-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
World Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-1573 e-ISSN: 2163-1581
2021; 11(2): 83-98
doi:10.5923/j.env.20211102.02
Received: Nov. 25, 2021; Accepted: Dec. 20, 2021; Published: Dec. 29, 2021

Contemporary Carwash Wastewater Recycling Technologies: A Systematic Literature Review
Agyen K. G.1, Monney I.2, Antwi-Agyei P.1
1Regional Centre for Energy and Environmental Sustainability, University of Energy and Natural Resources, Sunyani, Ghana
2Department of Environmental Health and Sanitation Education, Akenten Appiah-Menka University of Skills Training and Entrepreneurial Development, Mampong-Ashanti, Ghana
Correspondence to: Monney I., Department of Environmental Health and Sanitation Education, Akenten Appiah-Menka University of Skills Training and Entrepreneurial Development, Mampong-Ashanti, Ghana.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Faced with dwindling freshwater resources globally, many industries, including the carwash industry, have turned to wastewater recycling technologies. But the performance of these technologies, their environmental impacts, and economic viability have not been extensively examined. This systematic review examined the treatment efficiencies of modern carwash wastewater recycling technologies, their cost implications, and their by-products. The study drew on an extensive literature search spanning the last decade and found 34 research articles suitable. The results showed combined treatment methods as the most typical approach adopted for treating carwash wastewater. Combined technologies incorporating membrane filtration process almost completely remove COD (99%) and turbidity (99%), but flux reduction and membrane fouling present significant problems. Other technologies employing chemical or electrochemical coagulation produce sludge containing hydroxide and oxyhydroxide ions. But this sludge is mainly landfilled. The highest capital and annual operational costs for the technologies assessed are about US$10,000 and US$3000, respectively. The payback period ranged between 5 and 140 months and saves up to 5000m3 of freshwater annually, translating into savings of about US$20,000 yearly. This study generally observed an extensive focus on the treatment efficiencies of CWW recycling technologies to the neglect of their economic viability and environmental impact. Areas for further studies are discussed in the paper.
Keywords: Carwash wastewater, Treatment, Economic analysis, Sludge, Recycling
Cite this paper: Agyen K. G., Monney I., Antwi-Agyei P., Contemporary Carwash Wastewater Recycling Technologies: A Systematic Literature Review, World Environment, Vol. 11 No. 2, 2021, pp. 83-98. doi: 10.5923/j.env.20211102.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Car wash wastewater recycling (CWWR) technologies have been used for at least three decades and are rapidly growing in sophistication [1]. These technologies treat previously used wash water to remove impurities and reuse it in the wash process again. CWWR is practised as a way of conserving water in many countries. In a world faced with an increasing decline in freshwater availability, sustainable water management is considered imperative. Therefore, various countries have enacted laws that demand a wastewater recycling system and restrict water usage at car washing stations [2]. In response, car wash operators found in such regions have adopted environmentally friendly and modern technologies to save energy and conserve water [3]. However, while these countries apply stringent measures to control water wastage by car washes, others, mainly in developing and less developed countries, do not have such regulations [4]–[6]. Consequently, vast amounts of fresh water are wasted daily from car washing activities.Besides wasting water, car washes also contribute significantly to water pollution. Effluents from these activities are known to contain high levels of COD, TSS, Sulphates and other pollutants, which can be very harmful [4], [7]. Therefore, many treatment technologies including, electrochemical, membrane processes, and chemical coagulation [8]–[11], have been developed to avoid discharging untreated carwash wastewater into the environment. These technologies may seem feasible in some parts of the world but may not be possible in others due to economic differences. Meanwhile, available studies [12], [13] only focus on the type of technologies and their performance without considering the financial aspects (capital and operation expenditure, payback periods and revenues) and sludge production and disposal methods. Particularly in the developing world, where regulations do not exist to compel carwash operators to recycle wastewater, the only motivation to install a CWWR technology is the operational cost reduction benefit. The economic aspects of contemporary CWWR technologies thus need to be studied to inform future studies that would seek to reduce the capital and operating costs of the technologies.Moreover, these CWWR technologies may generate by-products requiring treatment before disposal and therefore becomes imperative to assess how the current technologies are handling these by-products. Therefore, this systematic review examines the diverse CWWR technologies available, their treatment efficiencies, financial implications, and sludge production and disposal methods. This is to extend the current boundary of existing knowledge and provide the basis for future studies on CWWR.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Selection Criteria
- The search was carried out using keywords and phrases that are relevant to the study being conducted. Databases where searches were conducted are PUBMED, ScienceDirect, Taylor & Francis and Google Scholar. The search was limited to only articles published in English and those published in the past decade: on or after 2010 up to 2020. Articles selected were those that were available electronically. The keywords and phrases were meshed, and where supported, wildcards were also included in the search strings to ensure all relevant documents were captured. The mesh terms used were as follows; [(‘carwash’ OR ‘carwash’, OR car wash’ OR ‘vehicle wash’) AND (Treatment OR Recycle OR reclaim OR reuse) AND (wastewater OR effluent)].
2.2. Screening
- The search from the four databases using the provided keywords and mesh terms returned 1,363 articles (Figure 1). These were then screened based on their relevance to the scope of the review. Titles and abstracts were used initially to obtain articles relevant to this work. Afterwards, a manual inspection of the relevant articles was done to further screen them based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. Articles included in this manual screening were those that qualified the inclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria were that articles should have information on carwash wastewater, the characteristics of the wastewater, a treatment method for the carwash wastewater, results for the treatment method used, and/or financial and sludge disposal aspects. Articles to be selected would have to meet these criteria. Other articles were also obtained from the bibliographies of selected articles during the manual inspection. After careful manual inspection, the number of articles was thinned down to 46. Since the searches were done in 4 different databases, duplicates were expected to manifest. Out of the 46 articles, 12 were duplicates. So eventually, 34 relevant articles were left for use in this study (Figure 1). The list of all articles used in this study is provided in the supplementary sheet.
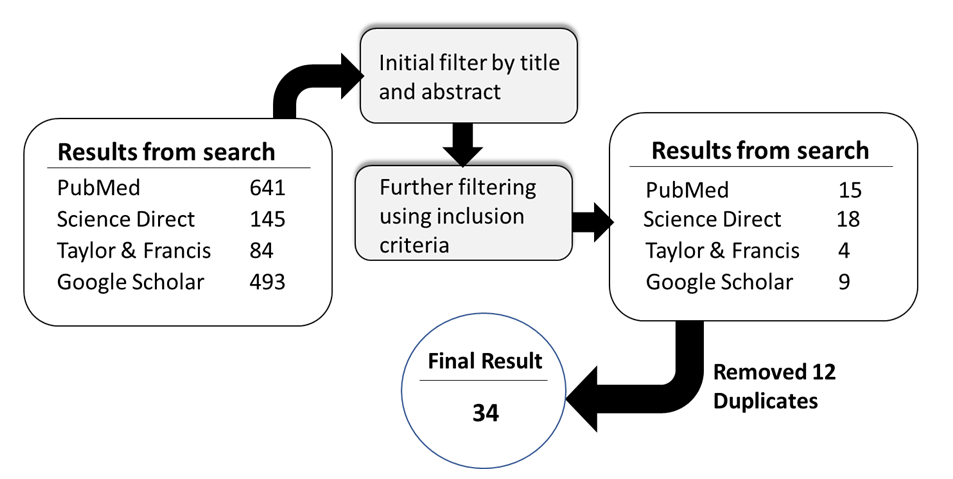 | Figure 1. The search and screening process flow chart |
3. Results and Discussion
- The results indicate that combined treatment technologies were the predominant method adopted for treating carwash wastewater (Figure 2). They involve two or more biological, physical, chemical, and electrochemical processes in treating carwash wastewater (CWW). The least applied were other advanced and complex methods, biological processes and treatment by coagulation and sedimentation only [10], [14]–[17]. Membrane processes were the second most common method. They were mainly applied as secondary treatment, preceded by coagulation and/or sedimentation, or as a tertiary treatment after sand filtration. Membrane processes show high removal efficiency for turbidity and COD, but this depends on the membrane pore size being used. However, due to the various pollutants found in CWW, an integrated technology that combines different processes (which may or may not include membrane processes) is perceived to be the better option [2], [18], [19]. Nonetheless, reusable treatment standards can be achieved either by membrane processes only or an integrated system.
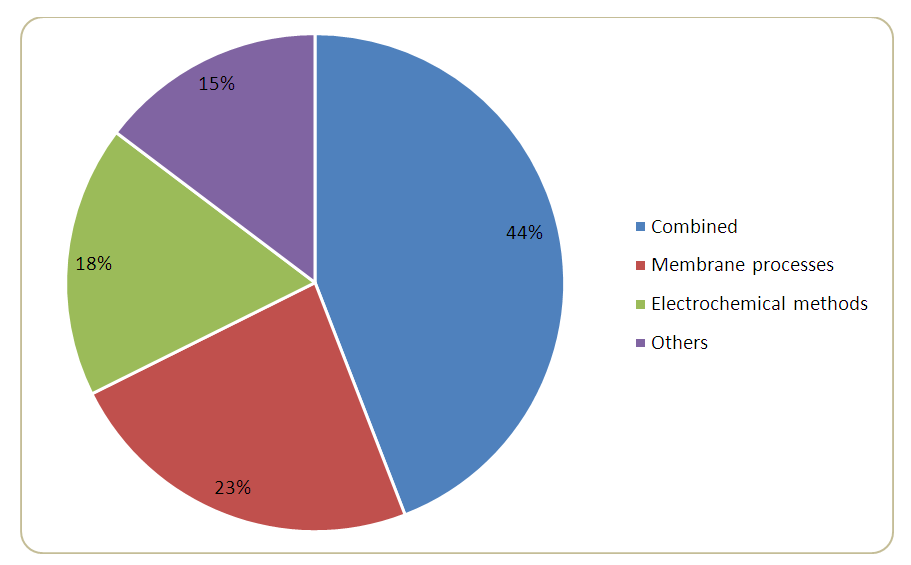 | Figure 2. The proportion of different technologies applied in treating CWW |
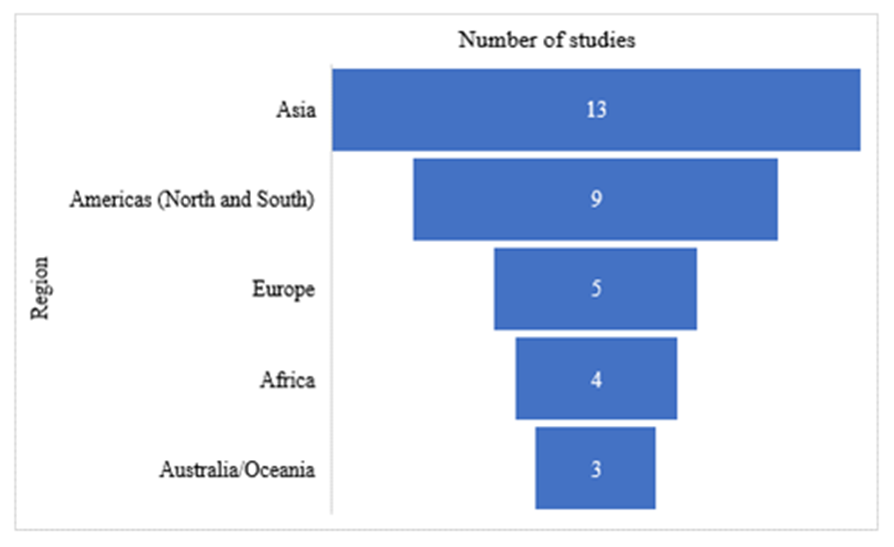 | Figure 3. Distribution of articles published per region |
3.1. Performance of CWWR Technologies
- The type of technology adopted for treating CWW depends on the nature of pollutants and the end use of the treated water. Carwash wastewater that is treated for discharge is mainly achieved through pre-treatment methods, while highly polluted waters either go through both pre-treatment and biological processes, membrane filtration, oxidation and/or adsorption processes [14], [16], [23]. Pollutant concentrations reported by numerous studies differ for different study locations, so other methods and technologies have been applied in different regions for treating CWW. Subsequently, the various technologies reviewed in this study and their pollutant removal efficiencies are presented.
3.1.1. Electrochemical Processes
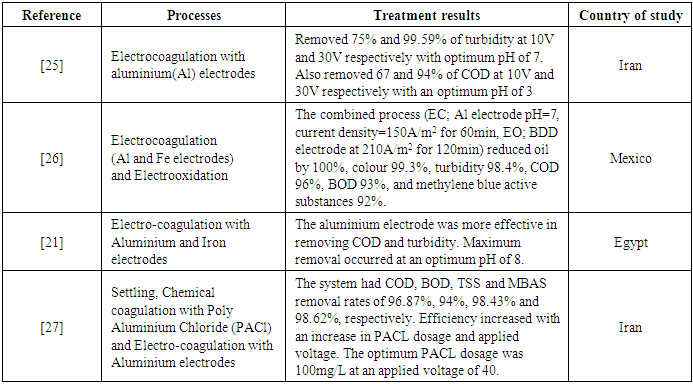
- Removing pollutants from wastewater using electrochemical processes is a relatively modern technology that uses the concepts of electricity and chemistry. It has proven to be proficient in removing turbidity and surfactants in CWW [24]–[26]. According to this review, it is the third most used technology in treating CWW. Electrochemical methods include electro-coagulation and electro-oxidation. While the former is popular in treating CWW, the latter is not very prevalent in the carwash industry. Electrochemical processes use electrodes to aid in the treatment of wastewater. For example, in an electro-coagulation process, an electrode is oxidised continuously while an electric current is being applied. This leads to the release of ions that disturb the stability of the suspension and facilitate particle clustering and settling [26].The main parameters that affect the performance and efficiency of an electrochemical process are electrode material, voltage/current density, pH and contact time [21], [24]–[27]. The electrode material commonly adopted are Aluminium (Al) and Iron (Fe). These are used separately or combined in the treatment process. The initial pH affects the stability of generated hydroxide species in the electro-coagulation process [26]. Therefore, the removal efficiencies increase as pH is increased. A study by [25] reported 99% turbidity and 88% removal of COD for Al electrode and 94% turbidity and 73% COD removal for Fe electrode at a pH of 7, a voltage of 30V and contact time of 90 minutes (Table 1). They observed that increasing the voltage caused a significant increase in removal efficiency. However, the amount of voltage supplied is related to the energy consumption, which is related to the cost of operation. Therefore, a reasonable compromise must be made in choosing the proper voltage that does not increase the operating cost too much [26]. While others reported electricity supplied to the electrochemical process in volts [25], [27], others also reported it in current density [21], [24], [26]. The current density (CD) is defined by [24] as the current per area of the electrode.Increasing the voltage or current density releases a greater number of ions that precipitate with pollutants in the wastewater. This creates tiny bubbles that improve floc generation for pollutant removal [24]. [26] reported that increasing the current density from 53 A/m2 to 210 A/m2 increased the removal efficiency of COD and turbidity (Table 1). At a pH of 7, contact time of 60 minutes and CD of 210 A/m2, 95% and 84% of turbidity and COD were removed respectively with an Aluminium electrode and 94% and 80% turbidity and COD removal with an Iron electrode. Another parameter of interest that also affects the performance of the electrochemical processes is contact time. The contact time is also inversely related to Voltage or CD. If the current density or the voltage decreases, more time is needed to achieve higher efficiencies and vice versa [26], [27]. According to the study, the optimum contact times ranged from 30 minutes to 120 minutes. [26] again reported results on electro-oxidation after performing the electro-coagulation. The results revealed that a higher contact time of 120 minutes could remove 100% oil-grease, 99% colour, 98% turbidity, 96% COD, 93% Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and 92% Methylene Blue Active Substances Assay (MBAS) and 90% chlorides. [21] also looked at another parameter; temperature. Per their study, the temperature can potentially impact the performance of the electrochemical treatment process significantly. However, their observation of a temperature change from 30 to 45°C were insignificant.
|
3.1.2. Membrane Treatment Processes
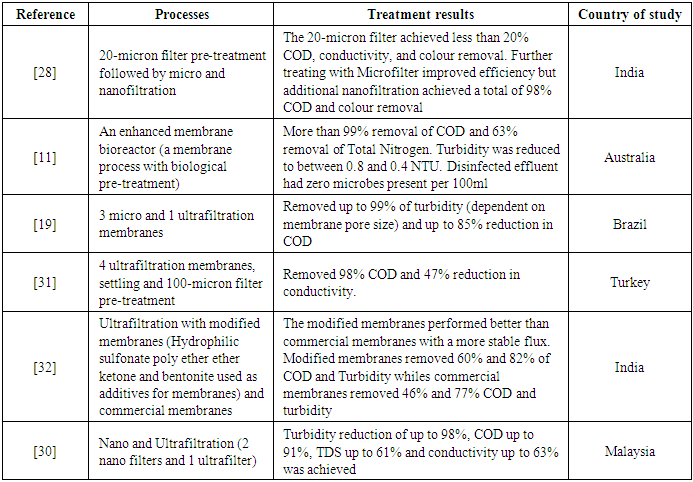
- Membrane technologies involve using a porous material for the transport of substances between two factions. It can be used for the separation of both gaseous and liquid streams. This process has been widely used to treat different types of wastewater [28]. It has proven very efficient in removing pollutants like Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) and turbidity. According to this review, membrane treatment methods constitute the second most common technology adopted in treating CWW. For the effective and reliable performance of membrane technology in treating CWW, the membrane material should be highly permeable, have high flux and have low retention [29]. However, the problem with using membranes to treat CWW is the reduction in flux over time and membrane fouling [11], [19], [30], [31]. The flux can decrease drastically to about 60% of the initial flux over a short time [19]. The loss in flux is dependent on membrane pore size, influent quality and type of membrane material [19], [28], [31]. Nanofiltration membranes generally perform better than Micro and Ultrafiltration membranes in terms of fouling and flux decline. Membranes with hydrophilic and negatively charged surfaces also prevent significant flux decline and reduce fouling [30], [31]. The hydrophilicity of the membrane can be achieved by modifying it with bentonite and sulphonate polyether ether ketone (SPEEK) [32]. Other studies ([28], [33]) also reported that pre-treating the membrane influent can significantly increase the flux to about three times higher than when the influent is not pre-treated.Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) also significantly affects the membrane’s flux. An increase in the pressure causes an increase in flux. However, too much pressure increase can reduce permeate quality or even lead to severe fouling, which might deteriorate the membrane’s lifetime [11], [19]. Higher pressures also translate to higher energy consumption, leading to a high cost of operation [19].Regarding treatment efficiencies (Table 2), membrane filters (micro, ultra and nanofillers) can produce permeate with high-quality standards. Turbidity, COD, TDS concentrations in permeate are well within acceptable ranges for reuse or discharge. COD removal efficiencies recorded varied from 60% to as high as 99.2% [11], [19], [30], [32], [34]. Complete COD removals are achieved when a biological process (Membrane Bioreactor) precedes the membrane process (Table 2). This is true when microorganisms in the bioreactor are stable [11], [34]. Other studies reported 99% [19], 88.6% [30] and 98.8% [32] removal of turbidity from CWW using membrane processes (Table 2). Removal efficiencies of pollutants like Total Organic Content (TOC) and Total Nitrates were also reported to be 97.3% and 60%, respectively [11], [34]. Reducing electrical conductivity was the most difficult to achieve by membrane processes [19], [30]. However, incorporating an ion exchange process or a reverse osmosis process has been shown to overcome this, thereby increasing the cost of operation.
|
3.1.3. Combined Processes
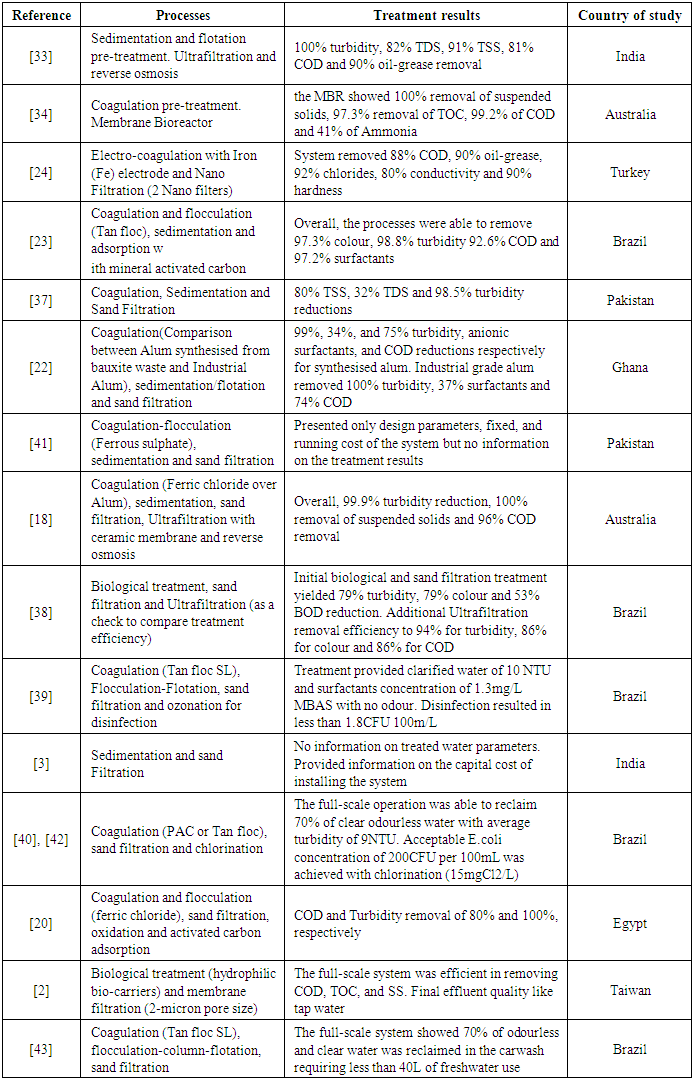
- Looking at the different pollutant compositions of CWW, a single treatment step will not be enough to remove all these pollutants altogether. Therefore, it is essential to complement it with other technologies that can effectively handle these diverse pollutants. This is where combined processes come into play. The idea is to integrate different treatment methods in the most cost-effective way that produces greater removal efficiencies for several types of pollutants found in CWW. Also, full-scale application of treatment systems mainly combines at least two or more treatment processes as it is more feasible, rational and economically viable than a single treatment step [35]. Literature from this review validates this statement. Table 3 shows the treatment efficiencies of combined processes reviewed in this study. All the full-scale CWW treatment technologies examined in this study were combined processes. Although the different combinations can yield better treatment efficiencies, the removal efficiency for a particular pollutant depends on the treatment methods combined for the treatment chain.
|
3.1.4. Advanced Oxidation (Photo/Electro – Fenton Process)
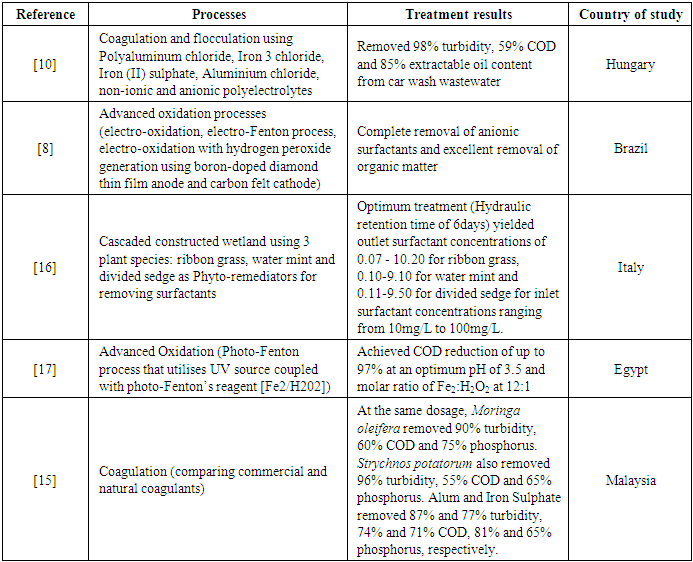
- Advanced oxidation processes utilise hydroxyl radicals to remove organic pollutants from wastewater. They have been widely used to treat different types of wastewater [44]. One of such processes is the Fenton process – a process that generates a hydroxyl radical (OH) from the reaction between aqueous ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). A modified version of Fenton process (photo/electro-Fenton) has been applied in treating CWW [8], [17]. An advantage of this modified process is its ability to regenerate Fe2+ ions needed as a catalyst to facilitate the oxidation process [45]. The process, just like many other treatment processes, depends on certain factors to be effective in its pollutant removal capabilities. Nevertheless, the process has proven effective in completely removing surfactants and COD from carwash wastewater [8] (Table 4).However, the efficiency of the electro-Fenton process is affected by pH, applied current, electrode material, the concentration of iron ions and its nature (Fe2+, Fe3+ or solid Fe III). Moreover, the photo-Fenton process is also affected by pH, H2O2 concentration and Fe2+ concentration. The study by [8] compared three types of advanced oxidation processes: electro-oxidation, electro-oxidation with H2O2 generation and electro-Fenton’s process, to remove surfactants and COD from CWW. All three processes were performed with acidified wastewater (pH=3). Their electrochemical advanced oxidation treatment employed a Boron-doped diamond thin film (BDD) anode and a carbon felt cathode. The removal efficiency was more remarkable for the Electro-Fenton process than the other two methods. It completely removed COD at a contact time of 6 hours and current of 500mA, and 96% surfactants at a contact time of 4 hours and current of 500mA. The removal efficiency of the process was improved when the current was increased from 250 to 1500mA. However, this also resulted in significant energy consumption. Complete removal of surfactant was achieved at 1500mA of current at a lesser contact time of 1hour. Another study by [17], which involved using the photo-Fenton process as an advanced oxidation treatment method for treating CWW, saw almost complete (97%) COD removal from the CWW (Table 4). They used a UV source for the photo-Fenton process coupled with Fenton’s reagents (H2O2 and Fe2+). Concentrations of H2O2 and Fe2+ significantly influenced removal efficiency. Increasing these parameters saw a significant increase in COD removal. However, raising them beyond a particular concentration saw a decline in removal efficiencies. pH also played an essential role in the processes. A pH of 3 was considered the optimum for higher removal efficiencies.
3.1.5. Biological Treatment
- Biological wastewater treatment involves using living organisms, especially microbes, to remove pollutants (primarily organic) from wastewater. It is commonly used to complement and enhance traditional treatment methods [46]. It is considered simple and less costly than other chemical and physical processes. There have been a handful of biological treatments applied in treating CWW. Since the biological treatment alone cannot eliminate the different pollutants in CWW, they are usually combined with other treatment methods to effectively remove these diverse pollutants in the wastewater. [2], [11] combined biological treatment with other processes to treat CWW. The biological treatment was used alongside a membrane filtration process, and eventually, they reported a significant decrease in the organic content of the CWW. [38] also combined biological treatment (Rotating Biological Contactors) with granular filtration to treat wastewater from a heavy-duty car wash station. Their system had overall removal of 79% turbidity and 86% BOD (Table 4). Chlorine was applied at the end of the process to deal with biological contaminants present in the wastewater. Grab samples from their system were additionally treated with an ultrafiltration membrane which further improved the treated water’s quality.
|
3.1.6. Simple and ‘Complex’ Coagulation Processes
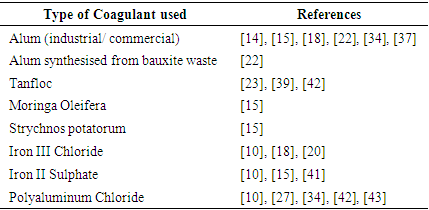
- Wastewater from various sources commonly contains organic and inorganic particles, which make it turbid and give it colour. CWW also contains these particles. Coagulation, a process that involves the destabilisation of particles found in wastewater to promote their agglomeration into larger particles (flocs) for easy settling and removal, has been reported to be efficient in reducing organic and inorganic particles concentration and improving turbidity of the wastewater [46]. It is mostly performed in traditional water treatment processes as a pre-treatment step to reduce pollutant load before other chemical, physical or biological treatment methods are applied to the wastewater [47]. Similarly, it has been applied in treating CWW and reported to be efficient in removing turbidity, colour and COD from CWW [15], [22], [42].In all the treatment technologies reviewed in this study, more than 70% employs coagulation in their processes. The most commonly used chemicals for coagulation are Aluminium and Iron salts. However, other natural organic substances and electrochemical methods have been equally adopted to achieve the same outcomes. Table 5 shows a list of different coagulants applied in CWW treatment technologies. As mentioned earlier, coagulation processes are not performed in isolation. However, [15] conducted a study to compare the efficiency of coagulants alone in treating CWW. They compared natural coagulants; Moringa oleifera and Strychnos potatorum, with chemical coagulants; Alum and FeSO4 [Iron (II) Sulphate]. While Alum and FeSO4 performed better in removing COD from the CWW, with removal efficiencies of 80% and 77%, respectively, S. potatorum performed better in removing turbidity (95% reduction) at a lower dosage concentration of 50mg/L. However, when they compared the efficacy of both coagulants in removing phosphorus, the chemical coagulants performed better (85% removal efficiency).
|
3.2. Sludge Characterisation and Disposal
- Sludge is an unavoidable waste that results from all water treatment plants [41], and CWW treatment technologies are no exception. The amount of sludge and the rate of sludge generation for the CWW treatment depends on the type of technology being used. [10] reported an increase in sludge generation with an increased coagulant concentration with the addition of Na bentonite (clay mineral), slightly reducing its quantity. All the technologies reviewed in this study had some sludge generated from their processes. Out of the 34 articles reviewed, 11 mentioned sludge production from their technologies, representing about one-third of the total articles. [40] reported a sludge volume of 0.4m3 after 20 weeks of operating their full-scale treatment system. Their produced sludge was accumulated in a sand bed and disposed of in a landfill. A hybrid Bio-MF treatment system by [2] also produced sludge that was removed every three days and disposed of without any treatment or reuse. The different processes combined by [18] to treat wastewater also had a significant sludge production, 12.5% of the wastewater was turned into sludge by coagulation. Additionally, ceramic ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis also had 20%, and 28% of their feed water turned into sludge, respectively. The potential for sludge reuse will depend on its composition, and knowledge about its quantity and generation rate will also inform management measures. The composition of the sludge generated by [48] in their electrochemical treatment system was linked to the type of electrode used, Al electrode’s sludge had hydroxide and oxyhydroxide ions while Iron electrode’s sludge contained only oxyhydroxide ions. The sludge quantities were 11.6kg/m3 for the Aluminium electrode and 2.1kg/m3 for the Iron electrode. This was similar to the sludge produced by [26]. [24] in their study suggested the valorisation of their generated sludge by using it as an adsorbent due to its composition of ion complexes. Another characterisation was done to determine the morphology and constituent of sludge by [21]. They observed that the composition of the generated sludge was related to the adsorption of chemicals used in car washing and the dissolution of electrodes (Aluminium) used in their electrochemical process. Their sludge had an amorphous structure, and the main components were Al3O2, N and Ca.
3.3. Economic Analysis of CWW Treatment Systems
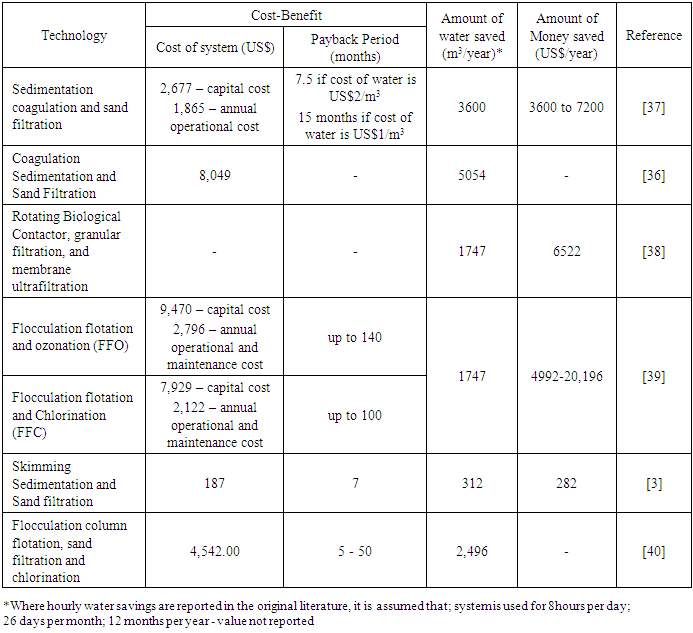
- CWW treatment systems are designed to protect the environment from pollution, conserve water, and, most notably, the carwash operator, save costs from water-related bills. Therefore, installing a treatment system at a carwash station is seen to be environmentally friendly and financially beneficial. This is true when the system is efficient in removing pollutants and economically feasible to invest in. It has been reported by [33] that treating CWW can reduce freshwater usage and save up to 88% of freshwater. [40] also reported less than 40L of fresh water being used per carwash after recycling CWW. This translates to cost savings when the operator must buy water for operation and discharge wastewater into sewers (in countries where discharge into sewers is billed). Where the clean water comes from a well, the cost savings will be associated with the energy consumption for pumping the water [38]. There have also been reports of as high as 80% cost savings on water-related bills after installing a recycling system [49]. The capital cost, payback period, treatment efficiency of the treatment system collectively play a role in whether a car wash operator will be willing to invest in such a technology. The suitability of an investment is related to its payback period. In the carwash industry, the amount of water being recycled/saved per day (water demand) and the cost of water and or energy consumption is what significantly affects the payback period [39], [40]. Therefore, a shorter payback period is preferred over a longer one. The invested money will not be held up for so long with a short payback period. This makes it possible to invest in other ventures in the shortest possible time. From the articles reviewed, only a few (primarily full-scale treatment technologies) had cost estimations for their systems. Table 6 shows an economic evaluation of some of these technologies. The capital costs observed from this review ranged from US$187 to US$9,470. The cheapest CWWR technology was developed in India. This system comprised skimming, lime and soda addition, sedimentation, and filtration. Conversely, the most expensive CWWR technology was a Flocculation flotation and ozonation technology developed in Brazil. The total cost is closely related to the treatment technology; the addition of a single treatment method can significantly increase the overall total cost of the treatment system. This is observed in a study by [39] where ozonation was replaced with chlorination for deactivating pathogens found in CWW. The operational cost was reported to have increased significantly due to high energy consumption by the ozonation process. Annual operational and maintenance costs also ranged between about US$2000 and US$3000. In terms of payback period, the literature reviewed in this study reported up to a payback period of 140months, with the least payback period being five months. Generally, a shorter payback period is acceptable for carwash operators to ensure that their investments yield the needed returns in no time. Carwash wastewater recycling technologies included in this study can save up to 5000m3 of freshwater annually and save carwash operations more than US$20,000 annually. The combination of coagulation, sedimentation and sand filtration provides the highest water savings, while Flocculation flotation and ozonation/chlorination, although relatively expensive, provide the highest annual returns (Table 6).
|
3.4. Strengths and Weaknesses of Carwash Wastewater Recycling Technologies
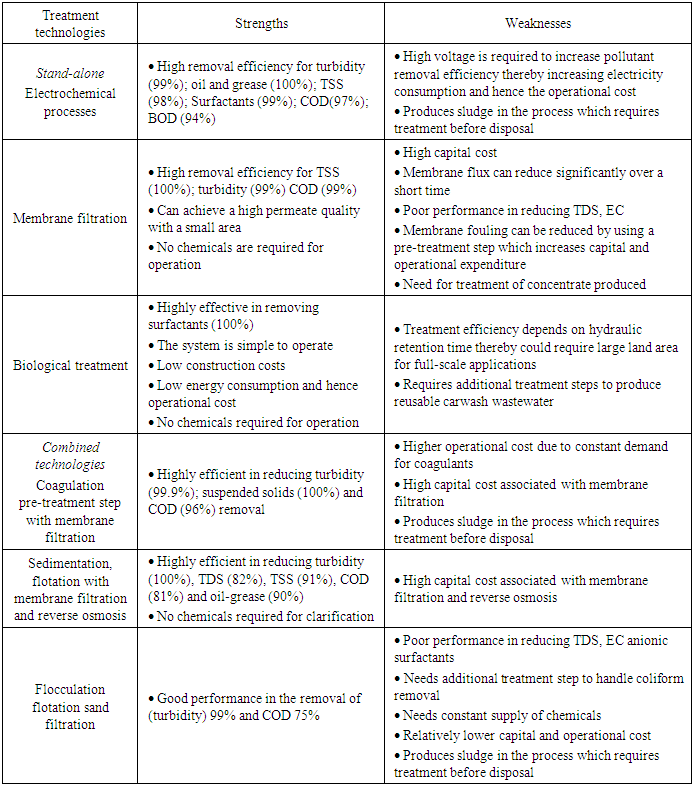
- Table 7 presents the strengths and weaknesses of contemporary carwash wastewater recycling technologies based on literature. The table depicts clearly that, over the years, the ability of a carwash wastewater recycling technology to remove pollutants from the wastewater with high efficiency has been the primary focus of research. Therefore, literature is awash with studies reporting on the technical performance of technologies for recycling carwash wastewater, while the economic viability and the environmental impacts largely remain neglected. Even in developed countries where regulations demand that carwash stations install recycling technologies for their wastewater, the cost of the technology plays a crucial decision-making role in selecting the technology. Because, given two technologies that can achieve the same pollutant removal efficiency, it will be financially imprudent for a carwash station operator to go for the more expensive option. Particularly in countries where wastewater legislations do not exist or are poorly enforced, the added benefit of increasing profit margins from installing such technologies will be a compelling reason for carwash operators to switch to wastewater reuse. Hence, although a given technology may be highly efficient in removing pollutants from wastewater, the cost factor needs to be considered. Moreso, the environmental impact of these technologies needs to be put under the lenses of researchers. For instance, although membrane filters and reverse osmosis filters are highly efficient in removing pollutants from wastewater, there is eventually brine solution (concentrate) generated from these technologies that need to be treated before disposal (Table 7). Additionally, combined technologies that employ a coagulation/flocculation or electro-coagulation process usually produce sludge. This sludge results from the agglomeration of colloidal particles and becomes another source of environmental pollution if not treated and disposed of properly.
|
3.5. Areas for Further Research
- This review has identified considerable gaps in the existing literature on carwash wastewater recycling technologies. First and foremost, many researchers have focused their lenses on the performance of the technologies in the removal of pollutants without considering other crucial aspects of the technologies they developed. At present, no cross-cutting research has been conducted to compare carwash wastewater recycling technologies vis-à-vis their performance, economic viability, and environmental impact. Therefore, future research will benefit from studies that compare these three fundamental aspects of carwash wastewater recycling technologies. Technologies developed in the future for carwash wastewater recycling must aim to fulfil these prerequisites: highly efficient in removing pollutants from carwash wastewater, have low capital and operational costs, have a short payback period, and do not pollute the environment in the process of recycling carwash wastewater. Secondly, this study has made it clear that combined treatment technologies are more effective than stand-alone treatment methods. However, the combination of stand-alone treatment technologies that checks all the acceptability requirements – performance, economic viability and environmental protection has not been examined. Further studies are needed in this area. A comparison of coagulation methods to determine an effective but low-cost coagulant for treating carwash wastewater and implications on sludge characteristics in different contexts still needs to be studied in the future. The available literature is scanty. Such studies will reduce operational costs associated with treatment technologies that employ a coagulation treatment step. Moreover, there is the need to comprehensively assess the characteristics of by-products (concentrate or sludge) resulting from carwash wastewater recycling and develop methods to treat and either reuse or dispose of them safely.
4. Conclusions
- This systematic review was conducted to critically examine the performance of the various treatment technologies for carwash wastewater, their sludge produced and economic aspects. Overall, the study reviewed 34 different research papers published over the past decade. Membrane processes, electrochemical methods and combined treatment methods were the most typical treatment technologies adopted for carwash wastewater treatment. Combined treatment technologies were the predominant method adopted for treating carwash wastewater. This was followed by membrane filtration and then electrochemical methods. Membrane filtration processes performed better at removing COD and turbidity than combined treatment methods. However, the major problems with using membranes to treat CWW are reducing flux over time and membrane fouling. Electrochemical treatment methods are also excellent at reducing oil grease colour and turbidity. However, their pollutant removal efficiencies tend to increase by increasing the voltage supplied. This increases energy consumption, which in turn increases the cost of operation. Although all these treatment technologies inevitably produce sludge as a by-product of their treatment processes, this study found scant literature on the characteristics of the sludge produced and the disposal mechanisms for the sludge. Per the studies reviewed, between one-fifth and one-third of the feedwater (CWW) used in membrane processes turned to sludge, while up to 12kg/m3 of sludge is produced for electrochemical treatment processes. For flocculation-flotation methods, 20L of sludge is produced weekly. The sludge contains hydroxide and oxyhydroxide ions and is mainly landfilled. An analysis of the economic aspects of the CWWR technologies showed that the flocculation flotation and ozonation (FFO) process has the highest capital (about US$10,000) and annual O&M costs (about US$3000). The payback period and the cost savings of the CWWR technologies are heavily reliant on the unit cost of water. For the technologies assessed in this study, the payback period ranged between 5 and 140 months, saving up to 5000m3 of freshwater annually and annual cost savings of more than US$20,000. This study provides a strong impetus for further investigations into the characteristics of sludge produced and extensive economic analysis of the technologies for recycling carwash wastewater. It is evident from this study that there has been a lot of focus on the performance of technologies for recycling wastewater in the carwash industry without focusing on technologies for reusing or safely managing the sludge produced. This study, therefore, argues that to reap the full benefits of wastewater recycling in the carwash industry, the technologies developed must also take care of the sludge/wastewater produced and be economically viable.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study was funded by the Regional Centre for Energy and Environmental Sustainability (RCEES) in the University of Energy and Natural Resources (UENR), Ghana, supported by the World Bank.
Competing Interests
- The authors declare no competing interests.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML