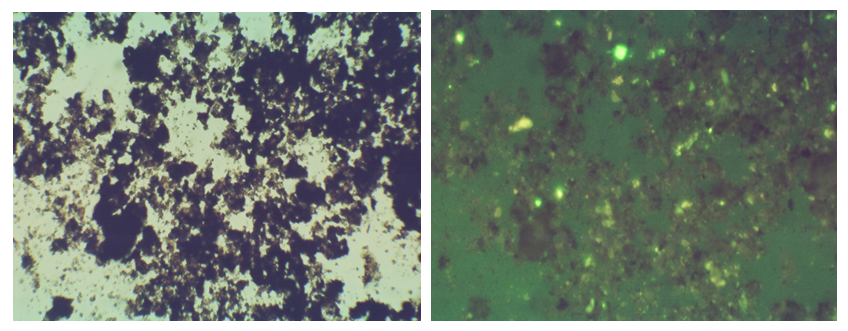 | Figure 5. Transmitted light photomicrographs of structureless (amorphous) organic matter showing the early maturity stage of organic matter of Chang 7 Member oil shale |
4.1.3. Maturity of Organic Matter
- The most important factor for the shale oil accumulation is the maturity of organic matter. Rock-Eval experiments are done to measure TOC, determine kerogen type and maturity. Nevertheless, the chemical composition of the kerogen and the presence of bitumen can lead to suppression of Tmax values which should ideally be a measure of maximum rate of hydrocarbon generation. Hence, Tmax value can be converted into an equivalent vitrinite reflectance (Ro) according to the equation (Jarvie et al. 2001):Ro = Tmax × 0.18-7.16Oil and gas zone boundaries can be set up utilizing vitrinite reflectance data. These boundaries are approximate and vary as per the kerogen type (Figure 6).
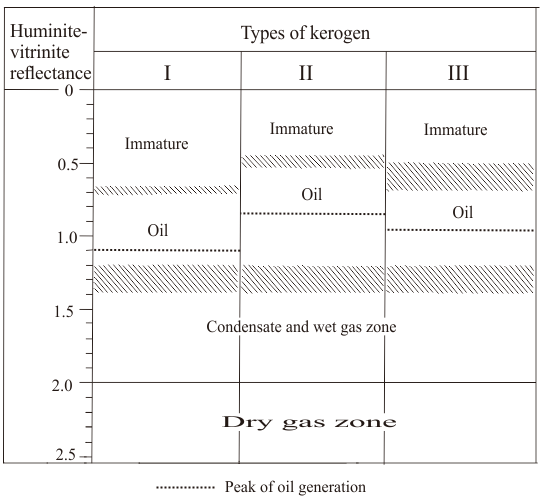 | Figure 6. Approximate boundaries for kerogen types I, II, and III. (Tissot and Welte; 1984) |
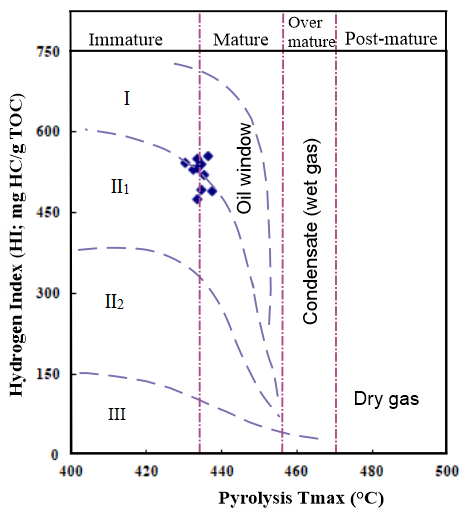 | Figure 7. Cross plot of the hydrogen index (HI, mg HC/g TOC) versus pyrolysis Tmax (°C) showing the kerogen type of the studied Chang 7 oil shale samples |
4.2. Hydrocarbon Retention Characteristics in Shale
- The retained hydrocarbons in the shale are of great significance for shale oil enrichment. The mechanism of hydrocarbons hydrocarbon retention in shale reservoirs system is not fully understood. The vast majority of researches concentrate on the features of expelled hydrocarbons and barely on the retained hydrocarbons which are considered the source for unconventional hydrocarbon accumulation. However, Zou set forward a retention and accumulation model for shale oil based on the FE-SEM observations. According to Zou’s model; liquid hydrocarbons mainly occur adsorbed on the surface or in the internal of organic matter, and in the nanoscale pore throat of mineral matrix (clay, quartz, feldspar, dolomite and calcite) (Zou et al., 2013). Nonetheless, the controlling factors of the retained hydrocarbons in shale include the lithological assemblage of source rocks, effective migration channels, stress distribution in the source rocks and micro-fracture development (Pepper and Corvi, 1995; Stainforth, 2009). The state in which the residual hydrocarbons occur is mainly controlled by the organic chemistry and inorganic mineral compositions in shale, reservoiring space, hydrocarbon compositions. The free retained hydrocarbons are effective contributors to the shale oil production capacity, and are commonly characterized by pyrolysis S1 and chloroform asphalt “A”. The geochemical analysis of the Chang 7 shale shows that the shale pyrolysis S1 is mainly distributed at 1.36 - 9.65mg/g, with an average of about 5.52 mg/g; the chloroform asphalt (A) is mainly distributed at 0.45% - 0.86 %, with an average of 0.66%. The oil saturation test was carried out on the shale core column samples. The oil saturation estimation results denote that the oil saturation ranges between 23.25% and 32.82%, with an average of 26.52%. The high oil saturation of the shale in the study area, whereas the volume of liquid hydrocarbons accounts for nearly 40% of the reservoir space implies a good hydrocarbons retention characteristic of the Chang 7 shale in the study area.
4.3. Thickness of Organic-rich Shale
- The Chang 7 shales shows high gamma (GR), high acoustic impedance (AC), and high resistivity on the well log hence the thickness of the Chang 7 shales and mudstones can be obtained effortlessly (Figure 8). A large number of drilling statistics show that the Chang 7 lacustrine shale formation is large-scale, and the shale with a thickness greater than 10 m can reach an area of 3×104 km2, but the thickness varies greatly, and the biggest thickness can reach 130 m (Dai et al., 2016, and Wang et al., 2015). However, the total thickness measured for the shale section in the studied wells ranges from 48 m to 54 m. The observations of logging curves indicate the presence of thin sandstone and siltstone interlayers within the Chang 7 shale section (Figure 8). The presence of thin sandstone interlayers makes Chang 7 oil shale conditions favourable for shale oil exploration and exploitation therefore; the oil generated in the shale can enter the sandstone interlayer only after a very short distance migration. Although they cannot be developed as a separate reservoir but they contribute through reservoir heterogeneity and stress distribution anisotropy of the whole shale section which leads to more brittleness.
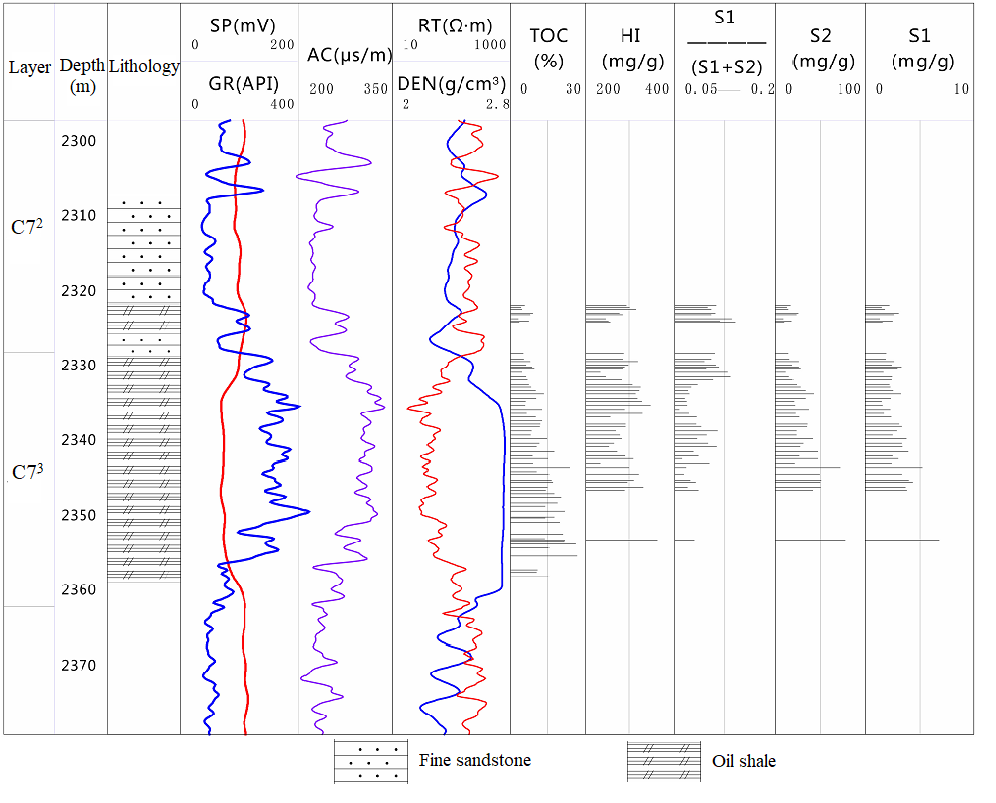 | Figure 8. The well log and organic geochemical feature of oil shale in Chang 7 layer |
4.4. Mineral Compositions of Shale
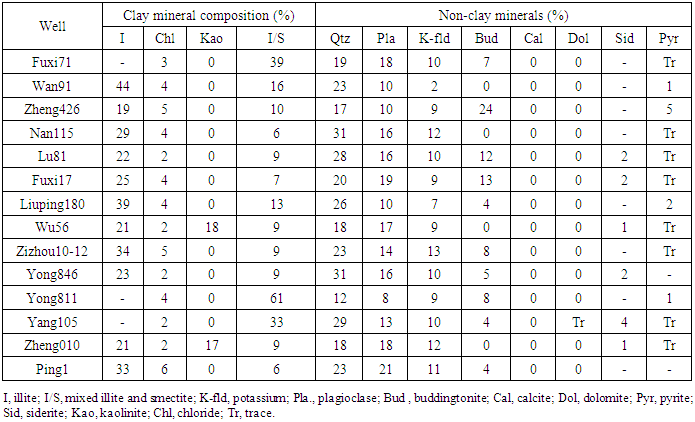
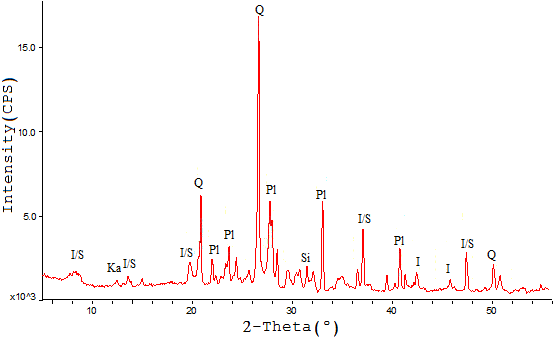
- Mineralogical assessment is not commonly involved in geochemical studies however; it appears to be an important factor for oil shale assessment as exploitation of this reservoir kind is completely different from other gas source. In fact, for unconventional gas production, the assessment of reservoir homogeneity and brittleness the mineralogical association, clay type, quartz and carbonate percentages are important parameters. Previous studies demonstrate that, shale with more silica tends to be naturally fractured and more productive, and hale with more silica, less clay can be easily hydraulically fractured and with more probability of stimulation treatment success (Rezouga et al., 2004). Shale oil investigation experience worldwide demonstrates the significance of the percentage of brittle minerals in shale such as quartz and feldspars. Shale rich in brittle minerals has good fracability, which is advantageous to the formation of natural fractures and induced fractures, and thus is favourable for shale oil exploitation and further development.The observation of the core and the rough grinding of the rock show that the rock of the Chang 7 shale is hard and X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed this point. 14 samples of Chang 7 shale were analyzed by XRD, and 12 samples were analyzed by QEMSCAN to determine their mineralogical composition. The most abundant non-clay minerals are quartz and feldspar; their concentrations are expressed in Table 2 as a percentage of the total sample. The mineral composition of the shale in the study area is dominated by clay minerals and quartz. The main mineral composition of the shale, by average, is 42.5% clay minerals, 26% quartz, and 22% feldspars. It is to be noted that Chang 7 shale contains a considerable amounts of buddingtonite resulted from the alteration of primary feldspar minerals.
|
4.4.1. Clay Type Distribution
- The mineralogy of clays is perplexing however; fundamentally three groups are the most significant; Illite, Kaolinite, and montmorillonite. Each of them has different effects on reservoirs. Illite and montmorillonite are more able to absorb gas than other clay types while Kaolinite, by and large, occurs as blocky crystals within the pore spaces that act by diminishing the reservoir porosity yet may have a minor effect on permeability (Selley, 1998).Clay type distribution determination for Chang 7 shale demonstrates high heterogeneity and big variability from well to another within the study area. Illite seems to be the most abundant clay mineral (Figure 9 and Figure 10) although its percentage varies considerably ranging from 21 to 70% while smectite shows a relatively stable distribution with an average of 4.9%. In fact, Kaolinite seems to be neglectable in most of the studied samples although samples from wells Wu56, and Zheng010 showed an unusual high Kaolinite content 18%, and 17% respectively (Table 2). However, montmorillonite seems to be very low to undetectable extent.
 | Figure 9. The QEMSCAN photographs of shale sample from the Chang 7 Member, sample number CS338R, well Liuping-177, 1475.7m depth showing the mineral composition of continental clay shale |
4.4.2. Quartz and Carbonate Content Distribution
- Quartz and carbonate contents are highly variable in the Chang 7 shale. Quartz seems to be abundant in the majority of studied samples ranging from 17% to 31% with an average of 22% (Figure 9 and Table 2) while carbonates seem to be virtually absent; only traces of calcite and dolomite were observed in some sample (Figure 11). However, the logging data indicates that there are thin sandstone interlayers within the shale and mudstone which increase the overall brittleness of the Chang 7 shale. Consequently, the attributes of the enrichment of brittle minerals in the Chang 7 oil shale have established the framework for shale oil investigation and assessment, which is favourable for the storage and exploitation of shale oil.
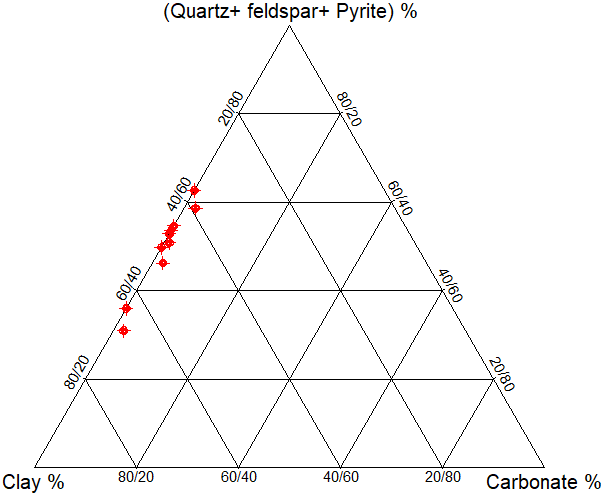 | Figure 11. Ternary diagram of the mineral composition of the Chang 7 |
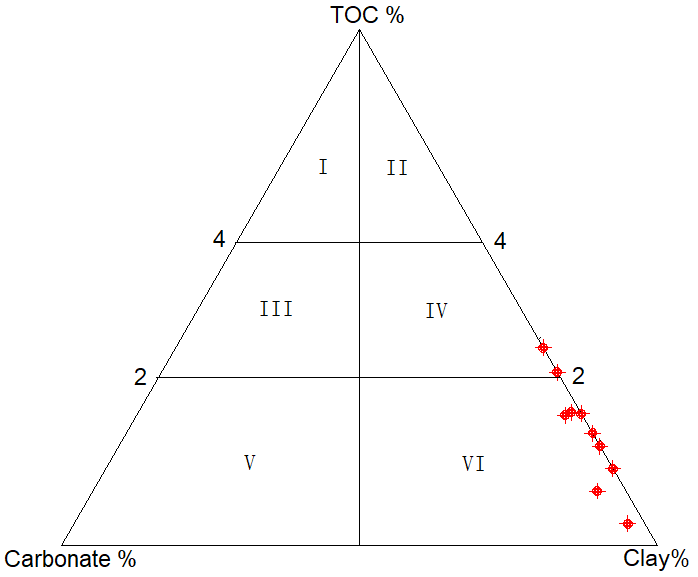
4.5. Rock Type (Shale Classification)
- Oil shale has gotten a wide range of names throughout the years, such as cannel coal, boghead coal, alum shale, stellarite, albertite, kerosene shale, bituminite, gas coal, algal coal, wollongite, schistes bitumineux, torbanite, and kukersite. Some of these names are as yet utilized for particular kinds of oil shale (Dyni, 2009). Recently, however, many endeavors have been made to systematically classify the wide range of sorts of oil shale based on the depositional environment, the petrography, the characteristics of the organic matter, and the parent material of the organic matter. One of the useful classification schemes of oil shales was developed by Kuila & Prasad (2012) which is based on clay minerals, quartz and feldspars, and Carbonate minerals content regardless of the content of organic matter. However, Jiang et al., (2016) in view of the significant role of organic matter in shale sedimentation, diagenesis, and reservoir formation, proposed that the characteristics of organic matter should be considered and the mineral composition ought to be taken as the primary standard in grouping shale types. Therefore, the type of shale is controlled by both the content of organic matter content and rock mineral compositions (Jiang et al., 2016). In the view of the three fundamental components of TOC, carbonate mineral and clay mineral, and taking TOC limit estimations of 2% and 4%, Jiang et al., (2016) classified shales into high-organic, moderate-organic and low-organic types (Figure 12). Accordingly, the Chang 7 shale mineral composition falls within class; IV, and VI areas which is argillite rock with moderate content of organic matter, and argillite rock with low amount of organic matter respectively on Jiang et al., (2016) oil shale classification scheme (Figure 12).
4.6. Organic Matter Content as a Function of Shale Reservoiring Capacity
- The key elements for the formation of shale oil reservoirs are the storage space and inter-connectivity of pore space of hydrocarbon-bearing shale and mudstone. The currently accepted reservoiring mechanisms include: (1) fracture network formed due to tectonic activities or natural hydraulic fracturing can serve as oil reservoirs, (2) different types of micro-pore and micro-fracture in the matrix of mudstone and shale as well make good shale oil reservoirs (Jiang et al., 2016). As a rule, the porosity and permeability of organic matter is higher than the associated rock matrix in shale and can provide pores and channels for of hydrocarbons flow in the reservoir. As kerogen thermally evolves and expulse the generated hydrocarbons, organic pores will be developed. In addition, pores may likewise be formed between matrix and organic matter due to the volume contraction of the organic matter. These organic matter-related pores are well-connected and have high abundance. Applicable investigations demonstrate that shale with a 7% organic matter can increase porosity by 4.9% through the consumption of 35% of organic carbon during the hydrocarbon conversion process (Jarvie et al., 2007). The porosity and permeability test was carried out on three shale samples using helium gas expansion method. The results show that the shale layer has an average porosity of 3.47%, and the average permeability value is 0.000136mD. According to the statistical data of the Chang 7 Member oil shale, Well Fuxi71, Wan91, and Zheng426, a rough positive correlation can be observed between TOC and porosity (Figure 13) suggesting the predominance of porosity in organic matter (Intra organic matter pores) in the Chang 7 Member shale oil reservoir.
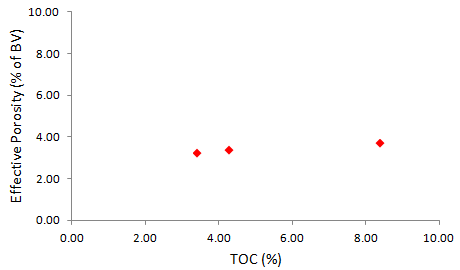 | Figure 13. Relationship among porosity and TOC of the Chang 7 shale |
5. Conclusions
- In view of the comprehensive evaluation of distribution characteristics, mineral petrology and organic geochemistry of Chang 7 oil shale reservoir, the following conclusions can be drawn:(1) Based on organic geochemical characteristics and mineralogical association of the Chang 7 oil shale reservoir and considering the TOC, S1, chloroform asphalt “A” and other indicators; the organic matter type, abundance, and Maturity, the Chang 7 oil shale reservoir meets the criteria of favourable areas of shale oil exploration.(2) The pyrolysis parameters and micro-component analysis results show that the Chang 7 oil shale contains abundant organic matter with an average organic carbon content being 13.14%. The kerogen type in the study area is mainly type I–II1, and the estimated maturity of the organic matter indicates that the Chang 7 shale is low-moderately mature (at the beginning of the oil window). The pyrolysis parameters S1, and chloroform asphalt (A) combined with the measured oil saturation indicate that the Chang 7 oil shale in the study area has a good hydrocarbons retention characteristic. (3) Based on well logs interpretation, the Chang 7 shale is developed in the study area with a total shale thickness ranging from 48 m to 54 m; nevertheless this thickness contains multiple thin sandstone interlayers that cannot be developed separately as reservoir units. The occurrences these thin sandstone interlayers contribute through the reservoir heterogeneity and stress distribution anisotropy of the whole shale section which leads to a better brittleness and fracability.(4) According to the assessment of the mineral compositions of Chang 7 oil shale in the study area, the shale is dominated by clay minerals, quartz, and feldspars respectively. Their percentage of the total sample by average is 42.5% clay minerals, 26% quartz, and 22% feldspars. Carbonate minerals are only traces.(5) Taking the content of organic matter into consideration along with mineral composition as it has been suggested by Jiang et al., (2016), the Chang 7 shale can be classified as argillite rock with moderate content of organic matter, and argillite rock with low amount of organic matter respectively.(6) In light of the estimation of the physical properties of shale, the measured porosity of the Chang 7 Member shale oil reservoir positively correlates with TOC, which indicates the predominance of porosity in organic matter (Intra organic matter pores) in the Chang 7 Member shale oil reservoir.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research was fully supported by China Scholarship Council. The first author would like to acknowledge the sponsorship from China Scholarship Council (CSC) for his master degree at Xi’an Shiyou University.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML