-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2015; 5(4): 122-126
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20150504.04
Microbiological Analysis of Three of Smoked Fish Obtained from the Ondo State, Nigeria
Felix O. Akinwumi1, Kehinde T. Adegbehingbe2
1Department of Environmental Biology and Fisheries, Adekunle Ajasin University, Akungba-Akoko, Nigeria
2Department of Microbiology, Adekunle Ajasin University, Akungba-Akoko, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Felix O. Akinwumi, Department of Environmental Biology and Fisheries, Adekunle Ajasin University, Akungba-Akoko, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The consumption of smoked fish usually obtained from the open shelf in most communities of the developing countries has raised some health related concerns. This research investigated the microbiological quality of three commercially important smoked fish, Clarias gariepinus (African mud catfish), Sardinella eba (herring) and Oreochromis niloticus (tilapia) obtained from fish mongers in three popular fish markets, Akure, Okitipupa and Akungba-Akoko in Ondo State, south west Nigeria. The total plate, coliform, Salmonella-shigella, Staphylococcus aureus and fungal counts of the heads, muscles and the heads of the fish samples were determined using standard methods. The ranges of the total plate, coliform, Salmonella-shigella, and Staphylococcus aureus were 1.3X104 cfu/ml - 2.8X105 cfu/ml, 3X103 cfu/ml - 1.9X105 cfu/ml, 1.2X104 cfu/ml - 5.4X104 cfu/ml and 1.4X104 cfu/ml - 2.8X105 cfu/ml respectively. The samples obtained from Akure market had the highest counts in most samples followed by those obtained from Okitipupa market while samples obtained from Akungba-Akoko market had the lowest counts. It is recommended that in order to prevent the spread of organisms that are of public health importance, fish should be processed, stored and distributed under safe hygienic conditions and good sanitary practices.
Keywords: Smoking, Fish, Microorganisms, Pathogens, Health
Cite this paper: Felix O. Akinwumi, Kehinde T. Adegbehingbe, Microbiological Analysis of Three of Smoked Fish Obtained from the Ondo State, Nigeria, Food and Public Health, Vol. 5 No. 4, 2015, pp. 122-126. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20150504.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Fish constitutes an important source of protein intake of many people, particularly in the developing countries. In Nigeria, where about 41% of the total animal protein intake is obtained from fishery products, the total fish consumption rate has risen to 2.66 million metric tons annually [24]. [23] reported that fish is a major source of animal protein and an essential food item in the diet of Nigerians because it is relatively cheaper than meat. Fish contains most of the important essential amino acids, particularly, lysine, methionine and tryptophan that are lacking in plant proteins. It is also an important source of vitamins and minerals which are important for good living [2]. Apart from its food value, fish has been reported to possess medicinal values, such as, in the amelioration of asthma, arthritis, coronary heart diseases, goitre and cancer [15].However, fish is a perishable food material that deteriorates soon after harvest at high ambient temperature [1], therefore, needs immediate preservation. The methods by which fish could be preserved include, freezing, salting, sun-drying, oven-drying, fermentation and smoking [10, 14]. In Nigeria, fish either obtained from a cultured pond or from the wild is sold to consumers as fresh, frozen, smoked or sun-dried. Smoked fish is highly desirable because of its enhanced flavour and texture in fish in addition to the protection offered by smoking against microbiological, enzymatic and chemical deteriorative alterations [27]. [5] observed that smoking demonstrated a better efficient method of fish processing in terms of the retention of protein value and reduction in the moisture content. [29] reported that smoke-drying had been used for centuries in preserving fish, and is still widely used for this purpose among several communities in the third world where up to 70% of the catch is smoked. In industrialized countries, however, fish smoking is done for enhancement of flavour and texture, often producing value added products whose preservation is achieved by other means. In many developing communities, smoked fish are usually hawked without taking cognizance of the microbial contamination from the environment. In Nigeria, smoked fish products could be contaminated with microorganisms from the processing units and the market centers before reaching the consumers because many processors and hawkers usually display them openly in a manner that could be potential sources of microbial contamination. The aim of this study, therefore, was to isolate the possible microorganisms associated with smoked fish with a view to assessing the level of their public health implications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
- The samples of dried smoked fish used for this study were obtained from fish mongers at popular fish markets in Akungba-Akoko, Akure and Okitipupa in Ondo State, Nigeria. The species of the smoked fishes sampled were catfish (Clarias gariepinus), herring (Sardinella eba) and tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). The fish were purchased in batches and were brought to the laboratory of the Department of Microbiology, Adekunle Ajasin University, Akungba-Akoko for microbiological analysis.
2.2. Preparation of Samples and Enumeration of Microorganisms
- The fish samples were surface sterilized separately in 3.5% sodium hypochlorite solution (w/v) with constant agitation for 7 minutes, rinsed thoroughly with sterile distilled water until the traces of hypochlorite were removed and were then dried in an oven at 45°C for 24 hours. The heads, muscles and the tails of the fish samples were pulverized separately using a blender (maker). Five milliliters were taken from each sample into a sterile bottle containing 450 ml of sterile peptone physiological saline to form a stock culture. The sample bottles were placed on a rotator shaker at 120 RPM for 1 hour. 10-fold dilutions were subsequently prepared with peptone physiological saline. Aerobic mesophilic bacteria were enumerated on plate count agar (PCA, Oxoid) at 37°C for 24 hours and reported as total viable count (TVC). Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) were enumerated on de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe Agar (Merck) and incubated anaerobically at 30°C for 48 hours. Presumptive LAB was confirmed by oxidase and catalase tests, and confirmed counts were reported as lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Enterobacteriaceae were enumerated on Violet Red Bile Glucose at 37°C for 24 hours while Staphylococci were counted on mannitol salt agar (Oxoid) at 30°C for 48 hours). Yeasts and moulds were enumerated on Oxy-tetracycline glucose yeast extract agar (OGYEA, Oxoid CM0545) 25°C for 72 hours.
2.2.1. Identification of Bacteria
- Inocula were aseptically transferred from each slide into plates of respective media using a streak plate technique. The isolates were purified by repeated streaking on their respective media. Bacterial plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours while fungal plates at 25°C for 72 hours. A 24 hour old culture was prepared from each plate for identification purposes. Bacteria isolates were identified based on their cultural characteristics, Gram staining reaction and various identification tests. Isolates were identified according to [19]. Lactic acid bacteria were also identified by assaying in API 50 CHL galleries (BioMerieux).
2.2.2. Identification of Fungi
- Mould isolates were cultured by three point inoculation on CYA and MEA at 25°C for 5 days. The young cultures of the isolates were stained with lactophenol-blue and identified to the genus level by colony and cell morphology and biochemical tests according to [7].
2.3. Determination of Water Content
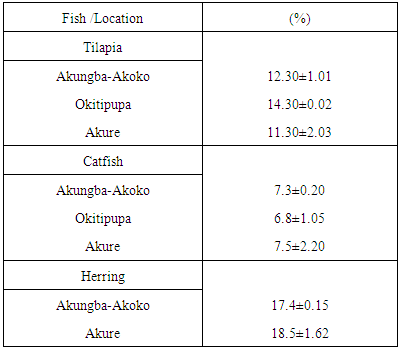
- The water contents in the smoked fish samples were determined through a standard laboratory procedure as described by [9].
3. Results and Discussion
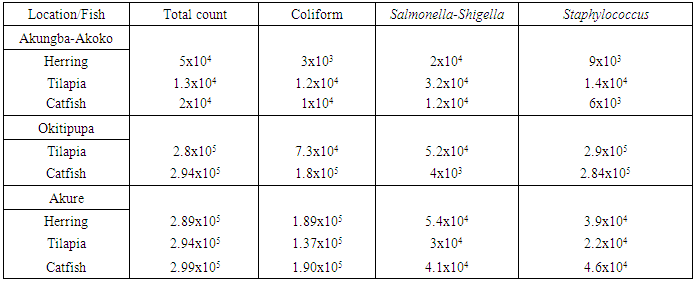
- The mean values of the total, coliform, Salmonella-shigella and Staphylococcus counts of the smoked fish samples are shown in Table 1. Among the tilapia species, the highest total count (2.9x105 cfu/g) was found in the samples obtained from Akure (AKR) market while the lowest count (1.3x104 cfu/g) was observed in the samples hawked in Akungba-Akoko (AKG). A similar trend was also observed in the coliform count of the tilapia sample with the highest value (1.37x105 cfu/g) and lowest (1.2x104 cfu/g) obtained in in the AKR and AKG markets, respectively. The highest Salmonella-Shigella (5.2x104 cfu/g) and Staphylococcus (2.9x105 cfu/g) counts were obtained in the tilapia samples displayed in Okitipupa (OKP) market in comparison to the lower counts of 3.0x104 cfu/g (Salmonella-Shigella) and 1.4x104 cfu/g (Staphylococcus) found in the AKR and AKG samples, respectively.
|
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
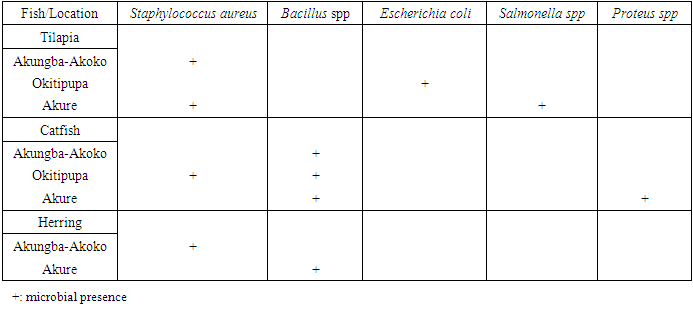
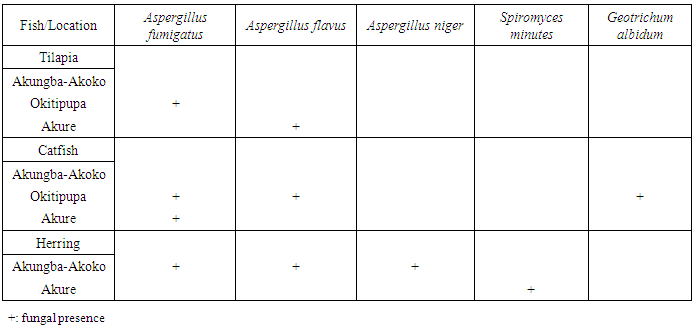
- The pathogenic microorganisms implicated in the smoked fish samples are of public health importance. Therefore, fish processors, retailers or vendors should be educated to observe strict hygienic measures. Potable water should be used during processing of smoked fish and they should be properly cooked before consumption because many consumers often eat hawked smoked directly fish without further processing. Proper storage of smoked fish is also necessary because poor storage methods and unhygienic handling of the items are known to predispose dried fish to microbial contamination. The identified organisms are entirely preventable by practicing good sanitation and proper food handling techniques. To prevent an incidence of food contamination and intoxication in foods, there is a need to educate and advocate for the importance of environmental sanitation and good food handling practices, especially, proper hand-washing practices among fish handlers.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML