-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2012; 2(4): 110-112
doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20120204.05
Dietary Antioxidant Profile and Control of Lipid Oxidation Characteristics of DaniellinTM
Gabriel O. Adegoke 1, Theophilus E. Nkpa 1, Adenike A. Oguntubo 1, Oludele A. Itiola 2
1Department of Food Technology, University of Ibadan, Ibadan. Nigeria
2Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan. Nigeria
Correspondence to: Gabriel O. Adegoke , Department of Food Technology, University of Ibadan, Ibadan. Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
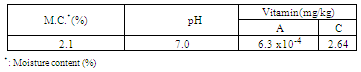
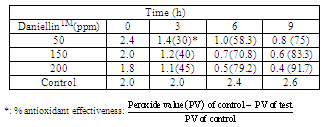
The aim of this present work is to study the possibility of using DaniellinTMas a dietary antioxidant and for controlling lipid oxidation in dairy milk.Daniellin TM found earlier to be able to control the production of ochratoxin A in a non-alcoholic beverage was produced in tablet form and it had (mg/g): vitamin A(6.3x10-4)and vitamin C(2.64). DaniellinTM dietary antioxidant with a moisture content of 2.1 %, pH 7.0 played an important role in lipid peroxidation because when it was added to fresh dairy milk at 50, 150, and 200 ppm ithad antioxidant effectiveness of 69.2%, 76.9% and 84.6% respectively.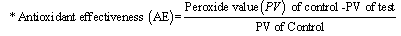
Keywords: Daniellintm, Antioxidant, Lipid Oxidation, Dairy Milk
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Dietary antioxidants are molecules that prevent cell damage against free radicals and are critical for maintaining optimum health in both animals and humans and apart from their beneficial effects on immune cell function dietary antioxidants are also useful for protection against infectious microorganisms(1).In order to helpthe prevention of or at least, delay the onset of several degenerative disorders, it is essential to have an adequate intake of antioxidant nutrients from an early age(2).Diets rich in antioxidant-containing components such as polyphenolic compounds, vitamins E and C,andcarotenoids are believed to be useful nutrients in the prevention of oxidative stress-related diseases(3).Furthermore,dietsrich in antioxidant-containing compounds have been reported to relate with lower risks of some cancers and coronary heart disease(4) and antioxidants have been found to have the ability to protect the body from damage caused by free radical oxidative stress(5).At 750 µg / ml, a fractionfrom the leaf ofAframomumdanielliwas reported to be potent in scavenging 1,1,diphenyl 1, 2 picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radicals(6). The antioxidantsobtained from A.danielli(7), the source of DaniellinTM, are more potent than synthetic antioxidants like butylatedhydroxytoluene (BHT) and butylatedhydroxyanisole(BHA).When DaniellinTMwas incorporated into a non-alcoholic beverage with storage at 26± ℃ for 5 days, the protein content and calorific value of treated samples increased and there was a 100 % reduction in the level of ochratoxin A in the samples(8). However, with a paucity of data on the application of Daniellin™ in food matrices, andwithmilk being a source of organic compounds and minerals(9), we became interested in the possibility of utilizing Daniellin™ as a dietary antioxidantand in order to control lipid oxidation in milkasA daniellifrom where DaniellinTMwas produced,has previously been used to control lipid oxidation in different food systems(10,11).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk
- Fresh cow’s milkobtained in Ibadan,Nigeria and was kept at 4-10℃ under aseptic conditions until used for analyses.
2.2. Preparation of Dietary Antioxidant
- Arising from experimental trial runs in order to determine the concentrations ofDaniellin™ ingredient to excipent for use in tablet formulation, the following (w/w) were chosen: Daniellin™, 4.8 %; ascorbic acid, 32% and lactose, 20 %, thereafter the materials weremixed by gentle turningusing pestle in a mortar. The method described by Adebayoand Itiola(12)for tablet productionwas modified as follows: 500 mg of mixture (Daniellin™-ascorbic acid- lactose) was compressed on a Carver hydraulic hand press machine(Model C, Carver Inc, USA) using a 10.50 mm diameter die and flat-faced puncheslubricated with 0.3 % (w/v) of magnesium trisilicate dispersed in acetone with dwell-time of 1 min and compression pressure of 1.0 Torr.After ejection, Daniellin™ dietary antioxidant tablets were stored over silica gel in a desiccator for 24-36 h to facilitate hardening and elastic recovery.
2.3. Moisture Content and pH
- For moisture content and pH determinations, the methods described by AOAC (13) were employed.
2.4. Minerals
- Into a macro-Kjeldal digestion flask was placed 5g of Daniellin™ dietary antioxidant, 20 ml ofconHNO3and20 ml of distilled water.The mixture was boiled to half of its original volume afterwhich it was cooled to 26 ± 1℃ and 10ml of con H2SO4 was added followed by heating until white fumes appeared.The mixture was cooled, boiled till white fumes appeared, filtered andusedfor detection of minerals with Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer(13). The procedure was done in duplicate.
2.4. Vitamin A
- The method described by Kirk and Sawyer(14) was modified as follows: to 2 g of Daniellin™ dietary antioxidantwere added: hydroquinone, 10g; ethanol, 40 ml and potassium hydroxide solution, 10 ml followed by boiling under reflux action for 30 min.The mixture after cooling was transferred along with 20 ml of distilled water into a 500 ml separatory funnel.Extraction was then carried out twice using 25 ml of diethyl ether. Washing of the extract was done using50 ml of distilled water and ether was thereafter distilled off.Absolute alcohol, 5 ml was added to the extract, evaporated to 5 ml in order to remove excess water.The residue was dissolved in isopropyl alcohol, centrifuged and optical density taken at 520 nm was used to calculate concentration of vitamin A:
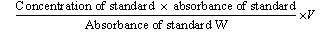 Where V = volume of solution containing sample weightW = weight of sample taken
Where V = volume of solution containing sample weightW = weight of sample taken2.5. Vitamin C
- For the determination of vitamin C (ascorbic acid), the method described elsewhere(13) was employed.
2.6. Antioxidant Effectiveness
- The methods for addingDaniellin™to milk, determination ofperoxide value (PV)and antioxidant effectiveness (AE) were similar to methods described earlier (7).
2.7. Microbialcounts
- Bacterial and fungal counts ofDaniellin™ dietary antioxidant were carried out as described by Adegoke(15).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemicalanalysis of DaniellinTM Dietary Antioxidant
- DaniellinTM dietary antioxidant with a moisture content of 2.1%had some minerals and vitamins (Table 1). The plant material from where DaniellinTM was produced had minerals like magnesium and calcium(10).DaniellinTMdietaryantioxidanthad vitamins E and C and other nutrients. In the prevention of oxidative stress-related diseases(3) ,vitamins A and C and other nutrients present in fruits and vegetables are known to be useful particularly as dietary antioxidants have been found to modulate the host susceptibility or resistance to infectious pathogens(1).With evidence-based science linking diet to reduction in non-transmissible chronic disease risks(15), the relevance offoods that provide attributes beyond nourishing properties (16) are relevant. Furthermore, in order to help prevent the development of, or at least delay the onset of several degenerative disorder, it might be essential to have adequate intake of antioxidant nutrients from early age as adequate amounts ofantioxidants that neutralize oxidant –mediated tissue injury can help prevent damage to the immune cells(2). When it is realized that intake of dietary antioxidant supplement can help to reduce the adverse effects of oxidative stress in man(17), DaniellinTMwith its nutrients and an antioxidant effectiveness of 84.6% at after9 hours of its addition to dairy milk (table 2),can be further explored foruse in stabilizing fat-containing foods and also providing additional benefits to consumers.With the use of DaniellinTM in the stabilization of the milk in this present study, it is possible that DaniellinTM can also be useful in other dairy products packed using transparent materials where light oxygen and light –induced changes have been reported(18).Microbiological characters of DaniellinTM dietary antioxidantUsing standard microbiological methods, DaniellinTM dietary antioxidant before being added to test milk was found to have an acceptable microbiological quality ( data not shown) had a count of 7.3 x 101 and this countis within the acceptable limit for orally administered solid in pharmaceutical preparations(19). DaniellinTM has earlier been found to have potent inhibitory activities against ochratoxin A and aflatoxins and extending the shelf life of a perishable beverage(10).
|
|
4. Conclusions
- DaniellinTM stabilized dairy milk and the dietary antioxidant has vitamins A and C.and minerals like iron ,calcium and magnesium.As some antioxidants of plant origin have been recommended for use as potential chemotherapeutic agents in place of the ones currently being used for treatment of some degenerative processes like cancer(21), and with the report of the protective effects ofAframomumdanielli (source of DaniellinTM) on liver cells andlowering of levels of some enzymes associated with liver dysfunction(22) DaniellinTM is beingexaminedfor its potential applications in agriculture and medicine.Furthermore, as Daniellin TM was ableto control lipid peroxidation in fresh milk, our future research works will highlight the synergistic effects of DaniellinTM with antioxidant nutrients in dairy milk.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML