-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2016; 6(2): 44-51
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20160602.03

Incidence and Plasmid Profiles of Multidrug Resistant Enterobacteria Isolates from Processed Convenience Foods in Some Countries of West Africa
Abimbola Owoseni 1, Abiodun Onilude 2
1Department of Biological Sciences, Bowen University Iwo, Nigeria
2Department of Microbiology, University of Ibadan, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Abimbola Owoseni , Department of Biological Sciences, Bowen University Iwo, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Previous studies have revealed the presence of multidrug resistant Enterobacteria in some processed convenience foods along the West African coast. The present study was carried out to determine the antibiotic sensitivity patterns and plasmid profiles of some of the Enterobacteria isolated from such foods in four West African countries. Antibiotic sensitivity testing was carried out to determine the sensitivity profiles of the isolates and the evidence for resistance plasmids was carried out by curing studies. Resistance plasmids were isolated using the alkaline phosphate method and the plasmid DNA was separated by electrophoresis on agarose gels. A total of forty three organisms were isolated and identified using standard physiological and biochemical methods. Generically the organisms were Citrobacter (6), Edwardsiella (2), Enterobacter (12), Escherichia coli (4), Klebsiella (4), Proteus (4), Salmonella (2), Serratia (2) and Shigella (7). Plasmid DNA was extracted from fourteen isolates i.e. four Shigella sp., two Salmonella sp., two Klebsiella sp., three Enterobacter sp., two Proteus sp. and one E. coli and it may be said that antibiotic resistance in these organisms were plasmid mediated. At the end of plasmid curing it was observed that sensitivity greatly increased. This study reveals that efforts being made by food standard regulatory bodies are inadequate to meet the Ready-to-eat food quality standards based on the sanitary levels. West Africa is a tourist destination hence high quality local market food is necessary and these findings would be useful in formulation of food-borne disease control and prevention strategies. Establishment and enforcement of a systematic and regular mechanism for surveillance and monitoring is needed to minimize the risks attached to consuming these foods.
Keywords: Multidrug Resistance, Plasmid profiles, Convenience/ready-to-eat Foods, Enterobacteria
Cite this paper: Abimbola Owoseni , Abiodun Onilude , Incidence and Plasmid Profiles of Multidrug Resistant Enterobacteria Isolates from Processed Convenience Foods in Some Countries of West Africa, Food and Public Health, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 44-51. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20160602.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Multidrug resistant strains of bacteria have emerged, possessing several resistant mechanisms against different antibiotic groups (Kocsis and Szabo, 2013). The discovery of antibiotics and their clinical potential in treating bacterial infections in humans represented an extremely important milestone in the field of medicine. Unfortunately as each new antimicrobial agent was introduced, resistant strains began to appear within a few years. Individual genes conferring multiple drug resistance have been identified and found to encode, among others, efflux systems consisting of membrane proteins able to pump a broad spectrum of chemical agents out of the cell (Edgar & Bibi, 1997).Plasmids are small double stranded deoxyribonucleic acid molecules, usually circular, that can exist independently of host chromosomes and are present in many bacteria (Carattoli, 2011) they are also present in some yeasts and other fungi. They have their own replication origins and are autonomously replicating and stably inherited. Plasmids have relatively few genes, generally less than 30, their genetic information is not essential to the host, and bacteria that lack them usually function normally. Plasmids often carry drug resistance genes and can sometimes confer resistance to a number of different drugs (Bennett, 2008). Characteristically, plasmids can be eliminated from host cells in a process known as curing. Curing may occur spontaneously or be induced by treatments that inhibit plasmid replication while not affecting the bacterial host cell reproduction. The inhibited plasmids are slowly diluted out of the growing bacterial population. Some commonly used curing treatments are acridine mutagens, UV and ionizing radiation, thymine starvation and growth above optimal temperatures (Hartwell et al., 2000, Amaral et al., 2007).Changes in the bacterium that enable it to resist the antimicrobial agent occur naturally or as a result of mutation or genetic recombination of the DNA in the nucleoid, or as a result of obtaining plasmids from other bacteria. Exposure to the antimicrobial agent then selects for these resistant strains of organism. Many Gram negative bacteria possess R (resistance) plasmids which have genes coding for multiple antibiotic resistance e.g. E. coli, Proteus, Serratia, Salmonella, Shigella (Kocsis and Szabo, 2013) and Pseudomonas. R factors or plasmids typically have genes that code for enzymes capable of destroying or modifying antibiotics. They are not usually integrated into the host chromosome. Genes coding for resistance to antibiotics such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and kanamycin have been found in plasmids. Some R plasmids have only a single resistance gene, whereas others can have as many as eight (Whiley et al., 1988). Often the resistance genes are within a transposon (a small piece of DNA that can insert itself into another place in the genome of the same cell) and thus it is possible for bacterial strains to rapidly develop multiple resistance plasmids. Because many R factors also are conjugative plasmids, they can spread throughout a population, although not as rapidly as the F (fertility) factor (Whiley et al., 1988; Ma et al., 2007).High quality and hygiene standards must be maintained in convenience foods to ensure consumer safety. Enterobacteriaceae have been implicated in various food-borne diseases in Europe (Bolton, 1999, Owoseni and Onilude, 2011). Considering the aforementioned, the aims and objectives of this study were to: sample processed foods in the West African sub-region; isolate and identify Enterobacteriaceae from the samples and systematically characterize the isolates using both classical and molecular techniques.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Sampling Sites
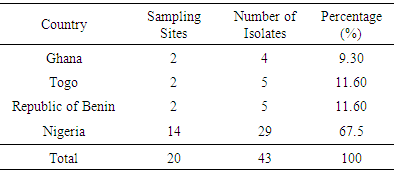
- The convenience food samples were collected from two Anglophone (Ghana and Nigeria) and two Francophone (Republic of Benin and Togo) countries in the West African sub-region during the wet and dry seasons (Figure 1).
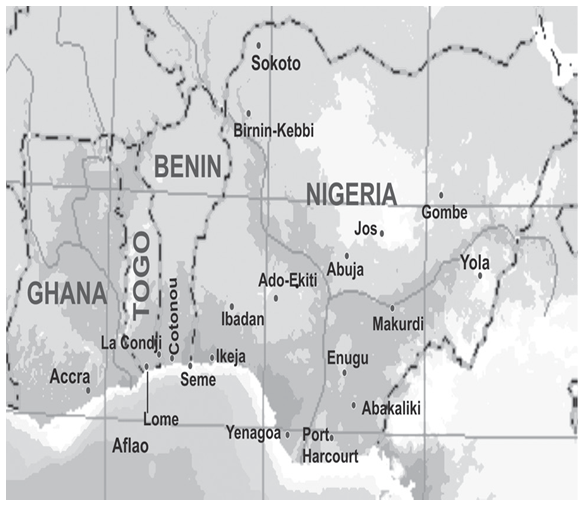 | Figure 1. Map of West Africa showing the four countries where sampling was carried out. ( • Dotted spot represent sampling site) |
2.2. Food Samples
- The convenience food samples collected included puff-puff (fried dough), egg rolls, buns, fried chicken, fish and meat pie, dried fish and cake.
2.3. Sampling Procedures
- The food samples were collected during the rainy (wet) season i.e. between April and October and harmattan (dry) season i.e. between November and March for two years. The food samples were collected in clean polyethylene bags and labelled. The polyethylene bags with the samples were transported aseptically in insulated rectangular, plastic food flasks (Kenchuang Co., China (30 cm x 17.5 cm x 30 cm) filled with ice chips to the Department of Botany and Microbiology laboratory, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Oyo State, where they were unloaded and refrigerated (10-15°C) immediately. Whenever possible, at least 100g of each sample was obtained for each sample unit. The average time of travel from sampling sites outside Nigeria (Ghana through Lome and Cotonou to Ibadan) was thirteen and a half (13.5) hours. Average travel time within Nigeria was eight and a half hours.
2.4. Sample Treatment to Obtain Isolates
- Twenty-five grams of each food sample was homogenised with nine times that weight or volume of buffered peptone water (Andrews & Hammack, 2002). The different food samples were handled separately. Each sample was mixed to ensure homogeneity. A portion (1g) of the resulting homogenate was then transferred into sterile test tubes and serially-diluted ten-fold according to the methods described by Pollack et al. (2002). The diluents were then plated out for incubation to get pure cultures and further work was carried out on the isolates (Andrews & Jacobson, 2003). The media for isolation were Nutrient Agar and Broth (Lab M), MacConkey Agar and Broth (Fluka); Salmonella-Shigella Agar (Lab M); Bismuth Sulphite Agar (Fluka) and EMB Agar (Fluka). All were prepared according to the manufacturers’ instructions. Pure cultures of isolates were stored on Nutrient agar slants at 4°C. The organisms were sub-cultured onto fresh slants every three months (90 days).
2.5. Characterization of Isolates
- The bacterial colonies were differentiated first on the basis of colonial morphology followed by microscopic examination after Gram staining. Biochemical tests were carried out to characterize the isolates (Pollack et al., 2001). Antibiotic sensitivity testing was carried out as described by Owoseni & Onilude (2011).
2.6. Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
- A 0.1ml overnight actively growing broth culture containing 1 x 106 cfu/ml of each bacterial isolate was introduced into a Petri dish and 20 mL of molten agar added. The antibiotic sensitivity discs (HJ04/P, Abtek Biologicals Ltd.) consisting of 10 different antibiotics namely nitrofurantoin (100µg), augmentin (30µg), norfloxacin (10µg), tetracycline (50µg), gentamycin (10µg), ciprofloxacin (5µg), chloramphenicol (10µg), ampicillin (25µg), nalidixic acid (30µg), and cefuroxime (20µg) were placed on the solidified agar surface. The plates were left overnight at 37°C. The relative susceptibility of each isolate to each antibiotic was shown by a clear zone of inhibition. Susceptible strains showed zone diameters of 22 to 24 mm (Bauer et al., 1966, Owoseni and Onilude, 2011). This was carried out before and after Plasmid curing.
2.7. Plasmid Curing Method
- Presence of antibiotic resistance plasmids was determined by curing reactions using the modified method of Ahrne et al. (1989) involving the use of Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS). To 100 mL of nutrient broth was added 10g SLS and pH adjusted to 5.5. The mixture was steamed for 1h and then removed as a stock solution. Overnight cultures of the test isolates grown in nutrient broth were diluted 100 fold and 0.5 mL was added to 30 mL of nutrient broth. Incubation was carried out at 35°C for 2h in a shaker-incubator followed by the addition of SLS-stock solution at 1% (w/v). The culture flasks were incubated for 72h with mild agitation before plating out. One hundred to two hundred colonies were picked and streaked onto nutrient agar plates and then restreaked onto selective media (Onilude et al., 1999).
2.8. Plasmid Profiles
- Organisms were sub cultured from slants onto fresh nutrient agar plates and incubated overnight. Alkaline phosphate method of Birnboim & Doly (1979) was followed for plasmid DNA isolation. Agarose gel electrophoresis was performed using 0.8% agarose gel in 5mL Tris-Borate (TBE) buffer with 2 drops of ethidium bromide added. Twenty (20) µL of λ-Hind III molecular weight marker (Roche) was loaded onto one of the wells. Twenty (20) µl of the plasmid DNA samples was mixed with 0.3 µl of bromophenol blue and loaded unto different wells. This was repeated for all the organisms. The gel was viewed and pictures taken in an ultraviolet transilluminator (Hoefer macrovue UV-25, Amersham Biosciences, UK).
3. Results
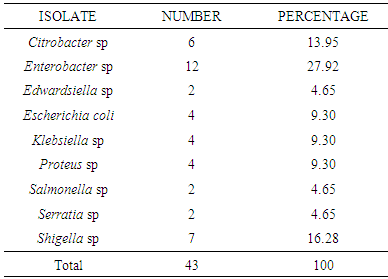
- Forty three organisms were isolated from the different food samples. Generically the organisms belonged to Citrobacter, Edwardsiella, Enterobacter, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia and Shigella. The number and frequency of occurrence are shown in Table 1, with Enterobacter recording the highest percentage of 27.92% while Edwardsiella, Salmonella and Serratia had the minimum occurrence of 4.65% each.
|
|
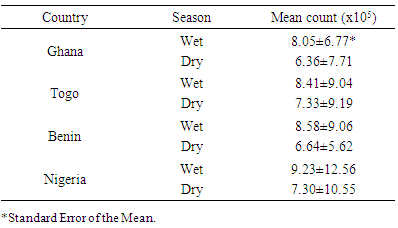
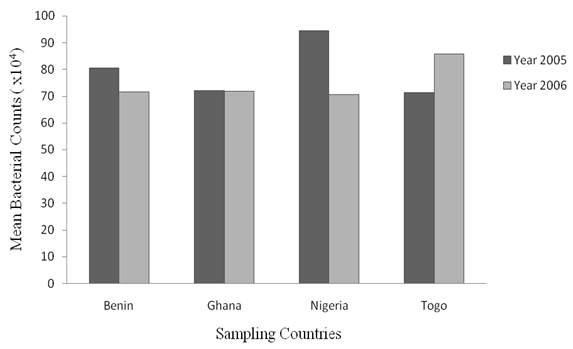 | Figure 2. Mean values of Counts of Enterobacteria isolates from Samples Collected in the Four Countries within Year 2005 and 2006 |
|
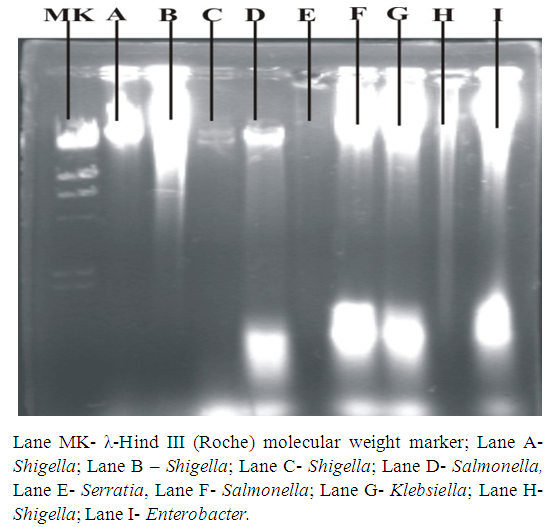 | Figure 3a. Plasmid DNA patterns viewed under UV light after agarose gel electrophoresis |
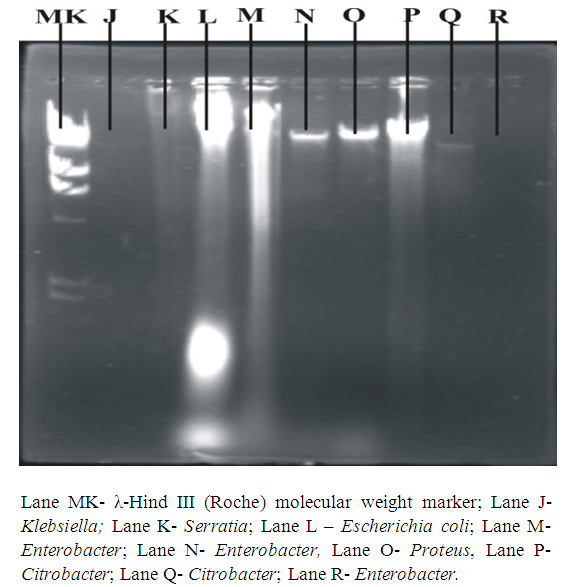 | Figure 3b. Plasmid DNA patterns viewed under UV light after agarose gel electrophoresis |
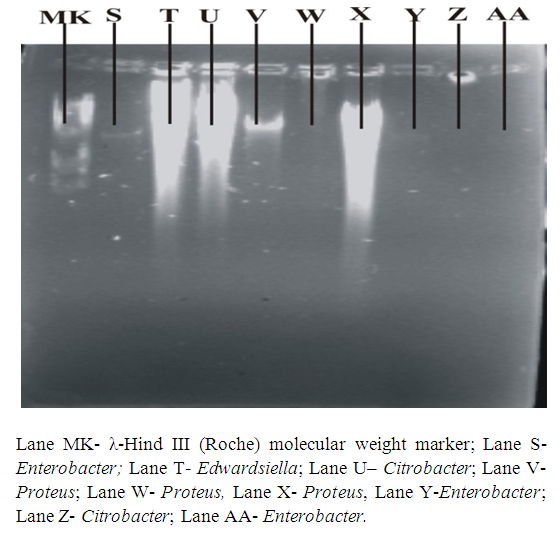 | Figure 3c. Plasmid DNA patterns viewed under UV light after agarose gel electrophoresis |
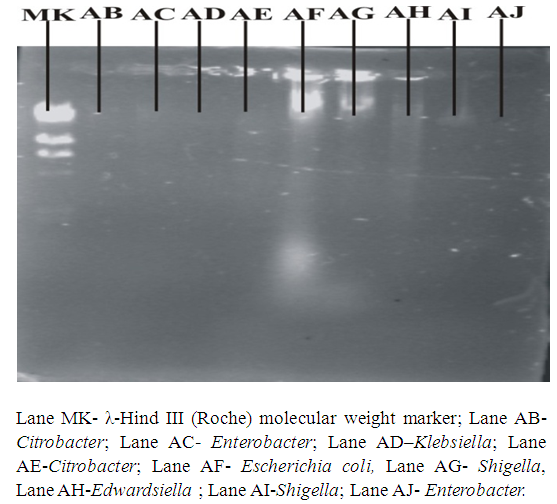 | Figure 3d. Plasmid DNA patterns viewed under UV light after agarose gel electrophoresis |
|
4. Discussions
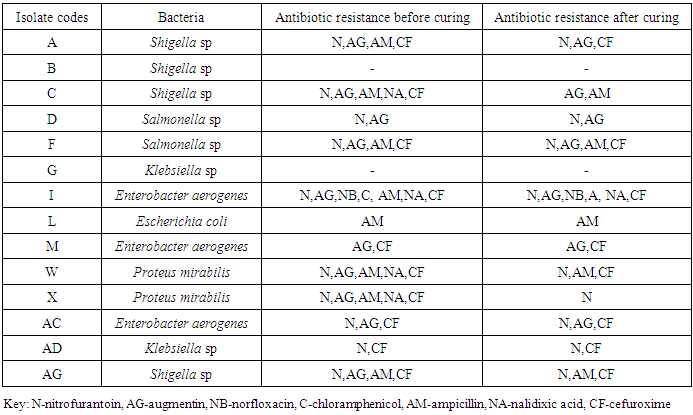
- The presence of enteric bacteria in the processed/ ready-to-eat foods is evidence of the poor microbiological quality of the foods in the different countries. Nwachukwu and Osuocha (2014) isolated enterobacteria as well as Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus aureus from ready-to-eat fruits. Lewis et al. (2005) showed that the presence of these bacteria especially Salmonella is due to improper disinfection and cross contamination from hands, packaging among other possible causes. The results of this work are in line with that reported by Vigano et al. (2007) in Pemba Island, Tanzania. Fifty eight percent (58%) coliforms were found in household meals and 98% in milk samples. E. coli was the most frequently isolated species and Salmonella spp was found exclusively in cow milk. The boiled or fried foodstuffs were faecally contaminated and the contamination was likely to have occurred after preparation and before consumption. Kaneko et al. (1999) reported isolating Listeria spp from two samples of raw vegetables and five kinds of cooked foods. The isolation rates for coliforms were 6.1 – 50% for intact vegetables and 50-66.7% for fresh products. The aerobic count and coliform values showed that the raw vegetables cut for salad were the most heavily contaminated among the six kinds of ready-to-eat foods examined. Room temperature, high water activity and a pH of >4.6 provides an environment conducive to pathogen growth (Kaneko et al., 1999).The use of DNA amplification to generate genomically distinct groups of products has played an increasingly important role in the differentiation of bacterial species, serotypes and strains (Jensen & Hubner, 1996). Plasmids are important agents of gene flux and have been found to be responsible for the dissemination of multiple antibiotic resistance genes (Compain et al., 2014). Bacterial plasmids are known to confer a wide variety of phenotypic modifications and genetic flexibility upon their hosts by carrying genes that may code for toxin production, iron sequestration, adhesiveness and serum resistance (Novick, 1982; 1989). The existence of such plasmids in Salmonella species (Holmberg et al., 1984) and Enterobacteria (Lamb et al., 1984) has been well documented and comparative plasmid DNA analysis has been useful for tracing the source of outbreaks of salmonellosis (Bakeri et al., 2003).Multidrug resistant strains of these enteric bacteria were observed in this study. These antibiotic resistance profiles indicate that they may be responsible for increasing the case fatality rates of enteric diseases (Lewis et al., 2005; Malla et al., 2005). The case fatality rates of Salmonella infections are increasing globally, especially in the south Asian countries (Crump et al., 2003; Galanis et al., 2006). Plasmid mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) determinants have been described in multiresistant clones with worldwide distribution (Woodford et al., 2011, Cruz et al., 2013). Continued resistance of the isolates, after curing, to Ampicillin maybe mediated by alternative mechanisms such as changes in penicillin-binding proteins as observed by Kessie et al. (1998). Many other reports indicate that MDR Salmonella sp are the leading pathogens responsible for opportunistic infections among AIDS patients in Africa (Cardinale et al., 2005). There is no evidence here that these multi drug resistant isolates have been spread under the selective pressure of antimicrobial use but in the case of Salmonella, clonal spread of multi resistant strains have been detected (Tamada et al., 2001; Kijima-Tanaka et al., 2005). Bhatta et al., (2007) reported resistance of Salmonella isolates to Nalidixic acid as an indication of decreased sensitivity to ciprofloxacin. In this work, all Salmonella spp were sensitive to both Nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin. Shigella, E. coli and Enterobacter whose symptoms are closely related were resistant to Nalidixic acid though they were all sensitive to ciprofloxacin. The possible linkage between biocide and antibiotic resistance has also been discussed by researchers but not in the specific case of Salmonella and E. coli (Maillard, 2002). Shigellosis is endemic throughout the world with over 165 million cases, of which majority are in developing countries (WHO/IVR, 2003). A more recent annual estimate of shigellosis throughout the world was estimated to be 90 million incidences and 108,000 deaths (WHO, 2009). Shigella dysenteriae and Shigella flexneri are the predominant species in tropical areas, whereas Shigella sonnei is predominantly isolated in industrialized countries. Besides the self- limiting duration of the disease, effective antimicrobial therapy reduces the duration and severity of the dysentery and can also prevent potentially lethal complications. Antimicrobial resistance in enteric pathogens is of major concern in developing countries, where the rates of diarrhoeal diseases are highest due to socioeconomic and behavioural factors. Because of the increased resistance to most of the widely used and inexpensive antibiotics (ampicillin, nalidixic acid, cotrimoxazole, tetracycline and chloramphenicol), effective treatment is becoming increasingly difficult (Sack et al., 2001). Increased incidence of resistance to antimicrobial agents among Shigella spp. presents a major threat in the control of shigellosis. In this work the antibiotic resistance profile of Shigella species was high. In many parts of the world, strains of all Shigella species have become resistant to all these low-cost antimicrobials, and quinolones- such as norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin- are one of the few remaining groups of effective drugs (Sack et al., 2001) although Enterobacteriaceae bacteria resistant to ciprofloxacin (62%) were isolated in Argentina and PMQR genes were detected in 33% (Halova et al., 2014). Multiple resistant strains have occurred in Africa (Egah et al., 2003), This is in agreement with the results of this work.Multidrug resistant Enterobacter sp was isolated in this study. There has been an increase in the reported incidence of plasmid-mediated extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) in Enterobacter spp. Infections caused by ESBL- producing Enterobacter cloacae have become a serious clinical problem in many countries such as USA, Taiwan and Korea (Park et al., 2005). In contrast to other opportunistic pathogens, Salmonella spp are causative agents of zoonotic rather than nosocomial infections. In this regard, widespread use of antimicrobial agents in domestic animals of economic importance may have also contributed to increased levels of resistance in Salmonella spp (Orman et al., 2002).In conclusion, the results of this study confirm that many of the existing antibacterial agents are under threat from the widespread emergence of bacterial resistance. New agents are therefore urgently needed to counter the threats posed by antibiotic-resistant organisms. Pathways and targets for existing antibiotics can further be exploited for the discovery of novel agents. This study reveals that the efforts being made by food standards regulatory bodies are inadequate to meet the RTE food quality standards. Establishment of a systematic and regular mechanism for surveillance and monitoring is urgently needed to minimize the risks attached to consuming these foods. The findings of this study could be useful in formulation of food-borne disease control and prevention strategies locally and internationally.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors wish to thank Dr. S. I. Smith for the use of the Biotechnology Laboratory at NIMR, Lagos, Nigeria.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML