-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Frontiers in Science
p-ISSN: 2166-6083 e-ISSN: 2166-6113
2013; 3(3): 96-101
doi:10.5923/j.fs.20130303.03
Study of Antibacterial Effects of a Self-Standing Agar Based Film Incorporated with ZnO
Durata Haciu1, Samim Saner2, Onur Türdoğru2, Uğur Ünal1, 3
1Koç University, Chemistry Department, Rumelifeneri yolu, Sarıyer, 34450 Istanbul, Turkey
2Kalite Sistem Labs Group, Kozyatağı, Kadiköy, 34742 Istanbul, Turkey
3Koc University, Koc University Surface Science and Technology Center, Rumelifeneri yolu, Sariyer., 34450 Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence to: Durata Haciu, Koç University, Chemistry Department, Rumelifeneri yolu, Sarıyer, 34450 Istanbul, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
An agar based film was prepared and incorporated with an antibacterial agent, ZnO (Zinc Oxide). ZnO was prepared by a reflux method and the product was characterized by x-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Synthesis of the agar based film and incorporation of the ZnO particles in the film was performed in a single pot method. The dispersion of ZnO particles in the films was revealed by SEM. A qualitative and quantitative study of the antibacterial activity of the films was carried out, after inoculation with the bacteria Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Visual results indicate that the synthesized films inhibit the growth of the bacteria inoculated. The optimum effective concentration of ZnO /film was found by the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS Z2801:2000 method to be 10mg ZnO/film. According to the same standard method, the antibacterial efficacy (R) of the films against E. coli and S.aureus was calculated as >2.0. Bacteriological tests performed on films, containing 5, 10 and 15 mg ZnO/film, show that the films exhibit a bactericidal effect at the concentrations used . The above results indicate that agar films incorporated with ZnO, are promising candidates in the packaging sector as antibacterial food packaging materials, to increase the safety of food.
Keywords: Antibacterial Agents, ZnO, Self-standing Film, Food Packaging Materials
Cite this paper: Durata Haciu, Samim Saner, Onur Türdoğru, Uğur Ünal, Study of Antibacterial Effects of a Self-Standing Agar Based Film Incorporated with ZnO, Frontiers in Science, Vol. 3 No. 3, 2013, pp. 96-101. doi: 10.5923/j.fs.20130303.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- A recent subject of intense studies is the integration of antibacterial properties in films. These films could act as catalyst supports, separation membranes and implantable drug-release materials where powders and supported films cannot be used. Some examples of these studies are: DNA Lipid films, having potential dental applications[1], and DNA lipid complex films exhibiting antifungal properties[2]. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticle embedded PDMS or polymer freestanding multifunctional films exhibiting antibacterial properties were also investigated[3-6]. Food industry is also an area in which self-standing films are becoming significantly important as protective packaging. Antibacterial films act upon the food surface by contact, helping thus maintain better quality of food and increased shelf life[7-12].Recently, natural (mostly edible) polymers have been used in the synthesis of films, especially when related to films used in food packaging[13]. Starches, because of the film forming characteristics of amylase have long been used in protecting foods from moisture and oxygen invasion, as well as, acting as carriers for antibacterial agents[14]. Starch has also been used to form crosslinked films with polyvinyl alcohol PVA[15]. Chitosan and polyvinyl pyrrolidone were also used as polymeric networks in biomedical applications[16]. Films based on biopolymers from marine sources like alginates are also common[17]. Agar-agar has similarly been used as a polymeric matrix for antibacterial films[18]. Usage of plasticizers tends to increase the tensile strength and elongation modulus of the film, and render it more stable compared to films consisting only of agar[19].In the present work an inorganic-organic hybrid was developed from ZnO powders. ZnO is an inorganic material of established antibacterial properties, in addition to its safety regarding human health[20, 21]. It has been used in antimicrobial fabrics[22, 23], to coat paper[24] as quantum dots[25], as well as ZnO films[26]. ZnO was dispersed in an agar-agar matrix to form a self-standing film. Plasticizers were used and the films were stable for a period of 6 months at a room temperature of 23℃. Their antibacterial performance was evaluated qualitatively and quantitatively using E.coli and S.aureus, according to a modified JIS Z2801:2000 industrial Standard[27].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of ZnO
- ZnO was synthesized using synthesis gradehexamethylenetetramine (C6H12N4), purchased from Merck and used as received. In a typical process, an aqueous suspension containing 50 mmoles of Zn and 200 mmoles C6H12N4 was refluxed for 24 h at 90℃, under N2. The resulting white solid was filtered and washed several times with water. After drying overnight at 100℃, the crystal structure of the powder was investigated by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD, Bruker D2 Phaser) and the morphology was observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Zeiss Evo). The particle size was calculated by the Debye-Scherrer Formula.
2.2. Synthesis of Self-Standing Film
- Agar (C12H18O9)x Mr3000-9000 (microbiology grade) used in this study was purchased from Fluka and polyvinylalcohol, [-CH2CH(OH)-,(av Mw85,000-124,000)from Alfa Aesar. Reagent grade sucrose and glycerol were purchased from Aldrich. About 0.20 g of agar-agar was dissolved in 15 ml deionized water with constant stirring, at 90℃ until a clear solution was obtained. To this solution was added, a well blended and ground mixture of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and glucose. Then, glycerol was added as a plasticizer. The ratio of (Agar: PVA: Glucose: glycerol) was 1:1:0.5:0.5 by weight. Heating with continuous stirring was required until a clear solution was obtained. A suspension of ZnO powder dispersed in water (5ml) under ultrasonic treatment was added at this stage. The obtained suspension was heated (at 90℃) with stirring for another 10 min. The resulting viscous suspension was sonicated for 5 min to get rid of air bubbles and then was poured on polyethylene petri dishes (9.27±0.1 cm diameter) and let to dry in air.Agar-agar films were also prepared in the same way without the addition of the ZnO suspension and were used as references or blanks in the tests. Different concentrations of ZnO were used, ranging from 5 to 35 mg (for films with a diameter of 9.27±0.1 cm) to find the minimum effective antibacterial concentration of ZnO.
2.3. Bacterial Cultures
- Two species of bacteria, S.aureus ATCC 25923 and E.coli ATCC 8769, were used as model bacteria in this study. Nutrient broth, Mueller hinton agar media were used as sources for culturing E.coli and S.aureus, at 37℃ in an incubator for 24 hours. The samples were then adjusted according to McFarland 0.5 standard and the necessary dilutions were made to obtain 2.5x10-5 cfu/ml. All materials were sterilized in an autoclave before the experiments
2.4. Antibacterial Testing
- Antibacterial properties testing for the ZnO containing self –standing films were carried out both qualitatively and quantitatively. For the qualitative test, the films on the petri-dishes were spray coated, evenly, with a bacterial solution on the surface and incubated at 35℃ overnight. The qualitative test results were determined visually by enumeration.For the JIS Z 2801:2000 tests, a cell suspension of the bacterial strain, was prepared in 1/500 nutrient broth. The test surfaces were prepared as follows: each film ( ZnO incorporated films and blanks) was placed in a sterilized petri dish making the test surface. 0.4 ml of the inoculum was instilled on each film. The instilled test inoculum was covered with sterile polyethylene. The polyethylene was pressed so that the test inoculum spread over the film. Three replicate samples per species of the ZnO containing film and 6 replicate blank samples were prepared for each ZnO concentration. A and B represent the blank films, and C , the ZnO containing film.Group A films ( blanks), were immediately diluted and underwent plate culture. The number of viable cells was determined by counting and averaging the number of colonies that grew in each Petri dish. The films corresponding to groups B (blanks) and C ( ZnO containing films) were incubated and tested as described below.The incubation times for the inoculated test surfaces were 15, 30, 60 min and 24 h, for samples containing 5, 10, 15mg of ZnO/film. The surfaces were incubated at 35℃ under aerobic conditions and 90% humidity. After incubation, the test bacteria were washed by addition of 10 ml nutrient broth. The samples were diluted and the viable cell count of bacteria was performed by the agar plate culture method. An average number of viable cells were obtained after incubation by averaging the numbers in the three replicate cells. The blanks were also processed in the same manner to provide base-line data.The tests were performed using S.aureus ATCC 25923 and E.coli ATCC 8769. (R) The antibacterial activity was calculated with the values obtained from the above tests performed on the films.A standard protocol was employed to determine bactericidal effect of ZnO. A suspension of ZnO (6.5 mg/ml in 1ml isotonic water) was prepared. The bacteria under inspection were adjusted according to McFarland 0.5. Then, ZnO suspension was added to it. In this way, a series of samples containing 6.5, 4.0 and 2.0 mg/ml concentrations of ZnO were prepared. The same was repeated for blanks in test tubes containing only the broth and no ZnO. The tubes were incubated overnight at 35℃. All tests were performed as triplicates. Bacterial growth was determined visually .To observe the bactericidal effect of ZnO, the test tubes containing the samples in which no bacterial growth was observed were used. They were inoculated once more using Mueller hinton agar plates and incubated overnight at 35℃. Then, the viable cell count of bacteria was performed as described above.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of ZnO
- The XRD pattern of ZnO is given in Fig. 1. The XRD pattern revealed the wurtzite structure of ZnO particles. The sharp and intense peaks show the high degree of crystallization of the oxide. The particle size was calculated using the Debye-Scherrer equation as 200 nm[28].As seen in the SEM images of the ZnO powder (Figure 2), the synthesis method resulted in approximately equilateral powders.
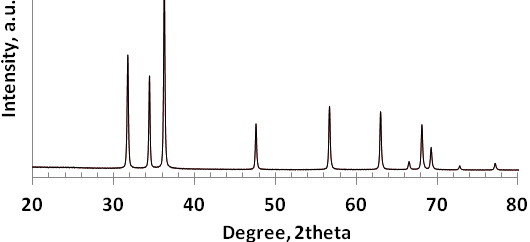 | Figure 1. XRD pattern of ZnO particles |
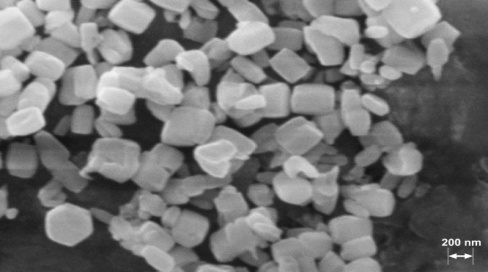 | Figure 2. SEM image of the synthesized ZnO particles before film preparation |
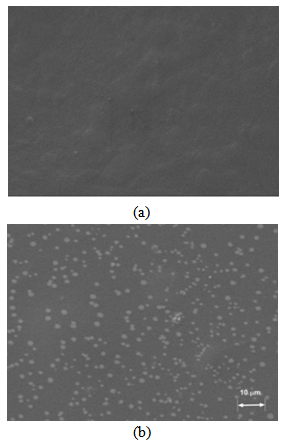 | Figure 3. SEM image of the blank film (a) and of the ZnO containing film (b) |
3.2. Physical Properties of the Film
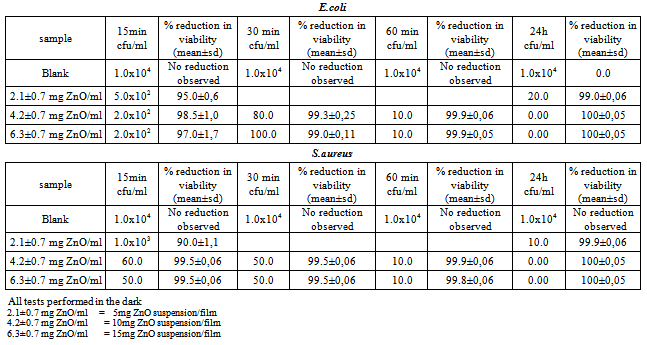
- The thickness of the synthesized films was measured after 24hrs drying in the air. The measurements were done on 6 samples using a micrometer. The average thickness was calculated as: 125 ± 1.8 mm.The average volume of the film was calculated using the thickness value in V=πr2t, and was found to be: 8.4 ± 0.7 mlThe average concentration/film was calculated as:2.1±0.7 mg ZnO/ml for a 5mg ZnO suspension4.2±0.7 mg ZnO/ml for a 10mg ZnO suspension6.3±0.7 mg ZnO/ml for a 15mg ZnO suspension
3.3. Qualitative Evaluation of Antibacterial Properties
- As revealed in Figures 4 and 5, for the case of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus respectively, the blank films are completely covered with the bacterial colonies after 24 h while the ZnO containing films are not. The tests were done in triplicate, all cases showed a similar situation.
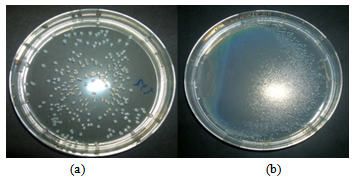 | Figure 4. E. coli colonies completely covers the blank film (b) after 24 h as compared to the ZnO containing film (a) |
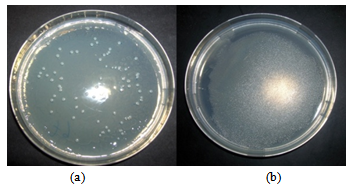 | Figure 5. S.aureus completely covers the blank film (b) after 24 h as compared to the ZnO containing film (a) |
|
3.4. Quantitative Evaluation of Antibacterial Properties
- The antibacterial activity of the ZnO containing films, were evaluated for different concentrations of ZnO , for different time periods. Films containing 35 and 35 mg of ZnO/film were very opaque and brittle. Tests were not performed on them because of the brittleness, which makes the film difficult to handle. Besides, excellent results were obtained with lower concentrations of ZnO/film. From the results listed in Table 1, it can be seen that 10 mg of ZnO/film (4.2±0.7 mg/ml) is the optimum effective concentration to be used with both strains.
3.5. Calculation of the Value of Antibacterial Efficacy
- R=[ log(B/A) - log(C/A)] =[ log(B/C)] [27].Here R is the value of antibacterial efficacy. This value shows the difference in the logarithmic value of viable cell counts between antibacterial products and untreated products after inoculation and incubation of bacteria. A is the average of the number of viable bacteria on blank films (group A). B represents the average number of viable bacteria on incubated blank films (group B) and C the average number of viable bacteria on incubated ZnO containing films (group C).The R value was calculated for the inoculation time and minimum ZnO concentration / film for which the test was effective (4.2±0.7 mg ZnO/ml or 10mg ZnO suspension/film, incubated for 15 min).R obtained by the testing methods of this standart should not be less than 2.0 for the antibacterial efficacy of antibacterial products. In this study, R for E. coli and S. aureus was found to be > 2. Disk diffusion tests were not performed as the ZnO dispersion diffuses poorly.
3.6. Bactericidal Effect
- Samples containing 6.3, 4.2 and 2.1 mg/ml of ZnO were used in this test. After inoculation and incubation (section 2.4), the samples on which bacterial growth was inhibited where inoculated and incubated again. No bacterial activity was observed on incubation of the colonies inoculated on the ZnO samples at any of the ZnO concentrations used It can be concluded that ZnO effectively inhibits bacterial growth and the effect is bactericidal. The same results were obtained in the case of E. Coli and S. aureus. (Figures 6 and 7)
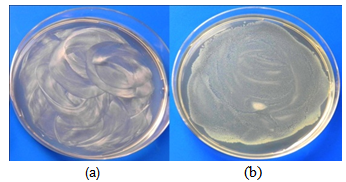 | Figure 6. State of E.coli culture on solid agar after overnight incubation at 35℃. (a) ZnO containing medium (b) Blank |
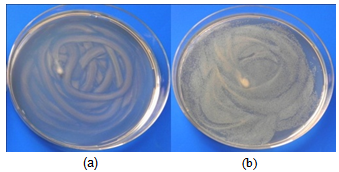 | Figure 7. State of S.aureus culture on solid agar after overnight incubation at 35℃. (a) ZnO containing medium (b) Blank |
3.7. Discussion of the Antibacterial Mechanisms
- A number of mechanisms have been proposed to interpret the antibacterial behavior of ZnO. Swinkels, et al., believe that the antibacterial effect is due to the zinc aqua complex Zn(H2O) attaining maximum acidity at pH 7, making ionization of water H2O to hydroxyl ions OH- possible[29] , even in the absence of light. Hydroxyl ions would then yield, hydroxyl radicals (dissolved) which would destroy bacterial cell[30]. But there is no comprehensive report concerning this mechanism, to our knowledge. Xhang et al., showed by electrochemical analysis that the antibacterial effect of ZnO, or the bacteria membrane damage may be partly due to the direct interaction of ZnO nanoparticles and bacteria membrane wall, in addition to active oxygen species generation[31].Sawai et al., attributed the antibacterial effect of ZnO to the production of H2O2 from a ZnO slurry. They investigated this property using four kinds of antibiotics. Changes in sensitivity of the bacteria used, to the antibiotics, suggested that H2O2 was a factor in the antibacterial activity of the ZnO powder slurry[32]. In another study by Sawai et al., hydrogen peroxide generated from ZnO, MgO and CaO slurries was detected using oxygen electrode and chemiluminescence analysis[33]. The amount of H2O2 generated was found to be proportional to the antibacterial activities of the above oxides. Furthermore in a study performed on activated carbon spheres containing ZnO, the generation of H2O2 was observed in physiological saline dispersed with activated carbons. The antibacterial activity was found to be caused by the generation of H2O2 from ZnO[34].
4. Conclusions
- A simple method was developed to obtain stable self-standing films as organic-inorganic hybrids of ZnO incorporated in an agar based matrix. The film components are all used as food additives and represent no health hazard [35]. The ZnO containing film exhibited antibacterial effect against E.coli and S. aureus at 5,10 and 15 mg ZnO/film, with a bactericidal effect, in comparison with films containing no ZnO. The antibacterial activity of the film were attributed to ZnO. This antibacterial effect is believed to be due to the generation of hydrogen peroxide from the surfaces of ZnO particles (section 3.7). The inhibitory effect of H2O2 is due to the fact that most living cells contain the enzyme catalase which attacks H2O2 and converts it to water (H2O) and oxygen (O2). Oxygen atoms attract electrons from the cell walls of bacteria, thus destroying the basic molecular structure of the cell proteins and the layer of lipids on the cell surface. The oxidized cells walls become damaged or even completely break apart[36].For practical applications, further studies would be necessary for measuring and optimizing mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elongation, as well as moisture absorbance and resistance to water disintegration .The antibacterial effects of ZnO against other food pathogens , which may cause health problems or food spoilage that shorten the shelf life of foods should also be investigated.10mg ZnO/film was found to be the optimum concentration to be used in food packaging , as it resulted in 100% reduction in viability after 15min contact (section 3.4).No irradiation is needed to activate the antibacterial agent: for example, it would inhibit bacterial growth on food, in dark storage areas as well as when food is on display under a light source.From the above, it could be concluded that the synthesized agar based films incorporated with ZnO, could possibly serve as antibacterial food packaging material for minimizing the risk of contamination and growth of bacteria, such as E. coli and S. aureus.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML