-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-5168 e-ISSN: 2166-5192
2015; 5(1): 24-32
doi:10.5923/j.food.20150501.04
Nutritional and Sensory Properties of Solar-Dried Carrot Slices as Affected by Blanching and Osmotic Pre-Treatments
Teferra F. Tadesse1, Solomon Abera2, Solomon Worku2
1School of Nutrition, Food Science and Technology, Hawassa University, Hawassa, Ethiopia
2Institute of Technology, Haramaya University, Dire Dawa, Ethiopia
Correspondence to: Teferra F. Tadesse, School of Nutrition, Food Science and Technology, Hawassa University, Hawassa, Ethiopia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study was conducted to investigate effects of varying levels of pretreatments on nutrient retention and sensory acceptance of solar-dried carrot slices. The carrot samples were blanched at 55, 65 and 75℃ for 45 minutes, soaked in 5%, 10% and 15% salt solutions for 5 hours and dried using an indirectly heated passive type solar dryer. The best nutrient retentions (5.25% protein db, 2.49% fat db, 2.17% fiber db and 71.94 ppm β-carotene) were recorded for samples treated at 55℃ whereas the 5% salt solution resulted in 2.88% fat, 2.46% fiber and 73.89 ppm β-carotene. The highest crude protein (5.68% db) and crude fiber (2.99% db) were recorded for the combination of 55℃ with 15%, and the highest crude fat (3.20% db) and β-carotene (74.97 ppm) were obtained from the samples subjected to 55℃ and 5%. High total ash contents were associated to high levels of osmotic concentrations irrespective of the blanching temperatures. Concerning the sensory acceptance, color, flavor, taste, texture and overall acceptance of samples blanched at 55℃ and soaked in 10% solution were most liked. In most cases, the physicochemical, nutritional and sensory acceptance of the samples treated with 55℃ blanching temperature and 5% salt concentration and combination of the two was observed to be superior to other treatment levels.
Keywords: Carrot, Blanching, Osmotic dehydration, Solar drying, Nutrient retention, Beta-carotene, Sensory acceptance
Cite this paper: Teferra F. Tadesse, Solomon Abera, Solomon Worku, Nutritional and Sensory Properties of Solar-Dried Carrot Slices as Affected by Blanching and Osmotic Pre-Treatments, International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2015, pp. 24-32. doi: 10.5923/j.food.20150501.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Carrot is one of the important root vegetable crops and is highly nutritious as it contains appreciable amount of vitamins B1, B2, B6 and B12. It also contains many important minerals [1]. Carrots have the highest β-carotene content among human foods [2-5], containing about 5–8 mg of β-carotene per 100 g [6]. The carrot pigment, β-carotene is a precursor of vitamin A. Carrot also has high fibre content [7], which contributes to healthy diet.Post-harvest decay is the major factor limiting the extension of shelf-life of vegetables and nearly 17% of world’s total production is deteriorated during post-harvest handling [8]. A number of techniques are used to minimize deterioration after harvesting. The keeping ability of carrot can be enhanced by drying and subsequent storage. Drying is one of the oldest methods of food preservation, and it represents a very important aspect of food processing. Although higher temperature causes wilt and result in poor appearance on the carrot, in many agricultural countries, large quantities of carrot are dried to improve shelf-life, lower shipping weights, minimize the loss of flavour and nutritional value [8-10].Dehydrated vegetables can be used in many processed or ready-to-eat foods in place of fresh foods and have several advantages such as convenience in transportation, storage, preparation and use [1, 12]. Dehydrated vegetables need to be rehydrated before consumption or further processing [13].Rehydration is an important step in the utilization of dried fruits and vegetables. For rehydrated vegetables, the most pertinent properties are related to the texture and flavor. Consumers usually tend to prefer processed rehydrated vegetables with a firmer texture than those typically produced by a conventional (well controlled) process. Therefore, textural improvement has become essential outcome of dehydration [14].Many studies were done to process carrot by air drying [15], sun drying [16], convection-microwave drying [17, 18], and combination of freeze drying, microwave heating and air or vacuum drying [19, 20] and solar drying [21] but few have attempted to combine different levels of pre-treatments prior to solar drying and the effect on the nutritional quality and sensory acceptance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
- The carotene type carrot with orange-red pigment commonly grown in Ethiopia was used for this study. The fresh root harvested at the optimum maturity was obtained from local market. The root was washed with tap water to remove the soils and dried in the air before it was stored in a refrigerator at 4℃ until it was required for preparation. A total of 100 kg of fresh carrot root was used for the study. The clean carrot removed from the refrigerator was cut manually into thin slices of 5±1 mm thickness using stainless steel knives.
2.2. Sample Pre-treatment
- The cut slices were divided in to three lots of equal weight and blanched separately in hot water at 55℃, 65℃ and 75℃ for 45 minutes (ensuring full coverage of the slices by water) [22, 23]. The temperature was kept constant throughout the blanching time using water bath and the slices were cooled immediately after blanching by dipping in cold water.Each of the blanched samples were further been divided in to three parts and soaked in 5%, 10% and 15% salt concentration at room temperature for 5 hours [24] ensuring full coverage of the slices by the solution.
2.3. Drying Experiment
- The carrot slices were dried using an indirectly heated passive type solar dryer. The temperature and relative humidity of the air at the entrance of the collector and the drying chamber were measured using digital thermo-hygrometer. A temperature range of 24-33ºC outside the dryer and 29-58ºC inside the drying chamber with a corresponding relative humidity range of 39-49% outside and 25-43% in the drying chamber, were recorded during the drying process.The trays were loaded with a single layer of slices and labeled/marked slices were being weighed at 1 hour interval on the first day and 2 hours interval on the following day(s) of drying. Drying continued until the slices attained a final moisture content of about 6%. The dried carrot slices have been packed in polyethylene plastic bags and stored at room temperature until they were required for the other tests.
2.4. Proximate Composition of Dried Slices
- The proximate composition of the dried and fresh samples was done using the AOAC methods [25]. The β-carotene content of the samples was determined using the AACC techniques.
2.5. Sensory Acceptance: Rehydrated Slices
- Consumer panel of 50 members was provided with coded samples and an evaluation form. The carrot samples that received the different treatments were separately evaluated for color retention; changes in taste, smell, texture and overall sensory acceptability after it had been rehydrated. The 5 point hedonic was employed, where 5 was the score for extremely liked and 1 was for the extremely disliked samples.
2.6. Experimental Design and Analysis
- The experiment was carried out in triplicates for all the measured parameters. A two way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using SAS statistical package (version 9) was used to investigate the significance of differences in the chemical composition and sensory quality of samples. The mean separation technique using the Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) was applied.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Properties of Fresh Carrot
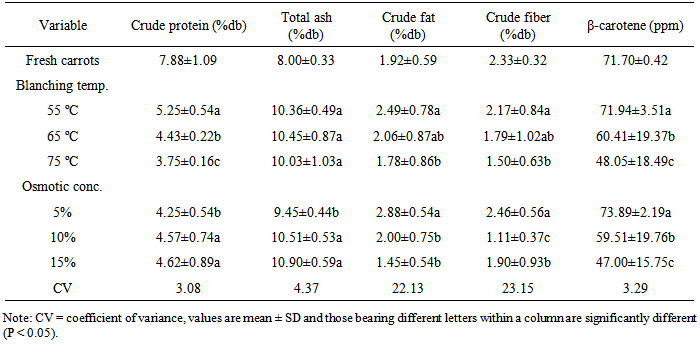
- The proximate properties of fresh carrot (Table 1) are in the ranges reported in literatures. Moisture content was in the range (80-90%) reported by [26] and crude protein was also close to the values reported by [27] and [28]. Similarly, total ash, crude fat, crude fiber and β-carotene of the carrot used in this study are in agreement with the report of [28].
3.2. Proximate and β-carotene Composition of the Dried Samples
3.2.1. Crude Protein
- Crude protein contents of samples treated with different blanching temperatures were significantly (P < 0.05) different (Table 1). The highest protein content (5.25%) was recorded for the carrot samples subjected to the least of blanching temperatures (55℃) and the lowest protein content (3.75%) was recorded for the carrot slices subjected to the highest blanching temperature (75℃). The crude protein content of the fresh carrot used in this investigation is 7.88% (Table 1) which is significantly higher than that recorded for the blanched and dried ones (Table 4). It seems that the protein content is leached due to cell membrane damage at higher temperatures of blanching.
|
|
3.2.2. Total Ash
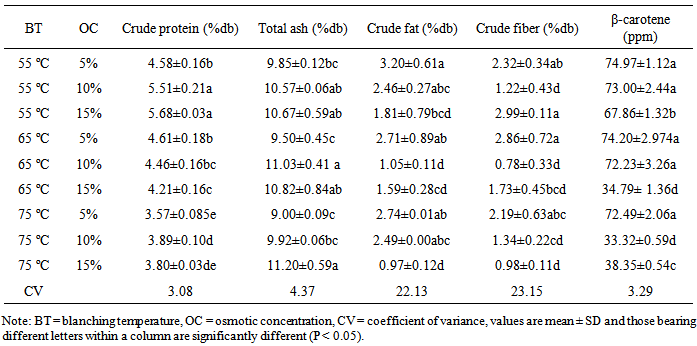
- The different blanching temperatures do not significantly (P > 0.05) affect the total ash contents of carrot slices. The ash content of the blanched and solar-dried carrot slices (Table 1) is generally higher than that of the fresh carrot.The carrot slices treated with different levels of osmotic concentration prior to drying were observed to have significantly (P < 0.05) varying amount of total ash. The highest ash content (10.90%) was recorded (Table 1) for the slices that were immersed in 15% whereas the lowest ash level (9.45%) was recorded for the sample immersed in the 5% sodium chloride solution. Table 2 shows values of total ash content of the carrot slices as affected by combinations of various levels of blanching and osmotic treatments. The interaction of blanching temperature with osmotic concentration significantly (P < 0.05) affected the ash content of the solar-dried carrot slices. Although, the means are not statistically well separated, the highest ash content (11.20%) was recorded for the sample blanched at 75°C and soaked in 15% salt concentration and the least ash content (9.00%) was recorded for the sample blanched at 75°C and soaked in 5% salt concentration. The ash content of the solar-dried carrots was observed generally increasing with the increase in the strength of the solution used for osmotic treatment. The increase in ash content is possibly due to sodium in the solution that might have diffused into the carrot as the water migrates out, since osmotic dehydration is the simultaneous process of water and solute diffusion [31-33]. Moreover, the crude ash content of the treated and dried carrot (Table 1) is reasonably higher than that of the fresh carrot.
3.2.3. Crude Fat
- The different levels of blanching temperature resulted in significantly different crude fat or ether extract contents of the solar-dried carrot slices (Table 1). The highest value of crude fat (2.49%) was recorded for the carrot sample which was blanched at 55℃ and the lowest value (1.78%) corresponded to the sample that received blanching treatment at the highest temperature (75℃). Increment in blanching temperature is related to degradation of the total fat composition of carrot slices and this might have been due to leaching and oxidative losses during osmotic treatment and drying respectively. The varying levels of osmotic treatment produced significant differences (P < 0.05) in the crude fat/ether extract content of the solar-dried carrot slices (Table 1). The highest crude fat value (2.88%) was recorded for the carrot slices soaked in the 5% concentration and the least crude fat amount (1.45%) was recorded for the sample treated with 15% salt concentration. The crude fat amount was observed to decrease with the increment in strength of solution used for osmotic dewatering. The crude fat content of the fresh carrot (1.92%) (Table 1) is close to the grand mean value (2.11%) for the dried carrots (Table 2). The fact that the fat content appeared to be higher in percentage level for the two dried samples than that in untreated (fresh) sample could be due to solid lost by leaching which lowered total dry matter. The crude fat of the blanched, osmotic treated and solar-dried carrot slices was significantly (P < 0.05) affected by interaction of the levels of blanching temperature and osmotic concentration (Table 2). Clear pattern in the crude fat content through the combined levels of blanching temperature and osmotic concentration was not observed. The highest amount of crude fat (3.20%) was recorded for the sample blanched at the least temperature (55℃) and soaked in the 5% salt concentration whereas the least amount (0.97%) corresponded to the sample treated at the highest temperature (75℃) and soaked in 15% solution. The fat content of the samples decreased with an increase in the strength of the solution in all levels of blanching temperature. The grand mean value (2.11%) of fat content of the pretreated and dried carrot slices is however, greater than the amount (1.92%) recorded for the fresh samples (Table 1). This might be due to the dry matter loss on the basis of which the computation was made.
3.2.4. Crude Fiber
- The crude fiber content of the carrots subjected to different levels of blanching temperature is significantly varying and is summarized in Table 1. The highest value of crude fiber (2.17%) was obtained from the carrots samples that received the lowest blanching temperature (55℃). The lowest value of crude fiber (1.50%) was obtained from the carrot that was blanched at the highest temperature (75℃). The value of crude fiber was observed decreasing with the increase of blanching temperature. The variation of crude fiber content of the solar-dried carrots due to the varying concentration of the brine solution used as a pretreatment prior to drying was significant (P < 0.05). The highest value (2.46%) was obtained from the carrot that was subjected to osmotic dewatering in 5% solution and the least (1.11%) was obtained from the slices subjected to the osmotic treatment in 10% salt solution. Soaking of carrot in the 15% solution resulted in medium fiber content when compared to that in 5% and 10% solutions. The fresh carrot used for the investigation (Table 1) has a mean value of crude fiber (2.33%) that is higher than the grand mean of the osmotic treated and dried carrot. The decrease in the percent crude fiber with the increase in the osmotic strength could be due to the increase in the percent ash content due to diffusion of solutes to the carrot on osmotic treatment.Amounts of crude fiber are presented in (Table 2) for the samples subjected to the different combination of levels of blanching temperature and osmotic concentration. The difference in crude fiber content induced by interaction of the levels of blanching temperature and osmotic concentration was statistically significant at P < 0.05. The highest crude fiber content (2.99%) was recorded for the sample blanched at the lowest temperature (55℃) and soaked in 15% salt concentration. The least crude fiber content (0.78%) was recorded for the sample blanched at 65℃ and soaked in the 10% salt concentration. The grand mean of crude fiber of the dried carrots (1.82%) is generally less than that recorded for the fresh carrot (2.33%) (Table 1).
3.2.5. Beta-Carotene
- Table 4 presents the β-carotene content of samples exhibiting significant (P < 0.05) variation with the blanching temperature. The highest value of β-carotene content (71.94 ppm) was observed in the sample blanched at the lowest temperature (55℃) and the least amount of β-carotene was observed in the samples treated at the highest blanching temperature (75℃). The β-carotene content of the fresh carrot used in the study was observed to be higher (71.70 ppm) than the grand mean (60.13 ppm) β-carotene content recorded for the blanched and dried carrot slices. The effect of various salt concentrations on β-carotene content of solar-dried carrot slices was observed to be significant (P < 0.05). The highest β-carotene value (73.89 ppm) was recorded for the carrot treated in 5% solution and the least value (47.00 ppm) corresponded to the carrot soaked in the 15% brine solution. The amount of β-carotene analyzed for the samples treated with combination of different levels of blanching temperature and osmotic concentration is shown in Table 2. Βeta-carotene content of pretreated and solar-dried carrot slices was significantly (P < 0.05) varying with combinations of the different levels of blanching temperature and osmotic concentration with lack of clear segregation for all the combinations. The highest β-carotene content (74.97 ppm) was recorded for the sample treated with the combination of the least severe conditions, (55℃ blanching temperature and 5% osmotic concentration), though it is not statistically different from that of the samples treated at four other combinations. The lowest amount of β-carotene (33.32 ppm) was observed in the sample blanched at 75℃ temperature and 10% osmotic concentration. The β-carotene content was generally observed to decrease with the increase in the severity of the pretreatment conditions, blanching temperature and osmotic concentration. A dramatic decrease (74.97 to 33.32 ppm) however, corresponded to the increase in the blanching temperature (55-75℃). The grand mean β-carotene content (60.13 ppm) of the pretreated and solar-dried carrot slices is less than that (71.70 ppm) of the fresh carrot (Table 1). The β-carotene content of the fresh carrot is less than those recorded for samples treated at combination of lower levels of temperature and concentration. Previous works also reported that processing slightly reduced total β-carotene content in untreated carrots [34]. The β-carotene content of both fresh and dried carrots obtained in the present study is close to that reported by [35].The reason for observed decrease of β-carotene of treated samples might be due to the fact that β-carotenes are highly unsaturated compounds with extensive conjugated double-bond systems and they are susceptible to oxidation, isomerisation and other chemical changes during processing and storage [36]. The β-carotene content of the pretreated, dried and rehydrated carrot slices decreased with the increase in the blanching temperature. The orange color intensity of processed carrot slices, which is related to the β-carotene content [37], was observed to be affected by the blanching temperature. The color of the carrot slices subjected to higher blanching temperature was darker at the periphery of the slices and the yellow interior part is less intense than that of the samples blanched at lower temperatures. The current result is similar to earlier works reported by [3] and [38] for heat treated carrot juice and canned sliced carrots respectively, with higher processing temperatures causing darkening, and a shift from red to yellow. Osmotic pretreatment was reported to retain β-carotene and lycopene in general [39] and at lower concentrations in particular it improves the stability of pigments during dehydration and the storage of dehydrated product [29, 30]. The decrease in the β-carotene content might be due to leaching of the pigments as the osmotic stress increased as a result of breakage of the cell structures.The β-carotene content of the carrot samples subjected to lower pretreatment conditions and solar-dried at a range of 29-58℃ was observed to be generally higher than that of the fresh carrot samples used in the study. The grand mean β-carotene content of the treated and dried carrot slices is less than that of the fresh carrots. The β-carotene content obtained for both fresh and dried carrot in present study was close to report of [35].
3.3. Sensory Acceptance of Dried Samples
3.3.1. Color
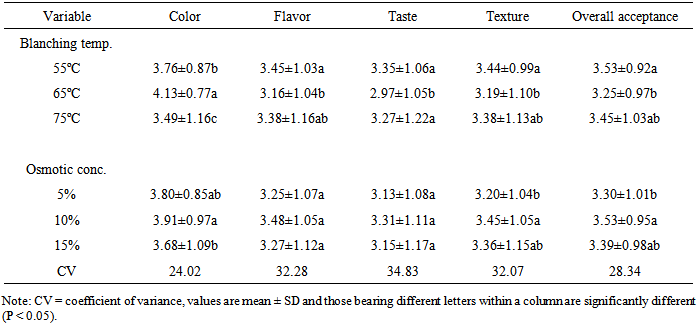
- The color acceptance scores of carrot samples subjected to various blanching temperatures were significantly (P < 0.05) different (Table 3). The highest score (4.13) was given to the sample that was blanched at the temperature of 65℃ and the least score (3.49) was given to the sample blanched at 75℃. The color scores of the carrot slices subjected to different concentration of osmotic treatment did not show significant differences.
|
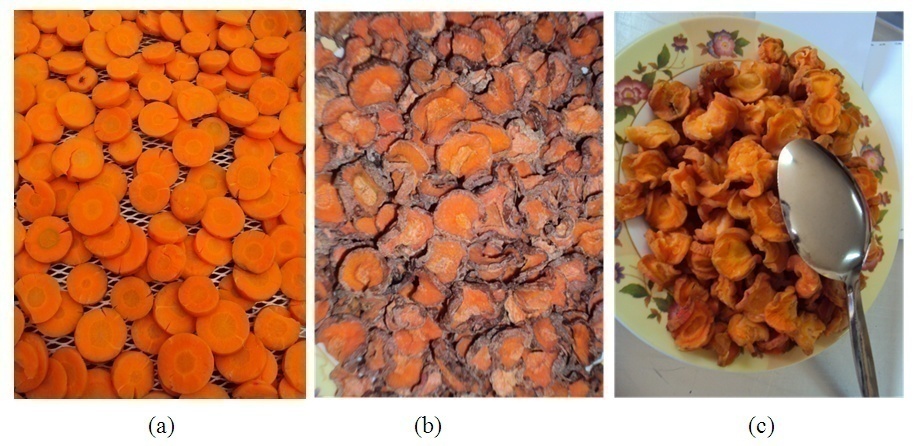
 | Figure 1. Sample preparation: cleaned fresh (a), blanched (b) and osmotic treated (c) carrots |
 | Figure 2. Drying and rehydration operations: samples drained and washed after osmosis (a), solar-dried (b), rehydrated (c) |
|
3.3.2. Flavour
- The mean score for flavor of solar-dried carrot slices was significantly (P < 0.05) different for the samples treated at the lowest and highest blanching temperatures (Table 3). The best flavor score (3.45 on the 5 scale hedonic test) was given to the sample subjected to the lowest blanching temperature (55°C) and the least score (3.16), although not significantly different from the score of sample blanched at 75°C, was given to the sample blanched at 65°C. Generally, the flavor of the rehydrated carrot samples blanched at different temperature levels was good and tended to be liked by the consumers despite the fact that samples were tasted after rehydration without addition of any ingredient or without sufficient cooking. The osmotic concentration as pretreatment prior to solar dehydration of carrot slices did not significantly (P > 0.05) affect flavor on rehydration. Similarly, the interaction effect of the pretreatments, blanching and osmotic concentration regarding flavor, was not statistically significant (P > 0.05) for most of the results obtained (Table 3).
3.3.3. Taste
- Blanching temperatures of different levels used in this study has produced significant differences in the taste score of the rehydrated carrot slices (Table 6). Samples blanched at the lowest temperature (55℃) was most liked by consumers (with 3.35 score) and samples blanched at the medium temperature (65℃) was least liked with a score of 2.97 on the 5 point hedonic scale. The taste of the carrot sample was not liked very well and the reason seems to be the fact that the carrots used in sensory evaluation was not ready-to-serve product and it was just rehydrated and was ready only for food preparation. The carrot was not prepared in to ready-to-eat products so as to eliminate effects of extraneous factors (like spices) on the flavor and other sensory attributes. Neither osmotic pre-treatment (P > 0.05) nor its interaction with the blanching temperatures (P > 0.05) produced significant difference in the taste scores of the rehydrated carrot slices.
3.3.4. Texture
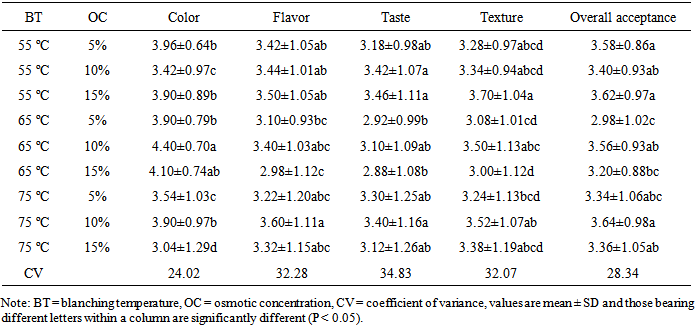
- The differences in the texture of the dried carrot slices were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). However, the scores given by consumer panels on 5 point hedonic scale (Tables 3 and 4) suggested that the texture of the samples tended to be liked by the consumers and this is similar with the report of [14] who reported the tendency of consumers towards dehydrated and rehydrated fruits and vegetables than fresh ones. The texture scores of the carrot slices treated with various levels of osmotic concentration prior to dehydration were not significantly different (P > 0.05) from each other. The interaction of the pre-treatment conditions on the texture of the rehydrated carrot slices produced a significant difference (P < 0.05) only for the samples that were treated with the combinations of blanching temperatures of 55℃ and 65℃ with osmotic concentration of 15%. The highest score (3.70) and the lowest score (3.00) corresponded to samples subjected to blanching temperature of 55℃ and 65℃ respectively, interacted with 15% salt concentration. The scores of the carrot samples treated with the rest of the combinations of the three levels of blanching temperature and the three salt concentrations as shown in Table 6, lacked clear pattern.
3.3.5. Overall Acceptance
- The overall acceptance of the samples treated at 55 and 65°C were significantly (P < 0.05) different. The sample blanched at the lowest temperature (55℃) was the most liked and that blanched at the medium temperature (65℃) was the least liked with scores of 3.53 and 3.25, respectively. Despite the absence of clear relationship between the overall acceptance and blanching temperature the rehydrated carrot is generally on the tendency of being liked with a score of greater than 3 on the 5 point hedonic scales.The overall acceptance of the carrot slices treated by 10% salt concentration was significantly (P < 0.05) higher than that by 5%. The sample treated at 15% salt concentration however, was not statistically different from the other two regarding the overall acceptance.Seven out of the nine scores of overall acceptance are not significantly different from each other at P < 0.05 level. The lowest score (2.98) attained by 65℃ and 5% salt concentration was significantly different from most of the remaining scores. The score of the carrot slices treated at the combinations of 55℃ with 5% and 15% concentrations as well as that treated at 75℃ and soaked in 10% solutions are significantly higher (P < 0.05) than the scores for the samples treated by 65℃ combined with both 5% and 15% salt concentrations. Neither clear trend nor statistically significant differences were noted for the remaining combinations of the two factors. This shows that the various treatments of blanching temperatures and salt concentrations may not bring differences in preferences of the consumers to the rehydrated carrot slices at P < 0.05.
4. Conclusions
- The lower levels of both blanching and osmotic pretreatments, separately and in combination, resulted in better nutritional quality and sensory acceptability of dried carrot slices. The severity in the pretreatment levels seemed to influence both the nutritional and sensory qualities of the dried carrot slices. Apart from retaining nutrients and structural integrity of the dried samples, the lower level of the pretreatments are advantageous in terms of fuel economy (for blanching), cost reduction for salt and also reduces the sodium intake by consumers, which is usually associated to chronic disease.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors appreciate the central laboratory and finance unit of Haramaya University for the technical and financial supports, respectively. The authors extend their gratitude to the food science and postharvest technology of Hawassa University for the drying laboratory facilities.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML