-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Energy and Power
p-ISSN: 2163-159X e-ISSN: 2163-1603
2014; 4(1): 16-28
doi:10.5923/j.ep.20140401.03
Existing and Recommended Renewable Energy Conversion Technologies for Electricity Generation in Nepal
Suresh Baral, Kyung Chun Kim
School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan, 609-735, Republic of Korea
Correspondence to: Kyung Chun Kim, School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan, 609-735, Republic of Korea.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Nepal has a huge potential for renewable energy, but there has been no systematic study of energy conversion technologies for electricity generation. The paper explores various renewable energy resources and conversion technologies for electricity generation. Hydropower plants are dominant in Nepal because it is estimated that 43000 MW power can be obtained through the many rivers in the country. The solar and wind energy potential are estimated to be 2100 MW and 3000 MW, respectively. In solar applications, concentrating solar power (CSP) and solar organic Rankine cycle (ORC) plants should be installed for rural electrification and national grid connection. In the case of biomass energy, only biogas has been used widely in remote areas for cooking purposes in homes. Direct biomass combustion, organic Rankine cycle process plants and gasification techniques will be suitable for electricity generation. Finally wind power conversion techniques involve small scale wind power plant and hybrid wind/photovoltaics for energy supply in the villages of the country are recommended. Although renewable energy resources cannot serve as an alternative to conventional energy resources, they may help supplement the long-term energy needs of Nepal to a significant level.
Keywords: Renewable energy, Hydropower, Solar, Biomass, Wind, Rural electrification, Energy conversion technologies
Cite this paper: Suresh Baral, Kyung Chun Kim, Existing and Recommended Renewable Energy Conversion Technologies for Electricity Generation in Nepal, Energy and Power, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 16-28. doi: 10.5923/j.ep.20140401.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
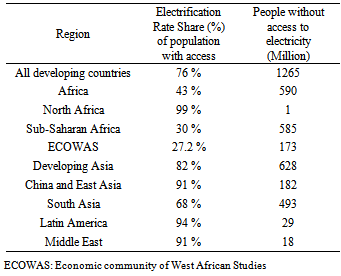
- Energy is fundamental to living and growing the economy. Many forms of energy utilization plants have been installed. The energy landscape has been transformed by the expanding population, economic growth and innovative technological developments. Modern societies are becoming increasing dependent on reliable and secure electricity supplies to support their economic growth and community prosperity but the world’s population is increasing. Rapid growth has transformed developing Asia’s presence in the world economy. The gross domestic product (GDP) of developing Asia is expected to more than quadruple from 2010 to 2035, and by 2050, the region will generate over half of the global GDP [1]. Electricity generation represents the largest energy use across many sectors and is the basic necessity in the lives of most people. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), approximately 1.3 billion people in the planet do not have access to reliable electricity, as listed in Table 1 [2]. The electric power demand has increased exponentially in the commercial, industrial and transportation sectors over the last few decades.
|
|
|
2. Methods
- Various methodologies have been implied for preparing an article on the renewable energy technology conversion for electricity generation in Nepal. The methods are discussed below:
2.1. Literature Survey
- Various literature surveys are carried out for the finding the renewable energy conversion technologies used in Nepal. The literatures relating energy consumption, energy potential such as solar, biomass, hydropower and wind power have been collected for preparing this article. Though there is not any kind of article that shows the recommended technologies suitable for generation of electricity from different renewable potential resources, this article could be useful for different interest of people relating to energy sectors.
2.2. Integrative Review
- The purpose of this review is considered to represent literature on a topic in an integrated way such as those new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. From this approach all the studies that addressing renewable energy technology for electricity generation in developing countries like Nepal has been sorted and incorporated in this article. From this method, the trends of consumption of energy during different years have been analyzed. In addition to, the energy policies that are practiced in Nepal so far has also been reviewed. The energy policies in Nepal have not been formulated and no strict measures have been taken due to instability of government.
2.3. Systematic Review
- The systematic review was aim to provide an exhaustive summary of current literature relavent to energy potential and policies of Nepal. For this a thorough search of relevant papers from the databases and citation indexes such as web of science, cross ref, DOAJ, scopus and ProQuest have been used inserting the keywords such as renewable energy, solar energy, biomass, hydropower, wind energy, Nepal.
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Nepal’s Energy Status
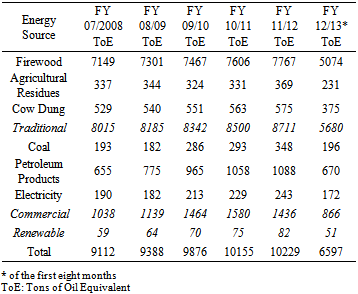
- Nepal has the lowest per capita electricity consumption in Asia; 93 units compared to 806 units for the rest of Asia. The per capita electricity consumption of India and China is 644 units and 2,942 units, respectively. The per capita electricity consumption of Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Pakistan is 279, 445 and 457 units, respectively [6]. According to the report [7], the total energy consumed from various sources of energy was 10229 TOE for the fiscal year 2011/12, and Table 4 lists the energy consumption mix for several years and shows that the huge population of people in Nepal relies on traditional bio-based fuels for their daily needs, which accounts for 85%. The contributions of various forms of biomass energy are firewood (89.16%), cow dung (6.6%) and agricultural residue (4.23%). These sources are commonly used in rural areas of the country where there is no grid connection to the main lines of electricity. The energy demand in fiscal year 2012/2013 was estimated to be 5446.3 GWh, out of which only 77.5% was supplied. Among the total supplied energy volume, the domestic generation contributed 85.6% with remainder imported from India [5, 8, 9]. Although Nepal has immense potential to produce electricity from a range of renewable energy resources, such as hydro, solar, biomass and wind, efforts to harness the resources for the country’s energy supply still remains.
|
3.2. Existing Hydropower Plants in Nepal
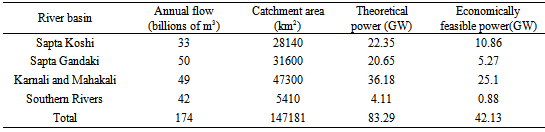
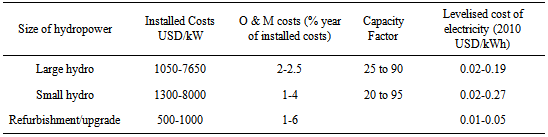
- Hydropower is the most advanced and mature renewable energy technology and provides electricity generation in almost every country. Hydropower plant has been used since ancient times. The energy of falling water was used by the Greeks to turn water wheels that transferred their mechanical energy to grinding stones to turn wheat into flour more than 2000 years ago. Hydropower plants convert the potential energy of flowing water into electricity. Hydropower schemes range in size from a few watts for Pico-Hydro to several GW or more for large–scales projects. Hydropower plants normally have long lifetimes; 30 to 80 years depending on the power component [10]. The water after generating electrical power is available for irrigation and other purposes. Nepal is rich in hydro-resources with one of the highest per capita hydropower potentials on the planet. The estimated theoretical power potential is approximately 83000 MW but the economically feasible potential is 43000 MW [10]. This is basically due to the high capital investment needed to develop hydropower and often involves socio-economic issues. The steep mountainous terrain and perennial flow in more than 6000 rivers/rivulets makes hydropower widely available throughout the hilly regions of Nepal. In addition, the country also has the potential for small hydro power plants. The small hydro power plants are seen as a single option that might be used as a local energy resource, particularly in remote areas for rural independent power generation. Despite having huge hydropower potential, Nepal has not been able to a harness this natural resource for various reasons including financial constraints, human resources, political scenarios and geographic conditions for development. Table 5 shows the total annual flow of the river basin of various sources with their theoretical and economic feasibility power generation capacity [11, 12]. These days, more work on the development of hydropower plants have been initiated by various private companies, local communities, NGOs, INGOS, donor agencies and government bodies. A small percentage of hydropower potential has been exploited in dams and hydroelectric power plants and from river run-off and canals. Therefore, Nepal has very low electrification rate compared to other south-Asian countries, and approximately 56% of the total population has access to electricity [12]. Hydropower development in Nepal can play a vital role in the overall development of the country. In addition, there is strong evidence that access to electricity will have a positive impact on the poor, through improvements in children’s education, better communications through radio and television, increase in rural production and improvement in health conditions of the rural people. From an economic point of view, the construction and installation of hydropower for different capacity power generation plant differ according the labor cost and materials available in the countries. Table 6 lists the typical costing of hydropower development [13].
|
|
3.3. Existing Solar Technology for Electricity Generation
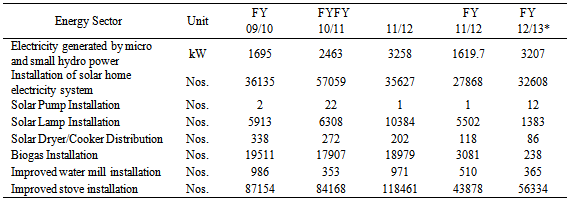
- Nepal lies on the good solar belt making the application of solar power attractive. In Nepal, it has been estimated that there is more than 6.5 hours of sunshine per day with approximately 300 days with the average isolation lying between 4-5 kWh per square meter per day [18, 19]. On the other hand, the use of solar energy is not utilized effectively for electricity generation. The major electricity demand in Nepal is for lighting in remote areas. People in such areas generally light their homes with kerosene lamps [20]. The common use of solar energy for electricity is only limited to photovoltaic (PV) and is popular. The other uses of solar energy are for water pumping for drip irrigation and drinking, which appears to be technically and economically feasible. In addition, it is used widely for solar water heating in the hilly and Terai regions in the country. The other applications include the drying of agricultural products, such as herbs and vegetables, and a solar cooking system. On the other hand, the solar cooking is not effective because of the trends, and traditional eating and cooking habits using food cooked with kerosene and biomass products [18]. The average cost of the installation of solar PV in the county ranges from USD 244 to USD 880 depending on the size of the system, even though the cost can be sensitive to factors, such as inflation and devaluation of the national currency [21]. The country has improved its expansion each year progressively due to the subsidies and tax policy for rural electrification programs and schemes from Government of Nepal. Table 7 lists the number of households benefiting from these programs.
|
3.4. Existing Technology for Electricity Generation through Biomass Energy
- In Nepal, biomass conversion to electricity is not being practiced. Only few institution-based studies have been conducted. Biogas technology is used widely all over the Nepal’s rural areas for the cooking of food. Biogas is a mixture of CH4 (40-70%), CO2 (30-60%) and other gases (1-5%) produced from animal dung, poultry droppings and other biomass waste in specialized bio-digesters. This gas is combustible and can be used to generate electricity [25]. Only rice husks, municipality solid waste (MSW), poultry droppings and bagasse are considered useful for electricity generation. MSW and bagasse can be used for grid power generation because sugar mills are connected to the grid network. Khatiwada et al. [26] reported that the total electricity generation would be 313 GWh with an installed capacity of 87 MW from nine sugar mills currently in operation in Nepal. Therefore, electricity generation through biogas digesters connected to internal combustion engines with slight modifications of the engines is good option for rural electricity in Nepal.
3.5. Existing Small Scale Wind Energy Technology for Electricity Generation
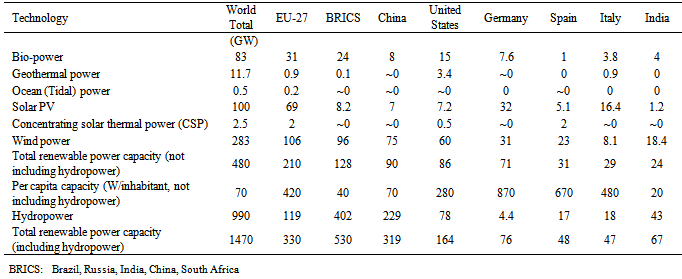
- Wind power technologies transform the kinetic energy of the wind into useful mechanical power. The kinetic energy of the air flow provides the motive force that turns the wind turbine blades that, via a drive shaft, provide the mechanical energy to power the generator in a wind turbine. Thus far, the worldwide wind power generation of electricity is 283 GW [3]. The installation costs in 2010 for onshore wind farms are as low as $1300 to $1400/kW in China and Denmark, but typically range from $1800/kW to $2200/kW in most other major markets. Preliminary data for the United States in 2011 suggests that wind turbine costs have peaked and that the total costs could have declined to $2000/kW for the full year (i.e. a reduction of $150/kW compared to 2010). Wind turbines account for 64% to 84% of the total installed costs onshore with grid connection costs, construction costs and other costs making up the balance. Off-shore wind farms are more expensive and cost $4000 to $4500/kW; with wind turbines accounting for 44% to 50% of the total cost [27].Micro wind electrification systems are an alternative with great potential for generating power in rural areas. Nepal’s attempts to harness wind energy have not been successful due to the continuous failure in the operation of pilot projects that are installed in various parts of the country. The first recorded effort for exploiting wind energy in Nepal was Rampur with American support in the early 1970s. Similarly, a wind turbine for pumping water was installed in Ramechap district in the late 1970s. Both projects, however, failed in operation. The most significant and systematic efforts to harness wind energy was undertaken by NEA in 1989. Two 10 kW wind turbine generators were installed and operated in Kagbeni of Mustang district. The electricity produced was distributed to 60 houses in villages but after two months, these turbines were broken due to structural problems. The investigation reported that wind turbulence due to the proximity of mountains was not considered while designing. Another feasibility study conducted by DANGRID, a Danish consulting and UNDP in 1992, reported that 200 MW of wind power can be produced in the 12 Km corridor from Kagbeni to Chusang alone [28]. The estimated electricity that can be generated annually was 500 GWh. The feasibility study conducted by [14], reported that the wind power density (WPD) should be more than 300 W/m2 for a commercial viable electricity generation through grid connection. The study concluded that if only 10% of the area is considered, the wind power developed could be 3000 MW, which is large enough for the current demand of the country. The Annapurna Conservation Area alone has a wind power density (WPD) of 300 W/m² and with 5 MW installed per sq. km yields 716 MW of energy. Most potential project sites lie in conservation zones in the mid-hills and high mountains. Nepal currently has some small-scale, stand-alone wind turbines. The AEPC has constructed six wind-solar hybrids – 400 W wind and 150 W solar, each capable of supplying a community with sufficient energy to run one radio and a CFL bulb in Pyuthan, Musgit and Palpa [29]. Wind turbines of few hundred watts are considered small scale and can be introduced in the windy sites of remote villages in Nepal. In the context of Nepal, the Alternative Energy Promotion Centre and Practical Action are two organizations working in the development of small wind turbine technology. Small scale wind energy technology is important for villages and to provide easier transportation in mountainous areas. The technology can still be a good option for electricity generation in remote villages where grid connection is not feasible. Finally, small wind turbines can be manufactured locally and are easy to install in the required areas. The existence of local manufacturers facilitates system maintenance and has the advantage of promoting enterprise development. Low cost wind turbines with timber blades represent a good solution for decentralized energy production in the off-grid regions of developing countries [30]. Small wind turbine systems have powers ranging from 50 W to 10 kW with rotor diameters ranging from 0.5 m to 7 m, which are used primarily in battery charging. The batteries can then be used to supply energy to houses, hospitals, farms, and telecommunication. Wind energy systems can also operate alongside diesel sets or solar PV systems. A 1.5 kW wind – solar hybrid system was installed in Pheriche in the Mount Everest Region. The system supplies electricity to the Rescue Hospital. The advantages of community scale wind turbines installed in each home will cover the domestic use of electricity for certain hours of the day. The electricity can be used as households lighting, listening radios, and charging cell phones. The energy in schools will power computers and projectors for educational purposes. The health center will benefited from the light, sterilizer and vaccine refrigerator. As a result of the wind turbines, families can reduce their expenditures in other energy sources, such as kerosene or candles, and save the time that they would normally need to collect wood for cooking lighting. Moreover families using energy will be engaged in the implementation of small businesses.
4. Discussion
- The government of Nepal is continuously imposing all the stakeholders, donor agency, international non-governmental organization, national governmental organization for investment on the energy sectors. So this paper deals with the appropriate technologies that are recommended for implementation in Nepal for electricity production. The following renewable technology helps in fulfilling the current demand in cities as well as rural areas of the country by adopting rural electrification programs which as discussed as:
4.1. Small Hydropower Plants (SHPs)
- Nepal's first major hydropower was constructed in Pharping with financial assistance provided by the United Kingdom (UK) in 1911. The Pharping hydropower plant had an installed capacity of 500 kW. Hydropower on a small-scale is one of the most cost-effective energy technologies to be considered for electrification in less developed countries. In general, Small hydropower refers to power varying from 5MW to 50MW [31]. Small hydropower plants are normally considered clean technology to produce electricity, on a decentralized basis, and are likely to attract considerable attention and investment in the coming years due to the increasing concerns on the overall attainment of the Kyoto emission goals [32]. Small hydro technologies are extremely robust (systems can last for 50 years or more with little maintenance) and are also one of the most environmentally friendly energy technologies available thus far. Small hydro power plants are built on run-of-river, and do not require huge infrastructure, such as reservoirs or dams to store large amounts of water. Moreover, there are fewer environmental problems, such as life of aquatic biodiversity. More generally, SHPs are found in isolated grids as well as in off-grid and central-grid settings. Small hydro power requires cross flow and Peltons turbines, and can be a widely adopted turbine technology for local manufacturer in Nepal. In Nepal, the concept for the construction of small hydropower is recommended. This is also beneficial because of the less time in constructing a power station. Typically, such a project requires 2.5 to 3 years [33, 34]. Nepal can benefit considerably from small hydro plant technology, particularly in hilly regions because of the location close to loads and fewer transmission lines needed to make its exploitation economical. Local management, ownership and community participation, technology transfer, and capacity building are the basic issues that will allow sustainable small hydropower plants to be developed in the country.
4.2. Storage Type of Hydropower Plant
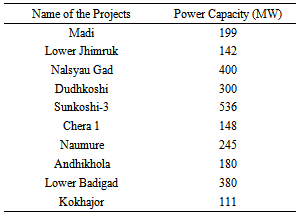
- The hydropower system in Nepal is dominated by run-of-river Projects, and there is only one seasonal storage project in the system [5]. This means there is a shortage of power during winter and a spill during the wet season. The load factor is quite low as the majority of the consumption is dominated by household use. This imbalance clearly shows the need for storage hydro plant projects. Reservoir-type hydropower plants involve impounding water behind a dam. This enables flow regulation throughout a season or the year. Reservoir-type hydropower plants are typically used for highly variable flows in the middle reaches of a river, or as energy storage in the upper reaches of a river. These plants are operated on a scheduled basis in accordance with data regarding water flow forecasts, market price and consumption. These plants are commonly used for intense load and to meet the peak demand. Hydropower plants with a small reservoir are sometimes also called pondage plants. They are designed to modulate generation on a daily or maximum weekly basis. Pondage plants can provide flexibility services mainly by balancing power. They also provide frequency and voltage control as ancillary services. Generally, hydropower plants with reservoirs (also called storage-type power plants) introduce unique benefits to the electricity system [35]. In Nepal, storage type of hydropower plants is necessary because of its hydrological characteristics, where there is continuous sedimentation in the riverbed. This scheme assists in the deposition of sediment in the storage during a period of time thereby causing less damage to the turbines and runners, and maintaining the constant efficiency of hydroelectric plants while in operation. According to the feasibility study conducted by NEA, there is the possibility installing 102 storage hydroelectric plants in Nepal. Recently, a study conducted by NEA and JICA proposed 10 promising and technically sound storage projects to power developers within the 20 year of master plan in electricity generation, which are listed in Table 8 [36] and these are key projects to reduce the power cuts in the country.
|
4.3. Pumped Storage Hydropower Plants (PSHP)
- Globally, there are approximately 300 pumped storage plants either operating or under construction, representing a combined generating capacity of more than 127,000 MW. Although the majority of these plants use single-speed pump-turbine machines, 36 utilize adjustable-speed machines; 17 of these are currently in operation (totaling 3,569 MW) and 19 are under construction (totaling 4,558 MW) [37-39]. The main advantage of this technology is that it is readily available. This technology uses the power of water, which is a highly concentrated renewable energy source. PSHP operates with two reservoirs: a lower and upper one. A river, lake or existing water storage can serve as a reservoir. In other cases, a new reservoir must be created, the characteristics (i.e. size) that depend on the site’s topographic and hydrological conditions. PSHP has a conversion efficiency of approximately 65–80% in terms of a power network depending on the equipment characteristics [40]. The PSHPs are operated daily and weekly cycles, and are designed to provide the peak electricity during periods of high electricity demand. This can be achieved in a very short time, i.e. within minutes. The water is released from the upper reservoir through the turbines to generate electricity. On the other hand, the duration of the electricity supply from pumped storage hydropower plants is limited. The upper reservoir normally contains a certain amount of water that can provide full operation for several hours. Water is typically pumped up from lower to higher-level reservoirs during the off peak periods (i.e. during the night) using the surplus electricity generated by conventional base-load power plants [38]. PSHP is inherently more flexible than thermal or nuclear plants, and one of the cheapest ways of providing peak load power. PSHP continues to grow in significance, largely due to its ability to provide ancillary services as shares of variable renewable generation. Accordingly, Voith Hydro (Germany) increased its emphasis on research and development, particularly for pumped storage technology [2]. PSHPs are characterized by a long asset life (typically 50–100 years), high capital cost, low operation and maintenance cost and round-trip efficiencies of 70–75%. The project costs for PSHPs are very site specific with some quoted costs varying from €600–3000/kW. In addition, capital costs depend not only on the installed power, but also on the energy storage and MW capacity at any given site [41]. PSHP technology has advanced significantly since its introduction and now includes improved efficiencies with modern reversible pump-turbines, adjustable-speed pumped turbines, new equipment controls, such as static frequency converters and generator insulation systems, as well as improved underground tunneling construction methods and design capabilities. Overall, the pumping/ generating cycle efficiency has increased the pump-turbine generator efficiency by as much as 5% in the last 25 years, resulting in energy conversion or cycle efficiencies greater than 80% [39]. In Nepal, pump storage hydropower plants should be installed to provide long term continuous power supply to the Nepalese during peaking periods, and will ultimately solve the electricity crisis there.
4.4. Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) Plant
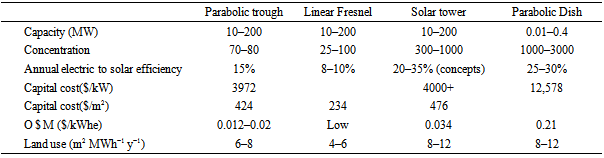
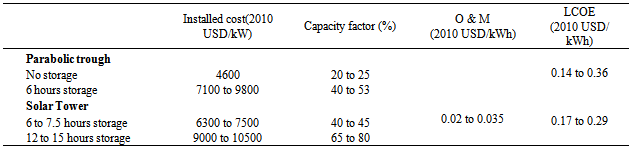
- Nepal should now focus on solar energy utilization for grid connection. Solar technology that uses solar energy for medium and large size electricity generation is not currently being used in the country. Because of the lack of skilled manpower and investment capital, Nepal has not been able to exploit this renewable resource extensively despite its huge potential. The following summarizes some of the recommended technology that should be utilized.Concentrating-solar-power (CSP) technologies are expected to be an important ingredient of any virtually CO2-free electricity market in a long-term scenario. According to recent estimations, CSP could produce as much as 7% of the total electricity needs projected for the world by 2030 and 25% by 2050 with potential growth in global deployment from 2.5 GW today to 0.2 EJ by 2030 [4, 42]. According to one report [43], small-scale CSP, from 100 kW to 2 MW, could reach 63 GW by 2050, mostly for process heat and rural on/off-grid applications around the globe.CSP is a power generation technology that uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate the sun’s rays and heat a fluid to produce steam. The steam drives a turbine and generates power in the same way as conventional power plants. Instead of steam, some other organic working fluids will be introduced for future CSP. Modern CSP plants are equipped with a heat storage system that helps maintaining a constant temperature to generate electricity, even when the sky is cloudy or after sunset, which increases the CSP capacity factor significantly compared to solar photovoltaics. This CSP technology facilitates both grid integration and economic competitiveness. The most widely used technology is parabolic trough collector technology for electricity generation. A heat transfer fluid (HTF) is circulated through the absorber tubes to collect solar energy and transfer it to a steam generator or to a heat storage system. Most existing parabolic troughs use synthetic oils as the heat transfer fluid, which are stable up to 400°C and a high temperature molten salt can improve the thermal storage performance considerably [3]. Table 9 compares the various CSP technologies discussed thus far including the operational and maintenance costs as well as the capital costs. A parabolic trough, linear Fresnel, and solar tower systems are suitable for the power generation capacities in the range of 10–200 MW, whereas the parabolic dish systems are better suited for lower generation capacity requirements between 0.01 and 0.4 MW [44]. The cost of CSP can be changed with storage tank installation for prolonged electricity generation even when the sky is cloudy and during the night, as listed in Table 10 [45]. In Nepal, recently the NEA is installing 20 MW solar power output generation in five different locations of the country namely Sindhupalchok, Panauti, Trishuli, Pharping and Kharipati, with an expected cost of approximately US$ 54.66 million, the loan provided by World Bank. In addition, the NEA signed an agreement with a Chinese solar energy company and the Japanese Government for the installation of a 30-MW solar and 680.4 kW station in the country [46].
|
|
4.5. Solar Organic Rankine Cycle Plant
- This is a new growing solar energy technology that is particularly suitable for developing countries, such as Nepal. Over the last decade, the organic Rankine cycle (ORC) has been studied widely to harness low-grade heat sources that provide temperatures ranging from 80-400 °C. This includes the same components to that of traditional Rankine cycle, i.e. a pump, evaporator, turbine, and condenser. The only difference is the choice of working fluid: where water is replaced with pure or a mixture of organic compounds. The commercial application began in the late 1970s and interest in this technology has increased exponentially over the decade. Currently, there are more than 200 installed and operating ORC plants around the world with an installed power of more than 1.5 GW [47]. For decades, solar ORC concepts for community power supplies have been discussed extensively but rarely implemented. A solar thermal organic Rankine cycle (ORC) can provide affordable energy supplies in remote regions. Small-scale solar ORCs of few kilowatts have been studied only in research-based institutions. Several authors [48-53] have examined the selection criteria for ORCs working fluids. The common solar ORC working fluid is R245fa [54]. For a solar ORC, the concentrating solar power is a well-proven technology: the sun is tracked and reflected on a linear or on a punctual collector, transferring heat to a fluid at high temperatures. The heat is then transferred to a power cycle generating electricity. The solar ORCs use the three main concentrating technologies, which are a parabolic dish, solar tower, and parabolic trough. ORMAT is only one manufacturer that has its solar ORCs commercial plants thus far in the market. ORMAT developed the 1MWe CSP plant working with ORC in Arizona, USA in 2006, which uses n-pentane as the working fluids provided that has an efficiency of 20% and the global solar to electricity efficiency of 12.1% on the design point [52]. On the other hand, there are several pilot projects on solar ORC for electricity generation, which are explained in the following [55]:a) A 1 kWe system was installed in Lesotho by the “Solar Turbine Group” for rural electrification. The goal was to develop and implement a small scale solar thermal technology utilizing medium temperature collectors and an ORC to achieve economics analogous to large scale solar thermal installations. The configuration aimed at replacing Diesel generators in off-grid areas of developing countries, thereby generating clean power at low normalized cost (~$0.12/kWh compared to ~$0.30/kWh for diesel).b) A prototype of 5 kWe solar ORC was constructed in 2009 within the frame of the project POWERSOL in Almeria, Spain, where the working fluid used was SES36, and showed an overall theoretical and ORC efficiency of 7% and 14% respectively.Still, no thermal power blocks are currently manufactured in the kilowatt range for small-scale ORCs. Therefore, many studies are being carried out focusing on solar energy for electricity generation [56-60].In Nepal, small-scale solar organic cycles will be well adapted for remote off-grid areas. Compared to the main competitive technology, the PV collector, Solar ORCs have the advantage of being locally manufactured. They are also more flexible and allow the production of hot water as a by-product. Therefore, this system can be considered a CHP plant for heating and cooling applications. The hot water produced can be applied for domestic proposes in health posts, clinics and schools in remote places. Therefore, the solar ORC will be quite popular if it can be installed successfully in many remote areas, where there is ample solar radiation.
4.6. Biomass Combustion
- In combustion, the chemical energy of the fuel is converted to sensible heat that the flue gases carry, which is then transferred to a working medium in a heat exchanger. The working medium expands in a turbine or other devices to create mechanical energy for power production. The combustion of biomass generates hot gases at high temperatures of 800-1000°C, producing steam to run an internal combustion engine for electricity generation [61]. Currently, more than 90% of the energy produced from biomass is generated using biomass furnaces [62]. No reports on biomass combustion in Nepal are available, but the availability of various agricultural biomass residues from crops, forest residues and dry animal dung makes combustion a viable means of electricity generation. This is currently the cheapest and most reliable route for producing power from biomass in stand-alone applications. Therefore, this technology is suitable for rural and urban areas of Nepal for isolated grid connection.
4.7. Biomass Based Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) Processes
- The ORC process is based on the Rankine process, just as the conventional steam process is. Instead of water, however, the working fluid is of organic compounds and has low boiling and condensation temperatures. Accordingly, the ORC process is suited to heat exploitation at lower temperatures. Nevertheless, the resulting efficiencies for biomass applications from a thermodynamic point of view must be lower than in a steam process due to the low temperature of the working fluid. The electrical efficiencies for ORC plants in operation are up to 15% [63]. The biomass based organic Rankine used bio-based materials such as straw, wood chips, etc. This can be very suitable for country like Nepal where there are lots of forests for the feeding materials to run biomass based ORC system.
4.8. Wind Power Conversion Technology through Hybrid Wind/Photovoltaic Systems
- Currently, standalone solar photovoltaic and wind systems have been promoted around the globe on a smaller scale. Solar and wind power alone are poor power sources as the wind does not blow all the time and does the sun shine all the time. Hybridizing solar and wind power sources together with storage batteries to cover the periods of time without sun or wind provides a realistic form of power generation. The system creates a stand-alone energy source that is both dependable and consistent. The hybrid solar wind turbine generator uses solar panels that collect light and convert it to energy along with wind turbines that collect energy from the wind. The solar wind composite power inverter contains the required AC to DC transformer to supply the charge to the batteries from the AC generators. Therefore, the power from the solar panels and wind turbines is filtered and stored in the battery bank. Moreover, small off-grid standalone hybrid power systems offer an imperative choice for decreasing the electricity gap in remote areas of the country, where progress in grid extension is almost impossible because of the poor geographical condition, high capital cost and scattered population. According to [64] small-scale systems, even if they generate relatively little power, can enhance considerably the quality of life in remote areas.In Nepal, this hybrid power is mostly suitable in the Annapurna conversation area, where there is good wind and solar potential. This hybrid system not only replaces the diesel-based electricity but also improves the living standards of people living in remote areas. Although there are few cases of hybrid system power generation, as discussed earlier, this is not utilized to its full potential. Therefore, for countries like Nepal, this concept should be applied to the rural poor areas for electricity generation.
5. Conclusions
- The future economic development path for Nepal is likely to result accelerated demand. The potential of various renewable energy resources through different conversion technologies will help meet the current demand of the country. The renewable energy resources conversion technology presented in this paper is expected to help Nepal’s government energy planners, energy economists, donor agency, policy makers and researchers to understand the different technologies for electric power generation with the latest technology used widely around the world. In addition, the government of Nepal has decided to produce 10000 MW of electricity within 10 years. To implement the plan proposed by the government, the renewable energy resources should be harnessed by utilizing the recommended technology presented in this paper. Although only hydropower is being exploited for electricity generation in Nepal, other simple and economically feasible technology through solar, biomass and wind power can also be installed for power generation. This type of power generation requires fewer time frames and can be installed easily in remote and urban areas compared to hydropower plant construction. Small scale power generation technology is necessary to help solve the frequent power shortages in urban areas and provide rural electrification remote areas for lighting and other purposes. Therefore, in this context, the renewable energy resources may serve to supplement the long-term energy needs of Nepal. An integrated energy planning approach, consistency in government energy policies and rational policy instruments to deal with techno-economic and socio-political barriers are the pre-requisites for long-term sustainable development of the renewable energy technologies for power generation. The link between government, local and private communities is a key challenge for electrification in the country.To support these technologies for implementation in Nepal, energy policy should have given high priority. The policies regarding new technology need to strengthen the commitment in the implement of energy initiatives. Therefore, the starting point is an institutional arrangement. New technology for implementation cannot be realized without institutional and managerial structures and controls. In other words, the responsibilities of the various authorities need to be defined clearly. Another policy is the concern for the need of drafting and approving policies and regulations. The revised renewable energy policy must address the role of these technologies for rural electrification as a substitute for traditional energy sources, such as kerosene-based lighting. The new policy should be compatible with socio-economic and political aspects of the region or country for launching and strengthening. The final policy that needs to be addressed is the legal framework. For the legal frameworks, it is essential to consider the economics. If these technologies for rural electrification are to be promoted as a competitive component, financial parameters, such as capital costs, operation and maintenance cost, and payback period of the technology should be considered. Therefore, it is urgent to address these technologies in Nepal for rural peoples to provide one of the basic needs, electricity, as well as for improving the living standards and economic growth.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korea government (MSIP) through GCRC-SOP (No.2011-0030013). This work was also supported by the Energy Efficiency & Resources Core technology Program of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) granted financial resource from the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea (No. 20112010100030).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML