-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-5168 e-ISSN: 2166-5192
2015; 5(2): 88-95
doi:10.5923/j.food.20150502.03
Effect of Natural and Synthetic Food Coloring Agents on the Balance of Some Hormones in Rats
Ghada Mahmoud Khiralla , Safaa Ahmad Salem , Wagih Ahmad El-Malky
Division of Medical Foods, National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Giza, Egypt
Correspondence to: Ghada Mahmoud Khiralla , Division of Medical Foods, National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Giza, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The aim of the present work is to investigate the effect of beet (BE) and curcumin (CE) extracts as natural red and yellow color, edicol erythrosine and sunset yellow as recommended synthetic colors in addition to two unknown commercial coloring agents (red and yellow) on the balance of four hormones in the serum of male rats. Rats were divided into 11 groups and administrated daily for 60 days with 1 mL color solution contained the admissible daily intake (ADI) and overdose (5 times) of the synthetic recommended or commercial colors. BE (0.31 mg) and CE (7.87 mg) were also tested as natural colorants. No significant (p=0.05) changes were noticed in brain and testes weight due to treatment with the ADI dose of all studied colorants. Significant reduction in the testes weight was recorded when rats were treated with the overdose. The overdose applied in the present study led to elevation in the level of dopamine and noradrenaline and reduction in the concentration of testosterone and interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) in blood serum compared with the control group. These changes were associated with alterations in the histological architecture of brain and disturbance in the exploratory behavior. Correlation coefficient matrix indicated strong relationship between changes in the balance of studied hormones and histopathological alterations in brain induced by consumption of the artificial food colorants. The obtained results emphasis that, there is a need to re-evaluate use of edicol erythrosine and sunset yellow as synthetic food colorants. Moreover, beet and curcumin extracts could be used as alternative natural red and yellow colorants, respectively.
Keywords: Erythrosine, Sunset yellow, Brain, Dopamine, Noradrenaline, Testosterone, Interstitial cell-stimulating hormone, Exploratory behavior
Cite this paper: Ghada Mahmoud Khiralla , Safaa Ahmad Salem , Wagih Ahmad El-Malky , Effect of Natural and Synthetic Food Coloring Agents on the Balance of Some Hormones in Rats, International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 88-95. doi: 10.5923/j.food.20150502.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Artificial food colors have been utilized over the century for esthetic that make the foods attractive and stimulate appetite, however, in developing countries there has been a sharp increase in the use of synthetic food coloring agents. In the past years there is an uncontrolled use of synthetic color particularly in food mostly consumed by children [1]. Therefore, more attention must be focused on the physiological and pathological effects of color additives [2]. Worldwide, the use of colors in food faced with controversy, especially in children nutrition when added to food at high doses [3]. Erythrosine and Sunset yellow are widely used in food industry, pharmaceutical and cosmetics as red and yellow coloring agents, respectively. They are permitted by regulatory agencies of many countries [3, 4]. Synthetic coloring agents have been demonstrated as causal agents of certain damages in different organs of the experimental animals, i.e in brain and testes resulting in imbalance in neurotransmitters and exploratory behavior [5-6]. In this respect, repeated ingestion of erythrosine B in rats has developed behavioral hyperactivity [7-9]. A single very high dosage (10, 100 or 200 mg/kg) of erythrosine administration to young adult male rats had reduced motor activity maximally at 2 h and brain regional (medulla-pons, hippocampus and hypothalamus) serotonergic activity [5]. These acute effects could be referred to the change in some neurochemicals such as dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE) [10]. Few adverse effects in reproductive and neurobehavioral parameters had been observed when erythrosine was given in the diet of mice at levels of 0.005 to 0.045% (based on diet weight) from 5 weeks of age in the F0 generation to nine weeks of age in the F1 generation [11]. Testicular toxicity had previously demonstrated after oral administration of erythrosine in doses of 68 mg / kg for 21 days [6]. Recently, re-evaluating the use of some colorants in food such as erythrosine was suggested by European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) [12].Sunset Yellow FCF is one of the synthetic azo dyes that has been listed by National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as having behavioral effects in two rodent studies including coma and effect on seizure threshold. However, both were acute (LD50) studies in which very high doses of sunset yellow were administered by intra-peritoneal injection, convulsions and coma occurring prior to death in some animals. Sunset Yellow FCF had produced some adverse effects in reproductive and neurobehavioral parameters in mice when it was given in the diet of mice at levels of 0.005 to 0.045% (based on diet weight) from 5 weeks of age in the F0 generation to nine weeks of age in the F1 generation [13]. Some histopathological alterations in the testes and changes in the blood lipid profile have been observed by Mathur el al. [14, 15] in rats, after 90-day dietary exposure to sunset yellow FCF at dose levels equivalent to 250 and 1.5 mg/kg bw/day. These findings led to re-evaluating the use of sunset yellow FCF by EFSA [16]. Although synthetic food coloring agents have a long history of use, consumers have increasingly begun to consider synthetic colorants undesirable. Consequently, there has been increased effort to discover new natural alternatives [17, 18]. Therefore, the aim of the present work is to study the effect of different coloring agents (natural and synthetic) on the balance of some hormones in male rats due to oral intake of the normal and overdose. The exploratory behavior and histopathological changes in brain of rats were also considered.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
- Six different coloring agents were used in the present study. i) Two natural coloring agents extracted from beet and curcumin as natural red and yellow color, respectively ii) Two recommended coloring agents; edicol erythrosine #36003 and sunset yellow #1899 (purchased from Luna Co. for industrial investments, S.A.E, Egypt) and iii) two unknown coloring agents (yellow and red) commercially used in the local market.
2.2. Preparation of Natural Coloring Agents
- Beet and curcumin extracts were prepared and used as natural red and yellow coloring agents, respectively, as described previously [19]. Briefly, fresh Beetroots (Beta vulgaris var. rubra), purchased from the local market, Giza, Egypt, were washed, sliced and dried at 50°C for 12 h (to reach about 10% moisture content; dry basis). Dried slices were ground into powder in an electric blender. Curcumin (Curcumin longa) powder was purchased from the local market. Beet and curcumin extracts were prepared by adding 200 mL ethanol (70%) to 100 g dried powder. The mixture was shacked at room temperature for 2 h and then filtered through the Whatman No. 1 filter paper (Whatman International Ltd., Maidstone, UK). The extraction procedure was repeated 3 times. The filtrates were collected and the ethanol was evaporated at 50°C.
2.3. Animals and Treatments
- Sixty six male Albino strain rats were obtained from National Organization Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Giza, Egypt. Adult animals (120 – 150 ± 2g, 10 weeks age). The animals were housed in separate stainless steel cages under controlled conditions at constant temperature (24℃) and given free access to food and water throughout the experimental period (8 weeks). After adaptation period (15 days) rats were divided into eleven groups (n=6) and fed on basal diet (10% casein, 10% corn oil, 5% cellulose, 1% vitamin mixture, 4 % salt mixture, 70% corn starch (Lana Peter and Pearson, 1971) for 8 weeks. Rates were treated daily with 1 mL of color solution (containing the tested concentration of rat dose comparing human dose / Kg body weight) by oral stomach tube as follows: BE-Group: administrated beet extract as a natural red color (0.31 mg beet powder); NEE-Group: administrated Admissible Daily Intake (ADI) of edicol erythrosine) #36003 (0.06 mg); OEE-Group: administrated overdose of edicol erythrosine) #36003 (0.31 mg); NCR-Group: administrated ADI of an unknown commercial red color (0.06 mg); OCR-Group: administrated overdose of a unknown commercial red color (0.31 mg); CE-Group: administrated curcumin extract as a natural yellow color (7.87 mg curcumin powder); NSS-Group: administrated ADI of sunset yellow #1899 (1.57 mg); OSS-Group: administrated overdose of sunset yellow #1899 (7.87 mg); NCY-Group: administrated ADI of an unknown commercial yellow color (1.57 mg); OCY-Group: administrated overdose of an unknown commercial yellow color (7.87 mg).
2.4. Exploratory Behavior
- Spontaneous exploratory behavior was evaluated in an open field test as described by Dubovicky et al., [20]. All animals were exposed to the open field in an empty cage (36 x 48 cm, wall height 25 cm) for 6 min. The bottom of each cage was divided into six equal squares. Spontaneous motor activity (number of crossed squares) and vertical exploratory activity (number of rears: both forepaws lifted off the floor) were recorded on after 60 days.
2.5. Biochemical Assay
- At the end of experimental period, blood samples were collected from the eye plexuses of animals by a fine capillary glass tubes and placed immediately on ice. Blood serum samples were collected into dry clean centrifuge tubes; the serum was separated after centrifugation for 10 min at 3000 rpm (1500 xg) and kept at –20 ºC until analysis. Dopamine (DPA, Catalog No. MBS7214676, MyBioSource, USA), noradrenaline (NA, Catalog No. KAPL 10-0200, Biosource Europe, Belgium), testosterone (T, Catalog No. K00234, Dialab, Austria) and interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH also known as LH, Catalog No. Z02301, Dialab, Austria) concentrations were measured in triplicate in the blood serum of rats according to the producer's instructions.
2.6. Brain and Testes Weight
- At the end of the experimental period, rats were weighted and killed by diethyl ether. Brain and testes were cut off, washed in ice-cooled saline solution 0.15M KCl to remove blood, weighed and stored in 10% formalin solution until analysis [21]. The brain and testes weight percentages (relative weights) were calculated as a percentage from the body weight on the sixty day.
2.7. Histopathological Assessment
- Autopsy samples were taken from the brain of rats in different groups and fixed in 10% formal saline for 24 h. Washing was done in tap water then serial dilutions of alcohol (methyl, ethyl and absolute ethyl) were used for dehydration. Specimens were cleared in xylene and embedded in paraffin at 56ºC in hot air oven for 24 h. Paraffin bees wax tissue blocks were prepared for sectioning at 4 microns thickness by sledge microtome. The obtained tissue sections were collected on glass slides, deparaffinized and stained by hematoxylin & eosin stain for routine examination through the light electric microscope [22].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
- All values are means ± SE obtained from six animals. Data were analyzed with SAS software (SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.) using SAS analysis of variance (PROC ANOVA). Significant differences between means were determined by Tukey's multiple range test (P = 0.05). Correlation coefficient matrix was created between different studied variants using statistical analysis tools in Excel program, Microsoft office, USA.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Exploratory Behavior
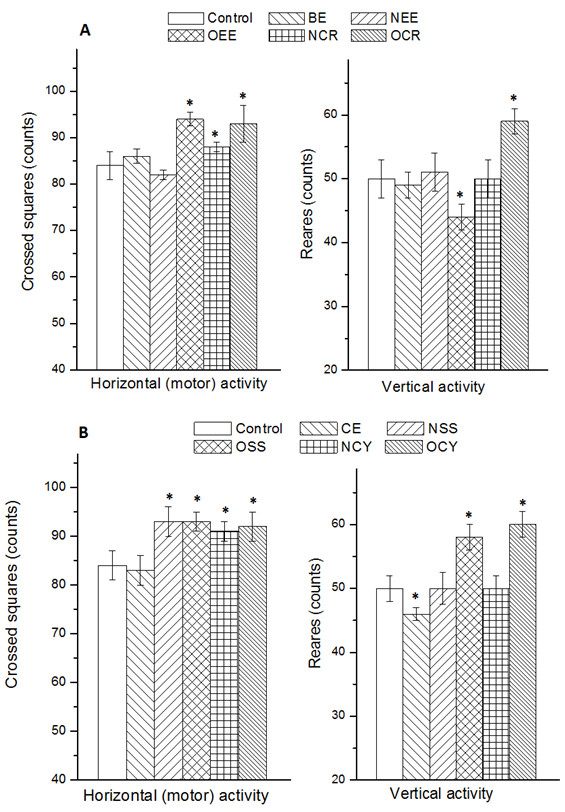
- Spontaneous exploratory behavior has two components: Horizontal and vertical. Characteristic horizontal activity (motor activity) are walking, running and sniffing. Vertical activity of exploratory behavior is manifested by attempts to turn the head up, before the animal is able to stand on its hind legs (stereotypical movements). All investigated rats displayed both types of behavior. Effect of the studied natural and synthetic red colors on the exploratory behavior was shown in Fig. 1A. At the end of the experimental period no significant change (p>0.05) in the horizontal activities were observed by BE- and NEE-group compared with the control group (Fig 1A). However, significant decreases (p<0.05) in the horizontal behavior were recorded in the rats of OEE-, NCR- and OCR-group. The vertical activity was not affected in BE- NEE- and NCR-groups, while significant increase and reduction was measured in the vertical activity of OCR- and OEE- group, respectively. Concerning the natural and synthetic yellow colors (Fig. 1B), the horizontal activity was elevated in NSS-, OSS-, NCY- and OCY-group, whereas the vertical activity was increased in the rats given overdose of sunset yellow (OSS) and the commercial yellow color (OCY). On the other hand, rats administrated the natural curcumin extract (CE) did not show significant change in their horizontal activity, while they observed significant reduction in their vertical activity. Generally, the results obtained in the present study indicated that the overdose (5 times of the ADI) of the synthetic coloring agents for 60 days induced considerable changes in both horizontal and vertical activity of tested rats. Despite the differing conditions of the present experiment, the obtained findings are in agreement with those stated in other previous studies [5, 7-9]. Moreover, in experimental animal, it is well known that long-term administration of erythrosine and sunset yellow, like other synthetic food color [23, 24] causes significantly increases the movement activity of exploratory behavior in a dosage dependent manner [11, 13]. On the other hand, a very high single dose of erythrosine (10-200 mg / kg) had been described as a motor activity suppression agent in rats as an acute effect after 2 hours [5], while the dose of 1 mg/kg had no effect when used as a single dose. In the present study, erythrosine was applied at the level of 0.06 mg/kg/day for 60 days, which showed an accumulated effect resulting in increase in the horizontal activity (hyperactivity).
3.2. Organ Weights
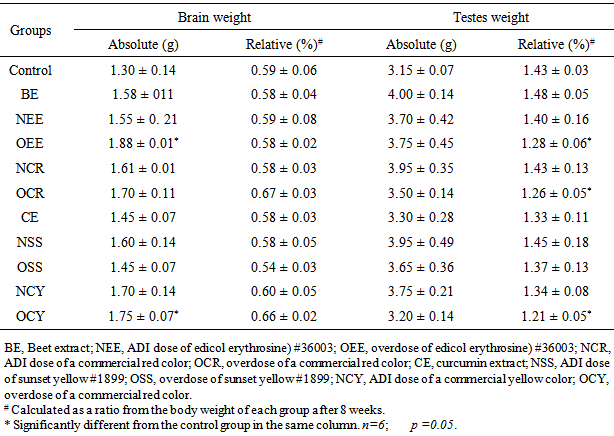
- Absolute and relative weights of brain and testes are shown in Table 1. Absolute brain weights of rats in NEE-group (administrated 0.06 mg edicol erythrosine / 1ml, daily) and OCY-group (given an unknown commercial yellow color of 7.87 mg / 1ml, daily), were significantly (p<0.05) increased compared with the control-group. However, all tested groups showed no significant differences between their relative brain weights compared with the control (Table 1). On the other hand, no significant changes were noticed in the absolute weight of testes of all rat groups compared with the control. In accordance with the present finding, Hashem et al [3] demonstrated that sunset yellow and curcumin did not displayed significant changes in the relative or absolute weights of some organs in rats. Also, diet supplemented with 2% of erythrosine did not cause any changes in the organ weights of rats after 6 months [25]. On the other hand, the obtained results indicated that only three groups (OEE, OCR and OCY) displayed significant decrease in the relative weight of testes compared with the control.
|
3.3. Hormones
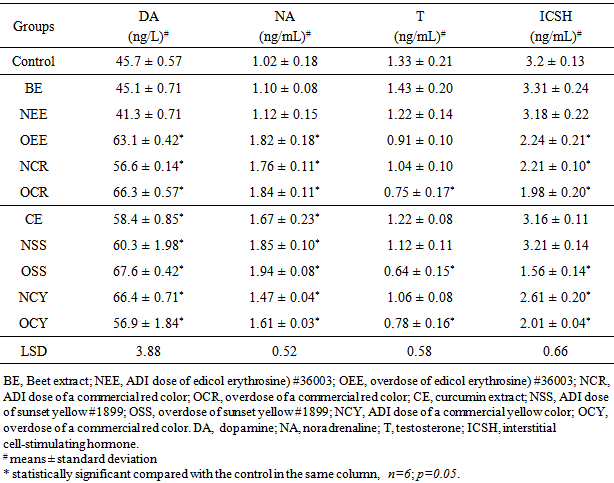
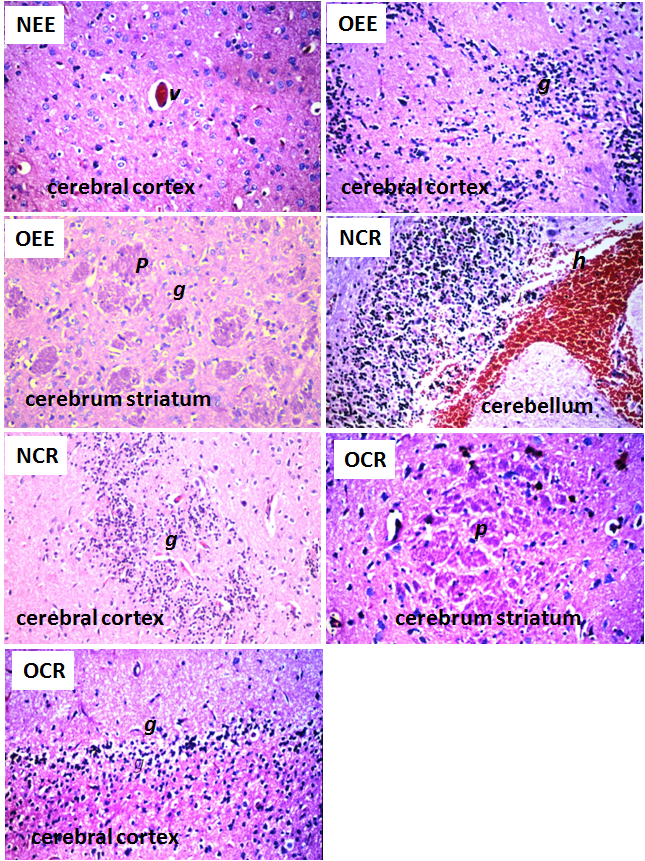
- Neurotransmitters are a class of chemical messengers in the body that help regulate many body functions [26]. Several common neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline (also known as epinephrine and norepinephrine) have been studies to indicate the imbalance in hormone levels [27]. Here, dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline (NA) as neurotransmitters in addition to testosterone (T) and interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) were determined to indicate the hormone levels in blood serum of male rats after treatment with some natural and synthetic coloring agents (Table 2). No significant differences were obtained between DA and NA concentrations in blood serum of BE- and NEE-group compared with the control. On the other hand, the other groups showed significant elevation in the concentrations of both hormones. Rats administrated overdose coloring agents (OEE-, OSS-, OCR- and OCY-group) and ADI dose of the commercial colorants (NCR- and NCY-group) displayed considerable reduction in ICSH. However, only OSS-, OCR-, OCY-groups showed decrease in testosterone level in the blood serum compared with the control. In accordance with the obtained results, different previous studies demonstrated the negative effect of the synthetic coloring agents on the hormone balance in the experimental animals [6, 11, 14, 27, 28].
|
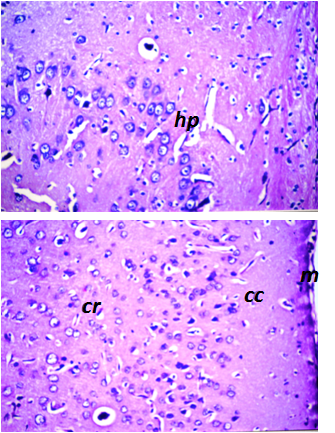
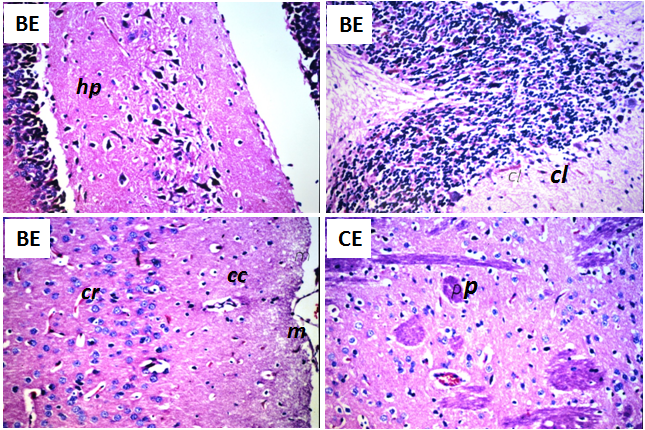
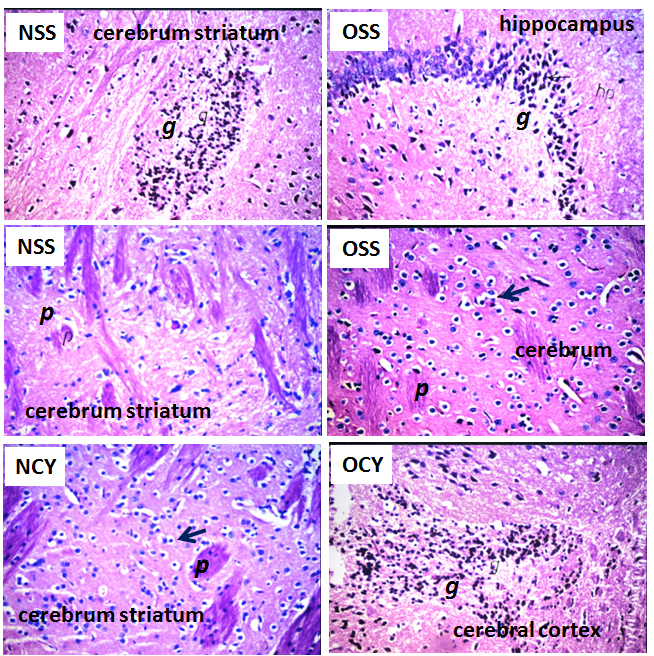
3.4. Histopathological Changes of Brain
- Different regions in the brain of rats were examined for the histopathological alterations. These regions included the meninges (m), cerebral cortex (cc), cerebrum striatum (cr), hippocampus (hp) and cerebellum (cl). Fig. 2 shows the normal histological architecture of all tested brain regions of control group. The histopathological changes in brain of the rats after 60 days of daily oral intake of beet extract (BE) and curcumin extract (CE) as natural red and yellow colors, respectively, were presented in Fig. 3. In BE-group (administrated beet extract) all investigated brain regions showed normal histological architecture as shown in Fig. 3. However, focal eosinophilic plagues were noticed in the cerebral striatum showed.
|
4. Conclusions
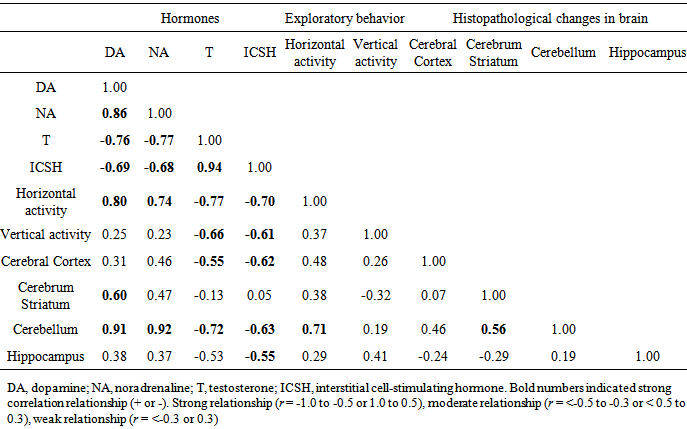
- The results obtained in the present investigation indicated the normal brain histology and hormones level in blood serum when the natural colorant beet and curcumin extracts were used as red and yellow colorants, respectively. The use of ADI of edicol erythrosine and sunset yellow as recommended synthetic red and yellow colors, respectively, caused hyperactivity and imbalance in the concentration of both dopamine and noradrenaline associated with histopathological alterations in different brain regions. Therefore, it can be concluded that, there is a need to re-evaluate use of edicol erythrosine and sunset yellow as synthetic food colorants. On the other hand, sever changes in histological architecture of brain (cerebrum striatum, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and hippocampus) were demonstrated when overdose of the synthetic colorants have been applied. These changes were associated with hyperactivity and hormone imbalance (including dopamine, noradrenaline, ICSH and testosterone). This conclusion was statistically confirmed by the strong correlation coefficient (r) between the histopathological changes in cerebellum region and the elevation of dopamine and noradrenaline levels. Generally, the present study sheds light on the nutritional hazards due to the uncontrolled use of synthetic colorants. The excessive use of synthetic coloring agents should be controlled via replacement by alternative colorants from natural sources such as beet and curcumin extracts applied in the present study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would to thanks Dr. Adel Bakeer Kholoussy, Prof. of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, for his valuable discussions and explanation of the obtained results.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML