-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2019; 9(5): 139-147
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20190905.01

Degumming Alternatives for Edible Oils and Biodiesel Production
Rafaela Menezes dos Passos1, Ramon Sousa Barros Ferreira1, Eduardo Augusto Caldas Batista1, Antonio J. A. Meirelles1, Guilherme J. Maximo1, Marcela Cravo Ferreira2, Klicia Araujo Sampaio1
1Laboratory of Extraction, Applied Thermodynamics and Equilibrium (ExTrAE), University of Campinas, Faculty of Food Engineering, Department of Food Engineering, Rua Monteiro Lobato, Campinas-SP, Brazil
2Faculty of Technology, University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Rua Pascoal Marmo, Limeira - SP, Brazil
Correspondence to: Rafaela Menezes dos Passos, Laboratory of Extraction, Applied Thermodynamics and Equilibrium (ExTrAE), University of Campinas, Faculty of Food Engineering, Department of Food Engineering, Rua Monteiro Lobato, Campinas-SP, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Vegetable oils are predominantly composed of triacylglycerols (>95%), besides that, a wide variety of minor components including free fatty acids, phystosterols, tocopherols, colour pigments, metals and phospholipids are present in oils and fats. The presence of phospholipids in vegetable oils can cause oil darkening during the deodorization step and the inactivation of the lipases during the enzymatic transesterification process. The first step of the refining process is the degumming, which is designed to remove phospholipids. Traditional degumming processes such as water degumming and acid degumming cannot guarantee the low phosphorus content required for physical refining. Enzymatic degumming is a new process that uses enzymes known as phospholipases, which hydrolyze the phospholipids releasing fatty acids or diacylglycerols, thus increasing the oil yield. Moreover, due to the reduced reaction time and/or to the increased productivity, the ultrasonic technique has also been recently employed in association with degumming processes. Therefore, the purpose of this review is to present relevant studies on enzymatic degumming for edible oils and biodiesel production, from enzymatic catalysis, considering the most recent alternatives for product quality improvement and process costs reduction, with a focus on the simultaneous use of enzymatic degumming and ultrasonic technique.
Keywords: Enzymatic degumming, Phospholipases, Ultrasound, Biodiesel
Cite this paper: Rafaela Menezes dos Passos, Ramon Sousa Barros Ferreira, Eduardo Augusto Caldas Batista, Antonio J. A. Meirelles, Guilherme J. Maximo, Marcela Cravo Ferreira, Klicia Araujo Sampaio, Degumming Alternatives for Edible Oils and Biodiesel Production, Food and Public Health, Vol. 9 No. 5, 2019, pp. 139-147. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20190905.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Vegetable oils are mainly composed of triacylglycerols (TAGs), which are formed by a molecule of glycerol with three esterified fatty acids. In addition, crude vegetable oils contain up to 5% of non-glyceridic materials, formed by different amounts of free fatty acids (FFA), phospholipids and other compounds. To obtain edible oils from crude oils, a series of refining operations, including degumming, neutralization, bleaching and deodorization are needed [1-3].Degumming is the first stage of the refining process and involves the removal of phospholipids, proteins, and colloidal substances. The oils used for the synthesis of biodiesel as well as the edible oils must be degummed for the removal of phospholipids and reduction of the final content of phosphorus to the specified limits (<10 mg/kg) [4]. The presence of phospholipids can cause oil darkening during the deodorization step and lipase inactivation during the transesterification process.The degumming process can be classified as aqueous, acid, or enzymatic degumming. The aqueous or water degumming process is effective when applied to the hydratable phospholipids, since in the presence of water they become insoluble in oil, and can be easily separated by centrifugation. The non-hydratable phospholipids, which are phospholipids combined with calcium, magnesium or iron cations, can be removed by the addition of acids, such as phosphoric or citric [5-6]. The acid and aqueous processes, considered traditional techniques, have as disadvantages the excessive consumption of chemicals and a high generation of effluents, respectively [7]. According to Cesarini et al [8], the traditional degumming processes result in a loss of 2.5% of the total oil amount, for crude soybean oil containing 900 mg/kg of phosphorus, considering the current market price of US$ 1,100 per ton, it corresponds to a loss of US$ 27.5 per ton of oil. The oil loss is associated with the drag of neutral oil along with the phospholipids, as well as the removal of intact phospholipids.Enzymatic degumming is a process for removing phospholipids from crude oil in which phospholipases are used. The enzymes hydrolyze the ester bonds present on the phospholipid molecules, resulting in diacylglycerols (DAGs) or FFA release, which will contribute to the oil yield [9]. A part from that, it has the advantage of lower generation of effluents, and reduction of operational costs [10].Currently, the combination of techniques to increase the efficiency and productivity of the degumming process and biodiesel production has been studied in the literature. The combination of lipases and phospholipases for the production of biodiesel allows the use of crude oils, in which phospholipases have the role of degumming and lipases the function of transesterification, all taking place in a single step, thus reducing the production costs [8;11]. Another alternative to accelerate enzymatic processes is the use of ultrasound. The ultrasonic cavitation technique is used to intensify mass transfer rates and, in consequence, to increase the rates of biochemical reactions [7]. The association of enzymatic degumming with ultrasound would reduce the content of phospholipids, improve productivity, and reduce refining time [12]. Therefore, the goal of this review is to evaluate the degumming of vegetable oils for edible oils and biodiesel production focusing on the use of enzymatic processes and ultrasound technique, to increase productivity, improve product quality and reduce reaction time.
2. Vegetable Oils Production
- The growing world population has resulted in a sharp increase in the demand of oils and fats. To meet this demand, the oil production has increased from 40.8 million tons in 1980 to more 200 million tons in 2019 [13-14]. As shown in Figure 1, the projection for the global vegetable oil consumption and production increases until 2020.
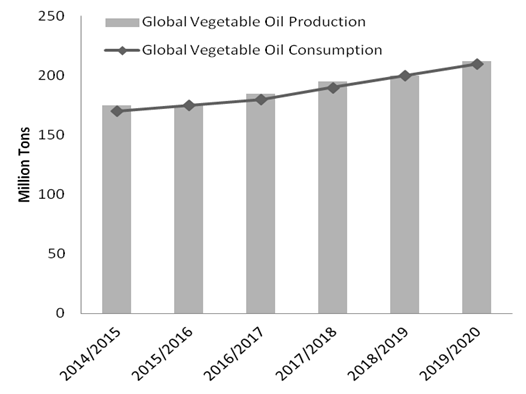 | Figure 1. Global Vegetable Oil Consumption and Production [14] |
3. Degumming
- Crude oils usually have impurities (phospholipids, FFAs, metals and etc) which during the refining process may cause damage to the oil's stability, color and flavor, so that their removal is necessary [19]. Degumming is the first stage of refining, in which phospholipids are removed. Phospholipids (PL) are derived from phosphatidic acid, a compound obtained by the condensation of glycerol with phosphoric acid and two fatty acids, as shown in Figure 2. The phospholipids, also known as gums, have a hydrophilic part and a hydrophobic region and are therefore compatible with organic (apolar) and aqueous (polar) environments, being widely used as emulsifiers in the food industry [20].
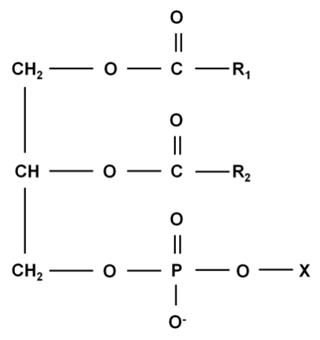 | Figure 2. Phospholipids structure (*X=Head group) |
|
3.1. Water And Acid Degumming
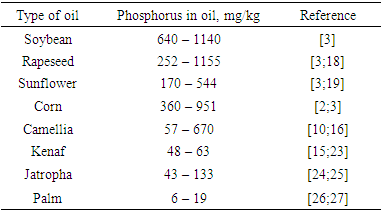
- Water degumming is effective when applied to the hydratable phospholipids, because when the water is added to the crude oil, the phospholipids are hydrated and can be separated by centrifugation [6]. This type of degumming still leaves about 80 to 200 mg/kg of phosphorus in the oil, depending on the quality and presence of non-hydratable phospholipids, which remain in the oil [19]. Sampaio et al. [2] performed the aqueous degumming of crude corn oil, which initially had a phosphorus content of 951.0 mg/kg, obtaining a final content of 67 mg/kg. Ye et al. [29] performed the aqueous degumming in crude rapeseed oil and obtained a decrease in phosphorus content from 690 mg/kg to 61 mg/kg. Both obtained a reduction of about 90% of the phosphorus content. However, the final phosphorus content is still higher than the level required for the physical refining.In the acid degumming, the non-hydratable phospholipids, namely those phospholipids combined with calcium, magnesium, or iron cations, are removed. For this procedure, it is necessary to add acids, such as phosphoric or citric [5-6]. Citric acid is used not only to decompose the metal salts, but also as a chelating agent to keep the metals soluble in the aqueous phase [30]. Mei et al. [31] performed the acid degumming of Silybum marianum seed oil using different types of acids, such as citric, phosphoric, oxalic, and tartaric acids. The initial phospholipids content in the oil was 273 mg/kg. The degumming using citric, phosphoric, oxalic and tartaric acids obtained the following results for the phospholipids content, respectively: 113.87 mg/kg, 197.83 mg/kg, 185.49 mg/kg, and 125.1 mg/kg. It was observed that the citric acid allowed the best result regarding the decrease of phospholipids content. Acid degumming requires the use of large amounts of acid solutions, high temperatures and also generates a lot of wastewater [10;24].Szydłowska-Czerniak; Łaszewska [33] and Jiang et al. [10], when evaluating the acid degumming applied to crude rapeseed and soybean oils, obtained a reduction of phospholipids content from 5655 mg/kg to 268 mg/kg and from 752 mg/kg to 32 mg/kg, respectively. Moreover, the final phosphorus content was still over 10 mg/kg, the maximal level usually considered appropriate for physical refining. In view of this, conventional degumming should be replaced by other processes that have operates at mild temperature, lower energy consumption, reduction effluent generation and increased oil yield. Taking into account these demands, enzymatic degumming has emerged as a key technology.
3.2. Enzymatic Degumming
- Enzymatic degumming is the process of removing phospholipids from crude oil using enzymes known as phospholipases. The main phospholipases types are A1, A2, and C, with their target sites varying according to their specificity (Figure 3).
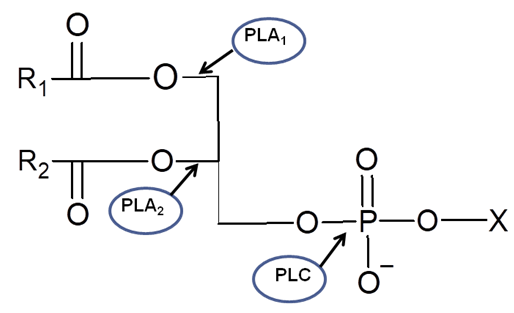 | Figure 3. Phospholipases action sites in the phospholipid molecule (*X=Head group) |
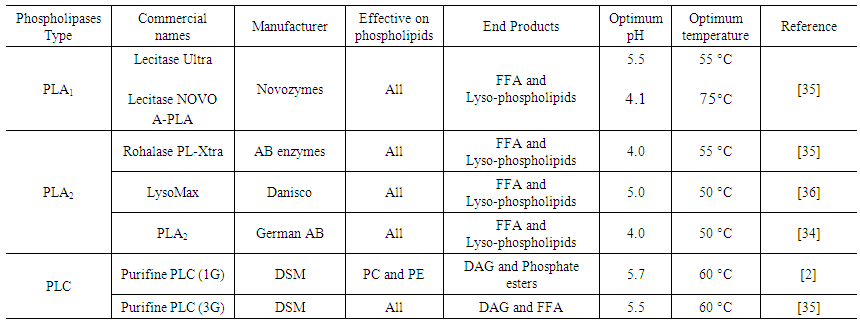 | Table 2. Phospholipases characteristics |
3.3. Ultrasound Improved Degumming
- Recently, the optimization of enzymatic degumming process has been studied combining the enzymatic process with other techniques, including ultrasound, which is a kind of cavitation technique.Cavitation is the formation, growth, and collapse of microbubbles that occur in a short time, releasing energy and generating high temperatures (in the range of 1000 - 15000 K) and pressures (in the range of 500-5000 bar) within a very restricted space region [29;30]. One of the main effects of cavitation is the release of a significant energy magnitude and the generation of local turbulence, which can increase the mass transfer efficiency and play an important role in enzymatic reactions. The use of ultrasound can intensify the degumming process, hence reducing the reaction time, amount of chemicals, energy consumption, and increasing the productivity.Jiang et al. [39] performed the enzymatic degumming of rapeseed oil in association with the ultrasound technique and obtained a reduction of the phosphorus content from 252 mg/kg to 6.5 mg/kg, reduction higher than 97%. Similar results were also found by More & Gogate [12] when evaluating the enzymatic degumming of soybean oil. Therefore, the use of ultrasound appears to be a good alternative for the optimization of enzymatic degumming. In Table 3, the phosphorus content and different types of catalysts used for each type of degumming are shown.
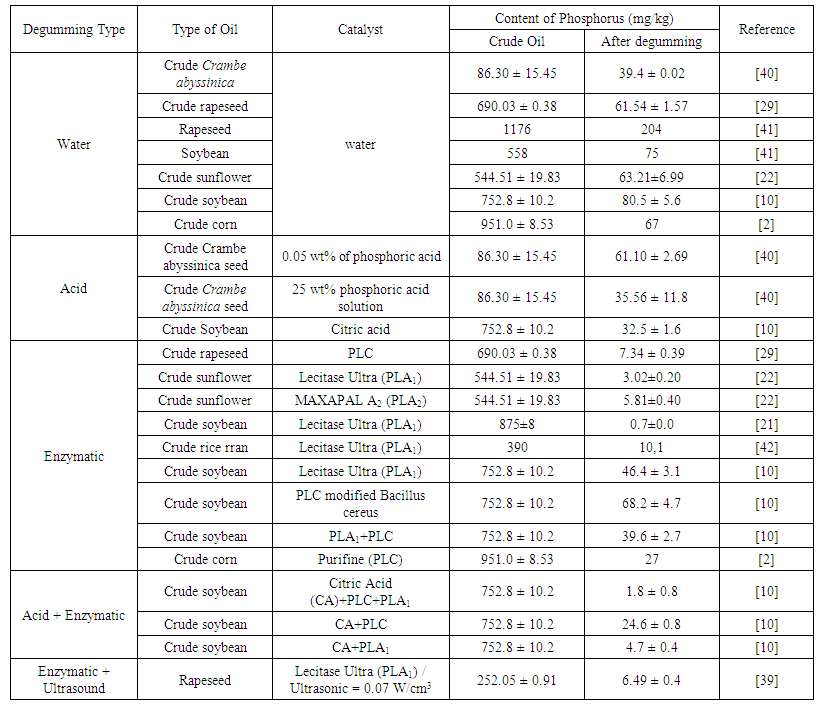 | Table 3. Content of phosphorus and types of catalyst for different degumming types |
4. Biodiesel Production
- Brazil is self-sufficient in the bioethanol business, with the production and distribution infrastructure as well as the domain of technologies involved in the sugarcane and ethanol production chain associated with the automotive sector. In addition, ethanol is a fuel that has low toxicity, is fully biodegradable and considered environmentally friendly. Bioethanol is obtained from renewable sources, thus being favorable for reducing the emission of greenhouse gases [43].In 2008 the Brazilian government decided on an incentive program to produce biodiesel and established adding 2% of this biofuel to diesel, a percentage that has been increasing over the years. In May 2019, the addition of 11% of biodiesel to diesel was fixed, with an increase until 15% up to the 2023 year [44]. Thus, with the government incentive and the use of techniques that could reduce the production costs, should result in the production of cheaper and more competitive biodiesel in the biofuels business.The production of biodiesel usually occurs through alkaline catalysis, with the use of refined vegetable oil as a source of triacylglycerols. However, the oil refining process generates high costs in biodiesel production. Therefore, the use of alternative processes that employs crude vegetable oils for biodiesel production is emerging as a feasible innovation, for example, through the use of enzymatic degumming for removal of phospholipids. Biodiesel is chemically defined as the monoalkyl esters of long chain fatty acids, obtained by the transesterification reaction (Figure 4) (alcoholysis) of vegetable oils or animal fats (triacylglycerols - TAG), or by the esterification of free fatty acids (FFA) with an (methyl or ethyl) alcohol, by the use of acidic, basic or enzymatic catalysts, which can be of the homogeneous or heterogeneous kind [45].
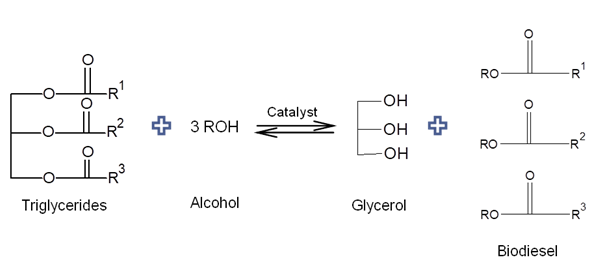 | Figure 4. Transesterification reaction |
5. Association of Enzymatic Degumming with Enzymatic Transesterification
- Recently, some researchers associated phospholipases with lipases, to perform the biodiesel production processing in a single step. According to the literature, in spite of being an enzymatic process, this combination can reduce costs compared to the traditional processes of biodiesel production [57].Jang et al. [58] used the association of PLA2 with the lipase C. rugosa and R. Oryzae (liquid form) in a proportion of 1:1, for the production of biodiesel in two steps from crude canola oil (10g), temperatura at 37°C, 10% (w/w of oil) of free lipase solution, 4.5 mL of methanol, during 60h. The results revealed a conversion to fatty acids methyl esters greater than 84.25% in 60 hours.Cesarini et al. [8] used the lipase Callera Trans L in liquid form along with phospholipases PLA1, PLC and LLPL-2 for the production of biodiesel from crude soybean oil and canola oil, were used temperature at 35°C, 1% of lipase, 2 to 3.5wt.%, 1.5eqs of methanol and reaction time was 24h. The authors obtained a content of fatty acid methyl esters higher than 95% and phosphorus content lower than 5 mg/kg in 10 hours. Li, Du & Liu [11] used the free lipase (NS81006) and Aspergillus niger modified PLA1 for the production of biodiesel from the crude soybean oil and obtained a fatty acid methyl esters content of 94.9%. From the results, it is possible to verify that the use of phospholipase A1 resulted in higher biodiesel yields. Thus, with the combination of phospholipases and lipases, in their optimum conditions, good results, in both conversion (>95%) and phosphorus content (<10 mg/kg), are obtained at the end of biodiesel production, as we can observe in the previous studies.
6. Conclusions
- The use of enzymatic degumming as a step to remove phospholipids, which is a common goal of degumming, increasing the oil yield has attracted attention of the vegetable oil industry. The association of enzymatic degumming with the enzymatic transesterification can provide numerous and sustainable benefits, which includes the use of non-refined and cheaper vegetable oils, less chemicals and mild processes. Besides, the combination of both processes involves a great efficiency increasing in the new era of vegetable oil and biodiesel production at industrial scale. The combination of the enzymatic degumming or the enzymatic transesterification with the ultrasound technique would potentiate the removal of phospholipids, reduce reaction time, energy consumption and increase productivity. Therefore, the mentioned processes and techniques are of great importance for the future studies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors thank the funding agencies: CNPq (429873/2018-2; 305870/2014-9; 308924/2017-7; 406963/2016-9; 132428/2018-0), FAPESP (2014/21252-0; 2016/08566-1). This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Supeior – Brasil (CAPES) – Finance Code 001.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML