-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2013; 3(4): 223-227
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20130304.06
Differentiation by Molecular Typing of Bacillus Cereus Isolates from Food in Morocco: PFGE-Eric PCR
S. Merzougui1, 2, M. Lkhider2, N. Grosset3, M. Gautier3, N. Cohen1
1Laboratoire de Microbiologie et d’Hygiène des aliments et des eaux, Institut Pasteur du Maroc
2Laboratoire de Biotechnologie, Biochimie et Nutrition, Faculté des sciences d’El Jadida, Université Chouaib doukkali, Maroc
3Laboratoire de Microbiologie et Hygiène Alimentaire, Agrocampus ouest, Rennes, France
Correspondence to: N. Cohen, Laboratoire de Microbiologie et d’Hygiène des aliments et des eaux, Institut Pasteur du Maroc.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Bacillus cereus is widespread pathogen. It is widely distributed in several environments such as soil and plants and is commonly isolated from food and additives. In this study we analyzed 18 foodborne B. cereus strains isolated in Morocco from food samples (milk and dairy products, rice salade and spices), in order to investigate the genetic diversity (assessed by PFGE and ERIC-PCR). The food samples were collected from hotels (n=38), restaurants (n=32) and private companies (n=26) in several cities in Morocco. The results obtained in this study confirmed the diversity of B. cereus strains. The results showed that PFGE analysis has good discriminatory power but it is long to implement, which promotes the use of ERIC-PCR as a complementary tool for molecular typing. However, additional studies involving cytotoxicity tests would be useful to better evaluate this potential and could provide a more accurate indication of the risk.
Keywords: Bacillus cereus, ERIC-PCR, Foodborne, Genetic Diversity, Morocco, PFGE
Cite this paper: S. Merzougui, M. Lkhider, N. Grosset, M. Gautier, N. Cohen, Differentiation by Molecular Typing of Bacillus Cereus Isolates from Food in Morocco: PFGE-Eric PCR, Food and Public Health, Vol. 3 No. 4, 2013, pp. 223-227. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20130304.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Bacillus cereus is gram-positive andendospore-forming opportunistic human pathogen, and commonly found in wide range of environments including foods[1], it represents one of the major pathogens because its elimination is not guaranteed by pasteurization and sanitation procedures[2]. Although the virulence of B. cereus depends onmultifactorial characteristics[3], upon ingestion of contaminated food, it may lead to two types of food poisoning syndromes: emetic and diarrheal[4-5]. Diarrheal syndrome is caused by the production of enterotoxins including hemolysin BL (HBL) and non-hemolytic enterotoxin (NHE), single protein enterotoxins cytotoxin K (CytK), and enterotoxin FM (EntFM)[6]. The symptoms of diarrheal type was abdominal pain and diarrhea, occur 8-16 h after ingestion of contaminated food[7].The emetic food poisoning is caused by cereulide, a small cyclic heat-stable dodecadepsipeptide toxin[8], the symptoms are characterized by vomiting and nausea, and occur within 1-5 h after ingestion of contaminated food[9].Different studies demonstrate that biochemical identification of B. cereus is not enough for characterisation of B. cereus isolates[10], hence the need of molecular methods for characterisation of B. cereus group.Several factors require consideration when selecting a molecular typing strategy. These include discriminatory power, reproducibility and typeability, as well as the biological basis for grouping similar strains, cost, and logistics[11]. Rapid and inexpensive PCR-based typing techniques, such as enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus-PCR (ERIC-PCR), can be used to screen for genetic relatedness, while the potentially more discriminatory techniques of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) help confirm results. Several molecular methods have been used to reveal the genetic relationship of the B. cereus group species[12-13-14-15-16]. Rapid and reliable molecular subtyping method to epidemiologically trace B. cereus is important in monitoring potential bacterial pathogens in foodstuffs[17]. Nevertheless, few studies have been conducted on the genotypic characterization of B. cereus isolates from Morocco in terms of foodborne poisoning concerns.The objectives of this study were to present the genetic diversity of B. cereus strains and to compare the effectiveness of PFGE and ERIC-PCR for differentiating the diversity of the B. cereus collection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
- A total 18 B. cereus strains related to food samples were used for this study. The strains were isolated from milk and dairy products, rice salads and spices. The food samples were collected from hotels (n=38), restaurants (n=32), and private companies (n=26) in several cities in Morocco (mainly from Casablanca, Tanger, Rabat and Marrakech).A portion of (10 g) of each sample were homogenized for 1 min with 90 ml of sterile 0.1% (w/v) buffered peptone water (BPW), Bio-Rad (Marne-la-Coquette- France), in a stomacher. Three series of three tubes containing 9 ml of modified PMYP (polymyxin-mannitol-egg yolk-phenol red) selective enrichment broth without mannitol, egg yolk and indicator were prepared[18]. Each series was inoculated with 1 ml per tube from the respective dilution. The tubes were incubated at 30°C for 24 h. The transfer of the positive tube-cultures to selective solid medium PMYPA (Malt, Yeast, Peptone, Agar) from Scharlau Chemie made possible to differentiate characteristics of the B. cereus colonies[10]. The cultures were incubated at 30°C for 24 h. Colonies presenting a pink or purple colour with an irregular edge surrounded by a white area were considered as positives and enumerated as described by Valero et al.[10]. The API 50CH galleries were filled, incubated and interpreted according to the instructions specified for each test. The isolates were subjected to a PCR test in order to make sure of their belonging to the Bacillus cereus group and kept frozen in a 50 % (v/v) glycerol solution at -20°C. For this study, all strains were plated on brain heart infusion agar (BHI) and grown at 30°C overnight. In general, cells from one single colony were inoculated in 10 ml BHI-broth.
2.2. PFGE Genotyping
- The protocol for the characterization of strains by PFGE is adapted and optimized from previous work[19]. Nine milliliter of cell suspension was centrifuged for 10 min at 7000×g at 4°C. The supernatants were removed and the pellets were resuspended in 1 ml of TE buffer (pH 8; 10 mM Tris, 1.0 mg lysozyme, 1 M NaCl and 50 mM EDTA), partially embedded in 500 µL agarose (Eurobio, les Ulis, France) and then digested with 2.0 mg of lysozyme (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) and 25 U of lysostaphin (Sigma). The plugs were transferred into a solution containing 0.1 % sodium lauryl sarcosine in 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8), and 200 mg of proteinase K, and the mixture was incubated overnight at 44°C with gentle shaking. DNA was digested with the enzyme SmaI (20 U) following migration performed with the CHFE DRII Biorad system (BioRad) in a 1.5 % agarose gel (Ultra-Pure Gibco BRL, Paisley, Ecosse) in 0.5 x TBE buffer at 14°C with a linear ramping time of 2 to 20 s over a period of 18 h, and a gradient of 200 V. After migration the gels were stained with 1 μg/ml ethidium bromide (BET) and photographed under UV light. (Vilber Loumat, Marne-La-Vallée, France).
2.3. ERIC-PCR Genotyping
- The primer ERIC1R:5′ATGTAAGCTCCTGGGGATTCAC3′ was synthesized to amplify the ERIC-PCR fingerprints of B. cereus. The PCR (25μl) mixture was described previously by Versalovic et al[20], with a modification that consisted of 200 μM of each dNTP, 1.8 U taq polymerase (Biolabs, USA), 3 mM MgCl2, , 10 mM Tris–HCl (pH=9.0), 1.0 μM primer for ERIC1R, 50 ng DNA templates, and an additional distilled sterile water to 50 μl. The amplification reaction was performed as follows: denatured for 5.0 min at 95°C, followed by 40 cycles of 5.0 min at 94°C, 1.0 min at 55°C, and 2.0 min at 72°C; and a final extension step at 72°C for 10 min. PCR results are visualized with an UV transilluminator on agarose gel 1% (Ultrapure DNA grade agarose, Biorad) containing TBE and 1 μg/ml ethidium bromide after migration to 80 V for 2h to record results[21]. Reproducibility was monitored when warranted by comparing the results of PFGE carried out with the same strains.
3. Results
3.1. PFGE Analysis
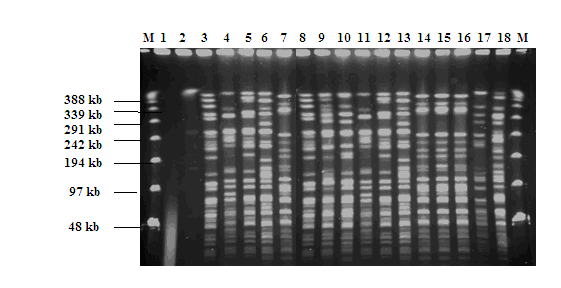
- After optimization on the protocol of Gautier et al[19], the protocol adopted has the advantage of being easily and feasible in short time (4 days). The SmaI macrorestriction profiles of DNA from all isolates tested are shown in Fig. 1. B. cereus genomic DNA digested with SmaI yielded fragments of approximately 48-388 kb. Eighteen PFGE profiles were founded. The lanes 1 to 18 represent the B. cereus strains isolated from different food. These isolates were designated as S1-S18, (isolates S3, S5, S7, S8, S9, S10, S12, S14, S15, S16, S17 and S18 were from milk and dairy products, S2, S4, S11 from spices and S1, S6 and S13 from rice salad). The profiles obtained showed a remarkable polymorphism existing among all strains.
3.2. ERIC-PCR Analysis
- The primers based on the repetitive element sequences were tested at different annealing cycle to select suitable primer. For all B. cereus strains, the ERIC-PCR patterns obtained with the parameters described in Materials and Methods were constantly reproducible. The eighteen strains typing by PFGE were also analyzed by ERIC-PCR.Analysis of major band in ERIC-PCR showed a multiple DNA fragments with various intensities. Those bands were generated for all investigated B. cereus strains (Fig. 2).
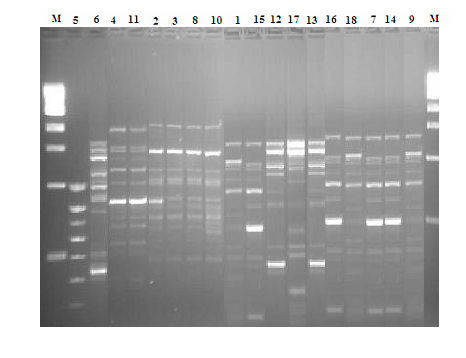 | Figure 2. ERIC-PCR profiles of B. cereus strains representing the same isolates typing by PFGE. M: Molecular weight marker, 100-bp DNA ladder (BioLabs, Beverli, England) |
3.3. Relationship between PFGE and ERIC-PCR
- Comparison of the typing results generated by the two techniques revealed few discrepancies (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2). The majority of strains had concordant typing results in PFGE and in ERIC-PCR (Example: S7-S14- S16; S12-S17), However, some strains had diverging results (Example: S9 -S18; S8-S10).Overall, the results obtained showed that all strains with identical PFGE profiles exhibited a profile similar in ERIC - PCR. However, some strains with identical ERIC-PCR profiles presented different PFGE profiles
4. Discussion
- PFGE and ERIC-PCR provide measures of geneticdiversity, but they are not equivalent. PFGE reveals restriction site polymorphisms arising from the genomic locations of SmaI sites; and ERIC-PCR reveals a profile of DNA fragments of different sizes based, in principle, on the genomic locations of specific repetitive sequences.The protocol of PFGE adopted in this study is reliable and has the advantage of being feasible in 4 days, which is very short compared with the protocol used for typing strains of group by Harrell et al.[12]. The latter, which was reused by Dubouix et al. indeed takes place on eight days[22].The use of PFGE and ERIC-PCR for typing strains of group B. cereus allows us to conclude that the high discriminatory power of PFGE makes it the “gold standard” for DNA fingerprinting techniques but it has some problems related to the implementation time and limited number of samples to be analyzed simultaneously. Chon JW et al. reported that PFGE is a gold standard method for various foodborne pathogens but its laborious[23].The ERIC-PCR is an inexpensive, sensitive, and fast tool for molecular typing which requires no prior knowledge of the genome[24-25]. Guimaraes AS et al. reported that the greatest discriminatory power and typeability observed to the ERIC-PCR could be explained by large number of isolates typed[26]. At our knowledge, this study is the first that provides a comparison of the PFGE (using the enzyme SmaI) with ERIC-PCR for typing isolates of B. cereus group. Otherwise, a same comparison has been the subject of some recent studies, including a study of Klebsiella pneumoniae[27] and another on Mycobacterium fortuitum[28]. These authors conclude that it was a very similar level of discrimination between the two methods. For Sampaio et al.[28], PFGE has a very powerful method for strain typing but it’s laborious, with only a limited number of samples to be analyzed at the same time.It is often desirable to combine several typing methods. The application of bacterial typing tools requiresunderstanding of both the strengths and limitations of the chosen bacterial[23]. For any bacterial strain assumed to be involved in food poisoning of humans, it is extremely important to possess a wide range of powerful molecular, identification and monitoring tools able to adequately characterize all these strains. Our suggestion for save the time is to use the ERIC-PCR to make a first screening of isolates. Only isolates that had identical profiles can be analyzed by PFGE, which will reduce the number of analyzes with this method more discriminating but also more expensive. In the case of finding a source of contamination in the food industry, ERIC-PCR may be sufficient to trace the bacteria, the high level of discrimination provided by PFGE was not helpful (detection, for example, spontaneous mutation affecting a restriction site). On the contrary, in the case of food poisoning, PFGE, which is the reference method should be used to remove any ambiguity on the differentiation of closely related strains.During this study we confirmed the ubiquitous nature of these bacteria. Our results indicate that some strains belonging to the same type of foods give the same profile in PFGE and in ERIC-PCR, knowing that different profiles are also obtained for strains of the same type of food, we can assume the existence of other influencing factors such as the environment.
5. Conclusions
- In conclusion, our study indicate that all isolates were successfully differentiated, indicating the diversity of B. cereus strains present in Morocco samples. The results showed that PFGE is a method that has a high discriminatory power but it is laborious, which promotes the use of ERIC-PCR to be used in priority and previously to PFGE as a typing strategy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are grateful to all collaborators in this study. We would like to thank RIIP (Réseau International de l’Institut Pasteur) for able finance collaboration.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML