-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Frontiers in Science
p-ISSN: 2166-6083 e-ISSN: 2166-6113
2012; 2(5): 119-126
doi: 10.5923/j.fs.20120205.04
Gamma Irradiated Bone Allografts Processed from Femoral Heads
Rita Singh 1, Durgeshwer Singh 2
1Radiation Dosimetry and Processing Group, Defence Laboratory,
2Defence Research and Development Organization, Jodhpur 342011, India
Correspondence to: Rita Singh , Radiation Dosimetry and Processing Group, Defence Laboratory,.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Disease transmission and bacterial infection in bone allograft transplantation is of significant concern. Screening of donor for disease, bacterial testing and aseptic processing, substantially reduce risk, but do not completely eliminate the possibility of allograft associated infections. Sterilization by gamma radiation is a definitive method for eliminating microorganisms and can prevent life-threatening allograft associated infections. In the present study, microbiological evaluation of bone allografts processed from femoral heads excised during surgery was carried out. 126 femoral heads obtained from living donors were processed, freeze-dried and sterilized by gamma irradiation at 25 kGy. The bioburden and type of microbial contamination associated with bone allografts was determined based on morphological characteristics and biochemical tests. Resistance of bacterial contaminants to gamma radiation was evaluated by exposing the bacterial cell suspension to different doses of 1 to 6 kGy and analysing for the surviving bacteria. Average bioburden of processed bone allografts for different batches was found to be in the range of 1.84 x 102 to 3.88 x 103 CFU/g. 60.2% of the isolates were found to be Gram-positive organisms. The D10 value of bacterial isolates ranged from 0.56 to 1.68 kGy. Verification doses for different batches of processing were 5.87 to 9.46 kGy. All bone grafts exposed to the verification dose were tested culture negative. The results validate 25kGy dose for sterilization of bone allografts processed from femoral heads.
Keywords: Bone Allografts, Femoral Head, Bioburden, Sterilization, Gamma Radiation
Cite this paper: Rita Singh , Durgeshwer Singh , "Gamma Irradiated Bone Allografts Processed from Femoral Heads", Frontiers in Science, Vol. 2 No. 5, 2012, pp. 119-126. doi: 10.5923/j.fs.20120205.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Bone grafts are frequently used to revise skeletal defects by replacement or augmentation. Autografts are the most effective as they are osteoconductive as well as osteoinductive and have osteogenic cells. However, harvesting bone requires an additional incision, increasing operating time, blood loss as well as costs. There is also a significant morbidity related to the donor site. Major complications, such as cutaneous nerve damage, chronic donor site pain, vascular injury, infection and fracture are reported in autografted patients[1]. This morbidity is in direct proportion to the quantity of graft retrieved. Several studies have reported minor and major complications, with a wide range of incidences varying between 1% and 39%[2]. By eliminating the need for an additional surgical procedure, allografts reduce the operating time, expense and trauma associated with the acquisition of autografts. Further since allografts do not compromise normal structures, they avoid the significant morbidity associated with the recovery of autologous bone graft. Allografts have the added advantage of being available in large quantity. This is particularly valuable in large defects or in children where the quantity of available autografts is limited.Bone allografts fill an important void in the surgical practice of orthopaedic surgery, and their use to replace and reconstruct musculoskeletal structures following injury or disease has gained increasing acceptance by orthopaedic surgeons[3]. Allogenic bone grafts are widely used in a variety of clinical situations. These include filling of cavities in benign tumorous conditions and infections, bridging of osteoperiosteal defects following trauma, infections or enbloc resection of malignant tumors and reinforcement of host bone prior to implantation of prosthesis. Bone allografts can improve substantially the quality of life for many patients. However, problem of bone allograft as implant material is mostly infectious disease transmission from donor to recipient. Infections associated with contamination of allografts can result in serious morbidity and death. Bacterial transmission may occur from infected donor to recipient such as tuberculosis and syphilis or through bacterial contamination during procurement, processing and storage of the bone allograft. Viral transmission may also come from infected donor such as HIV and Hepatitis. Hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) have all been transmitted by tissue transplantation[4]. The estimated incidence of viremia at the time of donation is 1 in 55,000 for HBV, 1 in 34,000 for HCV, 1 in 42,000 for HIV, and 1 in 128,000 for HTLV[5]. Screening of donor for disease, bacterial testing and aseptic processing, substantially reduce risk, but do not completely eliminate the possibility of allograft associated infections.Sterilization is a definitive method for eliminating microorganisms and can prevent life-threatening allograft associated infections[6]. Gamma radiation is used at commercial scale to sterilize healthcare products. Radiation process is a cold sterilization and is the preferred method for sterilization of biological tissues because of the several advantageous factors[7]. One of the principal advantages of radiation sterilization arises from its ability to destroy contaminating microorganisms with an insignificant rise in the temperature of the irradiated materials, thereby preserving the properties and characteristics of tissues. Gamma irradiation sterilization has been proven to eliminate viruses, bacteria, fungi and spores from tissue without affecting the structural or biomechanical attributes of tissue grafts[8]. The efficacy of allograft sterilization is supported by the absence of bacterial or viral allograft-associated infections in tissue processed by this method[9]. The behaviour of the microbial population on exposure to ionizing radiation is of greatest relevance in radiation sterilization practice. Since the destruction of microorganisms by gamma irradiation follows an exponential rule, the probability of survival is a function of the number and species of microorganisms present on the allograft and the lethality of the gamma irradiation process. The level of viable microorganisms on the product before sterilization and the radiation resistance of the contaminants determine the dose required for sterilization. The present study was thus carried out with the aim of microbiological evaluation of bone allografts processed from femoral heads and sterilized by gamma radiation. The incidence of femoral head microbial contamination and the efficacy of gamma radiation for allograft sterilization was examined. The type and magnitude of microbial contamination associated with bone allografts and their resistance to gamma radiation was evaluated. Sterilization of bone allografts using gamma irradiation was validated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procurement of Bone
- Femoral heads excised during surgery were obtained from living donors after necessary consent. Donor screening was carried out to exclude infectious diseases of bacterial or viral origin including HIV and Hepatitis, neurological disorders and diseases of unknown origin. The femoral heads were stored in an ultra low temperature freezer at -80℃ until processing. The records were kept for the donors and the femoral head received.
2.2. Processing of Bone
- 126 femoral heads were processed in 6 different batches. Femoral heads were dissected using surgical instruments to remove soft tissues. Dissected femoral heads were then cut into different forms like chips and cubes according to the surgeons requirements. The cut bones were washed to remove bone marrow and blood remains and pasteurized in a water bath at 58℃. The bone allografts were frozen at -80℃ and subsequently freeze-dried to remove 95% of the moisture. The freeze-dried grafts were double packed and sealed in polyethylene packets, in a laminar airflow biosafety cabinet.
2.3. Radiation Sterilization
- Processed bone grafts were sterilized by exposure to 25 kGy of 60Co gamma rays. Irradiation was carried out in the Gamma chamber GC-5000 at dose rate of 6.175 kGy/h. The freeze-dried irradiated grafts were stored at room temperature.
2.4. Bioburden Estimation
- Bone allografts from 6 batches of processing were checked for the bioburden. 10 random samples of bone allografts from each batch were selected and weighed. The samples were shaken in 0.01% saline polysorbate for 30 min. The solution was filtered through Millipore membrane filters. The filters were placed on soyabean casein digest medium and thioglycollate medium and incubated. The plates were observed for growth up to 7 days. Counts were calculated per gram of bone.
2.5. Isolation and Characterization of Microbial Contaminants
- Representative types of bacteria were isolated from different batches of bone during processing. Bacterial cultures were successively re-isolated on nutrient agar to obtain pure cultures. A total of 93 bacteria were isolated and maintained. Occurrence of different types of bacteria on bone was determined. The bacteria were characterized with reference to their gram-staining and their morphology as cocci and bacilli. The percentage occurrence of different morphological types was calculated. Preliminary identification of 6 bacterial isolates was carried out on the basis of various morphological, cultural and biochemical characteristics by standard methods[10].
2.6. Determination of Radiation Resistance of Bacterial Isolates
- 6 representative bacterial isolates from bone identified as Bacillus, Clostridium, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Pseudomonas and Klebsiella were tested for their resistance to different doses of gamma radiation. The bacterial cultures were grown in nutrient broth to a final density of about 1x108 colony-forming units (CFU)/ml. The cells were suspended in phosphate buffer and exposed to different doses of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 kGy. Thereafter, plating was carried out after making appropriate dilutions. For each irradiation dose, the survival fraction (S) was estimated dividing the number of viable cells after irradiation (N) by the initial viable cell number (No). Survival curves relating log S with irradiation dose in kGy were obtained for all the strains. The radiation decimal reduction dose values (D10) for the strains were obtained from the gradient of the linear portion of the inactivation curves.
2.7. Validation of Radiation Sterilization
- Verification dose experiment was carried out according to ISO 13409[11]. Test sample size was selected as per batch size. For production batch with uniformed samples between 20 and 79, 20 samples are selected for experiment. 10 samples were used for bioburden determination and 10 samples for verification dose experiment.
2.8. Determination of Sterility
- 10 random samples of bone from each of the 6 batches exposed to verification dose were tested for sterility. Samples were aseptically transferred to saline blank containing 0.01% polysorbate and shaken for 30 min. The solution was passed through the sterile membrane filters and the filters were placed on soyabean casein digest agar plates. The plates were incubated at 30 ± 2℃ and observed for growth up to 14 days.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Processing of Femoral Heads as Bone Allografts
- Femoral heads removed during hip replacement surgery are the most common source of allograft bone. 126 femoral heads excised during surgery were included in the present study. These included 61 male and 65 female donors. Number of donors in relation to age is presented in Table 1. Since the bones from femoral heads are processed for filling cavities or bone gaps and not for structural purposes, the donors from all age groups were included. Maximum numbers of donors were above the age of 50 years. 40 donors were in the age group 71-80 years followed by 28 in the age group 51-60 years and 26 in the age group 61-70 years. There was only one donor below 20 years. The repair of bony defects resulting from trauma or disease remains a major problem in trauma and orthopaedic surgery. Autologous bone grafts, though ideal, have the drawback of secondary surgery for autograft retrieval, complications of infection and donor site morbidity. Autologous bone is most commonly harvested from the iliac crest[12] or greater trochanteric region[13]. There is a substantial incidence of morbidity associated with the harvest procedure. Reported complications of harvest of the iliac crest bone graft include deep infection, osteomyelitis, haematoma, neurological injury, vascular injury, iatrogenic iliac wing or sacroiliac joint injury, persistent pain and cosmetic defects[1]. In particular, residual pain has been reported to occur in as much as 31% of the cases. Harvest of autologous bone from the greater trochanteric region may decrease bone strength of the donor site and increase risk of proximal femur fracture, which is a devastating complication for the patients[13]. Bone allografts obviate these difficulties and once replaced by invading osteoblasts can be as good as the patient’s own bone. Allografts also offer many advantages compared to metallic implants including joint reconstruction, incorporation of the graft to the host bone, and longevity. Synthetic biomaterials may be rejected if infected and can also cause erosion of underlying bone, as well as can extrude by eroding soft tissues. An allograft presents a more biological approach. However, extensive use of bone allografts has been limited due to the availability of safe and reliable processed bones.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.2. Bioburden Assessment and Characterization of Microbial Contaminants
- Microbiological evaluation of bone allografts processed from femoral heads was carried out. The bioburden of 10 random bone samples from each batch was assessed. Microbial load of bone allografts from 6 different batches of processing is presented in Figure 1. The counts for the different batches ranged from 0.98 to 3.87 log CFU/g. Maximum counts were recorded for the fourth batch of processing which ranged from 3.04 to 3.87 log CFU/g. Lowest microbial level of 1.09 to 2.49 log CFU/g were observed for the first batch. Type of microbial contaminants associated with bone allografts was determined. Ninety three bacterial isolates were obtained from different batches of bone processed. The bacterial isolates from different bone samples were categorized based on their morphology and Gram staining. Percent occurrence of different morphological types is presented in Figure 2. 41.9% of the isolates were found to be Gram-positive bacilli and 36.6% were found to be Gram-negative bacilli. 18.3% of the isolates detected were Gram-positive cocci followed by 3.2% Gram-negative cocci. 6 representative bacterial contaminants from different batches were identified based on biochemical tests. Four Gram-positive bacteria were identified as Bacillus, Clostridium, Staphylococcus and Enterococcus. Two Gram-negative isolates were Pseudomonas and Klebsiella. Microbiological analyses for aerobic bacteria, anaerobic bacteria and fungal contamination of bone allografts processed from femoral heads were carried out. Contaminant microbes consisted of mostly aerobic bacteria. No yeasts and molds were found. Other studies[15-17] have also reported a range of microorganisms isolated from femoral head bone retrieved from living donors during surgery.
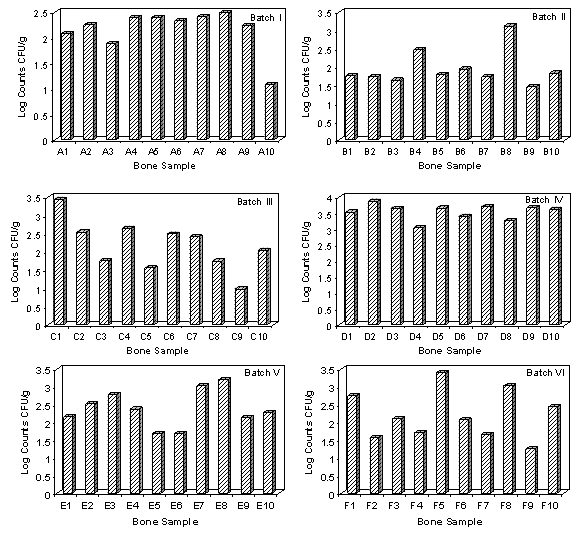 | Figure 1. Microbial load of bone allografts from different batches of processing |
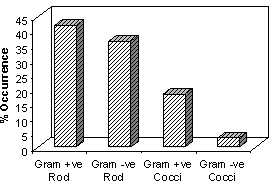 | Figure 2. Type of microbial contamination in bone |
3.3. Radiation Resistance of Bacterial Isolates
- Sterility is a dose dependent measure of probability which is determined by the initial microbial concentration, the radiation dosage administered and the unique radioresistance of a given organism. Representative bacterial isolates characterized from bone were tested for their resistance to gamma radiation. Survival curves (log N/N0) for the Bacillus, Clostridium, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Pseudomonas and Klebsiella at different doses of gamma radiation are presented in Figure 3.
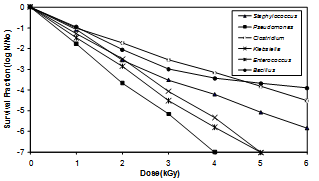 | Figure 3. Effect of gamma radiation on bacterial isolates from bone |
3.4. Validation of Radiation Sterilization
- Validation of radiation sterilization dose of 25 kGy for bone allografts was carried out according to ISO 13409[11]. The number of uniformed samples tested for validation per production batch size according to ISO standard was 20. 10 samples from each batch were used for bioburden determination and 10 for sterility test at verification dose. Average bioburden of freeze-dried bone grafts for different batches was found to be in the range of 1.84 x 102 to 3.88 x 103 CFU/g (Table 3). Verification doses obtained were 5.87 to 9.46 kGy. 10 samples from each batch were exposed to the verification dose and tested for sterility. According to ISO 13409, if during the sterility test of samples which are irradiated at the verification dose, positive growth is found in one sample or less after incubation for 14 days at 300C, the completed batch can be sterilized at 25 kGy. Sterility test results show that no positive growth was observed for 6 different batches of bone allografts processed from femoral heads. Based on ISO 13409, the results of verification dose are accepted and the radiation sterilization dose of 25 kGy is substantiated.
|
4. Conclusions
- Bone allografts processed from femoral heads were found to be contaminated and about 60% of the isolates were found to be Gram-positive bacteria. Maximum radiation resistance (D10 value) of 1.68 kGy was observed. Based on the average bioburden, verification doses for validation of 25 kGy gamma radiation were 5.87 to 9.46 kGy. Sterilization of bone allografts by gamma irradiation at 25 kGy was validated ensuring safety of the allografts processed from femoral heads for transplantation in orthopaedic reconstructive procedures.
Conflict of Interest
- None
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors are highly grateful to Director, Defence Laboratory, Jodhpur for the encouragement and support.
References
| [1] | Sen, M. K., Miclau, T., (2007) Autologous iliac crest bone graft: should it still be the gold standard for treating nonunions? Injury 38: S75-S80. |
| [2] | Violas, P., Chapuis, M., Bracq, H., (2004) Local autograft bone in the surgical management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 29: 189-192. |
| [3] | DeLong, W. G., Einhorn, T. A., Koval, K., McKee, M., Smith, W., Sanders, R., Watson, T., (2007) Bone grafts and bone graft substitutes in orthopaedic trauma surgery. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 89A: 2566-2575. |
| [4] | Eastlund, T., Strong, D. M., (2004) Infectious disease transmission through tissue transplantation. In: Phillips, G. O., (ed) Advances in Tissue Banking, Vol. 7, World Scientific, Singapore, pp 51-131. |
| [5] | Zou, S., Dodd, R. Y., Stramer, S. L., Strong, D. M., (2004) Probability of viremia with HBV, HCV, HIV, and HLV among tissue donors in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine 251: 751-759. |
| [6] | Dziedzic-Goclawska, A., Kaminski, A., Uhrynowska- Tyszkiewicz, I., Stachowicz, W., (2005) Irradiation as a safety procedure in tissue banking. Cell and Tissue Banking 6: 201-219. |
| [7] | Phillips, G. O., Morales Pedraza, J., (2003) The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) program in radiation and tissue banking: past, present and future. Cell and Tissue Banking 4: 69-76. |
| [8] | Summit, M. C., Bianchi, J. R., Keesling, J. E., Roberts, M., Mills, C. R., (2001). Biomechanical testing of bone treated through a new tissue cleaning process. Proc. 25th Annual Meeting of the American Association of Tissue Banks. Washington DC, 25-29 August 2001, pp 55. |
| [9] | Kainer, M. A., Linden, J. V., Whaley, D. N., Holmes, H. T., Jarvis, W. R., Jernigan, D. B., Archibald, L. K., (2004) Clostridium infections associated with musculoskeletal-tissue allografts. New England Journal of Medicine 350: 2564-2571. |
| [10] | Holt, J. G., Krieg. N. R., Sneath, H. A., Staley, J. T., William, S. T., (1994) Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 9th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore. |
| [11] | ISO, 13409., (1996) Sterilization of health care products – Radiation sterilization – Substantiation of 25 kGy as sterilization dose for small or infrequent production batches. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva. |
| [12] | Zhang, C., Zeng, B., Xu, Z., Song, W., Shao, L., Jing, D., Sui, S., (2005) Treatment of femoral head necrosis with free vascularized fibula grafting: a preliminary report. Microsurgery 25: 305-309. |
| [13] | Yoo, M. C., Kim, K. I., Hahn, C. S., (2009) Long-term follow up of vascularized fibular grafting for femoral head necrosis. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 466: 1133-1140. |
| [14] | Enneking, W. F., Mindell, E. R., (1991) Observations on massive retrieved human allografts. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, American Volume 73: 1123-1142. |
| [15] | Vehmeyer, S. B. W., Arnoud, R. M. S., Bloem, R. M., Petit, P. L. C., (2002) Bacterial contamination of femoral head allografts from living donors. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 73: 165-170. |
| [16] | Judas, F., Teixeira, L., Proenca, A., (2005) Coimbra university hospitals bone and tissue bank: twenty-two years of experience. Transplantation Proceedings 37: 2799-2801. |
| [17] | Singh, R., Singh, D., (2009) Evaluation of radiation resistance of the bacterial contaminants from femoral heads processed for allogenic transplantation. Radiation Physics and Chemistry 78: 810-817. |
| [18] | Varettas, K., Taylor, P. (2011) Bioburden assessment of banked bone used for allografts. Cell and Tissue Banking 12: 37-43. |
| [19] | Malinin, T. I., Buck, B. E., Temple, H. T., Martinez, O. V., Fox, W. P., (2003) Incidence of clostridial contamination in donors musculoskeletal tissue. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, British Volume 85: 1051-1054. |
| [20] | Deijkers, R. L., Bloem, R. M., Petit, P. L., Brand. R., Vehmeyer, S. B., Veen, M. R., (1997) Contamination of bone allografts: analysis of incidence and predisposing factors Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, British Volume 79: 161-166. |
| [21] | Dennis, J. A., Martinez, O. V., Landy, D. C., Malinin, T. I., Morris, P. R., Fox, W. P., Buck, B. E., Temple, T. H., (2011) A comparison of two microbial detection methods used in aseptic processing of musculoskeletal allograft tissues. Cell and Tissue Banking 12: 45-50. |
| [22] | Maso, A., Andollina, A., Bassi, A., Bertoni, G., Modelli, L., Quinto, C., Vaccari, M., Fornasari, P. M., (2003) Bacterial contamination of musculoskeletal allografts. La Chirurgia degli Organi di Movimento 88: 345-350. |
| [23] | Whitby, J. L., (1993) Microbiological aspects relating to the choice of radiation sterilization dose. Radiation Physics and Chemistry 42: 577-580. |
| [24] | Eastlund, T., (2006) Bacterial infection transmitted by human tissue allograft transplantation. Cell and Tissue Banking 7: 147-166. |
| [25] | Mankin, H. J., Hornicek, F. J., Raskin, K. A., (2005) Infection in massive bone allografts. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 432: 210-216. |
| [26] | Roberst., T. S., Drez, D. Jr., McCarthy, W., Paine, R., (1991) Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using freeze-dried, ethylene oxide-sterilized, bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. Two-year results in thirty-six patients. American Journal of Sports Medicine 19: 35-41. |
| [27] | Smith, R. A., Ingels, J., Lochemes, J. J., Dutkowsky, J. P., Pifer, L. L., (2001) Gamma irradiation of HIV-1. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 19: 815-819. |
| [28] | Grieb, T. A., Forng, R., Stafford, R. E., Lin, J., Almeida, J., Bogdansky, S., Ronholdt, C., Drohan, W. N., Burgess, W. H., (2005) Effective use of optimized, high-dose (50 kGy) gamma irradiation for pathogen inactivation of human bone allografts. Biomaterials 26: 2033-2042. |
| [29] | Hansen, J. M., Shaffer, H. L., (2001) Sterilization and preservation by radiation sterilization. In: Block, S. S., (ed) Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 729-746. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML