-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2014; 4(6): 266-271
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20140406.02
Policy Options on Reduction of Foodborne Diseases
Olasunmbo A. Ajayi1, 2, J. O. Oluwoye3, L. L. Williams4
1Department of Food and Animal Sciences, Alabama Agricultural and Mechanical University, Food Microbiology, AL, USA
2Department of Food Science and Technology, Bowen University, Iwo, Osun State, Nigeria
3Department of Community Planning and Urban Studies, Alabama Agricultural and Mechanical University, AL, USA
4Center of Excellence in Post-Harvest Technologies, North Carolina A and T State University, the NC Research Campus, USA
Correspondence to: Olasunmbo A. Ajayi, Department of Food and Animal Sciences, Alabama Agricultural and Mechanical University, Food Microbiology, AL, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
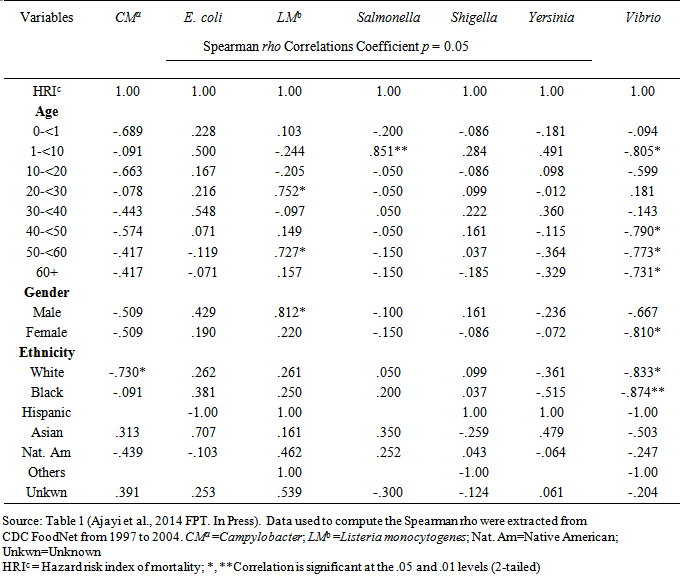
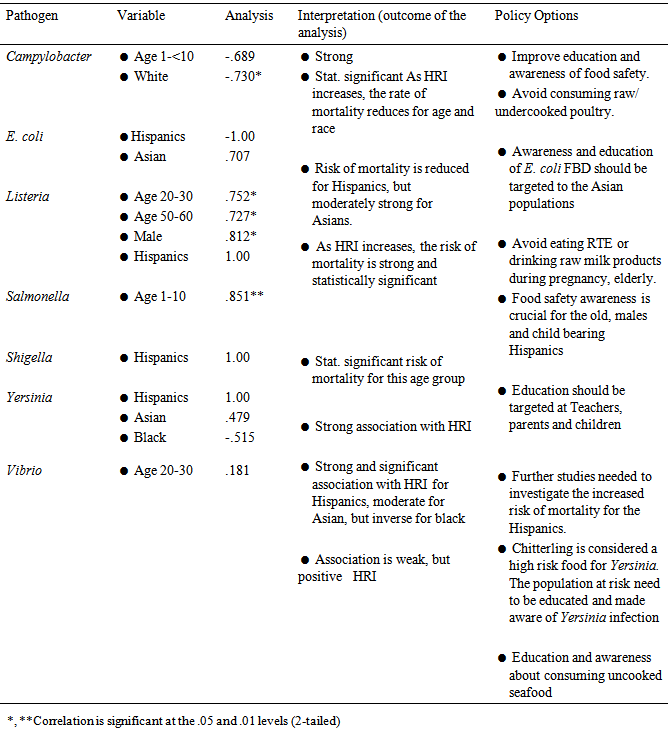
This study explores policy options that can reduce prevalence of foodborne diseases. Using FoodNet surveillance data from 1997-2004, hazard risk index of mortality (HRI) was calculated and the relationship between age, gender and ethnicity were explored and used to develop policy options. The results show there were significant association between risk of mortality from Salmonella outbreaks and children (rho=.851**, p=.007) and statistically significant (p<0.01); Listeriaoutbreaks and ages (20-30 (rho=.752, p=.032); 50-60 (rho=.727, p=.041)); and men (rho=.812*, p=.014). Finally, there were strong associations between HRI and Hispanics, (rho=1.00) for Listeria compared to all other ethnic groups and for E.coli and the Asian ethnicity (rho=.707, p=.050). The conclusion of this paper is that public education and awareness of foodborne diseases is not adequate. Because there were statistically significant (p<0.05) association between HRI and age, gender and ethnicity, policy options should include food safety education, with emphasis to the ethnic groups, daycare/nursing homes workers, young and old. Consumption of raw or undercooked animal/seafood should be discouraged. Conclusively, public education on food safety and awareness of foodborne pathogens should be the responsibility of the government, health-care givers, parents and teachers.
Keywords: Policy options, Foodborne diseases, Association between hazard risk of mortality and age, Gender
Cite this paper: Olasunmbo A. Ajayi, J. O. Oluwoye, L. L. Williams, Policy Options on Reduction of Foodborne Diseases, Food and Public Health, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 266-271. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20140406.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Most foodborne diseases (FBD) are sporadic and occur as isolated cases. In public health practice, a foodborne disease outbreak is defined as the occurrence of at least two cases of similar illness, resulting from the consumption of common food [1]. Foodborne disease has emerged as an important issue of growing public health concern and economic problem in many countries [2]. The ultimate goal of all food safety programs is to stop contaminated food products from reaching the consumer. Surveillance for foodborne diseases is conducted to delineate the occurrence and burden of important public health concern [3]. To further show the urgency of foodborne diseases, a recent reported estimate by Jones [4] suggests that about 30% of all newly globally emerging infections included pathogens commonly transmitted through food. The government has established several types of surveillance programs in reporting cases of foodborne disease in the US, including consumer complaints, notifiable disease surveillance, outbreak reports and detection of enteric diseases transmitted through food [5]. Food stuff in the US is considered to be one of the safest worldwide because of the different reporting or surveillance programs. Furthermore, FoodNet surveillance is enhanced and focused on a handful of enteric foodborne pathogens. It is considered to be active surveillance, because FoodNet investigators are in regular contact with the area laboratories in the catchment area in 10 states namely: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Maryland, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Oregon and Tennessee. Although the surveillance of foodborne diseases is commendable, it is not robust enough. It is further complicated by several other factors, which pose serious challenges to the public health. The challenges include underreporting and under-diagnosis [6], frequent contamination of raw food supply [7], expansion of global transportation and supply of perishable goods or foods from different parts of the world [8], consumers lack of awareness in safe food handling and preparations [7, 9, 10], consumers’ high risk behavior and desires for new taste and food experiences, continuous exposure of consumers to emerging foodborne pathogens and new vehicles of transmission of foodborne pathogens and increasing number of population at risk [11, 12]. It has been suggested that there are three major forms of protection against foodborne diseases. Ensuring food safety should be a three prong approach, in which the government, industry and the consumer play specific roles in ensuring a safe food supply. The role of the government include public health; encouraging the food industry including farmers by providing safe food handling training and guidance, to undertake voluntary measures to promote food safety. In addition, the industries are expected to produce food under Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), establish and employ The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system; and voluntarily establish necessary system for safety assurance of their products by adopting appropriate protocols and new technology for quick detection of pathogens in food. Immediate product recall and removal from shelves should be enacted in cases of accidental contamination. Educating all food handlers from “farm to table” or “boat to throat” [8] will improve the hygienic quality of raw food supply. Tauxe [3] reported that the food industry in the United States had more microbiological food safety challenges now more than before. The importance of food safety assurance should be conveyed to the directors and managers as well as the workers for the safety of their product [13]. Prompt response and detection of an outbreak may limit the negative impact on public health by improving confidence in food supply and preventing future outbreaks [14]. Moreover, individuals should have access to precise information about the food they consume [13]. Therefore, the main objective of this paper is to explore policy options that can reduce the prevalence of foodborne diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surveillance Data
- Secondary data of foodborne disease outbreaks were obtained from 1997 to 2004 from the Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet) [15]. FoodNet is an active population-based surveillance system. Foodborne diseases reported cases under surveillance per 100,000 individuals in the population for each bacteria pathogen (Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Listeria, Shigella, Yersinia and Vibrio), based on age, gender, ethnicity and mortality were used to develop Hazard Risk Index.
2.2. Hazard Risk Index (HRI) Development
- Hazard risk index of mortality due to foodborne diseases was developed for each of the seven bacterial pathogens for 1997-2004 as described by [16]. Briefly, HRI was calculated as the number of foodborne disease cases from the FoodNet active surveillance data minus the foodborne disease mortality; divided by the number of cases.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- SPSS [17] (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) was used to obtain descriptive analysis of the data. Descriptive analysis of the independent variable characteristics used to develop the hazard risk index (HRI) was demographic characteristics of foodborne disease cases including age; gender; ethnicity; and mortality rate. The Spearman rho correlation coefficient was used to determine the strength of the association between (HRI) of foodborne pathogens as dependent variable and the set of independent (age, gender and ethnicity) variables.
3. Results and Discussion
- Overall, from the analysis of the surveillance data retrieved from FoodNet, there is a continuous increase in prevalence of foodborne disease cases. Bacterial foodborne pathogens of major health concern are Escherichia coli, Campylobacter spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., and Yersinia spp. [18]. Pathogens such as Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, Yersinia spp. and Shigella spp. all have positive correlation with hazard risk index of mortality for children 1-<10 years old as shown in Table 1.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- Ensuring food safety should be a three prong approach, in which the government, industry and the consumer play specific roles in ensuring safe food supply. The goal of this paper is to explore policy options that can reduce the prevalence of foodborne diseases. The need to strengthen food safety education programmes for the prevention of foodborne diseases is increasingly being recognized by different countries [38]. Using secondary data from FoodNet surveillance on foodborne disease, this study finds that there were significant association between risk of mortality from Salmonella outbreaks and children (rho = .851**, p = .007) and statistically significant (p<0.01); Listeria outbreaks and ages (20-30 (rho = .752, p = .032); 50-60 (rho = .727, p = .041)); and men (rho =.812*, p = .014). There were also associations between HRI and ethnicity. Furthermore, policy options should include food safety education, with emphasis to the ethnic groups, daycare/nursing homes workers, young and old. Consumption of raw and un-cleaned plant foods or undercooked animal/seafood should be discouraged. Therefore, the conclusion of this paper is that public education and awareness of foodborne diseases is not adequate. There should be frequent and consistent public service announcements via the media outlets; schools; food stamp/Women Infants and Children (WIC) programmes; senior centers; nursing homes; and health care givers about foodborne diseases. Personnel from food safety programs should engage and teach school age children about the importance of proper hand washing, proper food handling and cooking technique. Reduction in the number of foodborne disease cases translate to reduction in absenteeism from school and market place.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML