-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
World Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-1573 e-ISSN: 2163-1581
2019; 9(2): 46-55
doi:10.5923/j.env.20190902.03

Treatment of Contaminated Ground Water Using Phytoremediation Technique at Anantapur, India
Piyush Gupta1, Paturu Siva Niveditha2, S. Sharada2
1Wood Plc (Formerly Amec Foster Wheeler), Environmental & Infrastructure, Kuwait
2Department of Chemical Engineering, JNTUA College of Engineering, Ananthapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India
Correspondence to: Piyush Gupta, Wood Plc (Formerly Amec Foster Wheeler), Environmental & Infrastructure, Kuwait.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

One of the burning problems of our industrial society is the high consumption of water and the high demand for clean drinking water. Groundwater is used for domestic, industrial water supply and for irrigation all over the world. Although three-fourths of the earth is being surrounded by sea only a little portion of it can be used for drinking purpose. The use of aquatic plants for water and waste water treatment is increasing nowadays. The aim of the project is to examine the phytoremediation potential of water hyacinth (Eichhornia Crassipes) and water lettuce (Pistia Stratiotes). The study area faces water scarcity as well as water quality problems. Therefore, attempts were made to treat the groundwater at Anantapur, India using these species. The growth parameters of species like the number of leaves, plant weight, length of principal root and number of roots were studied. The results of the treatment methods were compared with respect to removal efficiency of these species for different water quality parameters. The study revealed that water hyacinth had higher contaminant reduction capability than water lettuce for various physicochemical water parameters.
Keywords: Phytoremediation, Water hyacinth, Water lettuce, Physicochemical, Water quality, Constructed wetland, Removal efficiency
Cite this paper: Piyush Gupta, Paturu Siva Niveditha, S. Sharada, Treatment of Contaminated Ground Water Using Phytoremediation Technique at Anantapur, India, World Environment, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 46-55. doi: 10.5923/j.env.20190902.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Around 97.5% of the total available water on earth is saline water and only 2.5% is fresh water. The greater portion of this fresh water (68.7%) is in the form of ice and 29.9% exists as fresh groundwater. Water quality is essential for wellbeing of the people. It can be affected by physicochemical and biological pollutants. Contaminates such as bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, nitrate and salt have found their way into water supplies (Atta and Razzak, 2008).In arid and semi-arid regions, where well managed water transportation system and related infrastructures are not available, groundwater serves as chief source of drinking water. Groundwater is influenced by many factors, including composition of precipitation, mineralogy of the aquifers, climate, topography and anthropogenic activities (Kumar and Riyazuddin, 2008). According to the United States of Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA, 1993), groundwater becomes contaminated naturally or because of numerous types of human activities like residential, municipal, industrial and agricultural. In recent days, groundwater quality is decreasing day by day due to rapid urbanization and fast industrial growth. Unrestricted exploration of groundwater and excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides make possible the infiltration of detrimental constituents to the groundwater. These activities can contaminate groundwater quality of Anantapur and can cause health problems. Therefore, a detailed study was conducted to treat the groundwater of Anantapur area using phytoremediation technique.Phytoremediation is one of the biological wastewater treatment methods (Roongtanakiat et al., 2007) and is the concept of using plants-based systems and microbiological processes to eliminate contaminants in nature. The principles of phytoremediation system are to clean up contaminated water which includes identification and implementation of efficient aquatic plant; uptake of dissolved nutrients and metals by the growing plants; and harvest and beneficial use of the plant biomass produced from the remediation system (Lu, 2009). The most important factor in implementing phytoremediation is the selection of an appropriate plant (Roongtanakiatet al., 2007; Stefani et al., 2011) which should have high uptake of both organic and inorganic pollutants, grow well in polluted water and easily controlled in quantitatively propagated dispersion (Roongtanakiat et al., 2007). The uptake and accumulation of pollutants vary from plant to plant and also from specie to specie within a genus (Singh et al., 2003; Gupta et al., 2012). The economic success of phytoremediation largely depends on photosynthetic activity and growth rate of plants (Xia and Ma, 2006) and with low to moderate amount of pollution (Jamuna and Noorjahan, 2009). These systems are generally cost effective, simple, environmentally non-disruptive (Roongtanakiat et al., 2007; Wei and Zhou, 2004), ecologically sound (Xia and Ma, 2006) with low maintenance cost (Kirkpatrick, 2005) and low land requirements (Lu, 2009).Many researchers have used different plant species like water hyacinth [Eichhornia Crassipes (Mart.) Solms] (Gupta et al., 2015; Dar et al., 2011; Dhote and Dixit, 2007; Jamuna and Noorjahan, 2009; Lissy and Madhu, 2010; Valipour et al., 2010, 2011), water lettuce (Pistia Stratiotes L.) (Awuah et al., 2004; Dipu et al., 2011; Fonkou et al., 2002; Lu et al., 2010) for the treatment of water. At Anantapur, groundwater is a major source of water supply for the domestic purpose. The study conducted by Sunitha et al., 2012 revealed that mainly total dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC) and hardness exceed the standards of drinking water in the groundwater of Anantapur. Therefore, a detailed study was conducted to treat the groundwater using phytoremediation technique. The results of a present study will not only help to know removal efficiency, but it will allow to do low cost treatment and facilitate to create sustainable and pollution free environment.
2. Material and Method
2.1. Study Area
- Anantapur District is in the South-Western part of Andhra Pradesh, India. The study area lies between longitudes 770 30’ - 780 15’ east and latitudes 140 0’ - 140 30’ north and falls in the Survey of India Toposheet No: 57 F/14, F/15, J/3, J/4. The location map of the study area is shown in figure 1. The study area is mainly underlain by peninsular gneisses of Archean age. The major geomorphic units of the study area are Denudational Hills, Dissected pedimonts, Pediplain, and Alluvium. The study area comprises pink Granites, schists, composite gneisses of Dharwar intruded by a few pegmatite dykes and numerous dolerite dykes and the possible diamondiferous volcanic pipes. Geology of the study area is shown in the figure. The area experiences a semiarid climate (it has a moisture index of 33.7%) with mean monthly temperatures of 15°C in January to 39°C in May. The normal rainfall of the district is 553 mm by which it secures least rainfall when compared to Rayalaseema and other parts of Andhra Pradesh. The area under study is mostly cultivated where maize, groundnut and cotton are grown. Paddy is also grown where there are some irrigation wells (Sunitha et al., 2012).
 | Figure 1. Location map of the study area |
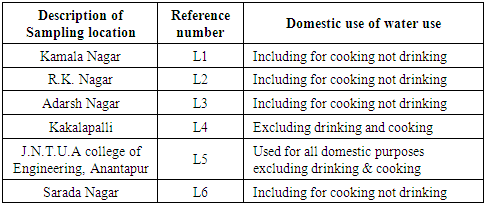
2.2. Sampling Locations
- A detailed survey was carried out within Anantapur to identify bore wells being used for domestic purposes. Based on the information provided by the local people, 6 wells were used for drinking in addition to other domestic purposes. Table 1 shows details of sampling locations and use of water for different domestic purposes (drinking, cooking, washing of clothes, utensils and house, etc.).
|
2.3. Sample Collection
- At first, the boreholes were pumped for 5-10 minutes until the pH remained constant. This phenomenon purged the stagnant water from the aquifers. After purging, fresh aquifer samples were collected. Similar approach was also followed by Gibrilla et al. (2010) for sample collection. Stoppered polyethylene bottles of two litre capacity were thoroughly cleaned and rinsed with water being sampled. The samples collected by grab sampling techniques from 12 bore wells of different locations were sealed and labelled properly. The study was conducted during May- June 2018.
2.4. Operational Procedure
- All the samples were analysed for different water quality parameters following the methods given in Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (APHA, 1992). In situ measurements of pH, Electrical Conductivity (EC), Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Salinity and Dissolved Oxygen (DO) were made with Water and Soil Analysis Kit calibrated according to the specifications from the manufacturer. Total acidity, total alkalinity and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) were determined by titration. Total hardness was measured by Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetic Acid (EDTA) titration method.
2.5. Plantation and Acclimatization
- Water hyacinth and water lettuce plant samplings were purchased from M/s Y. Munivenkatappa & Sons Nursery, Siddapur Gardens, Jayanagar Post, Bengaluru. Young saplings were collected because the treatment efficiency is more in comparison to old plants (Ayyasamy et al., 2009). Plants of similar shape and size were collected and were thoroughly washed several times using tap and distilled water until the surfaces appeared to be clean (Xia and Ma, 2006). Then the species blotted with clean blotting paper for any surface moisture avoiding damage to root and leaf apices (Mane et al., 2011).
2.6. Determination of Morphological Characteristics of Species
- The morphological characteristics of aquatic macrophytes i.e. number of leaves; number of roots; longest root and dry weight were determined by standard methods. Periodically at 2 days’ time interval, the same parameters were examined for 10 days to determine the botanical aspects of the plant. Histochemical analysis was carried out to determine the impact of pollutants on the plants.
3. Results and Discussions
- The plant species Water Hyacinth and Water Lettuce have the contaminant uptake capacity. So, for the treatment of the groundwater of Anantapur area, they were grown in the samples taken from different locations. The growth of this species was assessed on different days of interval. Number of leaves, plant weight, length of principal root and number of roots were considered during the growth studies of species for the assessment. The removal efficiency of the plants for different water quality parameters like pH, Electrical Conductivity (EC), Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Total Hardness, Salinity, Total Acidity, Total Alkalinity, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Dissolved Oxygen (DO) were determined.
3.1. Growth Status of Plant Species in Groundwater of Anantapur
- Growth status and removal efficiency of different plant species varied in the groundwater of Anantapur. The details are as under:
3.1.1. Water Hyacinth
- The quality and productivity of water hyacinth depends on the available nutrient supply (Reddy and Tucker, 1983). The values of number of leaves, weight of plants, length of principal roots, and number of roots were different, when they were immersed into groundwater of different locations (Fig. 2). No significant variations were observed in the number of leaves and length of roots at the end of 4th day of measurement. After that they continued shedding. It was observed that the roots were breaking from middle as the days increased. Number of leaves, weight of plants, length of roots and number of roots were on decreasing trend as the days increased. In most of the conditions, N is probably the major plant nutrient limiting productivity. Growth and nutrient uptake of water hyacinth are controlled by the sources of N (e.g., NH4+, NO3-, urea, or organic N) (Reddy and Tucker, 1983).
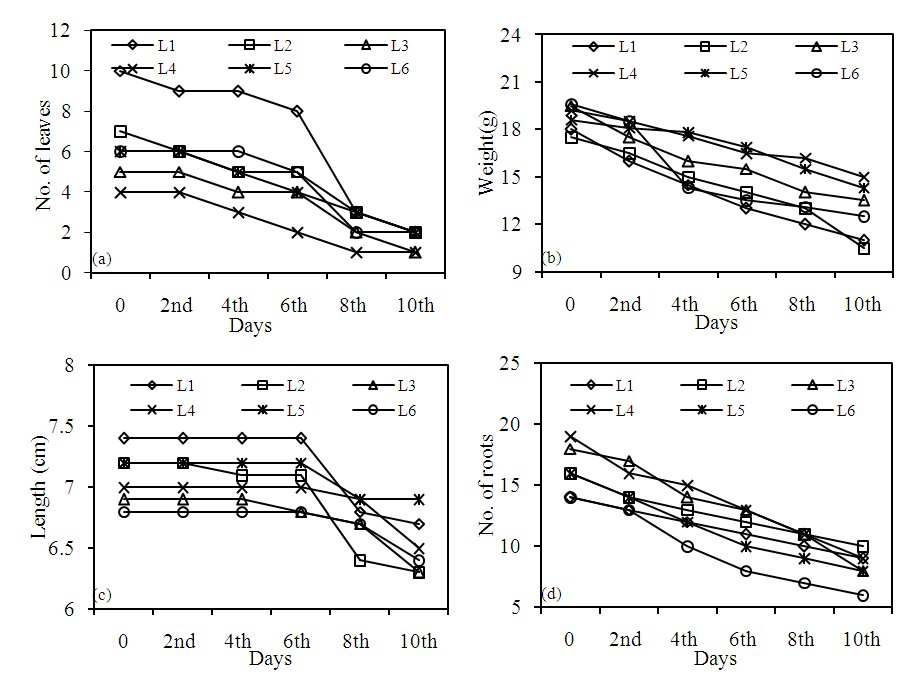 | Figure 2. Variation in (a) Number of Leaves, (b) Plant weight, (c) Length of principal root and (d) number of roots of water hyacinth in groundwater quality of Anantapur |
3.1.2. Water Lettuce
- Graphs of various morphological parameters of water lettuce were plotted with time (Fig. 3). It was found that growth decreased as the time increased. All the plant leaves for all locations are almost in dying condition at the end of 10 days. Since TDS and EC are proportional to each other therefore, increase in EC might have reduced the plant weight and leaf number of lettuce (Miceli et al., 2003). Reduction in weights of lettuce was also observed by Serio et al. (2001) due to increase in EC concentrations. This might have also reduced leaf numbers (Stanghellini et al., 1996; Serio et al., 2001), roots and plant height. Thus, concentrations and time influences the growth. Suppression of leaf expansion was observed as one of the morphological and physiological effects of salinity by Nieman (1964). Significant reduction in leaf area by high water salinity was also reported by Pascale et al. (1997). Chlorotic leaf margins, which indicated salinity stress, were visually observed in the high salinity treatments (Lu, 2009).
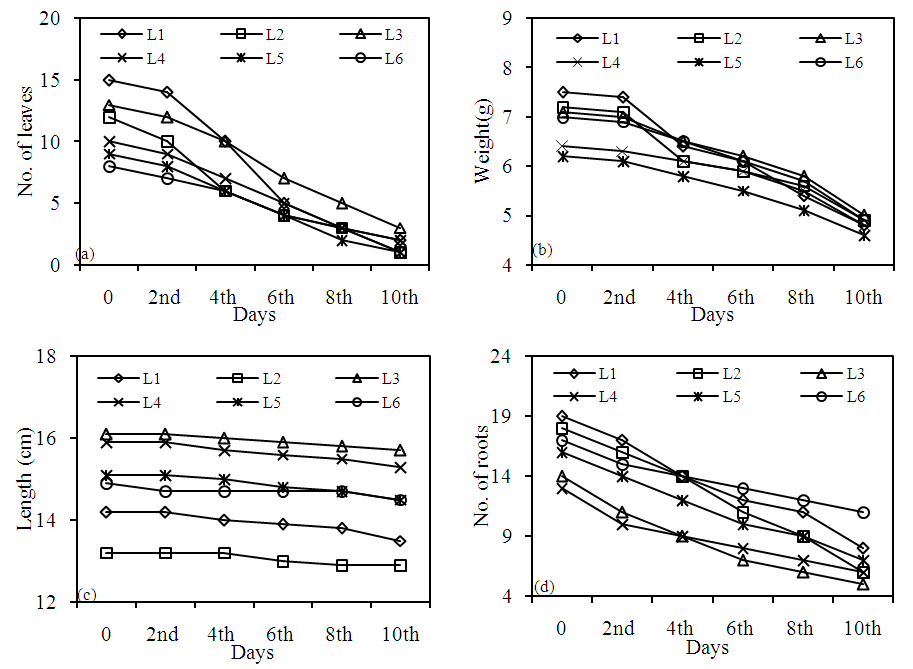 | Figure 3. Variation in (a) Number of Leaves, (b) Plant weight, (c) Length of principal root and (d) number of roots of water lettuce in groundwater quality of Anantapur |
3.1.3. Effect on Morphological Characteristics
- Both water hyacinth and water lettuce showed decrease in bio mass yield and death of the plant was evident after 10th day and certain other changes like yellowing of leaves, decrease in surface area of the leaves were also found. Histochemical analysis through microscope showed that the vascular bundles in the plant tissue are highly affected by high TDS. The presence of high TDS in the root zone of the plants stunts the growth of the plants.
3.2. Treatment Efficiency of Different Plant Species for the Groundwater of Anantapur
- Many researchers (Ayyasamy et al., 2009; Dipu et al., 2011; Borges et al., 2008; Shah et al., 2010) used the removal efficiency technique to know the plant uptake capability of water quality parameters. In this study, to determine the reduction in water quality parameters due to growth of the plant species, the following removal efficiency formula was used for each plant species.Removal efficiency (%) = (Ci – Ce) / Ci x 100where Ci and Ce are the initial and final constituents of pollutants.For all the tested water quality parameters, controlled structure was also plotted under same condition. The removal efficiency under controlled structure was ranged between 5-10% in all the parameters and hence showed the lowest removal efficiency. To get the actual removal efficiency by using different plant species the represented value of removal efficiency of plants is after deduction of controlled removal efficiency for various parameters.The growth status of different plant species in groundwater of Anantapur is dealt in preceding section. The removal efficiency for water quality parameters like pH, EC, TDS, total hardness, salinity, Alkalinity, Acidity, COD and DO was determined by using these plant species after 10 days for different locations.
3.2.1. pH
- pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration of a solution, solutions with a high concentration of hydrogen ion have a low pH and solution with a low concentration of hydrogen ions have a high pH. pH and hardness, play an important role in the concentrations of heavy metals of a given ecosystem.The removal efficiency for different locations by using plant species are shown in (Figure 4). The highest removal efficiency is observed at location L6 with 18.2% using of water hyacinth compared to water lettuce with 15.022% removal efficiency. The root of water hyacinth acts like having substrate for attached microorganisms which provide a significant degree of treatment thanks to their metabolism (USEPA, 1988). Water hyacinth showed the highest reduction capability for pH compared to water lettuce at different locations. According to (Dar et al., 2011) the pH absorption capacity is different for different types of plants. In addition, variation in the reduction of pH at different locations might be due to absorption of nutrients and other salts by plants or by the simultaneous release of H+ ions with the uptake of metal ions (Mahmood et al., 2005). The decline in the growth rate of the total weight of the water hyacinth on condition perilously close to neutral pH, may be caused by the decreasing availability of nutrients. Other studies have reported that more efficient absorption of nutrients in the young water hyacinth compared to the old, hence regular harvest old plant is very important (Ayyasamy et al., 2009).
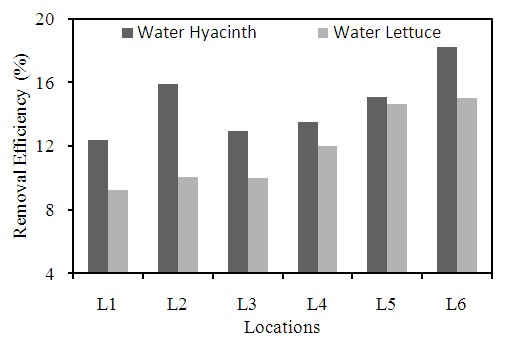 | Figure 4. Removal efficiency of different plants for pH at different locations |
3.2.2. Electrical Conductivity
- Electrical conductivity is defined as the measures the number of ions in a solution (Gupta and Roy, 2012). It exceeded the Standard of UPSH at all locations indicating high salinity in ground water. This is might be due to reduction of EC in water could be attributed to the adsorption of pollutants by the test plants (Dipu et al., 2011 and Mahmood et al., 2005). Often groundwater has higher EC compared to surface water. Excess values lead to scaling in boilers, corrosion and quality degradation of the product. The plant species reduced the EC concentrations at the different locations are shown in (Figure 5). The highest reduction was observed at location L2 with 66.57% removal efficiency by the water hyacinth compared to water lettuce. Similar results were observed by many researchers (Borges et al., 2008; Dhote and Dixit, 2007; Mahmood et al., 2005).
 | Figure 5. Removal efficiency of different plants for EC at different locations |
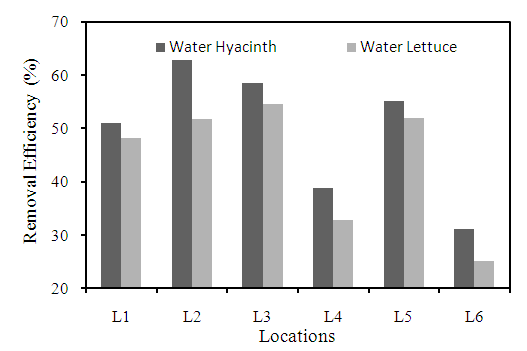
3.2.3. Total Dissolved Solids
- TDS mainly consists of inorganic salts such as carbonates, bicarbonates, chlorides, sulphates, phosphates and nitrates of calcium, sodium, iron etc. High TDS was recorded in all locations. The presence of high TDS will normally affect all the treatment process and removal of TDS is tedious under biological treatment system. The removal efficiency of different plant species in ground water of Anantapur is shown in Figure 6. The highest reduction of TDS was observed by water hyacinth at L3 location with 62.5% and the lowest removal efficiency by water lettuce at location L6 is 36.7%. Water hyacinth showed high TDS removal efficiency compared to water lettuce. This higher removal of solids could be attributed to the property particle sedimentation by the test plant (Gupta et al., 2015) or the ability of the root plant to retain coarse and fine particle and organic materials present in ground water. Decrease in TDS will lead to increase in pH and decrease in electrical conductivity. Controlled plots also showed TDS reductions with respect to time at the locations. Different researchers used water hyacinth for the treatment of various types of wastewater and observed considerable the amount of TDS reduction (Borges et al., 2008; Gamage and Yapa, 2001; Trivedy and Pattanshetty, 2002). Researchers also found reduction in TDS using water lettuce (Awuah et al., 2004; Fonkou et al., 2002) for the different types of effluents. As per drinking water standard (BIS, 1991), permissible limit of TDS is 500 mg/l. It was observed that water hyacinth can bring the TDS level within the norms. It was found that at the end of 10 days, the removal efficiencies varied from 36% to 65%, after that plants started dying. Therefore, it is suggested that to increase the removal efficiency some new plants can be added up in the treatment system to achieve the desired TDS concentration.
 | Figure 6. Removal efficiency of different plants for TDS at different locations |
3.2.4. Total Hardness
- Total hardness in water is due to the natural accumulation of salts from contact with soil and geological formations or it may enter from direct pollution by industrial effluents. Total hardness of water mainly depends upon the amount of calcium or magnesium salts or both. The total hardness of water varies from location to location. Hard water is high in dissolved minerals, both calcium and magnesium. The plants such as water hyacinth and water lettuce have reduced the total hardness concentrations at all the locations as shown in figure 7. The highest removal efficiency is observed at location L5 with 69.9% by using of water hyacinth. The lowest removal efficiency is indicated by water lettuce 39.6% at location L4.The hard water can cause indigestion problem and possibilities of forming calcium oxalate crystals in urinary tracks (Muthulakshmi et al., 2010).
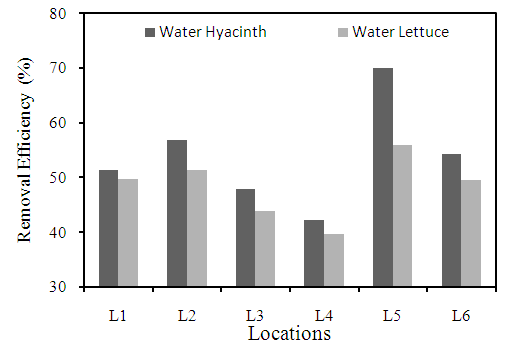 | Figure 7. Removal efficiency of different plants for total hardness at different locations |
3.2.5. Salinity
- Salinity is the measure of all the salts dissolved in water. The different plant species has reduced the salinity concentrations at all the locations (Figure 8). The maximum removal efficiency observed at location L3 is 66.4% by water hyacinth among all locations. The removal efficiency by water hyacinth varied from 55% to 67% whereas in water lettuce it was 41% to 61% at different locations. It can be clearly observed that water hyacinth has higher removal efficiency compared to water lettuce.
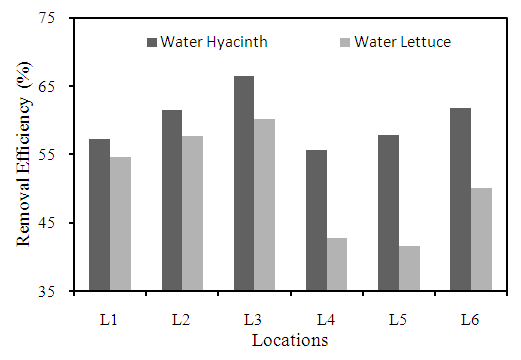 | Figure 8. Removal efficiency of different plants for salinity at different locations |
3.2.6. Acidity
- It is the measure of the ability of water to neutralize base (HCO3-, CO32-, and OH-). Carbon dioxide acidity is due to presence of free carbon dioxide in ground water. In this study, the higher removal efficiency was observed at location L1 & L5 with 63.5% by using of water hyacinth and the lowest by water lettuce with 42.4% at locations L3 & L4 compared to all locations (Figure 9). Drainage from abandoned mines having iron pyrites poses acidity in groundwater (Sawyer and McCarty, 1978).
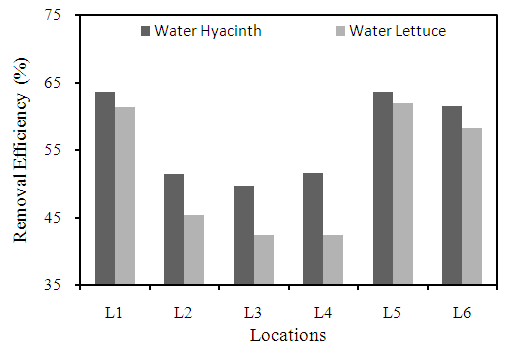 | Figure 9. Removal efficiency of different plants for acidity at different locations |
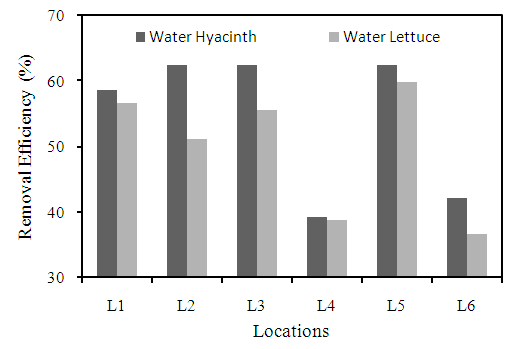
3.2.7. Alkalinity
- It is the measure of the ability of water to neutralize acids. It is due to the presence of bicarbonates, carbonates, hydroxide of calcium, magnesium or salts of weak acids and strong bases as borates, silicates, phosphates (Kotaiah and Swamy, 1994). The higher removal efficiency was observed at location L2 with 66.2% by using water hyacinth and for water lettuce 63.1% compared to other locations (Figure 10). Large amount of alkalinity imparts a bitter taste, harmful for irrigation as it damages soil and hence reduces crop yields (Sundar and Saseetharan, 2008).
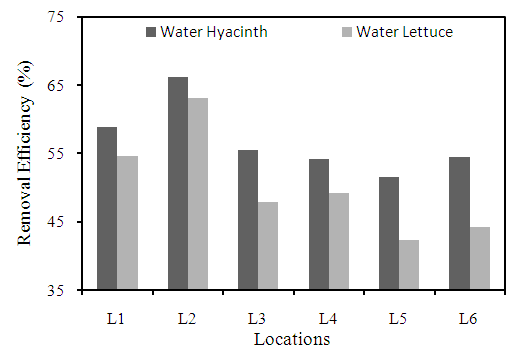 | Figure 10. Removal efficiency of different plants for alkalinity at different locations |
3.2.8. Dissolved Oxygen
- DO refer to microscopic bubbles of gaseous oxygen (O2) that are mixed in water and available to aquatic organisms for respiration. Aquatic plants release oxygen into the water as a by-product of photosynthesis. The level of DO in any water shows conditions of pollution level. The water hyacinth increased the DO level in all water samples at different locations. It showed an increase of the removal efficiency was 66.4% for water hyacinth and 64.4% for water lettuce at location L6 compared to all locations (Figure 11). Dar et al. (2011) and Shah et al. (2010) also observe increase on DO level whereas Mangas-Ramirez and Elias-Gutierrez (2004), Perna and Burrow (2005) found lower DO concentration beneath the test plant mats. The water hyacinth has higher reduction capacity compared to water lettuce.
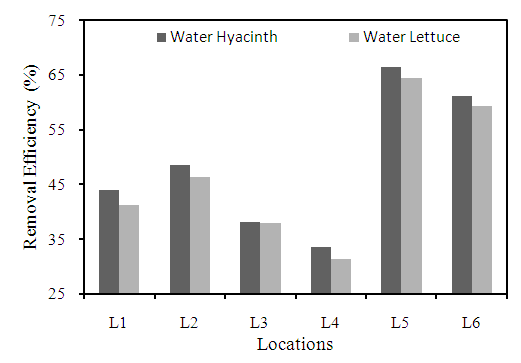 | Figure 11. Removal efficiency of different plants for DO at different locations |
3.2.9. Chemical Oxygen Demand
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is an indicative measure of the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by reactions in a measured solution. By using different plant species, the highest COD removal efficiency was recorded at location L6, it was 61.4% by water hyacinth and 58.7% by water lettuce (Figure 12). This high reduction in COD is attributed to the reduction in pH which on turn favours microbial action to degrade COD as stated by Reddy (1981), Al-Saadi et al. (1995), Mahmood et al. (2005), Borges et al. (2008).
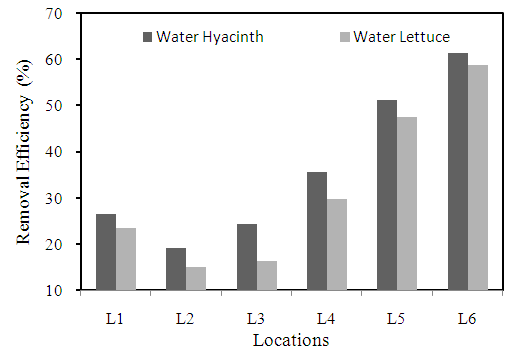 | Figure 12. Removal efficiency of different plants for COD at different locations |
4. Conclusions
- Water is indispensable not only for the existence of the mankind but also for human development and healthy functioning of eco-system. Higher values of certain parameters of groundwater indicate the unfitness of water for drinking purpose. The CW system studied here proved to be effective in treating groundwater, mainly the system containing aquatic plants with achieving maximum efficiency for most of the parameters studied, although at different retention times. Results suggest that both macrophytes can be effectively used for the removal of TDS ranging from 2600-4500 mg/L. Further the biological masses obtained after treatment can be used as manure for plant growth. These plants will also show higher efficiency in removal of EC, Salinity, COD, Total hardness proving that phytoremediation with floating aquatic macrophytes will be a promising technique in groundwater treatment.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML