| [1] | K. Edwin, Biofuels, climate change, and human population, in Global Economic and Environmental Aspects of Biofuels, CRC Press, 2012. |
| [2] | F. Cherubini, "The biorefinery concept: Using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals", Energy Conversion and Management, vol.51, no.7, pp.1412-1421, 2010. |
| [3] | R. Gupta, Demirbas, A., Renewable Energy Sources, in Gasoline, Diesel, and Ethanol Biofuels from Grasses and Plants, First Editionn ed., 2010. |
| [4] | D. Dhingra, M. Michael, H. Rajput, R. T. Patil, "Dietary fibre in foods: a review", Journal of Food Science and Technology, vol.49, no.3, pp.255-266, 2012. |
| [5] | D. Klemm, B. Philipp, T. Heinze, U. Heinze, W. Wagenknecht, General Considerations on Structure and Reactivity of Cellulose: Section 2.1–2.1.4, in Comprehensive Cellulose Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2004. |
| [6] | M. C. McCann, N. C. Carpita, "Designing the deconstruction of plant cell walls", Current Opinion in Plant Biology, vol.11, no.3, pp.314-320, 2008. |
| [7] | R. F. Evert, Cell Wall, in Esau's Plant Anatomy, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2006. |
| [8] | J. C. Thimm, D. J. Burritt, W. A. Ducker, L. D. Melton, "Celery (Apium graveolens L.) parenchyma cell walls examined by atomic force microscopy: effect of dehydration on cellulose microfibrils",NLM, Planta, vol.212, no.1, pp.25-32, 2000. |
| [9] | Y. Nishiyama, "Structure and properties of the cellulose microfibril", Journal of Wood Science, vol.55, no.4, pp.241-249, 2009. |
| [10] | M. E. Himmel, S. Y. Ding, D. K. Johnson, W. S. Adney, M. R. Nimlos, J. W. Brady, T. D. Foust, "Biomass recalcitrance: engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production", NLM, Science (New York, N.Y.), vol.315, no.5813, pp.804-807, 2007. |
| [11] | R. L. David, The Chemistry of Complex Carbohydrates, in Complex Carbohydrates in Foods, CRC Press, 1999. |
| [12] | P. Harmsen, W. Huijgen, L. Bermudez, R. Bakker, “Literature review of physical and chemical pretreatment processes for lignocellulosic biomass”, Wageningen UR, Food & Biobased Research, 2010. |
| [13] | H. V. Scheller, P. Ulvskov, "Hemicelluloses",NLM, Annual review of plant biology, vol.61, pp.263-289, 2010. |
| [14] | M. Borrega, K. Nieminen, H. Sixta, "Degradation kinetics of the main carbohydrates in birch wood during hot water extraction in a batch reactor at elevated temperatures", Bioresource Technology, vol.102, no.22, pp.10724-10732, 2011. |
| [15] | Y. Kim, T. Kreke, N. S. Mosier, M. R. Ladisch, "Severity Factor Coefficients for Subcritical Liquid Hot Water Pretreatment of Hardwood Chips", Biotechnology and Bioengineering, vol.111, no.2, pp.254-263, 2014. |
| [16] | X. Lu, S. Saka, "Hydrolysis of Japanese beech by batch and semi-flow water under subcritical temperatures and pressures", Biomass & Bioenergy, vol.34, no.8, pp.1089-1097, 2010. |
| [17] | M. Matsunaga, H. Matsui, Y. Otsuka, S. Yamamoto, "Chemical conversion of wood by treatment in a semi-batch reactor with subcritical water", Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.44, no.3, pp.364-369, 2008. |
| [18] | M. Carrier, A. Loppinet-Serani, C. Absalon, C. Aymonier, M. Mench, "Degradation pathways of holocellulose, lignin and alpha-cellulose from Pteris vittata fronds in sub- and super critical conditions", Biomass & Bioenergy, vol.43, pp.65-71, 2012. |
| [19] | L. Cheng, X. P. Ye, R. He, S. Liu, "Investigation of rapid conversion of switchgrass in subcritical water", Fuel Processing Technology, vol.90, no.2, pp.301-311, 2009. |
| [20] | K. Tekin, S. Karagoz, S. Bektas, "Hydrothermal liquefaction of beech wood using a natural calcium borate mineral", Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.72, pp.134-139, 2012. |
| [21] | G. Garrote, J. C. Parajó, "Non-isothermal autohydrolysis of Eucalyptus wood", Wood Science and Technology, vol.36, no.2, pp.111-123, 2002. |
| [22] | H. Pinkowska, "Low-temperature biomass gasification in subcritical and supercritical water", Przemysl Chemiczny, vol.86, no.7, pp.599-606, 2007. |
| [23] | Y. Zhao, W.J. Lu, H.T. Wang, J.L. Yang, "Fermentable hexose production from corn stalks and wheat straw with combined supercritical and subcritical hydrothermal technology", Bioresource Technology, vol.100, no.23, pp.5884-5889, 2009. |
| [24] | C. C. Song, H. Q. Hu, S. W. Zhu, G. Wang, G. H. Chen, "Nonisothermal catalytic liquefaction of corn stalk in subcritical and supercritical water", Energy & Fuels, vol.18, no.1, pp.90-96, 2004. |
| [25] | C. Sanchez, I. Eguees, A. Garcia, R. Llano-Ponte, J. Labidi, "Lactic acid production by alkaline hydrothermal treatment of corn cobs", Chemical Engineering Journal, vol.181, pp.655-660, 2012. |
| [26] | G. Garrote, E. Falque, H. Dominguez, J. C. Parajo, "Autohydrolysis of agricultural residues: study of reaction byproducts",NLM, Bioresour Technol, vol.98, no.10, pp.1951-1957, 2007. |
| [27] | S. Kumar, U. Kothari, L. Kong, Y. Y. Lee, R. B. Gupta, "Hydrothermal pretreatment of switchgrass and corn stover for production of ethanol and carbon microspheres", Biomass & Bioenergy, vol.35, no.2, pp.956-968, 2011. |
| [28] | R. Vegas, M. Kabel, H. A. Schols, J. L. Alonso, J. C. Parajó, "Hydrothermal processing of rice husks: effects of severity on product distribution", Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, vol.83, no.7, pp.965-972, 2008. |
| [29] | L. Kong, G. Li, H. Wang, W. He, F. Ling, "Hydrothermal catalytic conversion of biomass for lactic acid production", Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, vol.83, no.3, pp.383-388, 2008. |
| [30] | S. Hata, J. Wiboonsirikul, A. Maeda, Y. Kimura, S. Adachi, "Extraction of defatted rice bran by subcritical water treatment", Biochemical Engineering Journal, vol.40, no.1, pp.44-53, 2008. |
| [31] | T. Ingram, T. Rogalinski, V. Bockemühl, G. Antranikian, G. Brunner, "Semi-continuous liquid hot water pretreatment of rye straw", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.48, no.3, pp.238-246, 2009. |
| [32] | R. Singh, T. Bhaskar, S. Dora, B. Balagurumurthy, "Catalytic hydrothermal upgradation of wheat husk", Bioresource Technology, vol.149, pp.446-451, 2013. |
| [33] | B. A. Cinelli, J. A. López, L. R. Castilho, D. M. G. Freire, A. M. Castro, "Granular starch hydrolysis of babassu agroindustrial residue: A bioprocess within the context of biorefinery", Fuel, vol.124, no.0, pp.41-48, 2014. |
| [34] | M. Sasaki, T. Adschiri, K. Arai, "Fractionation of sugarcane bagasse by hydrothermal treatment",NLM, Bioresource Technology, vol.86, no.3, pp.301-304, 2003. |
| [35] | G. e. Luo, W. Shi, X. Chen, W. Ni, P. J. Strong, Y. Jia, H. Wang, "Hydrothermal conversion of water lettuce biomass at 473 or 523 K", Biomass & Bioenergy, vol.35, no.12, pp.4855-4861, 2011. |
| [36] | S. R. M. Moreschi, A. J. Petenate, M. A. A. Meireles, "Hydrolysis of ginger bagasse starch in subcritical water and carbon dioxide", Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, vol.52, no.6, pp.1753-1758, 2004. |
| [37] | M. Tanaka, A. Takamizu, M. Hoshino, M. Sasaki, M. Goto, "Extraction of dietary fiber from Citrus junos peel with subcritical water", Food and Bioproducts Processing, vol.90, no.C2, pp.180-186, 2012. |
| [38] | W. Daengprasert, P. Boonnoun, N. Laosiripojana, M. Goto, A. Shotipruk, "Application of Sulfonated Carbon-Based Catalyst for Solvothermal Conversion of Cassava Waste to Hydroxymethylfurfural and Furfural", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.50, no.13, pp.7903-7910, 2011. |
| [39] | E. Hermiati, J.-i. Azuma, S. Tsubaki, D. Mangunwidjaja, T. C. Sunarti, O. Suparno, B. Prasetya, "Improvement of microwave-assisted hydrolysis of cassava pulp and tapioca flour by addition of activated carbon", Carbohydrate Polymers, vol.87, no.1, pp.939-942, 2012. |
| [40] | E. Coelho, M. A. Rocha, J. A. Saraiva, M. A. Coimbra, "Microwave superheated water and dilute alkali extraction of brewers' spent grain arabinoxylans and arabinoxylo- oligosaccharides", NLM, Carbohydrate Polymers, vol.99, pp.415-422, 2014. |
| [41] | D. Nabarlatz, A. Ebringerová, D. Montané, "Autohydrolysis of agricultural by-products for the production of xylo-oligosaccharides", Carbohydrate Polymers, vol.69, no.1, pp.20-28, 2007. |
| [42] | S. Sabiha-Hanim, M. A. Noor, A. Rosma, "Effect of autohydrolysis and enzymatic treatment on oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) frond fibres for xylose and xylooligosaccharides production",NLM, Bioresource Technology, vol.102, no.2, pp.1234-1239, 2011. |
| [43] | J. S. Kim, W. I. Choi, M. Kang, J. Y. Park, J. S. Lee, "Kinetic study of empty fruit bunch using hot liquid water and dilute acid",NLM, Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, vol.167, no.6, pp.1527-1539, 2012. |
| [44] | H. Mazaheri, K. T. Lee, A. R. Mohamed, "Influence of temperature on liquid products yield of oil palm shell via subcritical water liquefaction in the presence of alkali catalyst", Fuel Processing Technology, vol.110, pp.197-205, 2013. |
| [45] | F. P. Cardenas-Toro, T. Forster-Carneiro, M. A. Rostagno, A. J. Petenate, F. Maugeri Filho, M. A. A. Meireles, "Integrated supercritical fluid extraction and subcritical water hydrolysis for the recovery of bioactive compounds from pressed palm fiber", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, In Press, 2014. |
| [46] | L. P. Ramos, "The chemistry involved in the steam treatment of lignocellulosic materials", Química Nova, vol.26, pp.863-871, 2003. |
| [47] | W. Vermerris, Composytion and Biosynthesis of Lignocellulosic Biomass, in Genetic Improvement of Bioenergy Crops, W. Vermerris. Springer Science+Business Media, Florida, 2008. |
| [48] | A. F. A. Carvalho, P. d. O. Neto, D. F. da Silva, G. M. Pastore, "Xylo-oligosaccharides from lignocellulosic materials: Chemical structure, health benefits and production by chemical and enzymatic hydrolysis", Food Research International, vol.51, no.1, pp.75-85, 2013. |
| [49] | D. R. Lu, C. M. Xiao, S. J. Xu, "Starch-based completely biodegradable polymer materials", Express Polymer Letters, vol.3, no.6, pp.366-375, 2009. |
| [50] | H. I. Syed, F. W. Delilah, A. A. Mohamed, C. Bor-Sen, G. W. Tina, M. G. Gregory, J. O. William, Starch, in Starch-Based Polymeric Materials and Nanocomposites, CRC Press, 2012. |
| [51] | H. N. Englyst, S. M. Kingman, J. H. Cummings, "Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions",NLM, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol.46 Suppl 2, pp.S33-50, 1992. |
| [52] | M. Sajilata, R. S. Singhal, P. R. Kulkarni, "Resistant starch–a review", Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, vol.5, no.1, pp.1-17, 2006. |
| [53] | S. I. Shin, H. J. Kim, H. J. Ha, S. H. Lee, T. W. Moon, "Effect of Hydrothermal Treatment on Formation and Structural Characteristics of Slowly Digestible Non-pasted Granular Sweet Potato Starch", Starch - Stärke, vol.57, no.9, pp.421-430, 2005. |
| [54] | T. L. Wang, T. Y. Bogracheva, C. L. Hedley, "Starch: as simple as A, B, C?", Journal of Experimental Botany, vol.49, no.320, pp.481-502, 1998. |
| [55] | J. Jay-lin, Starch, in Chemical and Functional Properties of Food Saccharides, CRC Press, 2003. |
| [56] | A. Buléon, P. Colonna, V. Planchot, S. Ball, "Starch granules: structure and biosynthesis", International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol.23, no.2, pp.85-112, 1998. |
| [57] | J. K. Charles, F. K. John, Starch, in Polysaccharides, CRC Press, 2004. |
| [58] | J. N. BeMiller, R. L. Whistler, Starch: chemistry and technology, Academic Press, 2009. |
| [59] | T. Hajime, Carbohydrate Active Enzymes for the Production of Oligosaccharides, in Handbook of Industrial Biocatalysis, CRC Press, 2005. |
| [60] | A. Eisentraut, Sustainable Production of Second-Generation Biofuels, OECD Publishing, 2010. |
| [61] | V. Ferreira-Leitao, L. M. F. Gottschalk, M. A. Ferrara, A. L. Nepomuceno, H. B. C. Molinari, E. P. Bon, "Biomass residues in Brazil: availability and potential uses", Waste and Biomass Valorization, vol.1, no.1, pp.65-76, 2010. |
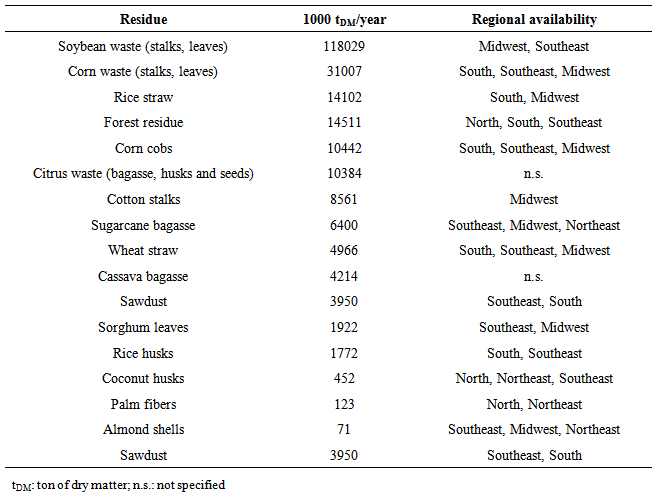
| [62] | L. F. de França, M. A. A. Meireles, "Modeling the extraction of carotene and lipids from pressed palm oil (Elaes guineensis) fibers using supercritical CO2", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.18, no.1, pp.35-47, 2000. |
| [63] | P. F. Leal, M. B. Kfouri, F. C. Alexandre, F. H. R. Fagundes, J. M. Prado, M. H. Toyama, M. A. A. Meireles, "Brazilian Ginseng extraction via LPSE and SFE: Global yields, extraction kinetics, chemical composition and antioxidant activity", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.54, no.1, pp.38-45, 2010. |
| [64] | P. Binod, K. Janu, R. Sindhu, A. Pandey, "Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production", Biofuels: alternative feedstocks and conversion processes, pp.229-250, 2011. |
| [65] | P. McKendry, "Energy production from biomass (part 2): conversion technologies", Bioresource Technology, vol.83, no.1, pp.47-54, 2002. |
| [66] | A. Demirbaş, "Biomass resource facilities and biomass conversion processing for fuels and chemicals", Energy conversion and Management, vol.42, no.11, pp.1357-1378, 2001. |
| [67] | A. Demirbaş, "Mechanisms of liquefaction and pyrolysis reactions of biomass", Energy Conversion and Management, vol.41, no.6, pp.633-646, 2000. |
| [68] | J. C. Serrano-Ruiz, R. Luque, A. Sepúlveda-Escribano, "Transformations of biomass-derived platform molecules: from high added-value chemicals to fuels via aqueous-phase processing", Chemical Society Reviews, vol.40, no.11, pp.5266-5281, 2011. |
| [69] | T. Rogalinski, K. Liu, T. Albrecht, G. Brunner, "Hydrolysis kinetics of biopolymers in subcritical water", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.46, no.3, pp.335-341, 2008. |
| [70] | G. Garrote, H. Dominguez, J. Parajo, "Hydrothermal processing of lignocellulosic materials", European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, vol.57, no.3, pp.191-202, 1999. |
| [71] | F. Jin, Y. Wang, X. Zeng, Z. Shen, G. Yao, Water Under High Temperature and Pressure Conditions and Its Applications to Develop Green Technologies for Biomass Conversion, in Application of Hydrothermal Reactions to Biomass Conversion, F. Jin. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2014. |
| [72] | C. Schacht, C. Zetzl, G. Brunner, "From plant materials to ethanol by means of supercritical fluid technology", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.46, no.3, pp.299-321, 2008. |
| [73] | K. Ehara, S. Saka, "Decomposition behavior of cellulose in supercritical water, subcritical water, and their combined treatments", Journal of Wood Science, vol.51, no.2, pp.148-153, 2005. |
| [74] | S. Ewanick, R. Bura, "Hydrothermal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass", Bioalcoholproduction, vol.pp.1, 2010. |
| [75] | J.W. King, R.D. Grabiel. “Isolation of phenolic compounds from fruits or vegetables utilizing sub-critical water extraction”, U.S. Patent 7 208 181, 2007. |
| [76] | W. Haynes, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th Edition (CRC Handbook of Chemistry & Physics), CRC Press, 2013. |
| [77] | P. E. Savage, "A perspective on catalysis in sub- and supercritical water", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.47, no.3, pp.407-414, 2009. |
| [78] | A. Kruse, P. Maniam, F. Spieler, "Influence of proteins on the hydrothermal gasification and liquefaction of biomass. 2. Model compounds", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.46, no.1, pp.87-96, 2007. |
| [79] | A. V. Bandura, S. N. Lvov, "The ionization constant of water over wide ranges of temperature and density", Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, vol.35, no.1, pp.15-30, 2005. |
| [80] | D. P. Fernández, Y. Mulev, A. Goodwin, J. L. Sengers, "A database for the static dielectric constant of water and steam", Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, vol.24, no.1, pp.33-70, 1995. |
| [81] | L. K. Tolonen, P. A. Penttila, R. Serimaa, A. Kruse, H. Sixta, "The swelling and dissolution of cellulose crystallites in subcritical and supercritical water", Cellulose, vol.20, no.6, pp.2731-2744, 2013. |
| [82] | Y. Yu, H. Wu, "Understanding the Primary Liquid Products of Cellulose Hydrolysis in Hot-Compressed Water at Various Reaction Temperatures", Energy & Fuels, vol.24, pp.1963-1971, 2010. |
| [83] | H. Pinkowska, P. Wolak, "Hydrothermal decomposition of rapeseed straw in subcritical water. Proposal of three-step treatment", Fuel, vol.113, pp.340-346, 2013. |
| [84] | H. Pinkowska, P. Wolak, E. Oliveros, "Production of xylose and glucose from rapeseed straw in subcritical water - Use of Doehlert design for optimizing the reaction conditions", Biomass & Bioenergy, vol.58, pp.188-197, 2013. |
| [85] | M. Moeller, F. Harnisch, U. Schroeder, "Hydrothermal liquefaction of cellulose in subcritical water-the role of crystallinity on the cellulose reactivity", Rsc Advances, vol.3, no.27, pp.11035-11044, 2013. |
| [86] | Y. Wang, J. Wan, Y. Ma, M. Huang, "Hydrolysis kinetics characteristic of recycled fiber in subcritical water", Bioresource Technology, vol.105, pp.152-159, 2012. |
| [87] | H. Ramsurn, R. B. Gupta, "Production of Biocrude from Biomass by Acidic Subcritical Water Followed by Alkaline Supercritical Water Two-Step Liquefaction", Energy & Fuels, vol.26, no.4, pp.2365-2375, 2012. |
| [88] | K. Nakahara, N. Kageyama, K. Nagami, "Enrichment of Vanillin in Barley Malt by Hydrolysis in High Temperature and High Pressure Steam", Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, vol.60, no.50, pp.12384-12387, 2012. |
| [89] | X. Lu, S. Saka, "New insights on monosaccharides' isomerization, dehydration and fragmentation in hot-compressed water", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.61, pp.146-156, 2012. |
| [90] | M. Herrero, M. Castro-Puyana, L. Rocamora-Reverte, J. A. Ferragut, A. Cifuentes, E. Ibanez, "Formation and relevance of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in bioactive subcritical water extracts from olive leaves", Food Research International, vol.47, no.1, pp.31-37, 2012. |
| [91] | Y. Yu, H. Wu, "Characteristics and Precipitation of Glucose Oligomers in the Fresh Liquid Products Obtained from the Hydrolysis of Cellulose in Hot-Compressed Water", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.48, no.23, pp.10682-10690, 2009. |
| [92] | M. Sasaki, Z. Fang, Y. Fukushima, T. Adschiri, K. Arai, "Dissolution and hydrolysis of cellulose in subcritical and supercritical water", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.39, no.8, pp.2883-2890, 2000. |
| [93] | T. Adschiri, S. Hirose, R. Malaluan, K. Arai, "Noncatalytic conversion of cellulose in supercritical and subcritical water", Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, vol.26, no.6, pp.676-680, 1993. |
| [94] | Y. Yu, Z. M. Shafie, H. Wu, "Cellobiose Decomposition in Hot-Compressed Water: Importance of Isomerization Reactions", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.52, no.47, pp.17006-17014, 2013. |
| [95] | Y. Zhao, W.-J. Lu, H.-T. Wang, D. Li, "Combined Supercritical and Subcritical Process for Cellulose Hydrolysis to Fermentable Hexoses", Environmental Science & Technology, vol.43, no.5, pp.1565-1570, 2009. |
| [96] | H. Pinkowska, P. Wolak, A. Zlocinska, "Hydrothermal decomposition of xylan as a model substance for plant biomass waste - Hydrothermolysis in subcritical water", Biomass & Bioenergy, vol.35, no.9, pp.3902-3912, 2011. |
| [97] | T. Miyazawa, T. Funazukuri, "Polysaccharide Hydrolysis Accelerated by Adding Carbon Dioxide under Hydrothermal Conditions", Biotechnology Progress, vol.21, no.6, pp.1782-1785, 2005. |
| [98] | G. Zhu, X. Zhu, Q. Fan, X. Wan, "Production of reducing sugars from bean dregs waste by hydrolysis in subcritical water", Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, vol.90, no.2, pp.182-186, 2011. |
| [99] | G. Garrote, H. Domínguez, J. C. Parajó, "Production of Substituted Oligosaccharides by Hydrolytic Processing of Barley Husks", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.43, no.7, pp.1608-1614, 2004. |
| [100] | S. E. Jacobsen, C. E. Wyman, "Xylose Monomer and Oligomer Yields for Uncatalyzed Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Bagasse Hemicellulose at Varying Solids Concentration", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.41, no.6, pp.1454-1461, 2002. |
| [101] | N. Sato, Y. Takano, M. Mizuno, K. Nozaki, S. Umemura, T. Matsuzawa, Y. Amano, S. Makishima, "Production of feruloylated arabino-oligosaccharides (FA-AOs) from beet fiber by hydrothermal treatment", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.79, no.0, pp.84-91, 2013. |
| [102] | M. Sasaki, B. Kabyemela, R. Malaluan, S. Hirose, N. Takeda, T. Adschiri, K. Arai, "Cellulose hydrolysis in subcritical and supercritical water", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.13, no.1-3, pp.261-268, 1998. |
| [103] | M. Sasaki, T. Adschiri, K. Arai, "Kinetics of cellulose conversion at 25 MPa in sub- and Supercritical water", American Institute of Chemical Engineers Journal, vol.50, no.1, pp.192-202, 2004. |
| [104] | Y. Zhao, W.-J. Lu, H.-T. Wang, "Supercritical hydrolysis of cellulose for oligosaccharide production in combined technology", Chemical Engineering Journal, vol.150, no.2-3, pp.411-417, 2009. |
| [105] | D. A. Cantero, M. D. Bermejo, M. J. Cocero, "Kinetic analysis of cellulose depolymerization reactions in near critical water", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.75, pp.48-57, 2013. |
| [106] | T. Rogalinski, T. Ingram, G. Brunner, "Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass in water under elevated temperatures and pressures", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.47, no.1, pp.54-63, 2008. |
| [107] | J. W. King, K. Srinivas, O. Guevara, Y.-W. Lu, D. Zhang, Y.-J. Wang, "Reactive high pressure carbonated water pretreatment prior to enzymatic saccharification of biomass substrates", The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, vol.66, pp.221-231, 2012. |
| [108] | D. Nabarlatz, X. Farriol, D. Montané, "Kinetic Modeling of the Autohydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass for the Production of Hemicellulose-Derived Oligosaccharides", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.43, no.15, pp.4124-4131, 2004. |
| [109] | D. Nabarlatz, X. Farriol, D. Montané, "Autohydrolysis of Almond Shells for the Production of Xylo-oligosaccharides: Product Characteristics and Reaction Kinetics", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, vol.44, no.20, pp.7746-7755, 2005. |
| [110] | J. Ishii, H. Saito, K. Fujie, H. Daimon, “Hydrolysis of Starch Processing Residues in Subcritical Water Optimal Conditions for Production of Valuable Materials”, Proc. 10th International Symposium on Supercritical Fluid, San Francisco, USA. 2012. |
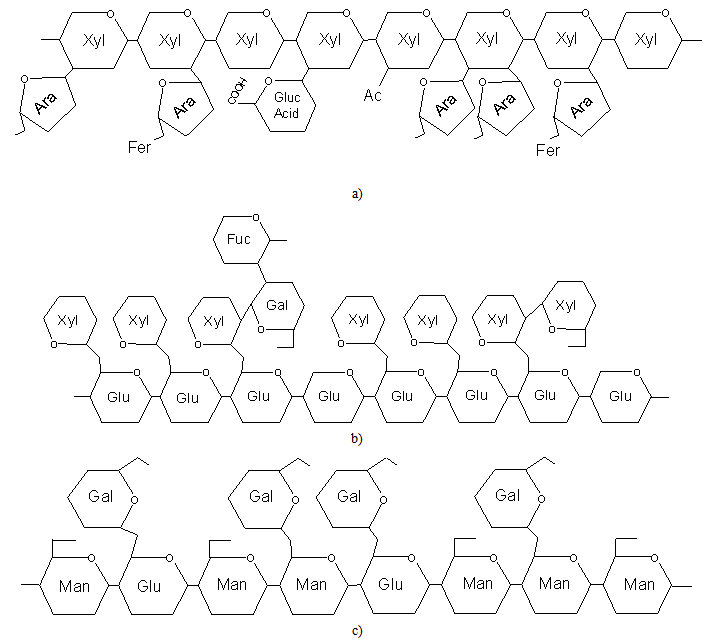
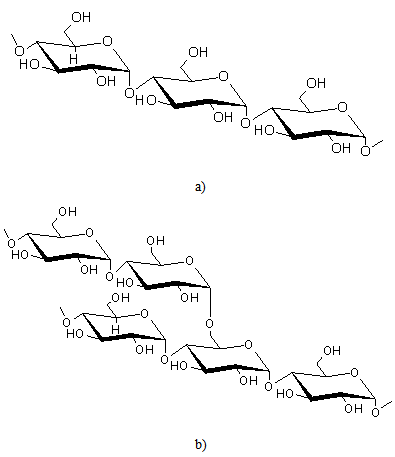
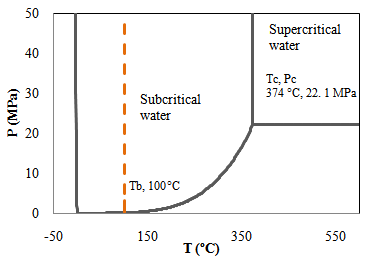
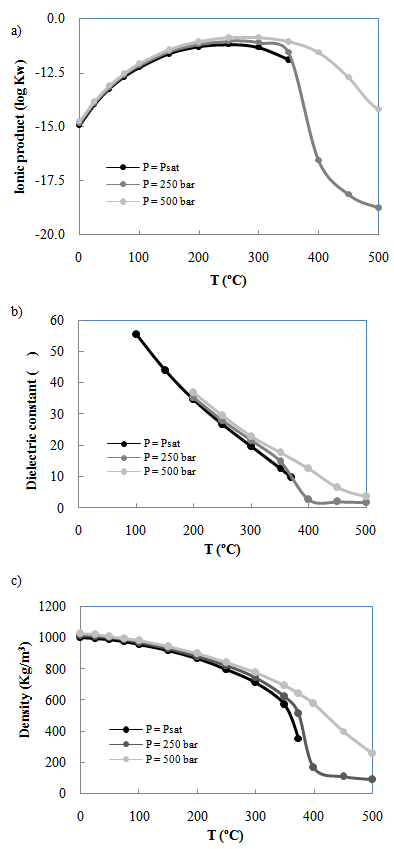
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML