-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2013; 3(1): 21-27
doi:10.5923/j.fph.20130301.03
MetabolicResponse of Sedentary Normotrophic Rats to Dietary Prehydrolyzed Whey Proteins
Daniela Gasparetto 1, Pablo Christiano B. Lollo 1, Carolina Soares de Moura 1, Flávia Maria M. de Paula 2, Everardo M. Carneiro 2, Jaime Amaya-Farfan 1
1Department of Food and Nutrition, School of Food Engineering, University of Campinas, Campinas, 13083-862, Brazil
2Department of Anatomy, Cell and Molecular Biology, Institute of Biology, University of Campinas, Campinas, 13083-865, Brazil
Correspondence to: Pablo Christiano B. Lollo , Department of Food and Nutrition, School of Food Engineering, University of Campinas, Campinas, 13083-862, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
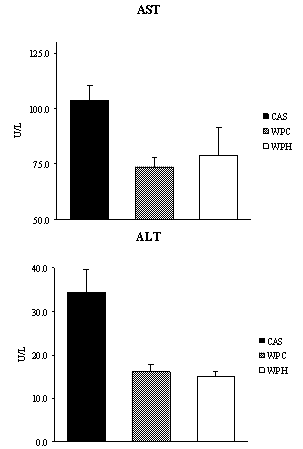
In this study we report that, unlike the case of obese or high-fat fed animals, consumption of a whey protein hydrolyzate can have a minimal impact on skeletal muscle metabolic gene expression in sedentary eutrophic rats and still a moderate effect on body fat. Male Wistar rats were fed diets with either whey-protein concentrate (WPC), a whey-protein hydrolyzate (WPH) or casein (CAS), during two weeks. Gastrocnemius and blood were withdrawn for analysis of the expression of the PPARα, PPARδ, PGC-1α, CPT-1β and myostatin genes, classical serum parameters, non-esterified fatty acids (NEFA), triacylglycerols (TAG), albumin, alanine and aspartate aminotransferases (ALT, AST), in addition to muscle and serum free amino acid profiles. The diet appeared to have no effect on the expression of any of the muscle genes besides, no significant changes being observed in serum NEFA, TAG or creatinine. Compared to CAS, the animals fed either WPC or WPH exhibited lower activities of ALT, AST, together with higher serum albumin levels in the WPC group. It was also observed that the diets containing the whey proteins produced increased levels of serum glycine, whereas in the muscle several amino acids were increased in the animals that consumed WPH. Although the whey protein diets did have an effect on the profile of free muscle amino acids and improved the outcome of classical enzyme biomarkers, consumption did not result in the exacerbation of such parameters of normal animals consuming normolipidic diets.
Keywords: Hydrolyzed Milk Whey, Dietary Protein, Body Composition, Gene Expression, Sedentarism
Cite this paper: Daniela Gasparetto , Pablo Christiano B. Lollo , Carolina Soares de Moura , Flávia Maria M. de Paula , Everardo M. Carneiro , Jaime Amaya-Farfan , MetabolicResponse of Sedentary Normotrophic Rats to Dietary Prehydrolyzed Whey Proteins, Food and Public Health, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 21-27. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20130301.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The milk whey proteins have amino acid profiles that exceed the recommendations for most nutritionally indispensable amino acids, including tryptophan, lysine, cysteine, leucine and isoleucine[1]. Because they are rich sources of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), the whey proteins are widely studied in relation to their benefits for physical activity, as documented by Pimenta et al.[2], Morifuji et al.[3] and Morifuji and Sakai[4]. One feature that distinguishes the whey proteins from casein is their ability to quickly raise the blood levels of amino acids, which has earned them the name of ‘fast metabolizing proteins’[5]. The consumption of the pre-hydrolysed proteins tends to enhance this phenomenon because the absorption of such hydrolysis products, which contain large amounts of di- and tripeptides, occurs faster than the uptake of free amino acids[6].Several bioactive peptides have been identified in the hydrolyzates of whey proteins[7, 8], and an implicit advantage of consuming a pre-hydrolyzed protein may reside in the ingestion of large concentrations of bioactive peptides at any one time, which may result in significant amounts of paracellular absorption. Previous results from various workers have shown that some of the benefits of consuming a protein hydrolyzate include the improvement of physical performance of rats[2, 9, 10], the preservation of muscle glycogen stores[10, 11], the sparing of serum albumin[2, 11], the resistance to the elevation of blood lactate[2] and the possible reduction of metabolic stress[9].A decrease in the activity of hepatic lipogenic enzymes has been attributed to the unhydrolyzed whey proteins, while up-regulating fatty acid oxidation in the muscle[3] thus suggesting that the whey proteins play an important role in suppressing hepatic fatty acid synthesis. According to those authors, therefore, the use of whey proteins may decrease the accumulation of body fat and prompt the skeletal muscle to use fat for energy production during prolonged exercise[3]. The intake of whey protein associated with a high fat diet, for instance, has been reported to lead to a lower body fat accumulation in female C57BL/6J mice. The consumption of a product based on whey protein promoted the greatest loss of body fat in adults[13]. Park et al.[14] observed decreased total serum lipids and triacylglycerols with diet formulated with whey proteins (both whole proteins and hydrolyzates).The expression of key genes involved in the management of lipid storage and utilization by the body has become a tool for assessing the effects of dietary ingredients on lipid metabolism. The isoforms α and δ of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) are related to the expression of genes involved with the use of lipids, lipid transport and fatty acid metabolism[15]. The PPARα is highly expressed in tissues with high mitochondrial and peroxisomal β-oxidation[16], and the isoform δ stimulates β-oxidation and the use of triacylglycerols through two pathways: the fatty acid oxidation and energy uncoupling[17]. The gene coding for the PPARγ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) is another protein involved in multiple physiological functions, such as adaptive thermogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, gluconeogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis[19], and its increased expression is critical for the activation of genes related to the oxidative metabolism of skeletal muscle[20]. The enzyme carnitine palmitoyl transferase I (CPT-1) is in turn considered responsible for a limiting step in the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria and therefore in the process of β-oxidation[21].Here, we wished to assess the effects that the consumption of prehydrolyzed whey proteins can cause on the expression of such genes involved in the utilization of lipids as PPARα, PGC-1α, CPT-1β, PPARδ, and myostatin, plus classical serum parameters relative to lipid metabolism in the skeletal muscle of sedentary normotrophic rats, all in comparison with the unhydrolyzed whey protein and casein.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Diets and Bioassay
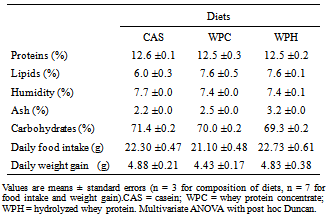
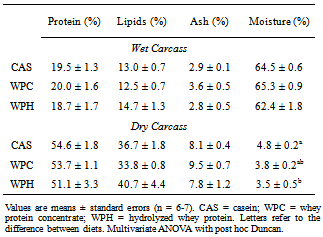
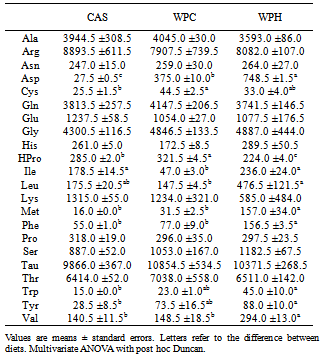
- Twenty-eight male Wistar rats were purchased from the Multidisciplinary Centre for Biological Investigations (Cemib, University of Campinas, Campinas, SP, Brazil) and housed in controlled ambient conditions (22 ± 2℃, 50–60% relative humidity, 12-hour inverted light-dark cycle, and free access to food and water. Animals were fed with commercial chow (Labina, Purina, Brazil) during four weeks for growth. At the end of this period, the animals were fed for two weeks the experimental diets for rodents (AIN 93-G)[22], except that the protein content was reduced to about 12%, different from the 17% recommended for maximal growth. The control protein sources were the commercial whey (intact) protein concentrate (Hilmar™ 8000), the experimental protein sources were a commercial whey protein hydrolyzate (Hilmar™ 8350), both from Hilmar Ingredients (Hilmar, CA, USA), and casein as the reference standard (Cow's milk casein, mesh 30, Conaprole, Uruguay). The proximal composition of every diet (Table 1) was determined by standard procedures: proteins, lipids, humidity, ash and carbohydrates were by the AOAC International procedures, using the 6.38 protein conversion factor for the diets and 6.25 for casein. The animals were subjected to minimal physical activity (10 min in a treadmill, twice weekly, at 12 m∙min-1) in order to minimize eventual alterations in metabolic responses arising from stressful handling. Rats were sacrificed by decapitation 48 hours after the last bout of exercise. Samples of blood, gastrocnemius muscles and intra-peritoneal plus epididymal fat were removed for analysis. The carcasses (less intestine, heart and liver) were liofilized and their compositions determined employing the same methods used for the diets. The research protocol was approved by the institutional Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation (University of Campinas).
|
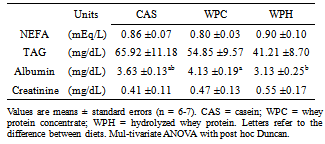
2.2. Serum Parameters
- Commercial kits (Laborlab Ltda, Brasil) were used to determine serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST, EC 2.6.1.1, cat nº 00300), alanine aminotransferase (ALT, EC 2.6.1.2, cat nº 00200), triacylglycerol (cat nº 02700), albumin (cat nº 03900) and creatinine (cat nº 01600). Non-esterified fatty acids were determined by commercial kit of Wako Chemicals (Neuss, Germany). All readings were realized in spectrophotometer (DU® 640, Beckman-Coulter, USA).
2.3. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
- Left gastrocnemius muscle was collected in TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, SP, Brazil). Total RNA was isolated according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and quantified by a spectrophotometry. The integrity of RNA was verified by agarose gel electrophoresis. Complementary DNA was prepared using 3 µg of total RNA and MultiScribe reverse transcriptase (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The Fast SYBR® Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) was employed to dye fluorescent color that binds only double-stranded DNA. The genes analyzed and sequences of the primers are in Table 2. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was carried out in the StepOne termocycler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). A total volume of 15 µL was used for the PCRs. Samples were first denatured at 94℃ for 5 min followed by up to 40 PCR cycles. Each PCR cycle comprised melting at 94℃ for 30 s, annealing at 57℃ for 30 s and extension at 72℃ for 30 s. Real-time data were analyzed using the Sequence Detector System 1.7 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Each PCR amplification was performed in duplicate. The purity of the amplified PCR products was verified by melting curves. Analysis of sequences and adjustments were made using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) to identify genomic sequence in the GenBank, National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI/ USA).
|
2.4. Serum and Muscle Free Amino Acids
- Measurements of the serum and muscle free amino acids followed the method of White and Hart[23] with some modifications. Volumes of 100 μL of serum were weighed and added with 100 μL of α-aminobutyric acid as internal standard, and the volume completed to 1,000 μL with 99% methanol. The mixture was vortexed to precipitate the proteins and centrifuged at 19000 g for 15 minutes. Muscle samples (right gastrocnemius) were processed in a similar manner. The supernatant was filtered and aliquots of 40 mL of filtrate were transferred to an evaporation tube and derivatized. After derivatization, the samples were dried, dissolved in 0.002M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 and injected into a chromatograph equipped with a Luna C18 Phenomenex column (100Å 5u 250 x 4.6mm 00G-4252-EQ; EUA).
2.5. Statistical Treatment
- The data were analyzed by multivariate analysis of variance, and Duncan’s post hoc test. All analyses were performed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 17, software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) adopting the standard criterion of significance of P < 0.05.
3. Results
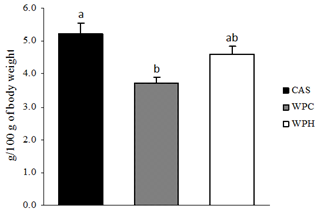
- The results of weight gain and food intake are displayed in Table 1, and those of adipose tissue mass in Figure 1. After consuming the diets for 14 days, no effects were observed in weight gain and food intake. However, the intra- peritoneal/epididymal adipose mass was decreased in the rats fed the whey proteins (WPC), compared to the ones fed the casein diet, although the lipid content in the carcasses did not change (Figure 1 and Table 3).
|
|
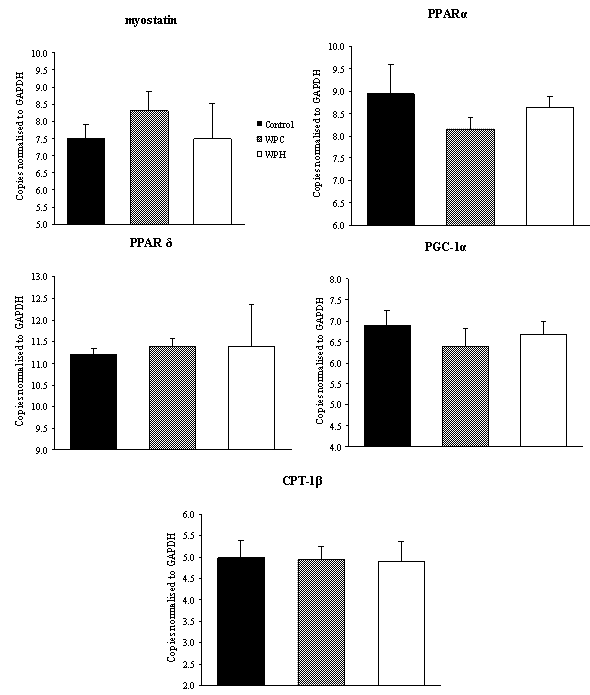 | Figure 3. Comparison of gene expression in the gastrocnemius muscle (n = 4). Control = casein; WPC = whey protein concentrate; WPH = whey protein hydrolyzed. Multivariate ANOVA with post hoc Duncan |
|
4. Discussion
- Under the conditions of the present study, i.e., chronic feeding of a balanced diet to eutrophic growing animals, it was possible to verify that consumption of a diet containing the whey protein concentrate (WP) resulted in a decrease of the total adipose tissue with respect to the standard diet. It has been reported that consumption of the milk whey protein can diminish body fat[12, 13, 24, 25], which is consistent with our findings. Although a net, yet non-significant, decrease in the fat tissue was observed in the animals that consumed the prehydrolyzed whey protein, we now report that the hydrolyzed protein did not exert a fat reducing effect in the sedentary young rat. It is possible that in the sedentary state, the short experimental period (2 weeks) was insufficient to demonstrate more substantial differences in serum and body parameters. However, we found a significant reduction in alanine and aspartate aminotransferases (ALT and AST) levels. No other results were found in the literature that could be used for comparison. The results obtained in this study, nevertheless, are consistent with reports by Chitapanarux et al.[26], who used cysteine-supplemented WPI in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients, by Silva et al.[27], who supplemented amyotrophic-lateral-sclerosis patients with whey proteins, and also by Watanabe et al.[28], who offered commercial product based on whey proteins for 12 weeks to patients with hepatitis B. The whey proteins have also been shown to reduce ALT and AST levels after induction of hepatotoxicity[29] and nonalcoholic fatty liver[30]. Nevertheless the opposite result was reported by Morifuji et al.[4] in rats subjected to physical training, where the diet with whey proteins produced higher levels of ALT liver than with casein. The authors interpretation was based on the greater enzyme activity recorded in the liver with increased plasma concentrations of alanine, in response to higher release of alanine from muscle to be converted to glucose in the liver (glucose-alanine cycle). These authors, however, did not observe differences in AST levels. Serum albumin was another parameter that was altered by the diet. Unlike observations made by Pimenta et al.[2] and Tassi et al.[11], albumin levels were higher in animals fed with WPC, than the ones fed with WPH. The intake of whey protein, either the WPC or WPH, did not produce any visible alterations in the expression of the genes PPARα, PPARδ, PGC-1α and CPT-1β. However, the lack of literature dealing with the relationship between the consumption of whey proteins and the expression of these genes makes it difficult to establish a discussion. In the case of PPAR, one paper dealing with the expression of the gene PPARγ isoform was found. Eller and Reimer[31] found that the gene for PPARγ in the liver of rats fed with whey proteins was downregulated compared to casein. Using whey proteins along with high doses of vitamin D and calcium in the study on reduction of weight gain before the consumption of diets rich in carbohydrates or fat, Siddiqui et al.[25] observed that there was an up-regulation of PGC-1α gene in muscle, whereas CPT-1β and myostatin genes showed no changes. The latter gene showed no difference in our study. The hydrolyzed whey proteins of our study influenced only the levels of the amino acid glycine in the serum. The WPH diet caused a significant increase in concentration of glycine, which was not seen with the WPC or casein diets. Adipocyte size and fat percentages are known to be reduced in mice fed lactoferrin and α-lactalbumin, which are rather rich sources of glycine[38]. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that the dietary supply of this amino acid associated to a body fat loss and to the reduction of adipocyte size[39]. Morifuji and Sakai[4] also observed increased levels of glycine, besides alanine and arginine in animals fed the whey proteins compared to ones fed with casein. With respect to the muscle free amino acids, it could be noticed that the WPH diet produced more pronounced increases than the WPC diet. It was interesting to note that, in addition to the large amounts of nutritionally indispensable, and hydrophobic amino acids. The of BCAAs, which are the most readily used amino acids under circumstances of proteolysis, were also present in higher levels in the muscle of rats fed with WPH, than in those fed WPC. The relevance of such differences could probably be more related to the composition of the dietary proteins than to the physiology of the muscle.
5. Conclusions
- This study was designed to assess the metabolic response of diets containing either whole milk whey protein (WPC) or these proteins after undergoing partial enzymatic hydrolysis (WPH), compared to the standard casein protein on sedentary normal rats. It was observed that the growing, eutrophic sedentary rat fed normolipidic diets containing either form of the whey proteins or casein as the sole source of protein showed essentially the same response with regard to lipid utilization, while WP and WPH tended to decrease intraperitoneal and epididymal fat, and no negative changes occurred in the muscle. This suggested that under normal metabolic and dietary conditions, prolonged consumption of the hydrolyzate was safe and that the changes in adipose tissue mass observed could be beneficial. In spite of that, the study also showed that consumption of whey proteins, whether whole or hydrolyzed, can alter the free muscle amino acid profiles lowering serum alanine and aspartate aminotransferase, key biomarkers of liver/muscle injury.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors thank Hilmar Ingredients, for the gift of the whey protein products, CAPES (Agency for the Improvement of Human Resources in Higher Education, Brazil) and FAPESP (Foundation for Research of the State of São Paulo, grant 2010/02419-0).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML