-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-5168 e-ISSN: 2166-5192
2013; 3(4): 49-54
doi:10.5923/j.food.20130304.01
Effect of Lupin Flour Supplementation on Chemical, Physical and Sensory Properties of Mediterranean Flat Bread
Dalia Z. Alomari1, 2, Selma S. Abdul-Hussain1
1Nutrition and Food Technology Department, College of Agriculture, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan
2Applied biochemistry group, Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research (IPK), Gatersleben, Germany
Correspondence to: Dalia Z. Alomari, Nutrition and Food Technology Department, College of Agriculture, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study was designed for improving nutritional value of Mediterranean flat bread (MFB) by adding different lupin flour (LF) levels (0%, 5%, 10%, 15% and 20%). Chemical (moisture, ash, crude protein and mineral content), physical (diameter, thickness, spread ratio and color) and sensory properties of bread were measured. LF significantly contain high amount of ash, fiber, protein and lipid as compared with WF. At 20% LF significantly contains the highest amount of ash (0.8% to 11.3%), fiber (0.3% to 1.9%), protein (10.8% to 15.2%) and lipid (0.95% to 5.82%) compared with control bread (CB, 100% WF), while carbohydrate decreased. LF inclusion in MFB making delayed farinograph arrival time, increased water absorption and decreased MFB volume. Increasing LF supplementation significantly increased bread yellowness, redness and decreased lightness. Bread crumb softness decreased when level and time of storage increased. Sensory evaluation indicated that there were no significant changes between CB and resulted LB in color homogeneity, taste, flavour, odor, tearing quality and overall acceptability at all LF levels. Our observations indicate that nutritional improvement of MFB by substituting WF with LF up to 20% level without affecting physical and sensory properties. Considering nutritional advantages, LF can be successfully used for bread production.
Keywords: MFB, Lupin Flour, Wheat Flour, Physiochemical, Sensory Properties
Cite this paper: Dalia Z. Alomari, Selma S. Abdul-Hussain, Effect of Lupin Flour Supplementation on Chemical, Physical and Sensory Properties of Mediterranean Flat Bread, International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Engineering, Vol. 3 No. 4, 2013, pp. 49-54. doi: 10.5923/j.food.20130304.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In the Middle Eastern countries Bread considered as a basic food, which can be found in many types and known by different names[1, 2]. Bread has a major importance in the human daily caloric intake and carbohydrate consumption. For instance, in Iran up to 52% of the daily energy requirements that obtained from wheat, largely consumed as bread[3]. According to the specific volume, bread can be divided into pan bread, French bread, rye bread, and flat bread[1, 3]. Flat breads can be classified into two groups with respect to their cross section: Single-layered and double-layered. The most common type of the double layered is pita or Mediterranean flat bread[1]. Mediterranean flat bread consider the most popular bread type in Jordan and the other Middle East countries and recently became popular in many countries around the world[3,4, 5].Generally, Mediterranean flat bread is prepared mainly from the essential ingredients containing: wheat flour, water, salt, and baker’s yeast[3]. Wheat protein consider low in the nutritional quality as compared with legumes protein due to it has low amounts of lysine, methionine, and threonine[6]. Nevertheless, demand for wheat-based bakery products is increasing, particularly in developing countries where the major grain is wheat[4]. The nutritional quality of these products could be improved by supplementation with non-wheat proteins. Since the success of using soybean as a plant protein source for human nutrition, attention had been paid to other plants that are rich in protein and could be grown at low cost in some areas. Among them is lupin (Lupinus albus) which would increase the protein content and improve the essential amino acid balance of the baked product. In addition, it has a unique physical and chemical characteristic[7-10]. Lupin seed includes high content of protein (45%), lipid (15%) and fiber (35%)[9, 10]. Due to high nutritive value, lupin has a potential to influence the nutritional profile of foods[11, 12]. For these benefits, the incorporation of lupin flour to wheat flour in MFB production will have promising increase the MFB nutritive quality. Moreover, information on incorporation of lupin flour in bakery products is inadequate. Thus, this work was conducted to increase the nutritional value of MFB by adding different levels of LF that would improve the health of consumers. For simplicity, we explain conceptually how LF increased nutritive value of MFB and showing the effect of substituting different levels of LF on the physical, chemical and sensory properties of the MFB.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Wheat flour (Triticumaestivum) with 84.1% extraction rate was obtained from Modern Flour Mills and Macaroni Factories (Amman, Jordan). Sweet lupin beans (Lupinusalbus) were purchased from the local market and were milled locally to get the flour. The other bread ingredients included: salt, sugar, and yeast were food grade and purchased from the local market at Amman, Jordan.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Proximate Chemical Analysis
- Proximate chemical analysis (moisture, protein, lipid, fiber and ash) on wheat flour (WF), lupin flour (LF) and all treated MFB were determined following the methods of AOAC and AACC[13, 14].
2.2.2. Lupin Milling
- Lupin seeds were cleaned by discarding small, broken, molded and damaged seeds. The cleaned lupin seeds were soaked in distilled water for 20 hrs, crushed then grounded in an electric mill (Braun, Model 1021, Germany) to pass through a 60 mesh sieve (British standard screen) to get the lupin flour[11,12]. The lupin flour samples were obtained in 50 kg tight polyethylene bags sealed and stored in a refrigerator (4°C) until required.
2.2.3. Mediterranean Flat Bread Formulation and Preparation
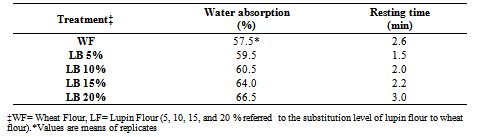
- LF was incorporated in Mediterranean flat breads at four substitution levels 5, 10, 15, and 20%. Bread treatment which prepared without the inclusion of LF to their ingredients was considered as a control. The formula used in the preparation of experimental breads was 1000 g wheat flour, 3 gm dried yeast, 2 gm salt, and water as reported by Maleki and Daghir[15] with some modifications. For all the recipes, the ingredients were mixed with the amount of water to be used was determined by the farinograph absorption value at speed two for 2 min and then at speed four for 7min in a Crypto mixer (Peerless®, UK) until a cohesive dough mass were obtained. The amounts of water needed for optimum dough consistency are shown in Table 1. The resultant bulk dough was fermented for 30 min. The fermented dough was divided into balls of 100 g each. The dough pieces were dusted with flour of the same formulation (~10 g) and rounded into ball shape. The balls were covered with a wet cloth and fermented for 10 min and then flattened into elliptical sheets and baked in commercial automated oven at 470°C to optimum crust color. After baking, bread treatments were cooled for 15 min, placed in polyethylene bags until evaluation.
2.2.4. Farinograph Procedure
- The dough mixing properties of the different wheat lupin flour blends were examined with the brabender farinograph (Brabender, Duisburg, Germany) according to the constant flour weight procedure[16,14]. Dough development time was defined as the time required for the dough development or time necessary to reach 500 brabender units (BU) of dough consistency.
2.2.5. Specific Volume of Mediterranean Flat Bread
- Breads were weighed (g) and then their loaf volumes (ml) were determined by sesame seed displacement. Bread specific volume (ml/g) was calculated by dividing the bread volume by bread weight.
2.2.6. Measurement of Mediterranean Flat Bread Crumb Softness Value
- Staling rate of Mediterranean flat bread was measured by compressibility with a penetrometer (PNR-10 Penetrometer, Petrotest Instruments Gmbh & Co. KG, Dahlewitz, Germany)[15]. Breads were stored in sealed polyethylene bags at room temperature (20°C), 12 h after removal of the bread from the oven. For crumb softness, two slices of 23 mm were taken from the center of the bread and each treatment was compressed in five spots by a weigh of 54.6 g for 5 seconds. The compression spots were marked by holes on the four corners and center of a 6 × 6 cm cardboard template placed on the cut surface of each treatment. Data for five points from each loaf were averaged to give the compressibility, measured with a penetrometer unit[1 penetration unit (PU) = 0.1 mm].
2.2.7. Color Measurement
- Crust color was measured with a Color Tech-PCM (Cole-Parameter International, USA). This defines color numerically in terms of lightness or L* value, (0 = black, 100 = white), a* value (greenness 0 to –100, redness 0 to +100) and b* value (blueness 0 to -100, yellowness 0 to +100). Color values of each Mediterranean flat bread treatments were determined at three different points.
2.2.8. Sensory Evaluation
- loaf face color, homogeneity of color, taste and flavor, the odor, chewiness, tearing quality and general acceptability of the MFB treatments were rated using hedonic scale marked with “Extremely unacceptable” followed by “Very unacceptable”, “Unacceptable”, “Neither acceptable or unacceptable”, “Acceptable”, “Very acceptable” and “Extremely acceptable”.Twelve panellists of both genders who were familiar with Mediterranean flat bread characteristics were chosen. Instructions were given in full to panellists beforehand. Examination took place in tasting booths under normal white illumination. Panellists were asked to mark a position anywhere along the scale that matched their perception. Bread treatments were removed from polyethylene bags before evaluation, and then selected at random from the different treatments. The breads were rated in comparison to control bread (without LF).
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
- The experiments were conducted under laboratory conditions with three replicates for each treatment. The data collected from experiments were analysed using SPSS version 11.5[17]. Analysis of variance ANOVA and student t-test were used to analyse treatments at ≤0.05 level.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Analysis of Flours and Mediterranean Flat Bread
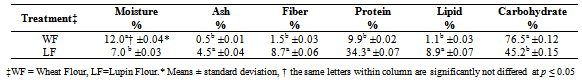
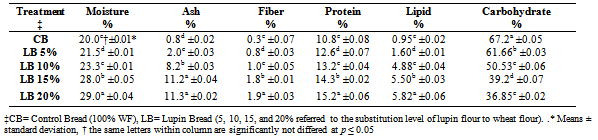
- The chemical compositions of wheat flour and lupin flour are shown in Table 1. The moisture content of LF is significantly (p ≤ 0.05) lower than the moisture content of WF, it could be attributed to LF composition contains oligosaccharides and polysaccharides which characterized as high water holding capacity[18 -22]. MFB with 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% of LF revealed, significantly high moisture content than CB as shown in Table 2. In the literature, it is reported that wheat-bean composite flour had greater water absorption capacities than WF[21]. Moreover, LF (high dietary fiber content) may retain water by preventing evaporation during baking. This result is in agreement with other researchers such as Grigelmo-Miguel et al.[23] who reported that muffins prepared by adding peach (high fiber content) had higher moisture contents than the control. Ash content of LF and LB (5%, 10%, 15% and 20%) are significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher than WF and CB. This means that LF usage from 0% to 20% increase ash content from 0.8% to 11.3% in bread treatments. The same finding for raw cowpea flour added to WF was reported by Hallenet al.[21].In this study, LF is significantly includes high fiber content than WF. This finding could be attributed to lupin seeds didn’t expose to hull removing before milling. Fiber content analysis for bread treatments indicated that increasing LF levels incorporation lead to significant increase in fiber content in LB (Table 2). The results suggest that producing high fiber bread with high nutritional and health benefits is possible by adding LF[24]. Crude protein content in WF and LF were 9.90 and 34.29 %, respectively as shown in Table 1. It is obvious that protein content of LF were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher than WF. Results of protein content of breads, revealed that there is a significant (p ≤ 0.05) increase in protein content of LB in comparison to CB. The more WF substituted with LF the more protein content were resulted. The same results were obtained from substituting germinated cowpea flour, chickpea and broad bean flour to WF in breads and cookies production[21, 25, 11, 12]. These results revealed that LB characterised with high content of protein and fiber could be used in special feeding programmes targeting young children in developing countries and school going children [26]. Table 1 shows that lipid content of LF is significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher than WF. LB20 contains 5.82 % lipid, while CB contains 0.95%. It is noticed that the more WF substituted with LF the more lipid content resulted. WF and CB has a significant high content of carbohydrate as compared with LF and LB.
3.2. Sensory Evaluation
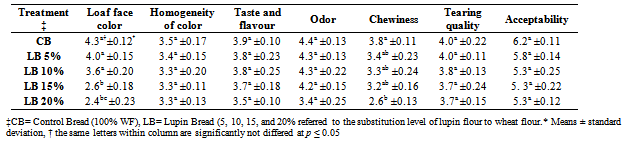
- Sensory analysis of Mediterranean flat bread treatments is presented in Table 3. LB15 and LB20 have a significantly (p≤ 0.05) high score in loaf face color as compared with the other bread treatments. LB5, LB10, LB15 and LB20 have no significant (p≤ 0.05) differences in homogeneity of color, taste and flavor, odor, tearing quality, and acceptability as compared with CB. LB treatments show significantly (p≤ 0.05) low score in chewiness as compared with CB.
|
|
|
3.3. Farinograph Results
|
|
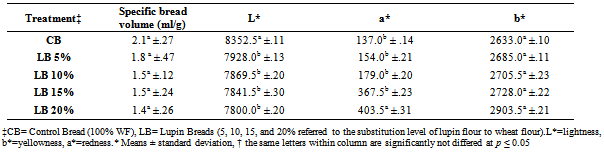
3.4. Specific Volume of Mediterranean Flat Bread
- The results showed that specific volume of the MFB decreased as the level of lupin flour increased, it is observe that CB and 5% LB give the highest volume, while 15% and 20% LB give the lowest volume of loaf bread. These results were in a partial agreement with those reported by Talley et al.[35] who found that 17% and 30% substitution of sunflower meal in wheat flour produced dense, compact loaves; however, 3% enrichment gave an attractive loaf.
3.5. Color Measurements
- A distinctive characteristic of the supplemented bread treatments was their color. Lupin flour color (yellow color) directly affected the color of bread treatments. All bread treatments which contained LF, particularly at higher amount of incorporation, exhibited a white-yellowish color and differences among the treatments were already visible without instrument aid. The lightness (L*), redness (a*), and yellowness (b*) values of the prepared breads are shown in Table 5. There was a significant decrease in lightness at LB5, 10, 15 and 20 as compared with CB. This observation agreed with previous results obtained in muffins made with some cereals[36], potato peel[37] and peach dietary fibre[21]. Supplementation with higher amount of LF increased bread yellowness and redness in MFB treatments especially at LB 15 and 20%. The natural dark pigmentation of bread treatments related to Maillard reaction which could be effective on this color change[38, 39, 40].
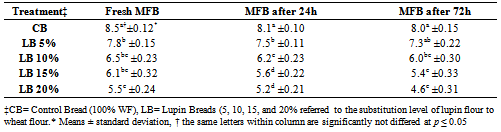
3.6. Measurements of Crumb Softness Value
|
- Crumb softness or firmness is a texture property, which has attracted most attention in bread assessment, because of its close association with human perception of freshness. Treatments which contain more LF yielded harder crumb structure than CB. The decrease in softness due to higher level of LF may be related to higher amount of ash available in LF. In general, longer storage time leads to harder crumb texture within LB treatments.
4. Conclusions
- The experimental results presented in this study provide that it is possible to produce healthy and nutritionally adequate bread rich in proteins, ash, lipid and fiber with long shelf life and good eating quality, by substituting WF with LF up to 20% level without affecting physical and sensory properties. Addition of LF rather improved the sensory properties of color and texture of MFB by making it more attractive. Therefore, substitution of LF could be implicated to develop new healthy and nutritious food products that are useful for dieting and feeding programs appropriate for people who need more protein per unit body weight as cancer patients and burn patients. Thus, we recommend using LF as a good source for MFB making due to its nutritional composition and health benefits.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to thank Dr. Radwan Ajo, Dr. Sofyan Maghaydah and Dr. Ahmad Alqudah for their assistance in this study.
Abbreviations
- LF: lupin flour, WF: wheat flour, MFB: Mediterranean flat bread, CB: control bread, LB: lupin bread
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML