-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2022; 12(1): 1-6
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20221201.01
Received: Feb. 8, 2022; Accepted: Feb. 22, 2022; Published: Mar. 15, 2022

Microbial Contamination of Cooked Foods Hawked in Tharaka Nithi County, Kenya
Cornellius Musembi Muendo1, 2, Gideon Kikuvi2, Susan Mambo2
1Department of Nursing, School of Nursing and Public Health, Chuka University, Chuka, Kenya
2Department of Environmental Health and Disease Control, School of Public Health, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Nairobi, Kenya
Correspondence to: Cornellius Musembi Muendo, Department of Nursing, School of Nursing and Public Health, Chuka University, Chuka, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Food hawking is an enterprise widely practiced both in developed and developing economies. Indeed, hawking cooked foods is an important livelihood activity in many households across the globe. However, the trade is associated with regular breaches in food safety standards and especially hygiene requirements. This certainly predisposes the hawked cooked foods to an increased likelihood of microbial contamination. The current study investigated cooked foods hawked in Tharaka Nithi for microbial contamination. A cross-sectional study design was used to collect 151 cooked food samples which were analyzed for Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, and Shigella. The results indicated that more than half (59%) of cooked foods hawked at Chuka town were contaminated with either one or a multiplicity of these microorganisms. Escherichia coli was detected in 51.7% of the foods, with the numbers in individual foods ranging from 0 to 444 cfu/g, and a mean of 46.6 ± 86.97cfu/g for all the foods. When categorized based on the established safety criterion for Escherichia coli, 68.9% of the foods were satisfactory, 13.2% in the borderline, and 17.9% unsatisfactory. Staphylococcus aureus was detected in 34.4%, whereas Shigella and Salmonella were detected in 21.2% and 15.2% of the foods respectively. Consequently, cooked foods hawked at Chuka town are not safe for human consumption. County government of Tharaka Nithi should develop and implement a policy and programs to prevent likely foodborne infections from the consumption of these foods.
Keywords: Hawked foods, Street vended foods, Food contamination, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella, Salmonella
Cite this paper: Cornellius Musembi Muendo, Gideon Kikuvi, Susan Mambo, Microbial Contamination of Cooked Foods Hawked in Tharaka Nithi County, Kenya, Food and Public Health, Vol. 12 No. 1, 2022, pp. 1-6. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20221201.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Hawking of cooked foods is an old and worldwide practice. Hawking of cooked foods has been highlighted as an important economic activity in several countries across the globe [1,2,3,4,5]. The economic significance notwithstanding, hawked cooked foods posts a major public health concern particularly due to the increased likelihood of contamination. Almost the entire chain in hawking of cooked foods is characteristically susceptible to exposures likely to contaminate food. Hawked-cooked foods are usually prepared in small factories, hawkers’ homes, or in makeshift structures located in busy streets such as bus parks [6]. A majority of the areas in which hawked cooked foods are prepared, displayed, and sold are usually disorganized, insanitary, dusty, open to flies, rodents, insects, and other environmental contaminants such as smoke from vehicle exhausts. The makeshift structures lack adequate basic sanitation and hygiene facilities such as toilets, hand washing facilities, running water, well-designated utensil washing areas, utensil drying racks, solid waste disposal facilities, and food stores [7,8]. Consequently, hawked cooked food handlers are technically unable to comply with good hygiene practices such as handwashing before handling food, washing hands after visiting toilets or handling soiled materials, proper disposal of garbage and sullage, proper washing of utensils, and separation of raw materials from cooked food. The safety of foods prepared at homes for sale to the public cannot also be guaranteed [9], especially due to the associated difficulties in enforcing compliance to food handling standards at the household level. Further, food prepared at home may take several hours [10] before reaching the market and in such prolong the period and critical points of possible contamination. The quality of water and other ingredients used to prepare hawked cooked foods is also a major concern. Evidence denotes access and use of potable water as one of the widespread challenges for food hawkers [11]. Inadequate supply of potable water has a direct implication on critical processes of food handling such as the washing of utensils and equipment, cleaning of the food premises, and observing standard personal hygiene practices. Besides preparing food under insanitary conditions, hawkers of cooked foods also use inappropriate packaging materials. Mostly, hawked food is packaged in plastic bags, used newspapers, old students’ notes, stained re-usable plastic containers, used cement bags, plant leaves, or nonetheless, handed directly to consumers without any form of packaging [6,12,13,14]. These derelictions certainly increase the odds of contamination of hawked cooked foods. This backdrop ignited the desire to carry out the current study, and particularly focus on microbial contamination. The most common microbial contaminants found in hawked foods in Kenya include Escherichia coli, Shigella, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Clostridium perfringens, and Campylobacter jejuni [7,15]. Thus, the current study focused on contamination from Escherichia coli, Shigella, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella. There was inadequate documented literature on microbial contamination of cooked foods hawked in Tharaka Nithi County hence the findings of this study provide an important reference for related policies and interventions.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Site
- The study was carried out at Chuka town in Tharaka Nithi County (TNC). Chuka town is the largest and most developed urban center in Tharaka Nithi County [16].
2.2. Study Design, Population, and Inclusion Criteria
- This was a cross-sectional study of cooked foods hawked at Chuka town. To be considered for inclusion in the study, a food sample had to be displayed for hawking by a person above the age of 18 years during the time of data collection.
2.3. Sample Size Determination and Sampling
- The sample size was based on the total estimated number of hawkers of cooked foods at Chuka town. According to Chuka Sub-County public health service level data, there were 164 cooked food hawkers in Chuka town as of December 2020. The study employed simple random sampling to collect 151 food samples, one from every eligible respondent.
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Identification of Respondents and Food Sample
- The study developed a movement plan covering all the streets of Chuka town. Research assistants followed the identified routes and by way of census identified 151 eligible cooked food hawkers. All the cooked foods from every identified respondent were listed and assigned numerical values based on the order in the record. Using the numerical values, a random generator application from a mobile smartphone was used to select a single food item from every respondent. A total of 151 food samples, each weighing about 250 grams, were collected. The samples were collected and delivered in the laboratory in their original packaged form, and where possible in whole pieces. All the samples were delivered to the laboratory within two hours after collection.
2.4.2. Detection and Enumeration of Escherichia coli
- Escherichia coli was analyzed based on the updated Food, Drugs, and Administration laboratory procedure [17]. Fifty (50) grams of a representative food sample were weighed into a blender, mixed with 450 ml of Butterfield’s phosphate-buffered water, and blended at high speed for about 2 minutes. Five (5) decimal dilutions of 10 ml each were prepared from the blended food sample. Two 1 ml aliquots from each of the five dilutions were transferred into separate Petri dishes, mixed with 10 ml of sterile Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA) media, and allowed to solidify. The sample mixture was further overlayed with 5ml of sterile VRBA media and allowed to solidify again before incubating at 35°C for 24 hours. Ten (10) Escherichia coli typical coliforms from each of the positive dishes were transferred into different tubes of Brilliant Green Lactose Bile (BGLB) broth, incubated at 35°C, and examined for gas production after 24 and 48 hours. In the case where a gas-positive BGLB tube showed a pellicle, a gram stain was carried out to rule out gram-positive, lactose fermenting bacilli.
2.4.3. Detection of Salmonella
- Twenty-five (25) grams of a representative food sample were mixed with 225ml of sterile nutrient broth and incubated at 35°C for 24hours. One millilitre (1 ml) of the mixture was transferred into 10ml of sterile selenite cystine broth and incubated further for 24hours at 35°C. The enriched sample was streaked on a selective media plate of Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate (XLD), incubated at 35°C for 24hours, then observed for typical Salmonella colonies. A portion of typical Salmonella colonies were inoculated into sterile TSI slants and again incubated at 35°C for 24hours. Presumptive positive Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) culture was confirmed by the urease test [18].
2.4.4. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus
- The procedure for detection of Staphylococcus aureus was adapted from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), Hardy technologies, and the recommendations from EI-Jakee and others [18,19,20]. 25grams of a representative food sample were mixed with sterile nutrient broth and incubated at 350C for 24hours. The enriched sample mixture was streaked on selective media plates of Mannitol Salt agar (MSA), incubated at 350C for 24hours, and examined for typical Staphylococcus aureus colonies. Presumptive positive colonies were confirmed by the coagulase test.
2.4.5. Detection of Shigella
- 25grams of a representative food sample were mixed with 225ml of sterile gram-negative broth, adjusted the pH to 7, and then incubated the mixture at 35°C for 18hours. The enriched broth culture was streaked on the surface of sterile MacConkey agar, incubated at 35°C for 24hours, and observed for typical Shigella colonies. A portion of typical colonies were inoculated into sterile TSI slants, incubated further at 35°C for 24hours, and observed for typical Shigella reaction. Presumptive positive TSI culture was confirmed by the urease test [18].
2.5. Data Management and Analysis
- Quantitative data were analyzed using Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) version 24. The data was first coded, entered into Microsoft Excel (Ms. Excel version 2016), and validated through double-checking before importing into SPSS. The results were described in form of mean, range, and percentage. Qualitative data from key informant interviews were analyzed using the thematic network analysis technique.
2.6. Ethical Considerations
- This study was reviewed and approved by Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology (JKUAT) through letter reference number JKU/2/11/HSH415-1449/2018. Further, the ethical merits of the study were independently reviewed by Chuka University Institutional Ethics Review Committee, following which an ethical clearance (CUIERC/NACOSTI/078) was issued. Finally, the study was licensed by Kenya National Commission for Science, Technology, and Innovation (NACOSTI), license number 798300. Permission to collect data at Chuka town was granted by the County government of Tharaka Nithi (TNC/CDH/R./VOL1/100). Most importantly, the study sought informed consent from all respondents before data collection.
3. Results
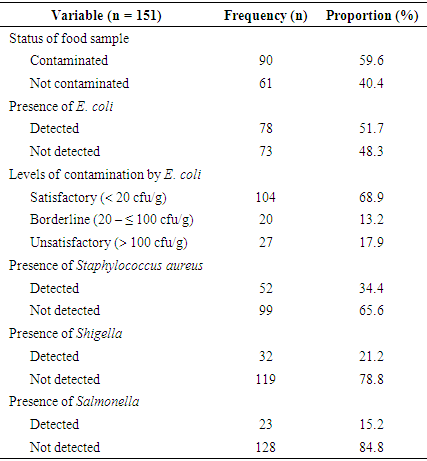
- The majority 90 (59%) of the samples were contaminated with at least one of the microorganisms. Escherichia coli was detected in 78 (51.7%) of the samples. The number of Escherichia coli ranged from 0 to 444 cfu/g per food sample, with a mean of 46.6 ± 86.97cfu/g. When categorized based on the established food safety criterion for Escherichia coli [21], 104 (68.9%) of the food samples were found satisfactory, 20 (13.2%) in the borderline, and 27 (17.9%) unsatisfactory. For the pathogenic microorganisms, Staphylococcus aureus was detected in the majority 52 (34.4%) of the food samples, whereas Shigella and Salmonella were detected in 32 (21.2%) and 23 (15.2%) of the food samples respectively (Table 1). The likelihood of contamination of cooked foods hawked at Chuka town with Escherichia coli and other microbes of public health importance including Shigella, Salmonella, and Entamoeba histolytica was also reported by key informants.
|
4. Discussions
- The majority (59%) of the cooked foods hawked at Chuka town were contaminated with either Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella, Salmonella, or more than one of these microorganisms. The proportion of foods contaminated with microorganisms of a public health concern as documented in this study compare closely with studies carried out in Nepal and Ethiopia where 54.6% and 61.1% of foods hawked at Bharatpur and Gondar town respectively contained microbes of public health importance [22,23]. Escherichia coli was detected in the majority (51.7%) of the samples. These findings were in agreement with a study by Bereda et al. [24] where Escherichia coli was identified in 51.5% of the samples collected from foods hawked at Jigjiga city. In Tanzania too, Escherichia coli recorded the highest presence (50%) compared to other bacteria investigated in foods hawked at the central business district of Tamale [25]. Also, Escherichia coli was the commonly (40%) isolated bacteria in foods hawked at various streets in Bangladesh [26]. When categorized according to the established contamination criterion for Escherichia coli, only 17.9% of the food samples were found unsatisfactory while 13.2% and 68.9% were in the borderline and satisfactory categories respectively. The proportion of unsatisfactory samples was much less compared to a study by Salamandane et al [27] in which 63% of foods hawked at Maputo in Mozambique were found to be unsatisfactory. Escherichia coli is an indicator organism whose presence implies the food item was subjected to poor hygiene practices during its processing and handling and thus is likely to be contaminated with pathogenic microorganisms [21]. The presence of Escherichia coli in cooked foods hawked at Chuka town is, therefore, a clear indication of poor hygiene practices by the food handlers. Consequently, the affected foods are not safe for human consumption. Escherichia coli is usually a member of colon microbiota in humans and some warm-blooded animals such as cattle. However, the bacteria can cause opportunistic infections particularly when it reaches the protected areas of the human body and in persons with suppressed immunity. Some of the common severe diseases caused by Escherichia coli include gastroenteritis, meningitis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, and sepsis [28,29].In terms of pathogenic microorganisms, Staphylococcus aureus was the most prevalent, identified in 34.4% of the food samples. These findings are consistent with a study carried out in Northwest Ethiopia in which Staphylococcus aureus was isolated in 35.54% of foods hawked at Gondar city. Similarly, Staphylococcus aureus recorded the highest occurrence (29.38%) in foods hawked in Jimma town [30]. The proportion of foods contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus was rather higher (50%) in foods hawked at Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) [31]. Staphylococcus aureus is usually a microbiota of the skin and nasopharynx and thus introduced to foods when they come into direct contact with the skin or the nose. [32,33,34]. Accordingly, cooked foods hawked at Chuka town may perhaps be contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus from the skin and nasopharynx of food hawkers through poor hygiene practices such as handling food with bare hands, or touching the nose and handling food without washing hands. Although Staphylococcus aureus is generally a microbiota of the skin, it can also result in debilitating disease conditions especially when it crosses into the protected areas of the body in large amounts. Staphylococcus aureus is known to cause pyogenic diseases in humans such as impetigo, boils, wound infections, pneumonia, and septic arthritis; and toxin-mediated diseases such as food poisoning, scalded skin syndrome, and toxic shock syndrome. Some of these diseases result in high fatalities especially when treatment is delayed [28].Shigella was the second prevalent pathogenic microorganism, identified in 21.2% of food samples. These findings compared closely with studies carried out in Bangladesh where culture results revealed that 20% of food samples were contaminated with Shigella [35]. In Ghana, Paul et al. [26] isolated Shigella in 36.7% of foods hawked at Tamale. The proportion of foods contaminated with Shigella was however comparatively small (10%) in foods hawked in Bangladesh [26]. In most cases, Shigella is introduced into food from the faeces of an infected person through contaminated hands, water, utensils, and other contaminated environments [36,37]. Thus, cooked foods hawked at Chuka town are possibly contaminated with Shigella from unsanitary practices such as handling food without washing hands, using contaminated utensils, using contaminated water, or displaying the cooked foods in contaminated environments. Shigella species usually cause shigellosis, a disease that presents as watery diarrhea and progresses into abdominal cramps and tenesmus within 1 to 2 days. Occasionally, bacteria dysentery can result particularly when the person is colonized by Shigella dysenteriae species. Just like Salmonella, Shigella species, too, can result in asymptomatic carriers, but in relatively few cases [28]. Salmonella was the least prevalent pathogenic microorganism found in 15.2% of the food samples. These findings were consistent with studies carried out in Ethiopia where 13.13% of samples collected from foods hawked at Jimma town were found to be contaminated with Salmonella. Bereda et al. [24] also documented somewhat comparable results in which Salmonella was isolated in 19.7% of foods hawked at Jigjiga city. The proportion of foods contaminated with Salmonella was also higher (57.1%) in foods hawked at Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of Congo [30]. Just like Shigella, Salmonella is a faeco-oral disease introduced into food through poor food hygiene practices [38,39,40]. Salmonella species are known to colonize and cause disease in a variety of animals, especially poultry and humans. Salmonella typhi is the most important human pathogen responsible for severe enteric fever and asymptomatic colonization of the gallbladder [28].
5. Conclusions
- Almost half of the cooked foods hawked in Chuka town are contaminated with either Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Shigella, or more than one of these organisms. Thus, these foods are not safe for human consumption. County government of Tharaka Nithi and other actors on food safety in the County should develop policies and interventions to prevent likely foodborne infections from the consumption of these foods.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We acknowledge Chuka University for providing laboratory facilities for this study, Jomo Kenyatta University and Agriculture and Technology for providing administrative services, and the research assistants for their tireless efforts in collecting quality data.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML