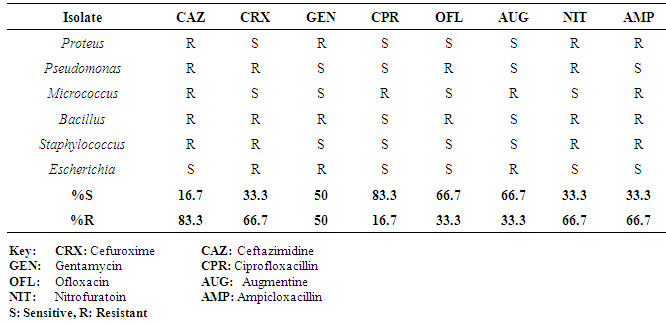
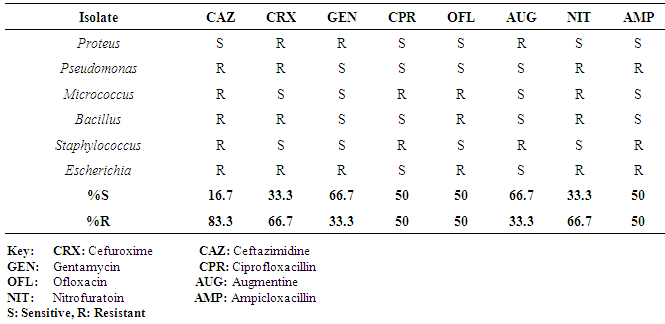
| [1] | Adebayo-Tayo, BC, Adegoke AA, Akinjogunla OJ (2008). Microbial and physicochemical quality of powdered soymilk samples in Akwa Ibom, South Southern Nigeria. Afr. J Biotechnol. 8 (13):3066-3071. |
| [2] | Adelekan AO, Adediran EA, Ngozi UA, Yetunde OA, Abidemi SD (2013). Nutritional, microbiological and sensory characteristics of malted soy-kunu zaki: An improved traditional beverage. Adv. Microbiol., 3:389-397. |
| [3] | Agboke AA, Uduma EO, Christian CO, Emmanuel CI (2011). Evaluation of microbiology quality of some soybean milk products consumed in Nigeria. Prime Res. Med. 1(2): 025-030. |
| [4] | Agwa OK, Uzoigwe CI, Wokoma EC (2012). Incidence and antibiotic sensitivity of B. cereus isolated from ready to eat foods sold in some markets in Port Harcourt, River State. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotech. Env. Sc. 14(1): 13 – 18. |
| [5] | Akhigbemidu W, Musa A, Kuforji O (2015). Assessment of the microbial qualities of noodles and the accompanying seasonings. Nig. Food J. 33: 48 – 53. |
| [6] | Akinyemi AA, Adejola AQ, Obasa SO, Ezeri GNO (2011). Aflatoxins in Smoked‐dried Fish sold in Abeokuta, Ogun State, South‐west Nigeria. Proceedings of the Environmental Management Conference, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, Nigeria. pp. 478 – 487. |
| [7] | Akissoe NH, Hounhouigan JD, Bricas N, Vernier P, Nago MC, Olorunda OA (2001). Physical, chemical and sensory evaluation of dried yam (Discorea rotundata) tubers, flour and Amala a flour derived product. Trop. Sci. 41: 151-156. |
| [8] | Bauer AW, Kirby WM, Sherris JC, Truck M (1966). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45(4): 493- 496. |
| [9] | Berghofer LK, Hocking AD, Miskelly D, Jansson E (2003) Microbiology of wheat and Flour Milling in Australia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 85:137-49. |
| [10] | Bush LM, Perez MT (2014). Pseudomonas and Related Infections. The Merck manual, Professional Edition. http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/infectious_diseases/gram-negative_bacilli/pseudomonas_and_related _infections. html. |
| [11] | Cheesbrough M (2004). District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries. Low price Edition part 2. Cambridge press, England. |
| [12] | Cheesbrough M (2005). District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries, Part 1. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. pp. 137-150. |
| [13] | CLSI (2002). Performance standards for antimicrobial; susceptibility testing. 12th Informational Supplement. CLSI Document Wayne, PA: CLSI. |
| [14] | Cowan and Steel (1985) Manual for the Identification of Bacteria. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [15] | Daniyan SY, Ajibo CQ (2011). Microbiological Examination of sliced fruits sold in Minna Metropolis. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2 (7): 124 -129. |
| [16] | Ellis, D., Davis, S., Alexiou, H., Handke, R., Bartley, R. (2007). Descriptions of Medical Fungi. Second Edition. Printed in Adelaide by Nexus Print Solutions, Underdale, South Australia. |
| [17] | Esho FK, Budbazar E, Akiko K, Keiko K (2013). Microbial Assessment and Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens in Natural Cheeses in Japan. BioMed. Res. Int. 3:101-105. |
| [18] | Gbolagade J, Ibironke A, Omitade Y (2011). Nutritional Compositions, Fungi and Aflatoxins Detection in Stored ‘Gbodo’ (fermented Dioscorea rotundata) and ‘elubo ogede’ (fermented Musa parasidiaca) from South western Nigeria. Afr. J. Food Sci. 5(2):105-110. |
| [19] | Harrigan, M.G. and McCane, M.E. (1976) Laboratory Methods in Food and Dairy Microbiology. Academic Press, London. |
| [20] | Hashem M (2011). Isolation of Mycotoxin-producing Fungi from Fishes Growing in Aquacultures. Res. J. Microb. 6: 862-872. |
| [21] | Holt JG, Krieg NR, Seath PHA, Satley JT, Williams ST (1994). Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 9th Ed., Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 804. |
| [22] | Izah SC, Aseiba ER, Orutugu LA (2015). Microbial quality of polythene packaged sliced fruits sold in major markets of Yenagoa Metropolis, Nigeria. Point J. Bot. Micro. Res. 1(3): 30 – 36. |
| [23] | Kolapo AL, Oladimeji GR (2008). Production and quality evaluation of Soy-corn milk. J. Appl. Biosci. (2): 40 - 45. |
| [24] | Nawal A, Hassanain MA, Hassanain WM (2013). Public Health Importance of Foodborne Pathogens. World J. Med. Sci. 9(4):208-222. |
| [25] | Nazim MU, Mitra K, Rahman MM, Abdullah ATM, Parveen S (2013). Evaluation of the nutritional quality and microbiological analysis of newly developed soya cheese. Intl. Food Res. J. 20(6): 3373-3380. |
| [26] | Ndife J, Abdulraheem LO, Zakari UM (2011). Evaluation of the nutritional and sensory quality of functional breads produced from whole wheat and soya bean flour blends. Afr. J. Food Sci. 5(8):466- 472. |
| [27] | Odom TC, Udensi EA, Nwanekezi EC (2012). Microbiological qualities of hawked retted cassava fufu in Aba metropolis of Abia state. Nig. Food J. 30(1): 53 – 58. |
| [28] | Odu NN, and Egbo NN, (2012). Microbiological quality of soy milk produced from soybean using different methods. Nature and Science. 10(8): 85-92. |
| [29] | Odu NN, Imaku LN (2013). Assessment of the Microbiological Quality of Street-vended Ready-To-Eat Bole (roasted plantain) Fish (Trachurus trachurus) in Port Harcourt Metropolis, Nigeria. Researcher, 5(3): 9-18. |
| [30] | Oranusi US, Braide W (2012). A study of microbial safety of ready-to-eat foods vended on highways: Onitsha-Owerri, south east Nigeria. Int. Res. J. Micro. 3(2): 066-071. |
| [31] | Orutugu LA, Izah SC, Aseibai ER (2015). Microbiological quality of Kunu drink sold in some major markets of Yenagoa Metropolis, Nigeria. Continental J. Biomed. Sci. 9(1): 9 –16. |
| [32] | Osho, A., Mabekoje OO, Bello OO. (2010). Comparative study on the microbial load of Gari, Elubo-isu and Iru in Nigeria. African Journal of Food Science. 4(10): 646 – 649. |
| [33] | Oxiod (1985). Oxoid Manual of Dehydrated Culture Media, Ingredients and Other Laboratory Services. Oxoid, Basingstoke |
| [34] | Pepper, I.L. and Gerba, C.P. (2005). Environmental microbiology. A laboratory manual. Second edition. Elsevier Academic Press. |
| [35] | Pratiwi C, Rahayu WP, Lioe HN, Herawati D, Broto W, Ambarwati S (2015). The effect of temperature and relative humidity for Aspergillus flavus BIO 2237 growth and aflatoxin production on soybeans. Int. Food Res. J. 22(1): 82-87. |
| [36] | Prescott LM, Harley JP, Klein DA (2005). Microbiology (6th ed). McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., New York. |
| [37] | Salim-ur-Rehman, GH, Haq N, Muhammad MA, Sarfraz HM and Shahid HS, (2007). Physico-chemical and sensory evaluation of ready to drink soy-cow milk blend. Pak. J. Nutr. 6 (3): 283-285. |
| [38] | Samson RA, Varga J (2007). Aspergillus systematics in the genomic era. CBS Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht. 206. |
| [39] | Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J (2010). Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean Nature (Nature Publishing Group) 463 (7278): 178–83. |
| [40] | Seiyaboh EI, Oku IY, Odogbo OM (2013). Bacteriological spoilage of Zobo (A Nigerian Drink prepared from the cayces of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. (Malvaceae). The Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2(11): 46 – 51. |
| [41] | Soya.be (2006). Soya- information about Soy and Soya products. http://www.soya.be/soy-health.php. |
| [42] | Srinu B, Vijaya Kumar A, Kumar E, Madhava Rao T (2012). Antimicrobial resistance of bacterial foodborne pathogens. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 4(7): 3734 – 3736. |
| [43] | Turnbull PCB (1996). Bacillus. In: Medical Medical Microbiology. Fourth Edition; 1996 [cited 2015 March 26]. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7699/. |
| [44] | Wild CP and Gong YY (2010). Mycotoxins and human disease: a largely ignored global health issue. Carcinogenesis, 31: 71-82. |
| [45] | Watanabe T (2010). Pictorial atlas of soil and seed fungi: morphologies of cultured fungi and key species 3rd ed. CRC Press, USA. |



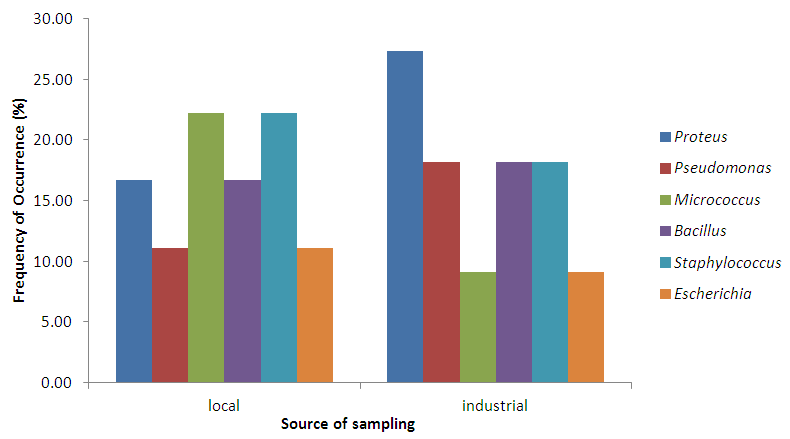
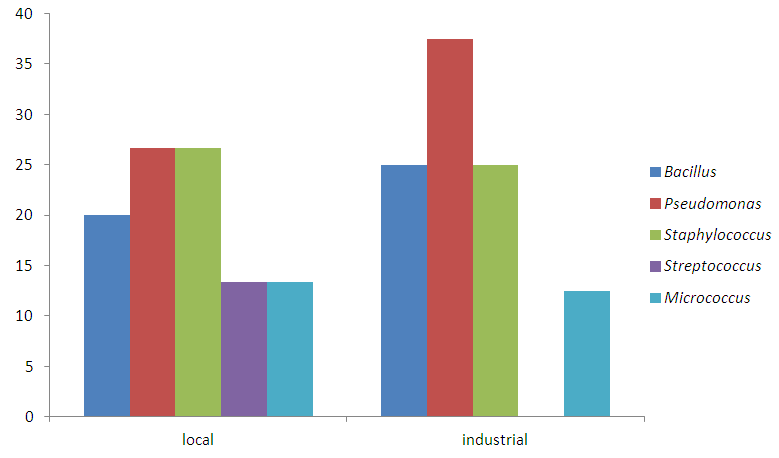
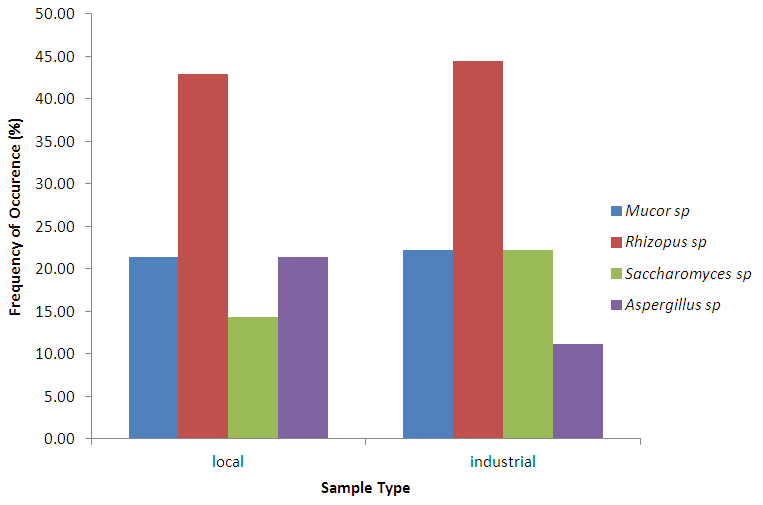
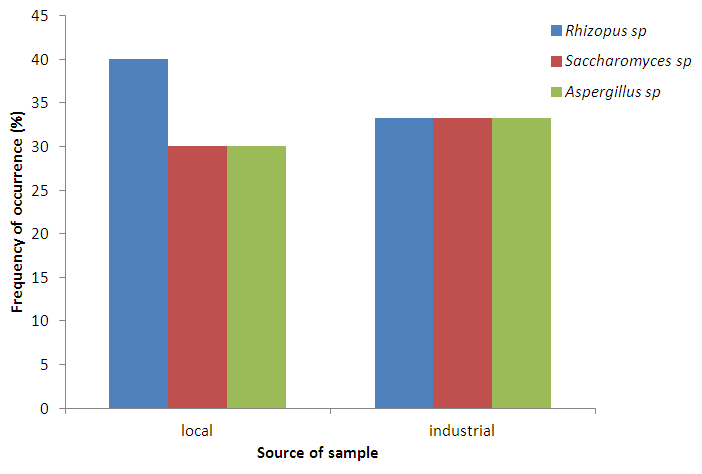
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML