-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2013; 3(6): 315-322
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20130306.08
Parental Perceptions and Microbial / Public Health Implications of Pre-Chewed Weaning Foods
Adenike A. O. Ogunshe 1, Doris A. Lahan 2, Oghenekaro J. David 2, Olayinka P. Verissimo 3
1Applied Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, University of Ibadan, Nigeria
2Department of Botany & Microbiology, Faculty of Science, University of Ibadan, Nigeria
3Department of Science Laboratory Technology, School of Pure and Applied Sciences, Moshood Abiola Polytechnic, Abeokuta, Ogun State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Adenike A. O. Ogunshe , Applied Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, University of Ibadan, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Introduction of pre-chewed foods to infants during weaning is a common parental practice. However, children can be exposed to mouth-to-mouth transmission of infectious and multi-drug resistant bacteria through pre-chewed foods, during complementary feeding. The aim of this study was to investigate the antibiotic resistance profiles of 103 easily-culturable oral bacterial strains of nursing parents, isolated from their pre-chewed meat samples. Using agar disk-diffusion and modified agar well-diffusion methods, Bacillus, Clostridium, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species exhibited total (100%) resistance against amoxicillin, augmentin, erythromycin, oxacillin and tetracycline antibiotic discs, while 7.1 - 100% resistance were exhibited by Enterobacter, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Morganella, Proteus, Salmonella, Shigella and Vibrio species. Significantly high resistance rates of 25.0-100% were generally exhibited by most of the bacterial flora against 30 oral paediatric antibiotic (ampicillins, cloxacillins, cotrimoxazoles, erythromycins, metronidazoles and trimethroprims) suspensions, with as high as ≥ 50.0% multiple antibiotic resistance (%MAR). Shigella flexneri and Streptococcus pneumoniae exhibited total (100%) resistance to 10 and 15 paediatric antibiotics respectively but the most-resisted paediatric antibiotics were brands of ampicillin and metronidazole. Only 4.9% of the bacterial strains exhibited %MAR of ≤ 10.0%, while none was totally susceptible to all the paediatric antibiotics. About 80.0% nursing subjects had earlier pre-chewed foods for infants; 25.8% felt nothing was wrong in pre-chewing foods, 12.2% were not sure of the implications of such feeding practice, while 62.0% knew that pre-chewing was wrong but did not know of alternative means of tendering certain foods like meat for infants’ feeding. In conclusion, this study corroborated that pre-chewing foods could account for increase in parent-to-child transmissible oral / gastrointestinal infections. Furthermore, children can be exposed to multiple antibiotic resistant bacteria through pre-chewed foods during complementary feeding, which can lead to public health implications of treatment failure in paediatric clinical conditions.
Keywords: Antibiotic Resistance, Cultural & Family Practices, Disease Transmission, Infant Health, Infant Mortality, Pre-mastication, Treatment Failure, Weaning Foods
Cite this paper: Adenike A. O. Ogunshe , Doris A. Lahan , Oghenekaro J. David , Olayinka P. Verissimo , Parental Perceptions and Microbial / Public Health Implications of Pre-Chewed Weaning Foods, Food and Public Health, Vol. 3 No. 6, 2013, pp. 315-322. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20130306.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In spite of the fact that worldwide, solid foods are introduced to infants by several methods, it is customary in many cultures for parents to first eat foods before giving such foods to babies, which is called pre-mastication or pre-chewing [1-3]. Pre-mastication (pre-chewing) of foods for infants has been more of a cultural practice that evolved through the ages, and which has become an adapted behavioural, nutritional mode of feeding infants during complementary feeding [4]. It is known that pre-mastication of food for weaning infants might have nutritional benefit [5] In Nigeria, like almost every other country of the world, breast milk is the main source of nourishment for children within their first months of life. Dependence on breast milk reduces exposure of children to infection and also affords them some protection; however, complementary foods are usually given between 4 and 6 months of age [8]. Though, the human mouth provides a suitable habitat for numerous bacterial species [9], series of acclaimed reasons for pre-mastication include provision of foods for babies, encouraging infants to eat adult foods, supplementation of iron, disease prevention, healing, cultural and spiritual beliefs [4, 5, 10]. Also, salivary immunoglobulin A has some bactericidal properties, which might be transferred to the child [11] but still, children are most likely to be exposed to oral microbial pathogens through pre-chewed foods [1, 4, 7, 12]. Chewing of foods is linked with potential risk of horizontal transmission of pathogenic microorganisms and diastatic enzymes into foods [1, 5, 10, 13, 14], and although bacteria are the most obvious inhabitants of the oral cavity [15], other microbes are often seen, which include several species of fungi, viruses and protozoa [16, 17]. Compelling evidence linking pre-mastication to HIV infection and cases of infantile syphilis transmitted by mouth-to-mouth feeding from actively infected relatives had also been reported [7, 12, 17, 18, 19, 20]. Similarly, transmission of Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B, Streptococcus mutans, Helicobacter pylori and group A streptococci, leading to group A streptococcal pharyngitis due to pre-chewed foods by parents have been documented as well [21-26].As far back as 1500 BC, when pre-mastication was first described in Egypt [27], the traditional practice of offering pre-chewed food to weaning infants had been reported from various parts of the world [2, 3], including Nigeria. The role of the family in maintaining and promoting health cannot be overlooked; however, this family / community / cultural practice is currently poorly documented. The major objective of this study therefore, was to determine and interpret the current prevalence and clinical implications of multiple antibiotic resistant bacterial flora from pre-chewed meat, which is the most-commonly pre-chewed food (meat) sample during weaning in Nigeria. Attitudes of nursing parents to such mode of infantile complementary feeding were also briefly assessed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
- Healthy male and female subjects between the ages of 19 and 68 years were randomly selected for the present study. They were briefed on the concept of the investigation and verbal informed consents were obtained from them.
2.2. Collection of Samples
- Fresh, defatted beef meat samples were bought from the market and properly cleaned with tap water before cutting into average size chunks. The meat chunks were rinsed again and well-seasoned with onion, garlic, ginger and Maggi knorr cubes (a salt-based Nigerian industrial food seasoning agent) and left for about 15 minutes in the pot before cooking. The cooked meat samples were pierced with tooth-picks and then wrapped in foil paper, as stick-meat, followed by sterilisation in the autoclave at 1210C for 15 minutes, allowed to cool, before being served aseptically to the subjects. The chewed meat samples were aseptically collected with sterile forceps from the subjects into sterile Petri dishes, and later transferred into sterile McCartney bottles containing sterile distilled water. The inoculated sterile water-meat samples were then incubated at 350C for 12 h.
2.3. Bacterial cultures
- Incubated sterile distilled water containing pre-chewed meat samples were later dispersed by a vortex mixer and separately serially diluted in sterile peptone broth as 1 ml aliquots in 9 ml sterile peptone water, followed by incubation at 350C for 12 h; thus, all the pre-chewed meat samples were processed within 24±1 h after collection. The incubated peptone water samples were then cultured on some differential, selective and general-purpose culture media: blood agar (BA), cystein lactose electrolyte deficient (CLED) agar, eosin methylene blue (EMB) agar, MacConkey (MCC) agar, plate count agar (PCA), thiosulphate citrate bile sucrose (TCBS) agar, Salmonella-Shigella (SS) agar and mannitol salt agar (MSA), all from Lab M, England. Plate count agar was used for the total bacterial plate counts and brain heart infusion agar (Oxoid, Unipath Limited, Basingstoke, Hampshire, United Kingdom) was used for culture slants. The culture media were incubated under anaerobic (10% CO2) and aerobic conditions for 24-48 h and all the different easily culturable colony types were isolated and identified by the use of established standard laboratory methods for phenotypic bacterial taxonomy [28, 29].
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test (Discs)
- Antibiotic susceptibility determination of various antibiotics was carried out on the bacterial isolates by the Kirby-Bauer agar disk-diffusion method. The entire surface of each sterile Mueller-Hinton agar plate was seeded (surface-streaked) with each test bacterial strain, and left for about 15 min. Antibiotic discs were later placed on the agar surfaces, followed by incubation of the plates at 350C for 24-48 hours. Zones of inhibition were measured and recorded in millimetre diameter according to the methods of Bauer et al. [30] and NCCLS [31]. Zones less than 10.0 mm in diameter or absence of zones of inhibition were recorded as resistant (R). The antibiotic discs, manufactured by ABTEK, Biologicals Ltd. (Liverpool, UK) used in this study were Gram-positive antibiotic discs: AMX (amoxycillin; 25µg), AUG (augmentin; 30µg), CHL (chloramphenicol; 30µg), COT (cotrimoxazole; 25µg), CXL (cloxacillin; 5µg), ERY (erythromycin; 5µg), GEN (gentamicin; 10µg), TET (tetracycline; 30µg). Gram-negative antibiotic discs: AMX (amoxycillin; 25µg), AUG (augmentin; 30µg), COT (cotrimoxazole; 25µg), GEN (gentamicin; 10µg), NAL (nalidixic acid; 30µg), NIT (nitrofurantoin; 300µg), OFL (ofloxacin; 30µg) and TET (tetracycline; 30µg).
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test (Paediatric Antibiotic Suspensions)
- Antibiotic susceptibility/resistance patterns and profiles of bacterial species isolated from the pre-chewed meat samples towards 30 commonly available oral paediatric antibiotic suspensions of six classes of antibiotics (ampicillins, cloxacillins), co-trimoxazoles, erythromycins,metronidazoles and trimethroprims) were also determined in this study by a modification of the agar well-diffusion method of Tagg et al. [32]. Sterile Mueller-Hinton agar was poured into sterile Petri dishes and allowed to set, while 6.0 mm wells were bored in the set sterile Mueller-Hinton agar plates, followed by surface sterilisation of the agar plates by flaming. Entire surface of each sterile Mueller-Hinton agar plate was then seeded with each test bacterial strain by streaking, after which the plates were left for about 10 minutes before aseptically dispensing 100μl paediatric antibiotic suspensions into the agar wells. Modification method employed was that antibiotic suspensions or specified antibiotic powder dissolved in recommended volume of sterile distilled water were separately incorporated into plain, sterile semi-solid agar and homogenised before being dispensed into the agar wells, to avoid spreading of the antibiotic suspensions on the agar surfaces. The plates were then incubated at 350C for 24–48 hours and zones of inhibition (diameter) were measured and recorded in millimetre but zones of inhibition less than 10.0 mm in diameter or absence of inhibition zones were recorded as resistant (R). Codes, active ingredients and respective batch numbers of the oral paediatric antibiotics used in this study were as presented in Table 1.
2.6. Administration of Questionnaires
- Questionnaires were administered on 360 females and 120 males nursing subjects whose consents were sought and obtained. Information obtained from the respondents included age, tribe, academic qualifications and classified attitudes to pre-chewing foods for infants.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
- Data obtained from the administered questionnaires were analysed using percentage values.
3. Results and Discussion
- World Health Organisation describes complementary feeding period as the period during which other foods or liquids are provided along with breast milk. Therefore, any nutrient-containing food or liquid (other than breast milk) that is given to young children during the period of complementary feeding is defined as complementary food [33]. According to Zhang [10], results of various lines of investigation suggested that pre-mastication has been a common practice in human societies but has been significantly under-reported, especially in ethnographic studies, and that infants who received pre-masticated foods are more likely to be fed complementary foods earlier than those who did not. Similarly, pre-mastication (pre-chewing) of foods for infants is a major cultural and domestic activity in almost, if not all tribes of Nigeria and even fathers, as well as other family members are involved in this practice.As shown in Fig. 1, 103 (Gram-positive = 14; Gram-negative = 89) bacterial strains isolated from pre-chewed meat samples in this study were phenotypically identified as, Bacillus cereus (2), B. subtilis (1), Clostridium perfringens (3), Enterobacter aerogenes (7), Escherichia coli (10), Klebsiella aerogenes (10), Klebsiella pneumoniae (10), Morganella morganii (1), Proteus mirabilis (15), Salmonella paratyphi (4), Shigella dysenteriae (14), Shigella flexneri (2), Shigella sonnei (12), Staphylococcus aureus (5), Staph. epidermidis (1), Streptococcus pneumoniae (1), Strept. marcecens (1) and Vibrio parahaemolyticus (4). Pre-mastication may have nutritional benefits but can also have negative consequences, such as depletion of nutrients from the food that is supposed to be nourishing to the baby, since saliva begins the digestive processes. This may also be hazardous for infant health, especially since some diseases are transmitted through human saliva. In an epidemiological study, maternal pre-mastication was positively associated with risk of H. pylori among children [34], while body fluids (saliva or others), which contain infectious AIDS virus, when in contact with activated lymphocytes or other susceptible cells bearing CD4+ receptor [monocytes, macrophages] may effect transmission of the virus to susceptible hosts like infants [35]. No documented scientific researches on pre-mastication in Nigeria could be accessed, while only few records from other African countries were available; however, obtainable results findings of the present study highlighted that the bacterial flora isolated from pre-chewed meat samples were among those commonly implicated in infantile gastroenteritic cases [36-38], Whereas, acute gastroenteritis has been found to account for the highest infant and childhood morbidity and mortality in tropical developing countries [39, 40] like Nigeria. It is well known that under-five mortality in Sub Saharan Africa remains disturbingly high and the highest rates of child mortality continue to be found in sub-Saharan Africa, where 1 in 8 children dies before their fifth birthday, i.e., nearly 20 times the average for developed regions (1 in 167) [41], meanwhile, decline in child mortality are far too slow to reach the fourth Millennium Development Goal, with the hope of reducing under-five mortality by two thirds between 1990 and 2015 [42]. Similarly, about half of global under-five deaths occurred in just five countries in 2009: India, Nigeria, Democratic Republic of Congo, Pakistan and China, and even as at 2009 and 2010, Nigeria ranked 7th with 150 and 9th with 143 in thousand under-five mortality rates [41]. It can therefore, be inferred that being fed with pre-chewed foods can also be additionally responsible for weaning diarrhoea, probably due to low immune status of the infants. Various antibiotics are the backbone of enterobacterial infectious treatments but the problem of antibiotic resistance in paediatric conditions have been continuously highlighted [43-45], which is most especially amplified in tropical developing countries. Phenotypic susceptibility/resistance patterns and profiles of the bacterial strains from pre-chewed meat samples to routine antibiotic discs in this study, as shown in Table 2 highlighted very high antibiotic resistance rates among the recovered bacterial species, mostly towards amoxicillin, augmentin, erythromycin, ofloxacillin, tetracycline and cotrimoxazole antibiotic discs. The Gram-positive bacteria were totally resistant to amoxicillin, augmentin, erythromycin, oxacillin and tetracycline, while very high antibiotic resistance rates of 40.0-100% were also recorded mostly towards chloramphenicol and cotrimoxazole but the least-resisted antibiotic (discs) were gentamicin and chloramphenicol (0.0-50.0%). Gram-negative bacteria were generally less resistant but relatively low / moderate to high resistance rates were also spatially exhibited against ofloxacillin (14.2-57.1%), nitrofurantoin (25.0-78.6%), amoxicillin (10.0-100%), nalidixic acid / tetracycline (25.0-100%), augmentin (10.0-75.0%) and cotrimoxazole (40.0-100%), while lower resistance rates of 7.1-28.6% were recorded against gentamicin (Table 2). Antibiotic disc-diffusion susceptibility testing is the generally adopted normal routine assay for determining the antibiotics that bacterial pathogens are susceptible to but this study went further to assay for the in vitro susceptibility / resistance patterns and profiles of the bacterial species towards commonly available paediatric antibiotic drugs in Nigeria. Recorded antibiotic susceptibility / resistance profiles and patterns of the bacterial species towards oral paediatric antibiotic suspensions varied in this study but higher resistance rates were exhibited towards the antibiotic drugs, except a brand of sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim (SUP1 and SUP2) to which some of the bacterial species were more susceptible, having overall resistance of ≤ 50.0%, with the exception of Shigella flexneri strains (Table 3). In spite of reports on several antimicrobial agents being available for use in newborns and children with suspected or proven bacterial infections [46], enterobacterial infections are still commonly more severe in the very young [47]. In addition, it is globally reported that drug resistance have decreased the effectiveness of antibiotics although they are still widely used, especially in the treatment of paediatric bacterial and non-bacterial infections in Nigeria. Meanwhile, in this study, the groups of paediatric antibiotics that are commonly administered on infants and children in Nigeria were found to be highly resisted by the oral bacterial species isolated from pre-chewed meat samples. Lowest percentage multiple antibiotic resistance (%MAR) rates among the bacterial strains towards the paediatric antibiotics were 16.7%, while as high as 100% MAR were recorded (Table 4). Just about five (4.9%) of the bacterial strains exhibited MAR of ≤ 10.0%, while none of the test bacterial strains displayed total (100%) susceptibility towards all the paediatric antibiotic drugs. Since almost all the isolated bacterial species of oral (pre-chewed) origin in this study exhibited multiple antibiotic resistance, there was indication of the risk of antibiotic treatment failure in associated bacterial infections, and the fear that such multiple antibiotic resistant bacteria could be transferred to infants and children from nursing parents during mouth-to-mouth complementary feeding. This can lead to inability of the paediatric antibiotics to control the implicated bacterial pathogens in cases of bacterial infectious outbreak in children. The implication is that such multiple antibiotic-resistant bacteria can cause diseases in children that can be untreatable with conventional paediatric antibiotics, even in cases of combined antibiotic therapy. Recorded high antibiotic resistance and MAR were not species-dependent but as shown in Table 4, the most totally-resisted paediatric antibiotic suspensions were BARB1 (ampicillin) / NAMP2 (ampicillin) ˃ EMG1 (metronidazole) ˃ EME1 (metronidazole) / EME2 (metronidazole), while as high as ≥ 50.0% MAR were exhibited by some of the bacterial flora from pre-chewed meat samples. Even of greater fear is the prevalence of fake and substandard antimicrobial agents in the country [48], which makes it a double jeopardy for children that could be infected through bacterial species acquired from pre-chewed food samples. This study is one of the very few studies that determined and compared the potencies of the readily available oral paediatric antibiotics in Nigeria, and it was observed that high resistance were exhibited towards the paediatric antibiotics by the oral bacterial species of nursing parents. However, a major limitation of the study was that more diversity of oral bacterial species, which were not easily recoverable could not be isolated. Similarly, in vitro susceptibility and resistance patterns and profiles of the bacterial species towards ascertained foreign paediatric antibiotics could not be determined in this study, although further studies are on-going in these regards.Administered questionnaires on a total of 480 [females = 360 (75.5%); males = 120 (25.0%)] nursing subjects aged between 19 and 68 years and from various tribes of the country were analysed, and results showed that 382 (79.6%) of the respondents had earlier pre-chewed foods for infants, while 98 (20.4%) claimed not to have pre-chewed foods for infants. Among the respondents, 124 (25.8%) felt there was nothing wrong in pre-chewing foods for infants during weaning, more so, since they were also fed with pre-masticated foods during infancy. A total of 59 (12.2%) were not sure of the implication of such feeding practice, while 297 (62.0%) felt that pre-chewing of foods for infants during weaning is wrong but there was no ready alternative means of tendering such foods for infants during weaning, and direct feeding of boiled meat chunks to babies often induced regurgitation. Meat, which was reported to be pre-masticated for babies in almost one third of the Chinese cultures, as studied by Zhang [10] was also the most-commonly pre-chewed food sample for infants during weaning in Nigeria (results not included), which was the sample microbially analysed in this study.
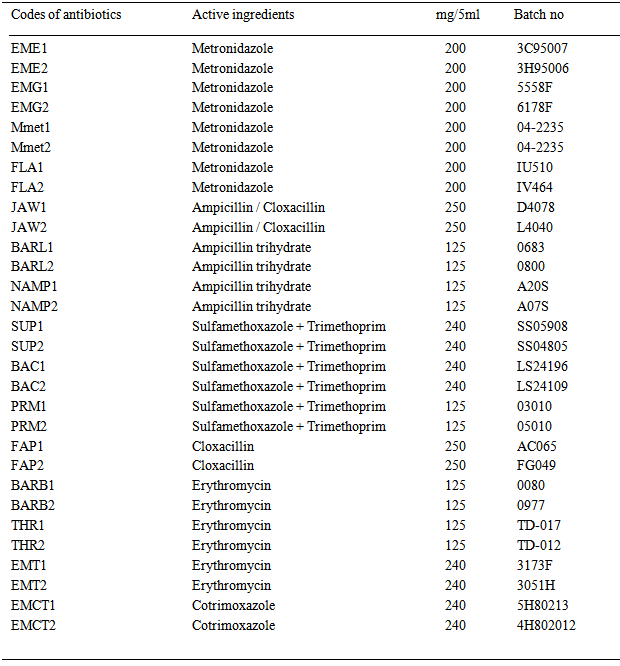 | Table 1. Characteristics of the test paediatric antibiotic suspensions |
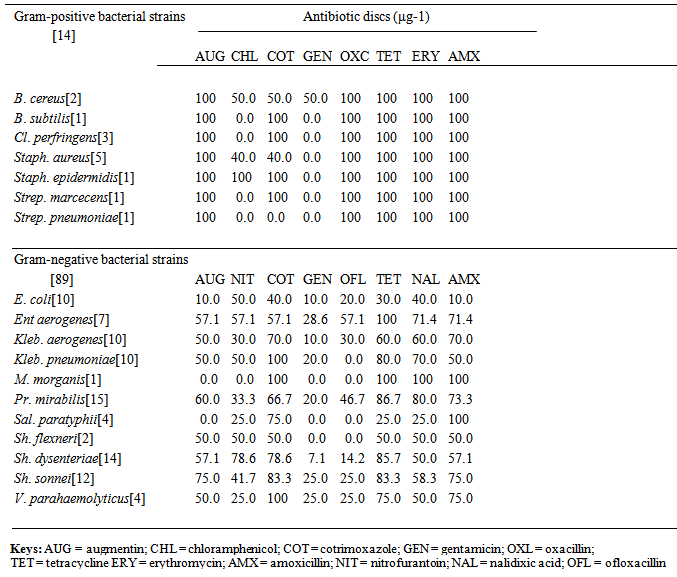 | Table 2. In vitro overall percentage antibiotic resistance profiles of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial flora from pre-chewed food samples (antibiotic discs) |
 | Table 3. In vitro overall percentage antibiotic resistance profiles of the bacterial flora from pre-chewed food (paediatric suspensions) |
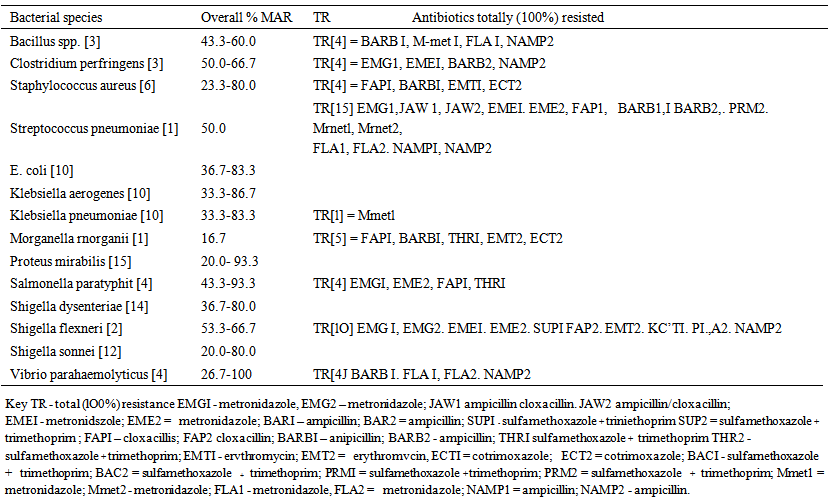 | Table 4. In vitro percentage multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) and total resistance (TR) profiles of the bacterial flora from pre-chewed food (paediatric suspensions) |
4. Conclusions
- Treatment failure is highly clinically relevant, and since infants are significant high-risk group, and in also considering the significantly high antibiotic resistance exhibited by the bacterial flora from pre-chewed meat samples to paediatric antibiotics in this study, it was therefore, concluded that pre-chewing, as a mode of complementary feeding practice can contribute to high incidence of infantile mortality and morbidity rates, through transmission of multiple antibiotic resistant oral pathogenic microbes from parents to infants, especially actively infected parents and relatives.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML