-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2015; 5(4): 138-143
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20150504.06
Safety Evaluation of Traditional Cheese Wagashi Treated with Essential Oils in Wistar Rats: A Subchronic Toxicity Study
Philippe Sessou1, Jean Robert Klotoe1, 2, Victorien Dougnon1, Sawab Deen Osseni1, Eustache Hounkpe1, Paulin Azokpota3, Youssao Issaka1, Frederic Loko1, Dominique Sohounhloue4, Souaïbou Farougou1
1Laboratoire de Recherche en Biologie Appliquée, Ecole Polytechnique d’Abomey-Calavi/Université d’Abomey-Calavi, 01 BP 2009 Cotonou, Bénin
2Laboratoire de Physiologie-Pharmacologie de l’Ecole Normale Supérieure (ENS) de Natitingou, Université de Parakou, BP: 72 Natitingou, Bénin
3Laboratoire de Formulations Alimentaires et de Biologie Moléculaire/ Faculté des Sciences Agronomiques/Université d’Abomey-Calavi, 01 BP 526 Cotonou, Bénin
4Laboratoire d’Etude et de Recherche en Chimie Appliquée, Ecole Polytechnique d’Abomey-Calavi/Université d’Abomey-Calavi, 01 BP 2009 Cotonou, Bénin
Correspondence to: Philippe Sessou, Laboratoire de Recherche en Biologie Appliquée, Ecole Polytechnique d’Abomey-Calavi/Université d’Abomey-Calavi, 01 BP 2009 Cotonou, Bénin.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This investigation was carried out to evaluate the safety of traditional cheese wagashi mixed with each essential oil of Cymbopogon citratus, Ocimum gratissimum, Pimenta racemosa and Syzygium aromaticum. Single dose of 2000 mg/kg b.w. of treated wagashi were daily administered to each two-month old rats by oral route for subchronic toxicity assessment based on combined OEDC guidelines 407 and 423 for 28 days. Three control groups received, respectively cheese mixed with sorbic acid, basal cheese and a commercial rat diet (Cecuri®) only during the same period. Blood collection from experimental animals was made at different times (0, 7, 14 and 28 days) for hematological and biochemical [creatinine, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and blood urea] parameters determination. The results showed that the mean values of parameters determined for rats fed with cheese treated with essential oils did not significantly vary (p<0.05) with respect to the control (basal cheese). At the end of the study, all the biochemical parameters sought decreased. Moreover, the rats, which have consumed wagashi mixed with sorbic acid have their hemoglobin significantly (p<0.05) decreased at the day 14. The study revealed that wagashi mixed with these oils had no toxicological effects and could possess hepatoprotective properties.
Keywords: Safety, Wagashi, Subchronic toxicity, Essential oil, Hematology, Biochemistry, Wistar rats
Cite this paper: Philippe Sessou, Jean Robert Klotoe, Victorien Dougnon, Sawab Deen Osseni, Eustache Hounkpe, Paulin Azokpota, Youssao Issaka, Frederic Loko, Dominique Sohounhloue, Souaïbou Farougou, Safety Evaluation of Traditional Cheese Wagashi Treated with Essential Oils in Wistar Rats: A Subchronic Toxicity Study, Food and Public Health, Vol. 5 No. 4, 2015, pp. 138-143. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20150504.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Dairy products like milk are consumed for the nutrition and maintenance of good health for a very long time. Milk is a major source of dietary energy, protein and fat, contributing on average of 134 kcal of energy/capita per day, 8 g of protein/capita per day and 7.3 g of fat/capita per day in 2009 [1]. Milk also contains nutrients critical for growth and development, including calcium, vitamin A, riboflavin and vitamin B12 [2]. Water is the main component in all milks, ranging from an average of 68 percent in reindeer milk to 91 percent in donkey milk. The main carbohydrate content in milk is lactose, which is involved in the intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium and phosphorus, and the utilization of vitamin D [3]. The demand for milk in developing countries is expected to increase by 25 percent by 2025 [4]. The milk is a highly perishable commodity which requires a treatment to extend its shelf life. In fact, because of its high water content and nutrients, milk undergoes rapid degradation under the influence of microorganisms which are in optimal conditions for their development in tropical countries. In the absence of a cold chain in these countries, this situation imposes to the actors of milk sector the development of preservation methods more or less adapted to the socio-economic and environmental conditions. In Benin, milk is processed into various products such as yoghurt, curd and especially wagashi, a cheese from a craft process controlled by the Fulani social group. The wagashi is the most popular and most consumed milk by-product in Benin [5, 6]. Wagashi is still produced on a small scale at cottage level, and its manufacturing is mainly based upon traditional techniques. Because of its production in unhygienic conditions and unregulated temperatures of production and preservation, wagashi has a very short shelf life. In view of this, various chemical substances such as propionic acid, sorbic acid were used to improve the quality of this product and extend its shelf life with probable occurrence of chemical residues in wagashi [7]. According to Shaw [8], the presence of chemical residues in foods such as wagashi is major concern because they affect consumer's health. As consumers have increasingly expressed a desire for safe foods and the preference for foods free of synthetic additives like benzoate, sorbate and propionate, the need for naturally derived compounds and other natural products with antimicrobial properties has been explored. Thus, great emphasis has recently been focused on the utilization of spices and their essential oils as natural agents for food preservation [9, 10]. Although the main role of these substances of plant origin is for flavoring and seasonings, they have strong medicinal, preservative and antioxidant properties, and thus contribute to the overall safety and preservation of foods [11, 12]. Essential oils are valuable plant products possessing good to excellent antioxidant and antimicrobial properties [13]. This lead to a new perspective on the potential application of essential oils in various food systems to improve their acceptability and durability. A variety of bioactivities of Pimenta racemosa, Cymbopogon citratus, Ocimum gratissimum and Syzygium aromaticum essential oils are known, with antioxidative, antimicrobial, antiinflammatory properties demonstrated. Furthermore, biopreservatives studies of these oils have been reported [14]. Despite the widespread use and biological tests on these oils, few scientific studies have been undertaken to ascertain their safety in combination with food especially with cheese. The main objective of this investigation is to evaluate the safety of wagashi samples treated with essential oil extracted from different plants such as Cymbopogon citratus, Pimenta racemosa, Ocimum gratissimum and Syzygium aromaticum.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
- A total of 42 male and female two-month old Wistar rats were selected after physical and behavioral examination for the study. Selected females were nulliparous and non-pregnant. The animals were maintained according to standard guidelines. In fact, the two-month old Wistar rats were kept under standard laboratory conditions (25°C) and 12/12h light/dark cycle. The animals were prior acclimatized for two weeks and received a commercial rat diet (Cecuri®) and tap water ad libitum. They were isolated in cages and divided into seven groups, each group composed of six animals. Each group of rats were fed with one of the following seven diets including: three control diets (basal cheese, cheese mixed with 1000 ppm of sorbic acid, commercial rat diet Cecuri® produced in Benin) and four test diets (basal cheese mixed with each of essential oil at 1000 ppm concentration).
2.2. Essential oils and Synthetic Preservative Studied
- Essential oils were extracted from Pimenta racemosa, Cymbopogon citratus, Ocimum gratissimum and Syzygium aromaticum using the method as described by [6, 14]. Sorbic acid was purchased and used as synthetic preservative for control.
2.3. Experimental Assay
- A single dose of 2000 mg/kg b.w of traditional cheese was orally administrated daily for 28 days by gavage to each Wistar rat for the subchronic toxicity studies according to a well-designed protocol based on Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Guidelines for Testing Chemicals, Health Effects Test Guidelines (OECD-guidelines 407 and 423) [15, 16]. The study was conducted in compliance with the OECD principles on Good Laboratory Practices. Biochemical (alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum creatinine and blood urea) and hematological (Red Blood Cell (RBC), White Blood Cell (WBC), hematocrit (Hct), hemoglobin (Hb), platelet count) parameters were evaluated. Blood Analysis: At each time (day 0, 7, 14and 28) of the assay, animals were fasted for hours, but allowed access to water ad libitum. Then anesthetized with chloroform, and the blood samples were obtained by retro-orbital puncture [17], using capillary tubes for hematological and biochemical studies, with and without anticoagulant, respectively. Hematological analyses were done using standard techniques. Red Blood Cell (RBC), White Blood Cell (WBC), hematocrit (Hct), hemoglobin (Hb), platelet count of blood samples were determined using fully automated hematology analyzer (Auto Hematology Analyzer, RT-7600, Rayto). Aliquots of whole blood samples were mixed with EDTA and applied to the analyzer. Blood samples for biochemical analyses were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 min and the plasma collected and analyzed. The blood level of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum creatinine and blood urea were determined by enzymatic kinetic method using spectrophotometer (BioLabo Diagnostics, Kenza Max, Biochemistry) at 505 nm [18].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- The data obtained were analyzed using SAS software (1989). The average values of each parameter determined were calculated by treatment at different times of bloods analysis taken. Comparisons between these means were made in pairs by Student's t test. The significance obtained for each effect was determined for each period of blood analysis by the F test after analysis of variance (ANOVA). The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
3. Results and Discussion
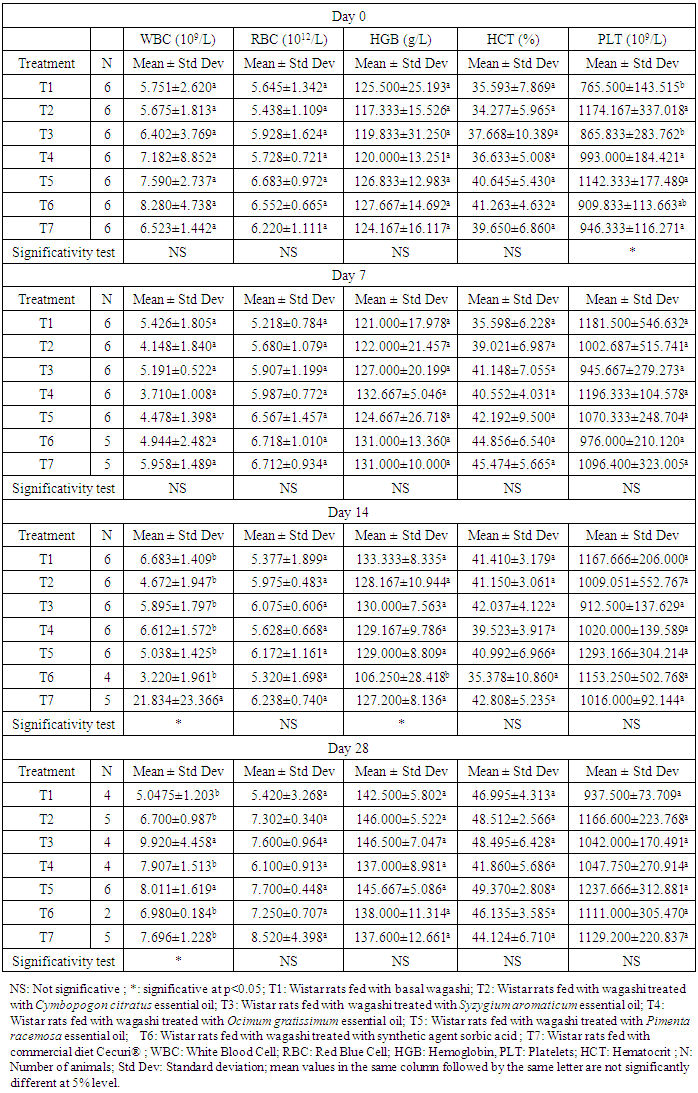
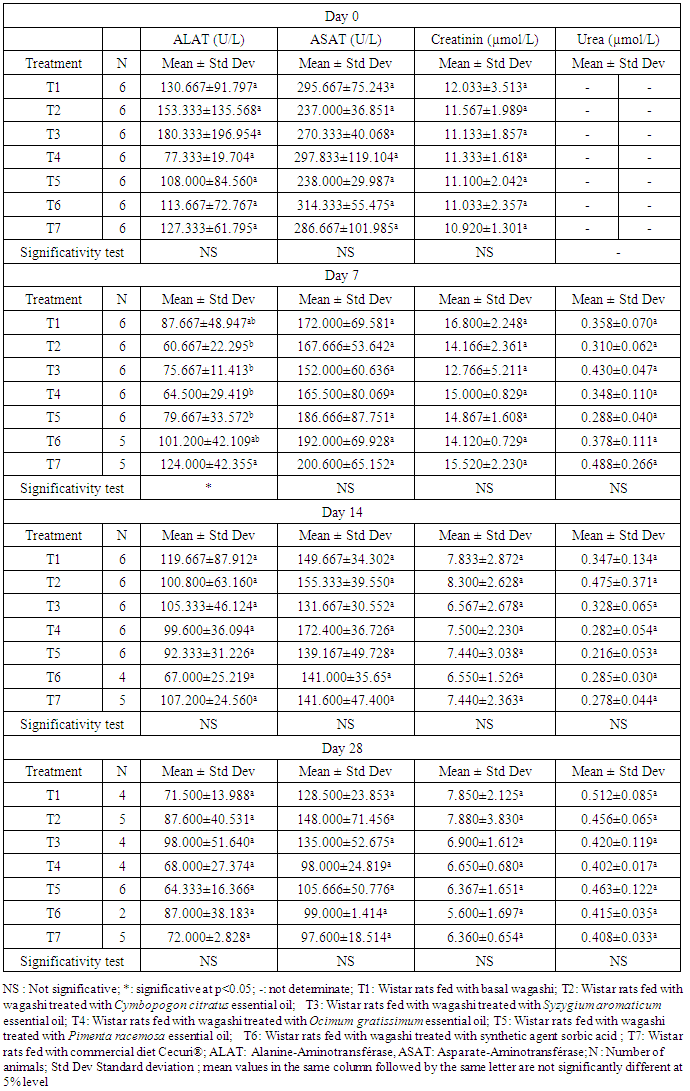
- The effects of treatments on hematological parameters and biochemical profiles (table 1 and 2) on rats’ groups during the assay has shown in table 1 and table 2, respectively. The results showed that except for a slightly increase in platelet counts of some treatment groups, compared to the control group (treatment with basal or natural cheese), there were no significant differences in the mean values of hematological and biochemical parameters in rats at the first (day 0). This means probably that the homogenicity of the treatment groups at the begining of the experimentation. Regarding the hematology, there were no treatment-related adverse effects of treated wagashi with essential oils on hematology parameters in rats (Table 1). However, some significant differences were observed when compared the control (basal or natural wagashi cheese) and treatment groups. Indeed, a statistically significant increase in mean values of WBC for the treatment 7 (rats fed with commercial diet Cecuri®) and significant decrease in hemoglobin concentration were noted in group of rats treated with cheese added ofsorbic acid at the day 14. The decreasing of hemoglobin noticed in this group may affect the transport of oxygen to organs that may be at the origin of death of rats noticed in this group during the blood collection. The significant increase of WBC for the treatment 7 and the statistically significance observed for platelets percentage at the begining of the experimentation may be incidental. In fact, according to [19], occasionally, statistical differences obtained from control values in hematology are judged to be incidental. The mean values of red blood corpuscle, white blood corpuscle, hemoglobin, hematocrit and platelets concentrations of all treatment groups were similar to control (fed with basal cheese) group animals. Concerning the serum chemistry, there were no treatment-related biologically significant adverse effects of cheese treated with essential oils on serum chemistry parameters in rats (Tables 2). However, some statistically significant differences were noted when the control (fed with basal cheese wagashi) and treatment groups were compared. Administration of the cheese treated at dose level of 2000 mg/kg/day to rats resulted in a decrease in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and serum creatinine. As increase in the activities transaminases ALT, AST and creatinine, good indicators of liver and kidney functions respectively, represents liver damage and kidney [20, 21, 22], decrease in the activities of these enzymes is not considered of any toxicological significance. It is then reasonable to deduce that all the treatment did not induce any damage to the liver and the kidneys. This may be further confirmed by the histological assessment. It is important to notice that a significant increase in alkaline phosphatase activity was observed in rats treated with commercial diet (Cecuri®) at day 7 and progressively decrease to the normal value of the control (basal cheese) the day 28th. Hence, change in this parameter in this group was not to be considered as treatment-related. Also, the mean values of serum urea of all treatment groups increase with the consumption of these feeds. This fact can be probably related to the high proteins value contents of the feeds (cheese and commercial diet) used. The increase of urea blood probably due to the consumption of protein by groups of rats is not considering as toxicological effect. Hence, there were no other statistically significant differences when the respective control and/or treatment groups were compared. The results of serum chemistry analysis from treatment groups show that administration of cheese treated with essential oils of Cymbopogon citratus, Ocimum gratissimum, Pimenta racemosa and Syzygium gratissimum at dose of 2000 mg/kg/day to rats for 28 days did not cause toxicologically significant adverse effects. Globally, the results obtained from this work showed that the mean values of parameters determined for rats fed with cheese treated with essential did not vary significantly with respect to the control (basal cheese) at any day of analysis expected the rats fed with cheese added of sorbic acid which had their hemoglobin value decreased. At the end of the study, all the biochemical parameters sought such as serum creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine especially aminotransferase (ALT) decreased for all the treatments groups. ALT is thought to be more specific for hepatic injury because it is present mainly in the cytosol of the liver and in low concentrations elsewhere, whereas AST is a mitochondrial enzyme found in the heart, liver, skeletal muscle, and kidney and is normally present in plasma [23]. The decreasing of biochemical parameter, especially ALT means that the samples of cheese treated with essential oils could have a hepatoprotective activity [18]. Moreover, the rats, which have consumed wagashi treated with sorbic acid have their hemoglobin significantly (p<0.05) decreased at after 14 days. The decrease of hemoglobin is probably due to the destruction of hemin which is the second constituent of hemoglobin by the sorbic acid. In fact, according to [24], use of food additives such as sorbic acid involved the reduction of hemoglobin due to the destruction of hemin and hence of part of hemoglobin. The study revealed that wagashi treated with each of these oils had no toxicological effects and could possess hepatoprotective properties. Consumption of wagashi treated with these oils may be promoted in order to benefit of its multiple nutritional and healthy advantages.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- Because of a lack of significant negative changes in the biochemical and hematological parameters of rats after 28 days daily feeding with treated wagashi with essential oils studied, it may be concluded that wagashi samples treated with each of essential oils of pimenta racemosa, cymbopogon citratus, ocimum gratissimum and syzygium aromaticum don’t appear to have significant toxicity. Further study on histological assessment may be done to confirm these results. Consumption of wagashi cheese treated with these oils may be promoted in order to profit of benefic effects of these oils and cheese wagashi.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors are grateful to International Foundation for Science for their financial support through Individual grant E5390. They are also thankful to Dr Joseph Hounhouigan, Full Professor at University of Abomey-Calavi for his scientific contribution. Authors do not forget Mr Rodrigue Towanou, Ferdinand Dougnon, Hornel Koudokpon, François Dossa, Serge Ahounou and Lauris Fah for their invaluable technical contribution.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML