-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Geosciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1697 e-ISSN: 2163-1719
2013; 3(3): 89-98
doi:10.5923/j.geo.20130303.02
Lime Chemical Stabilization of Expansive Deposits Exposed at El-Kawther Quarter, Sohag Region, Egypt
Hesham A. H. Ismaiel1, Mohamed M. Badry2
1Geology Department, Faculty of Science, South Valley University, Qena, 83523, Egypt
2Quality Control Sector, Nasr General Contracting Company, Cairo, 2919, Egypt
Correspondence to: Hesham A. H. Ismaiel, Geology Department, Faculty of Science, South Valley University, Qena, 83523, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work dealt with chemical stabilization of expansive soils (clayey silts) of Pliocene deposits exposed at El kawther quarter (Sohag region) using hydrated lime to reduce their swelling, to avoid a road heave and to improve their geotechnical properties. Several specimens (disturbed and undisturbed) of the studied expansive deposits were collected from El-Kawther sector of the upper Egypt-Red Sea road, east of Sohag city. Chemical analysis (XRF) of both the studied clayey silt and the used lime was conducted, as well as soluble salts (sulfates and chlorides) were determined. Microstructural changes were examined using scanning electron microscope (SEM) before and after the soil treatment. Geotechnical properties including plasticity, compaction parameters, unconfined compressive strength (qu), California bearing ratio (CBR), swelling percent using CBR-instrument as well as free swelling of the studied soil were measured before and after the treatment. An optimum lime content to treat the studied clayey silt was 5% according to pH-test. The results showed that the addition of lime led to a decrease in maximum dry density and to an increase in optimum water content. The addition led also to a reduction of a liquid limit, plastic limit and plasticity index. Both qu- and CBR-values were increased from 209.00 to 1574.10KN\m2 and from 1.20 to 86.70% respectively, after lime treatment, especially with increasing curing time from 7 to 28 days. Swelling percent using CBR-instrument and free swelling were reduced from 6.10 to 0.36% and from 80.00 to 6.70% respectively.
Keywords: Free Swelling, CBR-Swelling, Heave, California Bearing Ratio, Unconfined Compressive Strength
Cite this paper: Hesham A. H. Ismaiel, Mohamed M. Badry, Lime Chemical Stabilization of Expansive Deposits Exposed at El-Kawther Quarter, Sohag Region, Egypt, Geosciences, Vol. 3 No. 3, 2013, pp. 89-98. doi: 10.5923/j.geo.20130303.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Environmental conditions (arid or humid regions) are major factor affecting on swelling behavior of expansive soils. The desert area as arid region (at El-Kawther quarter east Sohag city, Figure 1) is the most promising area for development of territories outside the Nile valley. These diments of the arid region are characterized by an occurrence of expansive clay minerals, these clays may be lead to a heave of the roads constructing at this area. For this reason, there is urgency to treat the expansive clayey soils to avoid the swelling problem (Heave). Study of geotechnical properties of the expansive soils plays an important role in their engineering classification, an evaluation of their mech- anical behavior, and a prediction of their geotechnical problems, as well as a suggestion of the suitable methods for treatment.The chemical stabilization of the problematic soils(expansive soils and soft fine-grained soils) is very important for many of the geotechnical engineering applications such as pavement structures, roadways, building foundations, channel and reservoir linings, irrigation systems, water lines, and sewer lines to avoid the damage due to the swelling action (heave) of the expansive soils or to the settlement of the soft soil.
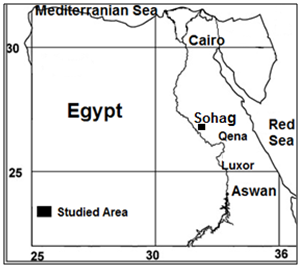 | Figure 1. Location map of the studied area |
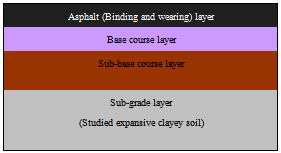 | Figure 2. A typical flexible pavement structure |
1.1. Previous Works
- Many geological investigations were carried out on the study area like[12],[13],[14],[15],[16] and others. Few geotechnical investigations for lime chemical stabilization in the studied area and in Egypt were achieved like[8] (at Idku city),[17] (at Toshka area) and[18] (at New Valley Governorate).
1.2. Scope of the Present Work
- This work dealt with an investigation of the geotechnical properties of a high plastic expansive clayey silt of Pliocene deposits exposed at El Kawther quarter (Sohag region) and occurring as sub-grade of upper Egypt-Red Sea (Sohag- Safaga) road. The main goal of this study was a chemical stabilization process of the studied sub-grade soil using hydrated lime to reduce its swelling percent, to avoid a road heave (Figure 3) and to improve its geotechnical properties.
 | Figure 3. A heave in asphalt layer of the studied road due to swelling of an expansive soil sub-grade at El-Kawther sector, Sohag-Safaga road (Km: 1+400m) |
2. Location and Geological Setting
- The study area (El-Kawther quarter) lies at the east Sohag city between old flood plain and El Maaza limestone plateau. It lies between latitudes 26° 30¯ and 26° 45¯ N and longitudes 31° 45¯ and 32° 00¯E (Figure 1). The Cretaceous, Eocene, Paleocene, Pliocene and Quaternary (Pleistocene and Recent) successions and related landforms are represented by a large carbonate plateau (called El Maaza plateau) and several terraces of variable levels intercalated occasionally by marl and carbonate sediments and covered with Quaternary sediments. The distribution of the sediments is mapped in some details in a geological map as shown in Figure (4). El Maaza plateau belonging to Eocene age is characterized by low relief topography with general inclination towards the west direction. The high of plateau reaches to 560m above sea level.The major wadis dissecting the limestone plateau (east Sohag) are summarized as Wadi Abu Nafukh, Wadi Kiman, and Wadi Dir El-Hadied, which connected with river Nile[13]. The studied soils (high plastic expansive clayey silts) are belonging to Issawia Formation having Pliocene age (Figure 5). Issawia Formation is composed of chocolate- brown clay and silt. It overlies older strata mostly Eocene and underlies alluvial deposits of Pleistocene age[19].
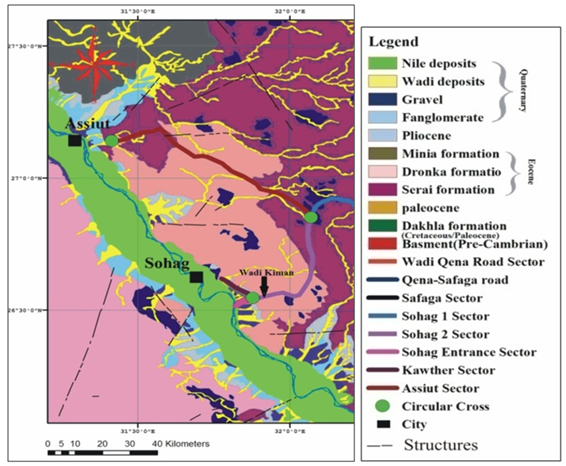 | Figure 4. Geological map of the studied area modified after[30] |
 | Figure 5. High plastic expansive clayey silts belonging to Pliocene Issawia Formation and exposed along El-Kawther sector, Sohag-Safaga road (Km: 1+400m) |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
|
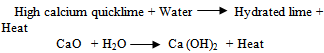 Hydrated lime is used in most of the lime stabilization applications. Quicklime represents approximately 10% of the lime used in lime stabilization process. Other forms of lime are sometimes used in lime stabilization applications such as dehydrated dolomitic lime, monohydrated dolomitic lime and dolomitic quicklime[9].
Hydrated lime is used in most of the lime stabilization applications. Quicklime represents approximately 10% of the lime used in lime stabilization process. Other forms of lime are sometimes used in lime stabilization applications such as dehydrated dolomitic lime, monohydrated dolomitic lime and dolomitic quicklime[9].3.2. Methods
- Chemical analysis (XRF, X-ray fluorescence) of both the studied clayey silt and the used hydrated lime was carried out. Soluble salts (sulfates[20] and chlorides[21]) were determined. Mineralogical analysis of the studied soil using XRD, X-ray diffraction, was conducted.Lime chemical stabilization program (Laboratory program) was carried out including four main steps. The first step was a preparation of the soil sample; soil sample was dried in the air and then it was put into the oven at 50°C for 24 hours. The dried soil was crushed in crushing-machine. The second step was a determination of the reactivity of the studied soil for lime stabilization. The third step was a determination of optimum lime content to stabilize the studied soil using pH-test[22]. The fourth step was a preparation of the treatedlime-stabilized compacted samples with the optimum lime content at a maximum dry density and optimum watercontent.Geotechnical properties including grain sizeanalysis[23 & 24], plasticity[25], compactionparameters[26], unconfinedcompressive strength[27], California bearing ratio[28], swelling percent using CBR-instrument as well as free swelling percent[29] of the studied soil were measured before and after the lime treatment.Microstructural changes of the studied soil were examined using scanning electron microscope (SEM) before and after the treatment.
4. Results
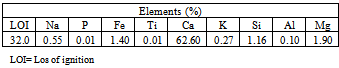
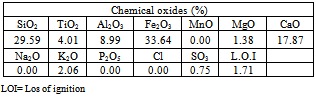
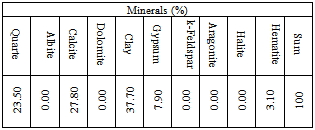
4.1. Results of Mineralogical and Chemical Analysis
|
|
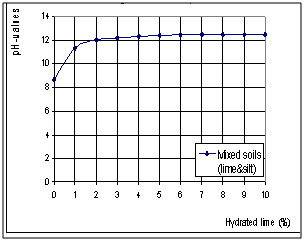 | Figure 6. pH-valus curve |
4.2. Results of Geotechnical Tests
4.2.1. Grain Size Analysis Test Results
 | Figure 7. Grain size distribution curves |
4.2.2. Plasticity Test Results
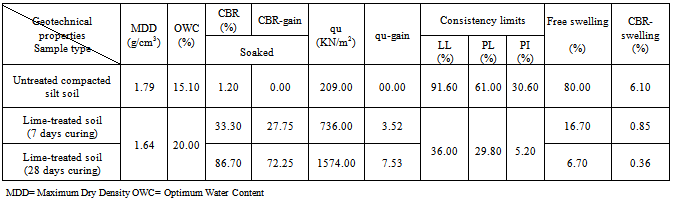
- Figure (8) and Table (4) illustrated the values of liquid limit (LL), plastic limit (PL) and plasticity index (PI), Atterberg limits, of the studied soil before and after the lime addition.
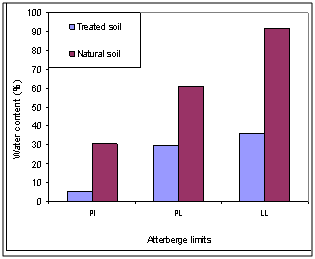 | Figure 8. Atterberg limits |
4.2.3. Compaction Test Results
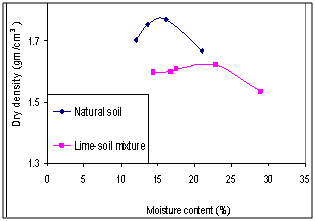 | Figure 9. Compaction curves |
4.2.4. Unconfined Compressive Strength Test Results
- Figure (10) illustrated the stress-strain curves. The results showed that the unconfined compressive strength of the natural compacted study soil was 209.00KN/m2 and its stress-strain curve had a ductile behavior.
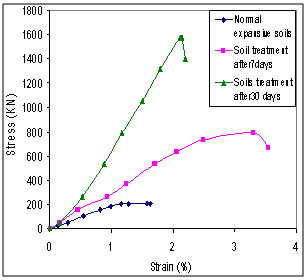 | Figure 10. Stress-strain curves |
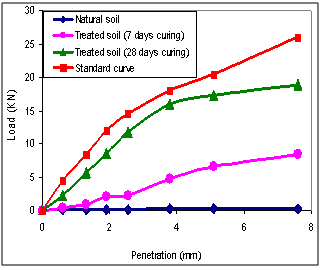 | Figure 11. Soaked CBR-curves |
4.2.5. California Bearing Ratio Test Results
- Figure (11) showed the CBR-curves. The results showed that the CBR-value of the natural compacted study soil soaked in water for 4 days was 1.20%. The addition of lime led to an increase in this value from 1.20 to 33.30% after 7 day curing. Increment of the curing time from 7 to 28 days resulted in an increment of the CBR-value to 86.70% (Table 4).
4.2.6. Swelling Test Results
- Table (4) illustrated the swelling percent values of the studied expansive soil before and after the treatment. The results showed that the swelling percent value of the natural studied soil used both the free swelling method and the CBR-instrument was 80.00 and 6.10% respectively. The addition of lime led to a decrease in these values from 80.00 to 16.70% using the free swelling method and from 6.10 to 0.85% using the CBR-instrument. Increasing the curing time from 7 to 28 days resulted in a decrement of the free swelling percent to 6.70% and the CBR-swelling percent to 0.36%.
4.3. Microstructural Changes
- The changes of microstructure and microstructural development of the soils due to lime addition play a significant role in the geotechnical properties and the mechanical behavior of these stabilized soils[7].Figure (12, a) illustrated the micrograph of the natural untreated expansive clayey silt which showed flaky arrangements of clay particles as matrix between detrital fine grains (silt and fine sand). Figure (12, b) showed the micrograph of the stabilized soil (with 5% lime) cured for 7 days. The micrograph showed crumbs of floccules with a porous nature and cementitous compounds, calcium aluminum hydrate (CAH) and calcium silicate hydrate (CSH), coating the relics of the silt particles and the flocs. The edges of the relics of the silt particles were attacked by lime and their boundaries had a ragged-form. Additionally, the reaction of lime with clay led to a formation of an aggregate of various sizes and that was responsible for the increase in porosity of the soil system. Similar microfabric was observedby[32],[33],[34],[35],[36] and[7]. Figure (12, c) illustrated the micrograph of the stabilized soil (with 5% lime) cured for 28 days. The micrograph showed the aggregated arrangements due to flocculation and formation of hydration reaction products coating and cementing the soil and the lime particles together. The pores of the stabilized soil (after 7 days) were reduced due to an increase in the curing time (after 28 days).
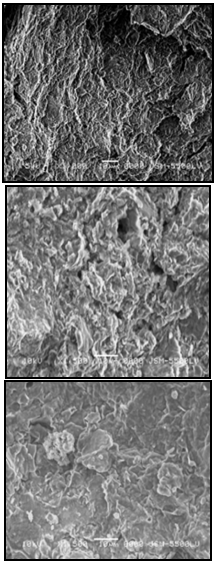 | Figure 12. Micrographs of natural and lime treated soil using SEM |
|
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
- The studied expansive soil was mainly composed of silica, iron, aluminum and calcium. It was mainly composed of clay, calcite and quartz. The soluble salts including sulfates and chlorides were 0.01 and 0.04% respectively. These values are very small and suitable for chemical stabilization. The optimum lime content to stabilize the studied expansive clayey silt soil was 5% using[22]. The studied Pliocene clayey silt soil was composed of sand (20.00%), silt (55.00%) and clay (25.00%). It is an expansive high plastic clayey silt and is classified as (MH) according to USCS and as A7-5 according to AASHTO and it is poor to very poor as sub-grade[16].The addition of lime led to a reduction of the liquid limit, plastic limit and plasticity index values from 91.60, 61.00 and 30.60 to 36.00, 29.80 and 5.20 respectively. This reduction was occurred by decreasing the thickness of the double layer of the clay particles, as a result of cation exchange reaction, which causes an increase in the attraction force leading to a flocculation of the particles[37]. The maximum dry density (Proctor density) and the optimum water content of the natural studied soil were 1.79g/cm3 and 15.10% respectively. In general, the addition of lime to the studied soil led to an increment of the optimum moisture content (from 15.10 to 20.00%) and a decrement of the maximum dry density (from 1.79 to 1.64g/cm3). Thebell-shaped compaction curve of the studied soil was converted to flattened-shaped compaction curve.The typical flattening of the compaction curve of the studied soil makes it easier to achieve the required density over a wider range of possible moisture contents[7]. The change in the shape and characteristics of the peak of the compaction curves can allow for significant savings in time, effort and energy[38]. The unconfined compressive strength of the natural compacted study soil was 209.00KN/m2 and its stress-strain curve had a ductile behavior. The addition of lime led to an increase in the strength value from 209.00 to 736.00KN/m2 after 7 day curing. Increasing curing time from 7 to 28 days led to an increase in the strength value to 1547.00KN/m2. The strength gain was also increased from 3.52 to 7.53. The stress-strain curves of the stabilized soil had a brittle behavior due to a formation of cementitious compounds.The formed cementitious compounds (as a result of the chemical reactions between the silica and the alumina and the additives) reduced the volume of the void spaces and joined the soil particles[7].
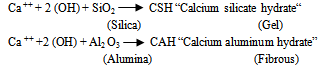 The improvements in the engineering properties of the soil as lime is added can be explained by two basic reactions; short-term reactions consisting cation exchange and flocculation and the long-term reaction, the pozzolanic activity. During the first stage of lime-clay reaction, excess of calcium ions in lime replace all other monovalent cations in the clay and change the electrical charge density around the clay particles. This results in an increase in the interparticle attraction causing flocculation and aggregation and a consequent decrease in the plasticity of the soil[39]. Pozzolanic reaction is time-bound and tempreturedependent. During this process, the high pH causes silics and alumina to be dissolved out of the structure of the clay minerals and to combine with the calcium to produce the new cementitious compounds calcium silicate hydrates (CSH), calcium aluminate hydrates (CAH) and calcium alumino- silicate hydrates (CASH)[39 and others]. Similar results were obtained by[8] (at Idku city),[17] (at Toshka area) and[18] (at New Valley Governorate).The CBR-values of the natural compacted study soil soaked in water for 4 days was 1.2%. The addition of lime led to an increment of this value from 1.2 to 33.3%after 7 day curing. Increasing the curing time from 7 to 28 days led to an increase in the CBR-value to 86.7% and to an increase in CBR-gain from 27.75 to 72.25 that due to a formation of new cementitious compounds and mineral crystals as a pozzolanic reaction product through the long-term curing contributed to an increment of the strength gain. The addition of lime to the studied expansive high plastic clayey silt soil led to a decrement of the swelling percents using the CBR-instrument and the free swelling method from 6.10 to 0.36% and from 56.70 to 6.70% respectively.Scanning electron microscope examination of the stabilized soil indicated that the microstructures of the tested soil changed due to the lime-addition. The lime stabilization process caused the formation of an open fabric structure characterized by a highly porous system. TheSEM-micrographs of natural and treated stabilized soils indicated the formation of new cementitious compounds and mineral crystals as a pozzolanic reaction product through the long-term curing. These cementitious compounds join the soil particles together and increase the strength gain[7].
The improvements in the engineering properties of the soil as lime is added can be explained by two basic reactions; short-term reactions consisting cation exchange and flocculation and the long-term reaction, the pozzolanic activity. During the first stage of lime-clay reaction, excess of calcium ions in lime replace all other monovalent cations in the clay and change the electrical charge density around the clay particles. This results in an increase in the interparticle attraction causing flocculation and aggregation and a consequent decrease in the plasticity of the soil[39]. Pozzolanic reaction is time-bound and tempreturedependent. During this process, the high pH causes silics and alumina to be dissolved out of the structure of the clay minerals and to combine with the calcium to produce the new cementitious compounds calcium silicate hydrates (CSH), calcium aluminate hydrates (CAH) and calcium alumino- silicate hydrates (CASH)[39 and others]. Similar results were obtained by[8] (at Idku city),[17] (at Toshka area) and[18] (at New Valley Governorate).The CBR-values of the natural compacted study soil soaked in water for 4 days was 1.2%. The addition of lime led to an increment of this value from 1.2 to 33.3%after 7 day curing. Increasing the curing time from 7 to 28 days led to an increase in the CBR-value to 86.7% and to an increase in CBR-gain from 27.75 to 72.25 that due to a formation of new cementitious compounds and mineral crystals as a pozzolanic reaction product through the long-term curing contributed to an increment of the strength gain. The addition of lime to the studied expansive high plastic clayey silt soil led to a decrement of the swelling percents using the CBR-instrument and the free swelling method from 6.10 to 0.36% and from 56.70 to 6.70% respectively.Scanning electron microscope examination of the stabilized soil indicated that the microstructures of the tested soil changed due to the lime-addition. The lime stabilization process caused the formation of an open fabric structure characterized by a highly porous system. TheSEM-micrographs of natural and treated stabilized soils indicated the formation of new cementitious compounds and mineral crystals as a pozzolanic reaction product through the long-term curing. These cementitious compounds join the soil particles together and increase the strength gain[7].5.2. Recommendations
- Cement Kiln Dust (by-product of cement industry) and/or mixture of lime and cement kiln dust were recommended to treat and stabilize the expansive high plastic soils as economical (cheaper) alternative to hydrated lime, Portland cement and other (expensive) chemical stabilizers. Where cement kiln dust is a pozzolan material (it is a source of silica and alumina with high surface area), and its composition is similar to raw materials of cement, it needs only water to react with soil and produce a cementitious compounds. In addition, it is not a hazardous waste material under united State Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) guidelines. The use of the cement kiln dust for chemical stabilization applications may be an environmental solution of the problems associated with its disposal process where a very huge amount of the cement kiln dust as by-product are daily produced from the cement factories in Egypt.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Greatly thanks to staff members of Qena faculty of engineering, Al-Azhar University for offering the laboratory facility to conduct the geotechnical tests of this work. Also, special thanks for the staff members of Nasr General Contracting Company, Cairo for valuable cooperation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML