-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Frontiers in Science
p-ISSN: 2166-6083 e-ISSN: 2166-6113
2014; 4(1): 8-11
doi:10.5923/j.fs.20140401.02
Honey’s Ability to Reduce Blood Pressure and Heart Rate in Healthy Male Subjects
Esther Olusola Aluko 1, Titilope Helen Olubobokun 1, Dara Ezekiel Atang 1, Victor Udo Nna 2
1Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Nigeria
2Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, College of Medical Sciences, University of Calabar, Calabar, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Esther Olusola Aluko , Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
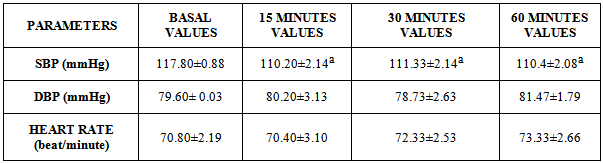
Food is the energy source of the body; honey is not only a natural sweetener that provides the body with energy, but has been used as a medicine for different diseases in different parts of the world. This study evaluated honey’s ability to reduce systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and heart rate in healthy male subjects. We assessed the systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and heart rate (HR) of fifty healthy male subjects, their basal SBP, DBP and HR were taken and was use as the control value. Each subject was give 20 ml of honey to consume and their SBP, DBP and HR were measured at different intervals; 15 minutes, 30 minutes and 60 minutes after the intake of honey. The blood pressure was measured, using sphygmomanometer/auscultatory method and heart rate was determined via palpating the radial pulse. Honey significantly (p= 0.05) decreased SBP from 117.80 ± 0.88 mmHg to 110.20 ± 2.14 mmHg after 15 minutes of honey intake. The significant (p= 0.05) decrease was maintained after 30 minutes of honey consumption at 111.33 ± 2.14 mmHg, and it was also observed after 60 minutes of honey intake at 110.4 ± 2.08 mmHg. The result shows that short-term honey consumption has the ability to reduce blood pressure in healthy male subjects and its consumption might have a beneficial effect.
Keywords: Diastolic blood pressure, Healthy male, Heart rate, Honey, Systolic blood pressure
Cite this paper: Esther Olusola Aluko , Titilope Helen Olubobokun , Dara Ezekiel Atang , Victor Udo Nna , Honey’s Ability to Reduce Blood Pressure and Heart Rate in Healthy Male Subjects, Frontiers in Science, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 8-11. doi: 10.5923/j.fs.20140401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diet is either beneficiary or detrimental to health, studies have associate the intake of sugar-sweetened beverages with elevated blood pressure [1] but interestingly, honey, a complex form of sugars has been documented to have several medicinal benefits: as remedy for diarrhea [2], gastric ulcers [3], wound healing [4], as skin disinfectant [5], as immune inducer [6], as anti-diabetic agent [7, 8], as antibacterial agent [2], as antioxidant [9], and also has an antimutagenic and antitumor activity [10]. Antimicrobial and antibacterial properties of honey have been ascribe to its sugar concentration plus other factors which include low pH, hydrogen peroxide, flavanoids, phenols and terpenes [11].Nigerian honey is produced by Apis mellifera adansonii a native of West Africa [12]. It physiochemical study shows it constituents to include 17.9% water, 28.3% glucose, 38.9% fructose, 4.4% maltose, 1.6% sucrose, 0.2% nitrogen and 8.5±2.7 mg/kg Hydroxymethylfurfural, has a pH of 3.9, total acidity of 21.5±5.6 meq/kg, and 15 mm2/s viscosity [13]. Traditionally it is used in the treatment of various ailments, thus; bronchial cough, feverish cough, colds, sore or irritated throats, ulcers in the mouth, tension, burns and wounds earache, and also taken daily to maintain good health [14]. Studies have documented its anti-diabetic property [14] and that it can also be use as a nutraceutical agent [15]. Arterial blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the arterial walls, it is expressed in millimeter of mercury (mmHg), the highest is systolic blood pressure and the lowest diastolic blood pressure [16]. Arterial pressure is the major factor that affects the effectiveness of the heart pumping action, the heart can be hypo effective, if arterial blood pressure is elevated [17]. High arterial pressure causes excessive workload on the heart and this may lead to heart failure, coronary heart disease or even death as a result of heart attack. Furthermore, high arterial pressure causes multiple hemorrhage in the kidney, consequently destroying the kidney tissues. The kidney plays an important role in normal functioning of the cardiovascular system [17].Diet is one of the risk factors associated with the development of high blood pressure. Various diets such as high salty diet has been documented to cause high blood pressure [18, 19]. Cholesterol is the factor responsible for atherosclerosis (narrowness of blood vessels) thus food rich in saturated fats and trans fats are detrimental to the heart [20]. High carbohydrate diet has also been documented to be detrimental to the cardiovascular system [21]. Honey, though constituted by mainly sugar has been reported to be cardioprotective; Maureen 2004 [22] recommended that eating honey can reduce blood levels of some macromolecules that are linked to an increased risk of heart disease, a study reported that systolic and diastolic blood pressure were reduced by honey inhalation in hypertensive patients [23]. Romero-Silva et al, 2011[24] in their animal study reported that honey decreased the increased blood pressure on carbohydrate-induced obesity in rats. This is consistent with another animal study which reported that honey decreased systolic blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats [25]. The risk of developing high blood pressure is gender related; males have been reported to have higher risk of developing high blood pressure compared with their female counterparts, and it is well documented that men have higher blood pressure then their age - matched women [26]. This study therefore evaluates honey’s ability to reduce systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DPB) and heart rate (HR) in healthy male subjects.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Honey
- The honey was obtained from the Agric-extension and was certified pure by the wildlife unit of Department of Forest Resource Management, Faculty of Agriculture of the University of Ilorin, Nigeria.
2.2. Subjects
- Seventy subjects randomly selected from University of Ilorin, mini campus were recruited for the study. The age ranges between 18 - 25 years, with weight of 56 - 70 kg and height of 1.62 - 1.82 m. Exclusion criteria were the presence of cardiovascular disorder, blood pressure above 120/80 mmHg in accordance to the JNC-7 [26] and use of any medications. After prior examination, 50 male subjects were certified fit to participate in the study. Each subject gave a written consent to participate in the study. The study was reviewed and approved by the ethical committee of the University of Ilorin teaching hospital on human subjects.
2.3. Experimental Procedures
- The experiment was done in the morning and all the subjects did not take breakfast prior to the experiment. The blood pressure was measured with the subjects in the sitting position after a 10 mins rest, with the arm supported and the forearm at the heart level, using a mercury sphygmomanometer with a cuff size of 12 x 26 cm. The heart rate was determined via palpating the radial pulse. The blood pressure and heart rate were measured three consecutive times at 1 minute interval between measurements and the average was recorded. After baseline recording, each subject was given 20 ml of honey. The blood pressure was then measured after 15 minutes, 30 minutes, and 60 minutes of administration.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- The results were presented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). Statistical differences were evaluated using the Student paired t-test and the Student independent t-test. The statistical significance was accepted at the level of p=0.05.
3. Results
- The study assessed the effect of honey intake on SBP, DBP and HR in healthy male subjects. Honey significantly (p=0.05) decreased mean systolic blood pressure after 15, 30 and 60 minutes of consumption when compared to the control value (table 1). The changes in mean diastolic blood pressure and heart rate were not significant when compared with the control value (table 1). The increase in mean systolic blood pressure, heart rate and the reduced mean diastolic blood pressure at 30 minutes when compared to that of 15 minutes after intake of 20 ml of honey was not significant. The mean systolic blood pressure, the increased mean diastolic blood pressure and the heart rate at 60 minutes compared to that of 15 minutes was also not significant (table 1). The decrease in mean systolic blood pressure, increased mean diastolic blood pressure and mean heart rate at 60 minutes compared to that of 30 minutes was not significant (table 1).The values are represented in mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). a- Significantly different from basal values after intake of 20ml of honey, (p=0.05, n= 50).
|
4. Discussion
- Food, an essential source of energy, can either maintain or deteriorate a person’s health. Some diets such as high salt diet, fatty diet and sugar sweeten food are detrimental to the cardiovascular system [1, 18, 19]. Honey is a natural sweetener that supplies the body with quick energy and is used in different parts of the world for diverse medicinal purposes. This study evaluates honey’s ability to reduce systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and heart rate in healthy male subjects after 15, 30 and 60 minutes of honey intake.We observed that honey decreased systolic blood pressure after 15, 30 and 60 minutes of honey intake, this is consistent with the study of Al-Waili 2003 [23], he reported that honey decreased SBP in hypertensive patients and mild reduction was observed in normal subjects, concurring animal studies have also reported a similar decrease in SBP after honey administration; Romero-Silva et al, 2011[24] reported that honey reduced the increased blood pressure in carbohydrate-induced obese rats and a study in spontaneously hypertensive rats reported same decrease in SBP [25]. Honey has no significant effect on DBP and HR differing from the findings of Al-Waili 2003[23], and Romero-Silva et al 2011 [24]. This may be attributed to the short duration of study. The mechanism through which honey elicits it hypotensive effect is not well understood. It might be via inducing synthesis of endothelium derived nitric oxide which results in vasodilatation, Al-Waili 2003[28] reported that honey contains various concentrations of nitric oxide (NO) metabolites and suggested that NO might be partially responsible for the biological and therapeutic effects of honey. It can also be suggested to be as a result of its ability to trigger insulin secretion; insulin facilitates absorption of magnesium ions which in turn cause vascular dilation. Al – Waili 2004 [29] in his study suggested that honey has an insulin sensitization effect, he explained that honey though a mixture of sugars – fructose, glucose, maltose, sucrose and other complex carbohydrates would be expected to raise the blood sugar level and its glycemic index should be similar to that of glucose, has been demonstrated to cause reduction in blood glucose in both normal and diabetic patients. It is an established fact that insulin secretion is mainly stimulated by high blood glucose, thus if honey decreases blood glucose level but increases insulin secretion, it is suggestive that honey might have a direct effect on the beta cells of the pancreas. The ability of insulin to increase cellular magnesium levels was first reported by Lostroh 1973 [30]. The result was consistent with that of Paolisso and Barbagallo 1997 [31] who reported that insulin directly stimulates magnesium ions absorption and might also contribute to its regulation. Magnesium ions have been demonstrated to cause nitric oxide independent coronary artery vasodilatation in human [32]. Honey has been documented to contain minerals like sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, copper, iron, manganese, chromium, and selenium [33]. However, this study did not assess the mechanism of action of honey, this is recommended for future study.
5. Conclusions
- The results of this study showed that short-term honey consumption has the ability to reduce systolic blood pressure in healthy male subjects and it might have the ability to decrease the risk of developing elevated blood pressure associated with male. However, to ascertain this, further study is needed to evaluate the long-term effect of honey in healthy males.
Limitation of Study
- The limitations of this study are as follows;The effect of honey was studied only in short term consumption, further studies (probably using animals) is required to ascertain possible long term effects.The study only compared the initial SBP, DBP and HR measured prior to honey consumption with after consumption, but did not evaluate a control group.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML