-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Frontiers in Science
p-ISSN: 2166-6083 e-ISSN: 2166-6113
2013; 3(1): 43-48
doi:10.5923/j.fs.20130301.06
Bacteria Colonisation and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Wound Infections in a Hospital in Abeokuta
Motayo B. O.1, Akinbo J. A1, Ogiogwa I. J1, Idowu A. A.2, Nwanze J. C.3, Onoh C. C.3, Okerentugba P. O.4, Innocent-Adiele H. C.4, Okonko I. O.4
1Microbiology Unit, Pathology Department, Federal Medical Center Abeokuta, Nigeria
2Department of Microbiology, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria
3Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Igbinedion University, Okada, Edo State, Nigeria
4Department of Microbiology, University of Port Harcourt, P.M.B. 5323 Uniport post office, Choba, East-West Road, Port Harcourt, Rivers State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Okonko I. O., Department of Microbiology, University of Port Harcourt, P.M.B. 5323 Uniport post office, Choba, East-West Road, Port Harcourt, Rivers State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Previous studies done on the microbial pattern of wound infections in Nigeria have revealed a high diversity of organisms and a high rate of isolation. In Abeokuta, Ogun State, there is a general lack of research data on wound infections leaving a huge knowledge gap in this regard. We therefore carried out a retrospective study from April 2009 to March 2010, on the rate of isolation and antibiotic sensitivity profile of wound infections at the Federal Medical Center Abeokuta. A total of 209 wound swabs were retrospectively studied, for colonial characteristics, gram reaction and antibiotic susceptibility. An isolation rate of 177(84.7%) was recorded with gender distribution of male 105(50.2%), female 104(49.8%), age group 16 to 30 gave 71(34.0%) and above 60, 21(10.0%). The bacteria isolation pattern was Pseudomonas aeruginosa 45(25.4%), E coli 42(23.8%), Klebseilla sp 36(20.3%), Proteus sp 28(15.8%) and Staphylococcus aureus 26(14.7%). Gentamycin was the most susceptible with a frequency of 40.0% followed by Ofloxacin 16.0%, 99.0% resistance was recorded for Ampicillin and Erythromycin gave 92.0% resistance to all isolates. The high diversity of organism and poor susceptibility pattern signifies the need for proper infection control and laboratory investigation of all patients presenting with wound infections.
Keywords: Bacteria Colonisation, Antibiotic Susceptibility, Wound Infections, Hospital, Abeokuta
Cite this paper: Motayo B. O., Akinbo J. A, Ogiogwa I. J, Idowu A. A., Nwanze J. C., Onoh C. C., Okerentugba P. O., Innocent-Adiele H. C., Okonko I. O., Bacteria Colonisation and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Wound Infections in a Hospital in Abeokuta, Frontiers in Science, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 43-48. doi: 10.5923/j.fs.20130301.06.
1. Introduction
- Wound is a breach in the skin, and exposure of subcutaneous tissue following loss of skin integrity providing a moist, warm and nutritive environment that is conducive for colonization and proliferation of opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms[1]. Wound can be classified into two types, mainly open and closed wound[2]. Open wounds include incisions, lacerations puncture wounds, gunshot wounds and abrasions. Closed wounds include contusions more commonly known as bruises, hematomas crush injury[2]. Most times contaminating microbes are eliminated by the host immune system and do not persist, but species that grow and divide may become established, causing wound colonization and infection. Infection in a wound delays healing and may cause wound breakdown, herniation, or complete wound dehiscence[2].The severity of complications depends largely on the infecting pathogen and site of infection[3]. Wound infection is a major concern among healthcare practitioners, not only in terms of increased morbidity to the patient but also in view of its burden on financial resources and the increasing requirement for cost-effective management within the healthcare system. In South Western Nigeria, studies have demonstrated the enormity of bacterial infections in wounds. In a study done at Ile-Ife by Shittu et al., an isolation rate of 95% was reported[4]. Another study done at Ibadan on burn wound infections gave an isolation rate of 71.4% from wound swab specimens and 90.2% form wound biopsy specimens[5]. In Abeokuta, Ogun State, Southwestern region of Nigeria, there is a general lack of data on bacteria colonization and isolation rate of wound infections. We therefore conducted a retrospective study on wound infections to establish the bacteria isolation rate and antibiotic susceptibility pattern in a government tertiary institution in Abeokuta, Ogun State, Southwestern region of Nigeria to serve as base line information and give a picture of the bacteria colonization pattern in wound infections in Abeokuta, Ogun State, Southwestern region of Nigeria.
2. Materials and Methods
- The study is a retrospective analysis of wound infection cases over a 12 month period from April 2009 to March 2010 carried out at the Federal Medical center Abeokuta. The results of wound swabs from various sites were retrieved from the Microbiology unit of the Pathology department. Information such as the laboratory number, age, sex, clinical condition, culture result, gram reaction and antibiotic susceptibility pattern were extracted.Wound was swabbed with a sterile swab stick before dressing and care was taken not to swab the surrounding skin around the infected wound. The swab was transported immediately to the laboratory for processing. The samples were cultured on Mac Conkay, Blood agar and Chocolate agar and incubated aerobically at 37℃ for 24h; theChocolate agar was incubated under microareophilic environment in a candle jar at 37oc for 48h. The isolates were gram stained and characterized using standard bacteriological procedure [6]. Antibiotic susceptibility was tested using Kirby-Bauer technique[7] for disk diffusion and results were interpreted using National Committee for Clinical LaboratoryStandards (NCCLS) standard[8] and Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI)[9].
3. Results
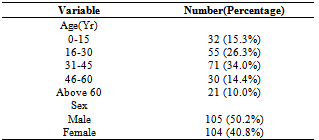
- A total of 209 samples from patients with various wound infections were processed for culture, with a frequency of 105(50.2%) from male patients and females accounting for 104(49.8%). The frequency of isolates from all cases was 177(84.7%) with 32(15.3%) yielding no growth. Age distribution for isolates ranged from 32(15.3%) for age group 0-15, 55(26.3%) for age group 16-30, 71(34.0%) for 31-45, 30(14.4%) for 46-60 and above 60yrs having a frequency of 21(10.0%) as shown in Table 1.
|
|
|
4. Discussion
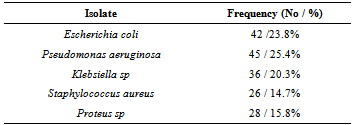
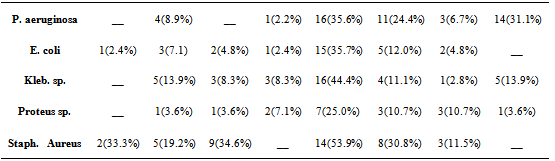
- The risk of developing a wound infection particularly with multi-resistant strains of pathogenic bacteria is on the increase. A newspaper report in Vangaurd newspapers of 12 January 2010, estimated the risk patients picking up a hospital acquired infection to be 20.0%[10]. In this study, a total of 177 isolates were recovered out of 209 samples processed giving a frequency of 84.7%. The difference in gender distribution was not significant (p< 0.05,X2), age distribution for 30yrs and below was 60.4% and for the upper extreme above 60yrs 10.4% this distribution is similar to other reports such as that of Kehinde et al.[5]. Gram negative organisms accounted for four times the number of isolates than gram positive, this is in agreement to a similar study such as the report of Kehinde et al.[5] that reported a frequency of 72.0% for gram negative organisms and 28.0% for gram positive, but is not in agreement with the report of Odugemi and Coker[11]. Gram negative organisms have been reported to easily acquire drug resistant properties particularly Extended Spectrum beta lactamase at a higher frequency that gram positive[12]. This tendency puts the afflicted patient at a high risk of developing multi-resistant infection particularly if proper laboratory follow up is not giving to the infected wound site. The organism with the highest frequency of isolation was Pseudomonas aureginosa with 25.4%. This was followed by Escherichia coli with 23.8% and Klebseilla sp with 20.3%. Staphylococcus aureus was the only gram positive organism isolated with a frequency of 14.7%, a major limitation to this study however was our inability to properly screen for methicillin resistance in staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Antibiotic susceptibility was done on all isolates using the most commonly prescribed antibiotics, generallygentamycin was the most broadly active antibiotic on all isolates tested with a susceptibility of 35.6% against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 25.0% against Proteus sp., 35.7% against E. coli, 44.4% against Klebsiella sp and 53.9% against Staphylococcus aureus. The high sensitivity of Gentamycin has also been reported by some other authors[13-15]. Although, about 67.7% of Staphylococcus aureus isolates were resistant to Ampicillin and 80.8% resistance was recorded for Augumentin, suggestive of a significantly high level of MRSA isolations in our study. Ofloxacin also displayed a fairly sensitivity (30.8%) for Staphylococcus aureus as well as erythromycin (34.6%) and ampicillin (33.3%). In an earlier study at Abeokuta by Motayo et al.[15], a rate of 38.9% for ofloxacin was reported for Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 40.0% for Proteus sp. and 42.9% for Staphylococcus aureus. Absolute resistance to Cefuroxime (11.5%) and augumentin (19.2%) by Staphylococcus aureus was seen. This shows an emerging resistance to these classes of antibiotics, particularly by the both gram negative and gram positive bacteria isolates which is one of the commonest causes of wound infections.The present study showed high resistance of the Klebsiella isolates to various antimicrobial agents and this corresponds with findings by Akiyoshi et al.[16] and Akingbade et al.[17]. A high level of resistance to most antibiotics by Klebsiella sp. was also reported by Okonko et al.[18]. Most of the Klebsiella sp obtained in this study showed resistance to all the antibiotics that are commonly prescribed except for gentamycin with 44.4%. There are reports covering high levels of resistance of Klebsiella sp towards these antibiotics in many countries[19]. The result of this study partially supports the recommendation of the aminoglycoside (gentamycin) as suitable antibiotics for treating Klebsiella infections[20]. The overall sensitivity reported for Cefuroxime (2.8%), and Ceftazidime (13.9%) was lower than the values reported in previous studies[17]. In a study by Shah et al.[21], Cefoxitin (31.66 %) and cefotaxime (30.00 %) were the antibiotics found to be sensitive against Klebsiella isolates. Similarly, Jain et al.[22] showed that ESBL-producing organisms were resistant to gentamycin. Resistance to ceftazidime was also reported by Enwuru et al.[23]. The values reported in this study were marginally lower than that reported in studies by Datta et al.[24], Shivaprakash et al.[25] and Akingbade et al.[17].The relatively high number of Pseudomonas aureginosa isolates is also suggestive of a high level of nosocomial infection particularly in hospitalized patients, again bringing up the need for strict infection control practices such as frequent hand washing and sterilization of wound cleaning instruments by wound care practitioners[26]. The incidence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in postoperative wound infection is becoming more serious in developing countries because of relaxation in general hygienic measures, mass production of low quality antiseptic, and medicinal solutions for treatment, difficulties in proper definition of the responsibility among the hospital staff[27]. Also the antibiotics resistance patterns observed for Pseudomonas aeruginosa in this study depict the occurrence of multi-resistant strains. This is similar to that obtained by Sekinguchi et al.[28], Daini et al.[29], Olayinka et al.[30], Daini and Charles-Onyeaghala[31] and Akingbade et al.[32]. In another study by Yoon et al.[33], 56% of Korean Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were multidrug resistant (MDR) out of which 44% showed resistance to five or more antibiotics. However, in a study by Goswami et al.[27], Pseudomonas aeruginosa was sensitive to ciprofloxacin (83.78%), gatifloxacin (51.35%), and meropenem(51.35%). In other parts of Nigeria, several studies have reported on the sensitivity of Pseudomonas isolates to fluoroquinolones (>60%)[34-37], while there was varying sensitivities to the cephalosporins (cefuroxime 76.6%, ceftazidime (50.7%) [37]. The report by Odusanya[38] showed varying degrees of resistance in which 30 isolates showed 43.3% sensitive to perfloxacin and cefuroxime. Resistance to high levels of antibiotics has been ascribed in most instances to the presence of plasmids[28-32, 39-40].In this study, the relationship between colonization and infection was not investigated, however evidence has shown that delayed healing in chronic wound infection with no clinical signs of infection is suggestive of critical colonization and is directly related to the microbial burden [41]. The impact of personal hygiene and wound care has been shown to contribute to wound healing. Administration of penicillin G to wound sites as practiced by many Nurses in developing countries should be discouraged, this practice has been reported to contribute to resistance of S. aureus isolates to Penicillin G and commonly used antibiotics[42].Gentamycin showed the highest susceptibility to isolates as shown in Table 3. This was followed by Ofloxacin and complete resistance was recorded to Ampicillin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella sp and Proteus sp. This shows the degree of resistance shown to some of the most commonly used antibiotics. It is also worthy of note to mention the high degree of susceptibility recorded to Gentamycin this is not in agreement with reports by other authors such as a study on burn wound infections at U.C.H Ibadan[5] and another done at the same center on multi - resistant Enterobacterieacea by Okeshola and Makanjuola [43]. Relatively high level of resistance was seen to Cefuroxime and Ceftazidime for instance 95.2% resistance was recorded for Escherichia coli to Cefuroxime and 100.0% resistance was recorded for Ceftazidime. This development is worrying because this is an indication of the emergence of potentially problematic pathogens such as Extended Specrtum beta lactamases (ESBL) in our environment. In a recent study done at the same center, a prevalence of 7.5% of ESBL strains of E. coli and Klebseilla sp was reported by Aboderin et al.[12].
5. Conclusions
- The importance of proper antibiotic treatment of infected wounds cannot be overemphasized. From our study it can be seen that it is pertinent to obtain samples for culture from every infected wound in other to determine the type of organism and its antibiotic sensitivity profile. There is also evidence to support the emergence of multidrug resistant bacteria such as ESBL bacteria and MRSA, which could be potentially life threatening if badly managed. However, we reported a high susceptibility to gentamycin from patients in our study setting. Gentamycin can therefore be considered for empirical use in Abeokuta pending availability of culture results. Wound care practitioners should also be trained on proper infection control practices to reduce the rate of nosocomial spread of infection to hospitalized patients. Further prospective studies are needed to determine relationships between colonization and infection in our setting.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML