-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Food and Public Health
p-ISSN: 2162-9412 e-ISSN: 2162-8440
2012; 2(1): 39-42
doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20120201.08
Determination of Aflatoxin Levels in Some Dairy Food Products and Dry Nuts Consumed in Saudi Arabia
Muhammad Waqar Ashraf
Department of Mathematics & Natural Sciences, Prince Muhammad Bin Fahd University, P.O Box 1664, Al Khobar ,31952, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: Muhammad Waqar Ashraf , Department of Mathematics & Natural Sciences, Prince Muhammad Bin Fahd University, P.O Box 1664, Al Khobar ,31952, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Three hundred and ninety-three samples of dairy products (124 samples of white cheese, 61 samples of cream cheese, 76 samples of Kashar cheese, and 132 samples of butter), 91 samples of cashew nut and 97 macademia nut marketed in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia during September 2010-September 2011, were analyzed for aflatoxin M1 (AFM1), total aflatoxin and AFB1 by microtitre plate enzyme linked immunosorband assay (ELISA) The incidence of AFM1 contamination in dairy products analyzed was 82%. Total aflatoxin contamination was determined in 84 (92.3%) of 91 cashew nut and in 88 (90.7%) of 97 macademia nut whereas total aflatoxin contamination was not detected in 3 (3.2%) of 91 cashew nut samples and in 12 of 97 macademia nut samples. AFB1 was found in 84 (92.3%) of 91 cashew nut and in 83 (85.5%) of 97 samples of macademia nut samples. AFM1 levels in 3 (2.4%) white cheese, 4 (3.0%) of butter, 2 (3.2%) in cream cheese and 5 (6.5%) of Kashar cheese samples were found higher than the maximum acceptable levels as set by European Union.Continuous surveillance program may be warranted to monitor regularly the occurrence of aflatoxins in foodstuffs.
Keywords: Aflatoxins, Dairy Products, Dry Fruits
Cite this paper: Muhammad Waqar Ashraf , "Determination of Aflatoxin Levels in Some Dairy Food Products and Dry Nuts Consumed in Saudi Arabia", Food and Public Health, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2012, pp. 39-42. doi: 10.5923/j.fph.20120201.08.
1. Introduction
- Incidences of food contamination have become increasingly frequent in recent years raising question about their human health and economic consequences. Aflatoxins (AFs) are highly toxic secondary mould metabolites. Mycotoxicoses, which can occur in both industrialized and developing countries, arise when environmental, social and economic conditions combine with meteorological conditions (humidity, temperature) which favor the growth of moulds. Aflatoxins are a group of structurally related toxic compounds produced by certain strains of the fungi Aspergillus flavus, which produce only B aflatoxins and Aspergillus parasiticus which produces both B and G aflatoxins. The major aflatoxins of concern are designated B1, B2, G1 and G2. These toxins are usually found together in various foods and feeds in various proportions. Aflatoxins M1 and M2 are oxidative metabolic products of aflatoxin B1 and B2 produced by animals and is usually excreted in the milk, urine and faces of dairy cattle and other mammalian species that have consumed aflatoxin-contaminated food or feed. Aflatoxicol is reductive metabolite of aflatoxin B1 (Kumar et al, 2008; Bakirci, 2001; Galvano, Galofaro, & Galvano, 1996; Galvano et al. 2001; Kotsonis, Burdock, & Flamm, 1996; Stubblefield & Shannon, 1974). Many researchers reported that there was a linear relationship between the amount of AFM1 in milk and AFB1 in feed consumed by the animals (Bakirci, 2001).The most pronounced contamination has been encountered in the tree nuts, peanuts, and other oil seeds, including corn and cottonseed. Therefore, data on the occurrence of aflatoxins in foods and feeds are needed to enable exposure assessment and estimate the effects of regulatory limits. AFM1 may or may not be present in dairy products in a particular year depending on the weather conditions for that period. Hence, widespread and frequent monitoring should be carried out (Galvano et al., 1996). Aflatoxins are acutely toxic, immunosuppressive,mutagenic, teratogenic and carcinogenic compounds. The main target organ for toxicity and carcinogenicity is the liver (Aflatoxins in Foods: Risk Assessment Studies, 2001; Kocabas & Sekerel, 2003; Kotsonis et al., 1996; Peraica, Radic, Lucic, & Pavlovic, 1999).Milk and milk products are a major nutrient for human especially children. However, at the same time these products may be contaminated with AFM1 resi- dues, a human health hazard. For this reason, many countries have regulations to control the levels of aflatoxin B1 in feeds and to propose maximum permissible levels of AFM1 in milk to reduce this risk (Rastogi, Dwivedi, Khanna, & Das, 2004; Sarımehmetoglu, Kuplulu, & Celik, 2004).A number of survey and monitoring programs have been carried out in several countries attempting to obtain general pattern of extent of food contamination (Abdulkadar, Abdulla, & Jasim, 2000; Aycicek, Yarsan, Sarımehmetoglu, & Cakmak, 2002; Galvano et al., 1996; Gunsen & Buyukyoruk, 2002; Oruc & Sonal, 2001; Rastogi et al., 2004). Current aflatoxin analysis is done by various methods including thin layer chromatography (TLC), liquid chromatography (LC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ELISA (Abdulkadar et al., 2000; Bakirci, 2001; Dagoglu, Keles, & Yildirim, 1995; Garden & Strachan, 2001; Sarımehmetoglu et al., 2004). The European Commission have set limits for maximum levels of total aflatoxin and AFB1 allowed in groundnuts, nuts, dried fruit and their products. For foods ready for retail sale, these limits are 4 µg/kg (total aflatoxins) and 2 µg/kg (AFB1), and for nuts and dried fruit to be subjected to sorting, or other physical treatment, before human consumption or use as an ingredient in foodstuffs the limits stand at 10 µg/kg (total aflatoxins) and 5 µg/kg (AFB1). The EU Commission legal limits for AFM1 in milk, butter and cheese are 0.05 µg/l (Codex Alimentarius Commission, 2001; Commission Regulation, 2002; Turk Gda Kodeksi Teblig, 2002). Saudi Arabia is the largest consumer of dry fruits in the GCC. On the other hand, dairy products have been produced and consumed widely in Saudi Arabia. Purpose of this study was to determine occurrence and levels of aflatoxins in some dairy products and dry fruits consumed by Saudi people.
2. Materials and Methods
- A total of 124 samples of white cheese, 61 samples of cream cheese, 76 samples of Kashar cheese, 132 samples of butter (393 dairy products) and 91 samples of cashew nut and 97 samples of macademia nut (total 188 samples) were obtained randomly from markets in Eastern Province were analyzed from September 2010 to September 2011 and aflatoxin concentrations were determined by enzyme linked immunosorband assay, ELISA (Ridascreen, aflatoxin M1-r- biofarm) in our laboratories. All samples were collected and analysed before their expiration dates exceeded. The samples were analysed as procedure which described by R- Biopharm GmbH (Enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative analysis of aflatoxins, 1999). Immunoaffinity columns were used for samples (RIDA-Aflatoxin column-r- biopharm) clean up prior analysis of aflatoxin M1 and B1 levels in dairy products (cheese and butter) and dry fruits (cashew nut and macademia nut). The basis was antigen- antibody reaction. The column contained a gel suspension to which monoclonal antibodies were attached covalently. The antibodies were specific for the aflatoxin B1 and M1 (Figures 1 & 2).For aflatoxin M1 analysis, 2 g of samples and 40 ml dichloromethane were used for extraction. The suspension was filtered and a 20 ml extract was evaporated under nitrogen. The extraction procedure was repeated with 0.5 ml phosphate buffered solution (PBS) and 1.0 mL heptane and centrifuged for 15 min at 2500 rpm and 15℃. The methanol layer was used for AFM1 testing. Detection limit was <10 ppt.For total aflatoxin analysis, 2.0g of sample was weighed into a screw-top glass vial. Ten milliliter methanol/distilled water (70/30) was added and mixed by using shaker for 10 min at room temperature (20-25 C). Extract was filtered by using Whatman 41filter paper, 100 µL of the filtrate diluted with 600 µL of sample dilution buffer and 50 µL of diluted filtrate was transferred per vial in the assay. The mean recovery rate has been determined to be 85% with a coefficient of variation of 15%.
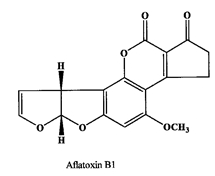 | Figure 1. |
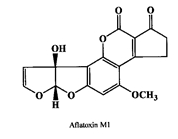 | Figure 2. |
3. Results and Discussion
- In this study, AFM1 contamination in the dairy products (cream cheese, butter, white cheese and Kashar cheese) was 80.4% (316 samples of 393) whereas AFM1 was not detected in 77 samples (19.4%). AFM1 levels in the cream cheese, butter, white cheese and Kashar cheese samples were 80.3% (49 of 61), 71.2% (94 of 132), 84.6% (105 of 124) and 96.0% (73 of 78), respectively. AFM1 contamination was not detected in 12 (19.6%) cream cheese, 19 (15.3%), white cheese, in 5 (6.5%) Kashar cheese, and in butter 41 (31.0%) samples (Table 1). AFM1 levels in 3 (2.4%) white cheese, 4 (3.0%) of butter, 2 (3.2%) in cream cheese and 5 (6.5%) of Kashar cheese samples were found higher than the maximum acceptable levels (cheese: 250 ng/kg, butter: 50 ng/kg) of the Turkish Food Codex (Turk Gda Kodeksi Teblig, 2002). Total aflatoxin contamination was determined in 84 (92.3%) of 91 cashew nut and in 88 (90.7%) of 97 macademia nut whereas total aflatoxin contamination was not detected in 3 (3.2%) of 91 cashew nut samples and in 12 of 97 macademia nut samples. Total aflatoxin level in one of the cashew nut (1 of 91) and three of macademia nut (3 of 97) samples were found higher than the EU(European Union) and Turkish legal limit (10 µg/kg) (Commission Regulation, 2002; Turk Gda Kodeksi Teblig, 2002).AFB1 was found in 84 (92.3%) of 91 cashew nut and in 83 (85.5%) of 97 samples of macademia nut samples. AFB1 was not detected in 7 (7.6%) of cashew nut and in 14 (14.4%) of macademia nut samples. AFB1 level of only six cashew nut samples (6 of 91) exceed the legal limits (5µg/kg), whereas six of macademia nut was higher than legal limits (Table 2). Results of the present study were compared with the ones reported from other parts of the world. Bakirci (2001) reported AFM1 in 79 (87.77%) of 90 of the milk samples. Thirty five (38.89%) of the positive samples were found higher than the maximum limit (0.05 ppb) accepted by EU, Turkey and some other countries. Sarımehmetoglu et al. (2004) detected AFM1 contamination in 327 (81.75%) of 400 cheese samples. The number of cheese samples which exceed the legal limits of 250 ng/kg were 110 (27.5%). Oruc and Sonal (2001) examined AFM1 levels in milk and cheese from Bursa, Turkey and found 89.5% of cheese samples with range of 0-810 ng/kg were contaminated. We found AFM1 in 80.4% of dairy product samples whereas AFM1 contamination in white cheese was 80.3%. Aycicek et al. (2002) studied on occurrence aflatoxin M1 in 183 sample of white cheese and butter in Istanbul in 2001 and incidence of AFM1 in white cheese and butter samples were found as high as 65% and 81%, respectively. Dagoglu et al. (1995) analysed 75 white cheese samples and AFM1 contamination was 42%. Gunsen and Buyukyoruk (2003) analysed 86 fresh Kashar cheese for AFM1 and 28 (32.5%) of samples exceed allowed limits. These results were higher than reported in the present study. Pietri, Bertuzi, and Piva (1997) checked 223 samples of Grana Padano cheese manufactured in 4 years (1991-1994) and it has emerged that only one sample exceeded the maximum tolerated level in cheese in some European countries (250 ng/kg). Most samples (91%) were found in the range 5-100 ng/kg and only 15 (6.7%) was found in the range 100-250 ng/kg. Abdulkadar et al. (2000) analysed edible nuts for aflatoxin contamination which imported in Qatar between June 1997 and December 1998. Eighty-one nut samples were analysed in the second half of 1997 and contamination was detected in 19 samples with total aflatoxin varied from 0.53 to 289 lg/kg. Aflatoxin B1 levels in common Egyptian foods was determined by reversed-phase liquid chromatography with UV detection and the highest prevalence of AFB1 contamination was found in nuts and seeds (82% of 17 samples) (Selim, Popendrof, Ibrahim, Sharkawy, & Kashory, 1995). Gunsen and Buyukyoruk (2002) analysed 25 cacao hazelnut cream and found AFB1 asaverage of 1076.5 ± 194.4 ng/kg.
|
References
| [1] | Abdulkadar, A. H. W., Abdulla, A., & Jasim, A. (2000). Aflatoxin contamination in edible nuts imported in Qatar. Food Control, 11, 157,160 |
| [2] | Aflatoxins in Foods: Risk Assessment Studies. (2001). Report No. 5 Food and Environmental Hygiene Department |
| [3] | Aycicek, H., Yarsan, E., Sarımehmetoglu, B., & Cakmak, O. (2002). Aflatoxin M1 in white cheese and butter consumed in Istanbul, Turkey. Veterinary and Human Toxicology, 44(5), 295-296. Bakirci, I. (2001). A study on the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk products produced in van province of Turkey. Food Control, 12, 47-51 |
| [4] | Codex Alimentarius Commission (2001). Comments submitted on the draft maximum level for aflatoxin M1 in milk. Codex Committee on food additives and contaminants 33rd session, Hague, The Netherlands.Commission Regulation (EC) No. 257/2002. (2002). Amending Regulation (EC) No. 194/97 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs and Regulation (EC) No. 466/2001 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Communities. 13.2.2002. L41/ 12-15. |
| [5] | Dagoglu, G., Keles, O., & Yildirim, M. (1995). Peynirlerde aflatoksin duzeylerinin ELISA ilearastırlması. Istanbul Universitesi Veteriner Fakultesi Dergisi, 21, 313-317 |
| [6] | Enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative analysis of aflatoxins. (1999).M1 Art. No.: R-1101, B1 Art. No.: R-1201 and Total aflatoxin Art. No.: R-4701. R-Biopharm GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany. |
| [7] | Galvano, F., Galofaro, V., & Galvano, G. (1996). Occurrence and stability of aflatoxin m1 in milk and milk products: a worldwide review. Journal of Food Protection, 59(10), 1079-1090. |
| [8] | Galvano, F., Galofaro, V., Ritieni, A., Bognanno, M., De Angelis, A., & Galvano, G. (2001). Survey of the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in dairy products marketed in Italy: second year of observation. Food Additives and Contaminants, 18(7), 644-646 |
| [9] | Garden, S. R., & Strachan, N. J. C. (2001). Novel colorimetric immunoassay for detection of aflatoxin B1. Analytica Chimica Acta, 444, 187-191 |
| [10] | Gunsen, U., & Buyukyoruk, I. (2002). Aflatoxins in retail food products in Bursa, Turkey. Veterinary and Human Toxicology, 44, 289-290 |
| [11] | Gunsen, U., & Buyukyoruk, I. (2003). Determination of bacteriological qualities and aflatoxin M1 levels of commercially available fresh Kashar cheeses. Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Science, 27, 821-825 |
| [12] | Kocabas, C. N., & Sekerel, B. E. (2003). Does systemic exposure to aflatoxin b1 cause allergic sensitization Allergy, 58, 363. |
| [13] | Kotsonis, F. N., Burdock, G. A., & Flamm, W. G. (1996). Food toxicology. In Cassarett and Doull’s Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons (pp. 938-939). McGraw-Hill (Chap. 30) |
| [14] | Kumar V., Baso M.S., Rajendran T.P (2008). Mycotoxin research and mycoflora in some commercially important agricultural commodities. Crop Protection, 27, 891-905 |
| [15] | Moss, M. O. (2002). Risk assessment for aflatoxins in foodstuffs. International Biodeteration & Biodegredation, 50, 137-142. |
| [16] | Oruc, H. H., & Sonal, S. (2001). Determination of aflatoxin M1 levels in cheese and milk consumed in Bursa, Turkey. Veterinary and Human Toxicology, 43, 292-293 |
| [17] | Peraica, M., Radic, B., Lucic, A., & Pavlovic, M. (1999). Toxic effects of mycotoxins in Humans. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 77, 754-766 |
| [18] | Pietri, A., Bertuzi, P. & Piva, G. (1997). Aflatoxin M1 occurrence in samples of Grana Padano cheese. Food Additives and Contaminants, 14, 341-344 |
| [19] | Rastogi, S, Dwivedi, D. P, Khanna, K. S., & Das, M. (2004).Detection of Aflatoxin M1 contamination in milk and infant milk products from Indian Markets by ELISA. Food Control, 15, 287-290 |
| [20] | Sarımehmetoglu, B., Kuplulu, O., & Celik, T. H. (2004). Detection of aflatoxin M1 in cheese samples by ELISA. Food Control, 15, 287-290 |
| [21] | Selim, M. I., Popendrof, W., Ibrahim, M. S., Sharkawy, S., & Kashory, E. S. (1995). Aflatoxin B1 in common Egyptian foods. Folia Microbiology (Praha), 40, 297-300 |
| [22] | Stubblefield, R. D., & Shannon, G. M. (1974). Aflatoxin M1 analysis in dairy products and distribution in dairy foods made from artificially contaminated milk. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 57, 847 |
| [23] | Turk Gda Kodeksi Teblig. (2002). Resmi Gazete, 23 Eylul 2002, Sayı: 24885. Ankara: Basbakanlık Basmevi |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML