-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2013; 3(5): 247-256
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20130305.03
First Survey on the Use of Antibiotics in Pig and Poultry Production in the Red River Delta Region of Vietnam
Dang Pham Kim1, 2, Claude Saegerman3, Caroline Douny2, Ton Vu Dinh4, Bo Ha Xuan5, Binh Dang Vu5, Ngan Pham Hong6, Marie-Louise Scippo2
1Central Laboratory, Faculty of Animal Science & Aquaculture, Hanoi University of Agriculture, Vietnam
2Department of Food Sciences, Laboratory of Food Analysis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, CART (Centre of Analytical Research and Technology), University of Liège, Belgium
3Department of infectious and parasitic diseases, Research unit of Epidemiology and risk analysis applied to veterinary sciences (UREAR), Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Liège, Belgium
4Center for Interdisciplinary Research on Rural Development, Hanoi University of Agriculture, Vietnam
5Department of Animal genetics and breeding, Faculty of Animal Science & Aquaculture, Hanoi University of Agriculture, Vietnam
6Department of Veterinary Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Hanoi University of Agriculture, Vietnam
Correspondence to: Dang Pham Kim, Central Laboratory, Faculty of Animal Science & Aquaculture, Hanoi University of Agriculture, Vietnam.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In Vietnam where epidemics occur regularly in animal production, the farmers consider antibiotics as one of the solutions to fight against livestock diseases, thus the risk of abuse, even illegal use of antibiotics in livestock is very high. However, this is a recent issue and has not yet been thoroughly investigated. A cross-sectional study on the use of antibiotics in pig and poultry production as well as the farmer’s knowledge on the danger of the antibiotic use in three different animal production systems (farm household, semi-industrial and industrial) was conducted from July 2009 to March 2010 on 270 entities, in 3 representative localities of the Red River Delta (RRD). The results showed that a large volume of antibiotics was used arbitrary in all animal production systems. Animals were not only treated for acute diseases, but also for disease prevention, and for growth promotion. At least 45 antibiotics of more than 10 classes were used. Fifteen antibiotics were used in pig and poultry feed. For diseases treatment and prevention, antibiotics were used abusively and even illegally (e.g. chloramphenicol) by both farmers and veterinarians. The findings of this survey will permit developing new strategies for prudent use of antibiotics in livestock in Vietnam. These results will help not only to strengthen issues such as veterinary networks; antibiotics use guidance, residues monitoring systems and food safety, but also to improve awareness and ethics of producers and veterinary drug sellers.
Keywords: Antibiotics, Animal Production, Veterinary Drugs, Red River Delta, Vietnam
Cite this paper: Dang Pham Kim, Claude Saegerman, Caroline Douny, Ton Vu Dinh, Bo Ha Xuan, Binh Dang Vu, Ngan Pham Hong, Marie-Louise Scippo, First Survey on the Use of Antibiotics in Pig and Poultry Production in the Red River Delta Region of Vietnam, Food and Public Health, Vol. 3 No. 5, 2013, pp. 247-256. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20130305.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In Vietnam, a country with more than 85 million inhabitants and a very high population density, especially in the Red River Delta (RRD), urbanization andindustrialization increase rapidly. The demands of foodstuff from animal origin for domestic markets are more and more growing. The annual average consumption of animal products per Vietnamese capita in 2009 is 35 kg of carcass meat; 3 kg of milk and 80 eggs[1]. The development objective by 2020 is 56 kg of carcass meat, over 10 kg of milk and over 140 eggs[2]. As a consequence, the increase of intensive livestock husbandry models is an indispensable trend in the Vietnamese context. However, because of the low level of hygiene in livestock husbandry, the inadequacy of husbandry zone planning and the lack of state management and development strategies, it results in some new problems such as environmental pollution, as well as frequently occurring and uncontrolled epidemic diseases [2-4]. In 2003, during the avian influenza crisis, about 44 million poultry have either died because of the disease or have been slaughtered because of the crisis. The Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS), and the Foot-and-Mouth disease have also been a constant threat causing regular outbreaks in recent years[5]. In 2006, an epidemiological analysis about swine diseases in Northern Vietnam based on 4000 declarations highlighted a high incidence of porcine respiratory disease (50% of total reported cases). The proportion of digestive tract infections in piglets and reproductive disorders in newly raised exotic sows were 30% and 10% of total reported cases, respectively [6].Facing this situation, producers consider antibiotics, used for disease prevention and therapeutic purposes, as one of the solutions to fight diseases in livestock. In fact, antibiotics are the most common registered drugs (70% of all veterinary drugs) used in animals in Vietnam[7]. However, the knowledge of famers is still very restricted while the state inspection and management haven’t met practical demands yet[8]. The use of antibiotics in animal production by farmers in a casual, unmethodical manner, without any veterinary prescription and supervision, may lead to the presence of residues in animal products and to antimicrobial resistance[9-11]. These residues cause a danger for public health[12], and bad influences on environment and animal therapeutic sciences. A high proportion of the antibiotics used in animal production is excreted in urine or faeces and are found in manure[13]. When manure is applied on lands, these antibiotics can enter surface and/or groundwater and potentially alter the environment microbial ecosystem [14-16]. It could also contribute to the presence of antibiotic- resistant zoonotic agents and bacteria in the food chain [17-22]. The situation in Vietnam is amplified by the integrated agriculture-aquaculture (IAA) farming system encouraged by the government, which often involves an aquaculture system that is sustained through human and livestock waste. This creates an environment that greatly increases the ease through which antibiotic resistance genes can be spread[23]. These antibiotic resistance genes can be easily transferred to both human and animal pathogens, creating a severe health risk by greatly limiting the antibiotics that can be used to treat infectious diseases[24]. In recent years, Vietnam had many alerts about veterinary drug residues in general and antibiotics in particular. These alerts have caused warnings to authorities and alarmed consumers. Therefore, this problem has been discussed on several occasions in meetings of the Vietnam National Assembly[25-27]. However, until now, there is no systematic monitoring neither is there any regulation and control strategy on antibiotic use in food animals, and little information is available on antibiotic use. For the reasons above, as well as to contribute to a long-term strategy of the Vietnamese Government on food safety, the collection of detailed information about antibiotics used in animal production is necessary. The aim of this study was to provide information on the use of antibiotics in different pig and poultry production systems in the RRD of Vietnam. This information can assist new strategies in the control of antibiotic use in pig and poultry production in Vietnam.
2. Experimental
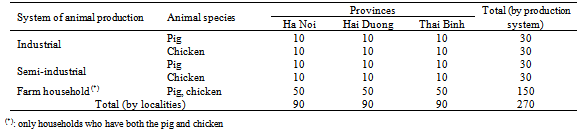
- A cross-sectional study of antibiotic use in pig and poultry production as well as farmer’s knowledge about food safety related to the use of veterinary drugs in the region of the RRD was designed and conducted from July 2009 to March 2010, on 270 entities representing 3 different systems of livestock husbandry: farm household, semi- industrial and industrial, in 3 representative localities of the RRD (Hai Duong, Thai Binh and Ha Noi) (Fig. 1)(Table 1).
|
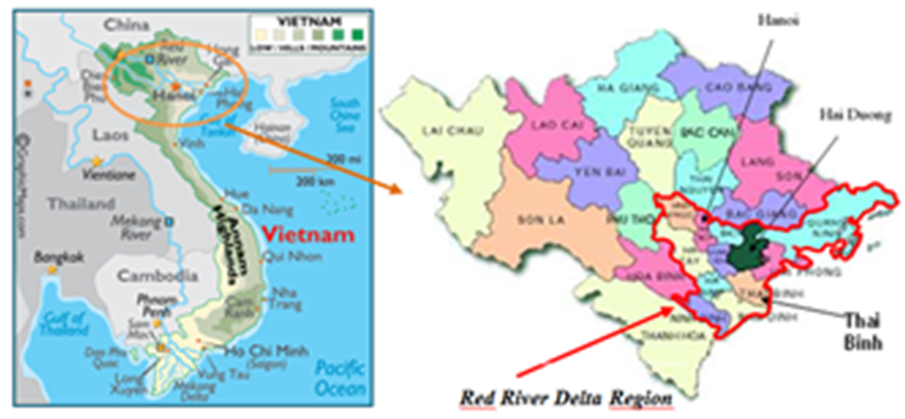 | Figure 1. Map of Red River Delta region indicating the three representative localities where the samples were collected (Hai Duong, Thai Binh and Ha Noi) |
2.1. Sampling Area
- The Red River Delta region is a flat plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries joining in the Thai Binh River in Northern Vietnam. It is an agriculturally rich area and densely populated (1225 persons/km2, 4.8 times higher than the average population density of Vietnam). It includes the capital, Hanoi, and 10 others surrounding provinces (Fig. 1). The pig and poultry production of this region are the most developed of Vietnam (about 50% of the whole country production) with 7.0 million pigs, 66.5 million poultry in 2008[28]. Three representative provinces were selected not only for their production capacity but also representative of their geographic location and population density: Hanoi (3344 km2), Hai Duong (1661 km2) and Thai Binh (1542 km2). The population density of Hanoi, Hai Duong and Thai Binh are 1943; 1030 and 1155 persons/km2, respectively. The population of pig and poultry is the largest in Hanoi (1.2 106 pigs and 15.7 106 poultry), followed by Hai Duong (0.6 106 pigs and 6.9 106 poultry) and Thai Binh (1.0 106 pig and 7.9 106 poultry)[28].
2.2. Sampling Method
- In each province, on the basis of the list provided by the local agricultural office (for industrial and semi-industrial systems), as well as from the lists provided by local veterinarians, 50 farm households who have both pig and poultry, 20 semi-industrial farms (10 for pig and 10 for poultry) and 20 industrial farms (10 for pig and 10 for poultry) were selected by random sampling for the survey. Official local agricultural criteria were used to classify the different farming systems. Farm household system displays a small number of animals, primarily for home consumption or local markets or ceremonial use. Livestock is raised in the garden, near the house of the farmer, and are fed with available vegetables, product and by-products of agriculture, or leftovers of the family kitchen (there is no supplementary feeding). Semi-industrial systems are farms with at least 50 pigs or 10 sows for the pig and 200 animals for the poultry.
2.3. Information Collection
- Questionnaires, contents of which were compiled after test survey and adjustment, were used for direct interviews of owners, technical collaborators or veterinary doctors of the farm. The information of veterinary drugs, antibiotic components and active elements which weren’t noted in the farm were tracked down and collected through labels on remedy packs or jars left around animal housing or at local veterinary medicine pharmacy. In order to ensure the objectivity of full remedy use information exploitation, all householders’ names and addresses were kept in security through encoding addresses just at the survey time. In this survey, antibiotics are considered to be used abusively when they are used unscientifically and incorrectly (under/overdosing, no exact diagnosis or result of a susceptibility testing …).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
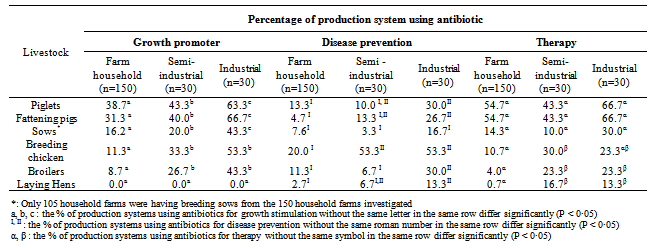
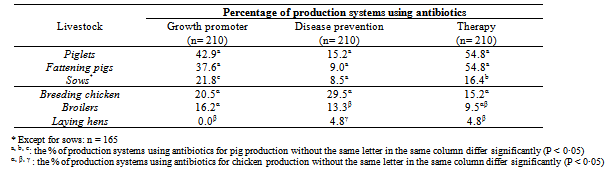
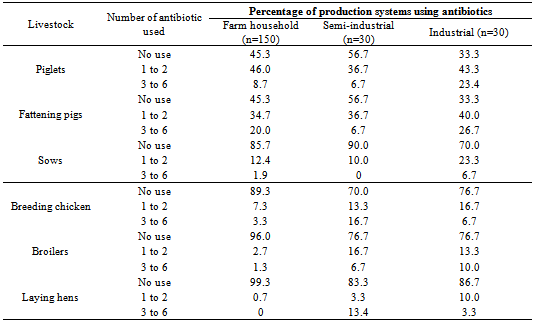
- All data and information were registered and checked using Microsoft Excel 2003. The data were analysed statistically and compared, in 2x2 and 2x3 contingency tables, using the chi-square test and the Fisher's Exact Test, when the chi-square test was not relevant, using the SAS® Software 9.0. A Fisher exact test was performed using the data of number of production system using antibiotics for disease prevention, therapy or growth promotion (Table 2a), in order to assess if there is a significant difference with p<0.05) in the use of antibiotics between the three production systems (household farms, semi-industrial and industrial production systems), as well as to assess if there is a significant difference in the use of antibiotics (total of the three production systems) between the different production stages (piglets, fattening pigs and sows for the pig production) and production systems (breeding poultry, broilers and laying hens for the poultry production) (Table 2b).
|
|
|
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of Antibiotics Used in Pig and Poultry Production in the RRD
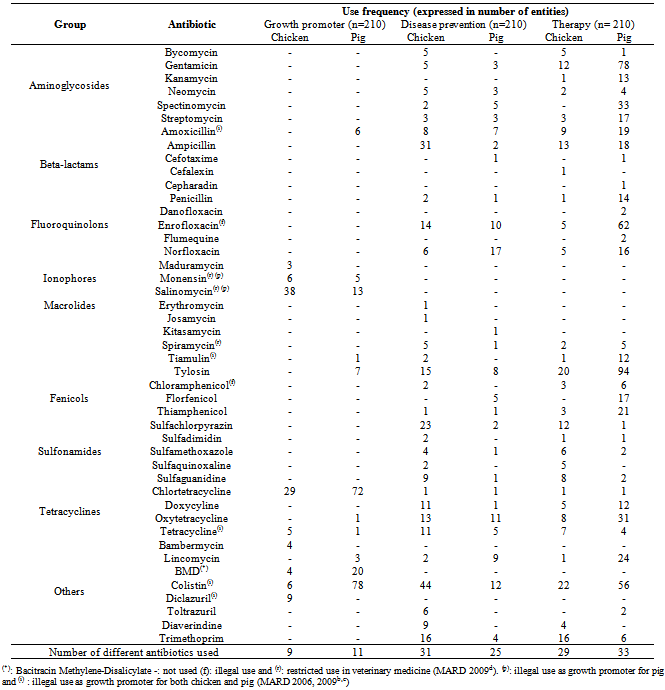
- At least 45 antibiotics representing more than 10 classes were used in pig and poultry production in the provinces studied, not only for treatment of diseases, but also for disease prevention and to promote growth. For disease prevention purpose, 31 and 25 different antibiotics were found to be used in poultry and pig production, respectively, while the number of different antibiotics used for curative purpose in pig and poultry were 33 and 29 respectively (Table 3). These data show that in pig production, antibiotics from aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, fenicols, beta-lactams and fluoroquinolones groups are the most commonly used for mostly disease treatment, and to a lesser extent for disease prevention. In poultry, antibiotics from sulfonamides, beta-lactams, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides and ionophores, as well as colistin are commonly used mostly for disease prevention and to a lesser extent for therapy. For both prophylactic and therapeutic purposes, most producers use antibiotics to prevent infection diseases not according to the prophylactic or therapeutic dosage, length of treatment and withdrawal time indicated on the product label, but most of them use a higher dosage and don’t respect the recommendations of the drug producer.In the 45 antibiotics identified in this survey, colistin, chlortetracycline and oxytetracycline are the most commonly used. Chlortetracycline was overall used for growth promoter purpose, oxytetracycline for disease prevention and therapy, while colistin was used for all three purposes. In particular, colistin was indicated for prevention and therapy of gastrointestinal disorders in piglets and poultry caused by gram negative bacteria (in particular E. coli and Salmonella spp).
3.2. Antibiotic Use in Different Systems of Livestock
- It appeared that the use of antibiotics as growth promoters in pig production was significantly different (p<0.05) in the three production systems, displaying the following order: industrial production system > semi-industrial production system > farm household. In breeding poultrys and broilers production, growth promoters are significantly less used in farm households (11.3% and 8.7% respectively) than in semi-industrial and industrial production systems (up to 53.3% of the farm for breeding poultrys), for which there is no significant difference (Table 2a).The use of antibiotics for disease prevention is significantly different with p<0.01 for piglets and with p<0.05 in farm households than in semi-industrial or industrial production systems for fattening pigs, breeding poultry, broilers and laying hens, but not in sows (Table 2a). In piglets, fattening pigs, breeding poultry and laying hens, the use of antibiotics for disease prevention is lower in farm households than in industrial systems (Table 2a).When the antibiotics are used for therapy, a significant difference (p<0.05) between farm household and industrial production systems is observed only for poultry production (breeding poultry, broilers or laying hens), but not for pig production (Table 2a).In a general manner, antibiotics are less used in farm households, and equally used in both semi-industrial and industrial production systems, except for growth promotion purpose in pig production, where the industrial systems are the largest antibiotic users (up to 66.7 % for fattening pigs), and for disease prevention purpose in broilers, where farm households and semi-industrial production systems use less antibiotics than industrial systems (11.3% and 6.7% against 30.0% respectively) (Table 2a).In pig production, the use of antibiotics is not significantly different between the three kinds of age groups (piglets, fattening pigs and sows), when the antibiotics are used for disease prevention. On the contrary, the use is significantly different (p<0.05), when the antibiotics are used for therapy or for growth promotion (Table 2b).For growth promotion and therapy, antibiotics are less used in sows than in piglets, and are equally used for piglets and fattening pigs (Table 2b).In poultry production, the use of antibiotics is significantly different (p<0.05) between the three production systems (breeding poultry, broilers and laying hens), for all considered purposes (disease prevention, therapy or growth promotion) (Table 2b).Growth promoters are equally used in breeding poultry and broilers and not used in laying hens. Antibiotics are more used in breeding poultry for disease prevention, equally used for therapy of breeding poultry and broilers, and less used for therapy of laying hens (Table 2b).If we consider the overall use of antibiotics for the 3 purposes, in the 3 production systems, the number of farms which do not use antibiotics are the following: 2 out of 150 farm households, 13 out 30 semi-industrial pig farms, 2 out of 30 semi-industrial poultry farms, 1 out of 30 industrial pig farms and 6 out of 30 semi-industrial poultry farms.Besides the non-compliance with dosage, length of treatment and withdrawal time, the number of different antibiotics used in each production system appeared to be high. The data in the Table 4 show that up to six categories of different antibiotics can be used in a production system for therapy of pig and poultry. The rate of breeders who used from 1 to 2 antibiotics is high for all kinds of livestock and production systems. Except for breeding poultry raised in semi-industrial systems, the rate of farmers using from 3 to 6 antibiotics is higher than those using 1 or 2 antibiotics (16.7% compared with 13.3%). For fattening pigs, the rate of farmers using from 3 to 6 antibiotics in the three production systems (farm household, semi-industrial and industrial) is rather high (20%; 6.7% and 26.7% respectively).
|
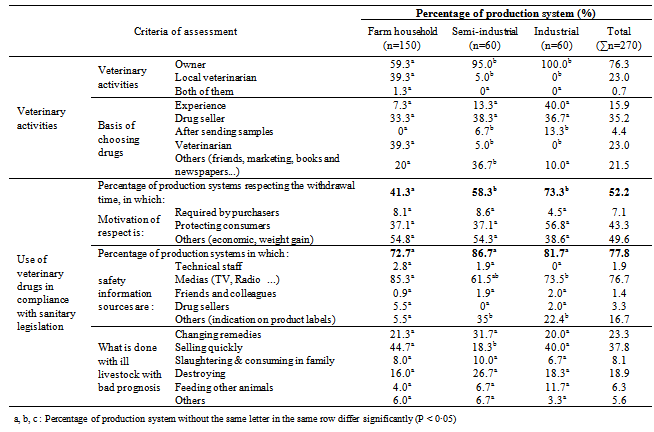
3.3. Veterinary Activities and Issues Linked to Food Safety in the Use of Antibiotics
|
4. Conclusions
- The antibiotic overuse and illegal use in pig and poultry production in the region of the RRD is highly worrisome. Livestock breeders have very low awareness of the reasonableness and safety of antibiotic use as well as the food safety. Their use of antibiotics is very unmethodical and unscientific, mainly based on their experiences of on advices from veterinary drugs sellers after describing symptoms.These preliminary results will be the basis for developing new strategies for a prudent use of antibiotics in food animals in the context of Vietnam. It is necessary not only to strengthen the monitoring system, veterinary network, antibiotic use guidance issues, but also to improve awareness and ethics of producers and veterinary drug sellers as well as training of para-veterinarians and farmers, public awareness and strength of surveillance systems in slaughterhouses.In conclusion, antibiotics have been used largely and even illegally (e.g. chloramphenicol) in both poultry and pig production for disease prevention and treatment.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This study was financially supported by BTC (Belgian Technical Cooperation), the Belgian University Commission toward Development (CUD) and HUA. Thanks to all local veterinarians, Ir. Dong Bui Quang - Researcher of Center for Interdisciplinary Research on Rural Development, Ngai Pham Thi and Tuyen Tran Thi - Veterinary students of HUA for their co-operation to this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML