| [1] | Abdul-Wahab, S. A., Bakheit, C. S., & Al-Alawi, S. M. (2005). Principal component and multiple regression analysis in modeling of ground-level ozone and factors affecting its concentrations. Environmental Modelling and Software, 20, 1263–1271. |
| [2] | Ho, W.C., Hartley, W.R., Myers, L., Lin, M.H., Lin, Y.S., Lien, C.H. and Lin, R.S. (2007). Air Pollution, Weather, and Associated Risk Factors Related to Asthma Prevalence and Attack Rate. Environ. Res. 104: 402–409. |
| [3] | Karakatsani, A., Kapitsimadis, F., Pipikou, M., Chalbot, M.C., Kavouras, I.G., Orphanidou, S. D., Papiris, S. and Katsouyanni, K. (2010). Ambient Air Pollution and Respiratory Health in Mail Carriers. Environ. Res. 110: 278–285. |
| [4] | Neidell, M. and Kinney, P.L. (2010). Estimates of the Association between Ozone and Asthma Hospitalizations that Account for Behavioral Responses to Air Quality Information. Environ. Sci. Policy 13: 97–103. |
| [5] | Mills, G., Hayes, F., Simpson, D., Emberson, L., Norris, D. Harmens, H. and Buker, P. (2011). Evidence of Widespread Effects of Ozone on Crops and (Semi-) Natural Vegetation in Europe (1990-2006) in Relation to AOT40-and Flux-Based Risk Maps. Global Change Biol.17: 592–613. |
| [6] | Huang, H.L., Lee, M.G. and Tai, J.H. (2012). Controlling Indoor Bioaerosols Using a Hybrid System of Ozone and Catalysts. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 12: 73–82. |
| [7] | Fuhrer, J., Skarby, L. and Ashmore, M.R. (1997). Critical Levels for Ozone Effects on Vegetation in Europe. Environ. Pollut. 97: 91–106. |
| [8] | Song, F., Shin, J.Y., Atresino, R.J. and Gao, Y. (2011). Relationships among the Springtime Ground-Level NOx, O3 and NO2 in the Vicinity of Highways in the US East Coast. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2: 374–383. |
| [9] | Chelani, A.B. (2012). Study of Extreme CO, NO2 and O3 Concentrations at Traffic Site in Delhi: Statistical Persistence Analysis and Source Identification. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 13: 377–384. |
| [10] | Sharma, U.K., Kajii Y. and Akimoto, H. (2000). Characterization of NMHCs in Downtown Urban Center Kathmandu and Rural Site Nagarkot in Nepal. Atmos.Environ. 34: 3297–3307. |
| [11] | Atkinson, R. (1997). Gas-phase Troposphere Chemistry of Volatile Organic Compounds: 1. Alkanes and Alkenes. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 26: 215–290. |
| [12] | Atkinson, R. (2000). Atmospheric Chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 34: 2063–2101. |
| [13] | Tang, J.H., Chan, L.Y., Chan, C.Y., Li, Y.S., Chang, C.C., Liu, S.C., Wu, D. and Li, Y.D. (2007). Characteristics and Diurnal Variations of NMHCs at Urban, Suburban, and Rural Sites in the Pearl River Delta and a Remote Site in South China. Atmos. Environ. 41: 8620–8632. |
| [14] | Tang, W.Y., Zhao, C.S., Geng, F.H., Peng, L., Zhou, G.Q., Gao, W., Xu, J.M. and Tie, X.X. (2008). Study of Ozone “Weekend Effect” in Shanghai. Sci. China, Ser. D Earth Sci. 51: 1354–1360. |
| [15] | Davidson A. (1993). Update on ozone trend in California's south coast air basin. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 1993; 43: 226–7. |
| [16] | Wakamatsu S, Ohara T, Uno I (1996). Recent trends in precursor concentrations and oxidant distribution in the Tokyo and Osaka areas. Atmos Environ 1996; 30: 715–21. |
| [17] | Duenas C, Fernandez MC, Canete S, Carretero J, Liger E (2004). Analyses of ozone in urban and rural sites in Malaga (Spain). Chemosphere; 56: 631–9. |
| [18] | Elminir HK (2005). Dependence of urban air pollutants on meteorology. Sci Total Environ; 350: 225–37. |
| [19] | Camalier L, Cox W, Dolwick P (2007). The effects of meteorology on ozone in urban areas and their use in assessing ozone trends. Atmos Environ; 41: 7127–37. |
| [20] | Carvalho A, Monteiro A, Ribeiro I, Tchepel O, Miranda AI, Borrego C, et al (2010). High ozone levels in the northeast of Portugal: analysis and characterization. Atmos Environ.; 44: 1020–31. |
| [21] | Garcia MA, Sanches ML, Perez IA, Torre B (2005). Ground level O3 mixing ratios at a rural location in northern Spain. Sci Total Environ; 348:135–50. |
| [22] | Nishanth M. K, Satheesh Kumar and. Valsaraj T.K (2012). Variations in surface ozone and NOx at Kannur: a tropical, coastal site in India, J Atmos Chem 69:101–126. |
| [23] | Kassem. Kh.O, Elshazly S. M, Masaaki Takahashi, El-Nouby adam M, Hassan. A A and Emad. A.A (2010). Diurnal and seasonal variations of surface ozone in Cairo and Alexandria, Egypt. |
| [24] | El-Hussainy, F.M., Sharobiem, W. M., Ahmed, M. D., (2003) Surface ozone observations over Egypt. Quarterly Journal of Hungarian Meteorological service. Vol, 107, No.2 April-June, pp.133-152. |
| [25] | Shampa Sarkar (2015) Seasonal Monitoring of Ozone Concentration and its Correlation with Temperature and Relative Humidity. Int. Res. J. Environment Sci. Vol. 4(7), 81-85. |
| [26] | Hesham A. Al-Jeelani (2014). Diurnal and Seasonal Variations of Surface Ozone and Its Precursors in the Atmosphere of Yanbu, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Environmental Protection, 5, 408-422. |
| [27] | M. I. Khoder. M. I (2009) Diurnal, seasonal and weekdays–weekends variations of ground level ozone concentrations in an urban area in greater Cairo, Environ Monit Assess, 149:349–362. |
| [28] | Abdul-Wahab, S.A., Al-Alawi, S.M., 2002. Assessment and prediction of tropospheric ozone concentration levels using artificial neural networks. Environmental Modelling and Software 17, 219–228. |
| [29] | Abdul-Wahab, S.A., Bouhamra, W., Ettouney, H., Sowerby, B., Crittenden, B.D., 1996. A statistical model for predicting ozone levels in the Shuaiba Industrial Area in Kuwait. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 3, 195–204. |
| [30] | Abdul-Wahab, S.A., Bouhamra, W., Ettouney, H., Sowerby, B., Crittenden, B.D., 2000. Analysis of air pollution at Shuaiba Industrial Area in Kuwait. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry 78, 213–232. |
| [31] | Jun, T., Xia, Z., Wang, H. and Li, W. (2007) Temporal Variations in Surface Ozone and Its Precursors and Meteorological Effects at an Urban Site in China. Atmospheric Research, 85, 310-337. |
| [32] | Dueñas, C., Fernández, M.C., Cañete, S., Carretero, J. and Liger, E. (2002) Assessment of Ozone Variations and Meteorological Effects in an Urban Area in the Mediterranean Coast. Science of the Total Environment, 299, 97-113. |
| [33] | Lehman, J., Swinton, K., Bortnick, S., Hamilton, C., Baldridge, E., Eder, B. and Cox, B. (2004) Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Tropospheric Ozone across the Eastern United States. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 4357-4369. |
| [34] | Satsangi, G.S., Lakhani, A., Kulshrestha, P.R. and Taneja, A. (2004) Seasonal and Diurnal Variation of Surface Ozone and a Preliminary Analysis of Exceedance of Its Critical Levels at a Semi-Arid Site in India. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 47, 271-286. |
| [35] | Saito, S., Nagao, I. and Kanzawa, H. (2009) Characteristics of Ambient C2-C11 Non-Methane Hydrocarbons in Metropolitan Nagoya, Japan. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 4384-4395. |
| [36] | Zhang, B.N. and Oanh, N.T.K. (2002) Photochemical Smog Pollution in the Bangkok Metropolitan Region of Thailand in Relation to O3 Precursor Concentrations and Meteorological Conditions. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 4211-4222. |
| [37] | Negar Banan, Mohd Talib Latif, Liew Juneng, Fatimah Ahamad (2013): Characteristics of Surface Ozone oncentrations at Stations with Different Backgrounds in the Malaysian Peninsula. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 13: 1090–1106. |
| [38] | T. Nishanth & M. K. Satheesh Kumar & K. T. Valsaraj Variations in surface ozone and NOx at Kannur: a tropical, coastal site in India. J Atmos Chem (2012) 69:101–126. |
| [39] | Topcu S, Incecik S. Surface ozone measurements and meteorological influences in the urban atmosphere of Istanbul. Int J Environ Pollut 2002; 17: 390–404. |
| [40] | Topcu S, Incecik S. Characteristics of surface ozone concentrations in urban atmosphere of Istanbul: a case study. Fresenius Environ Bull 2003; 12: 413–7. |
| [41] | Im U, Tayanç M, Yenigun O. Interaction patterns of major photochemical pollutants in Istanbul, Turkey. Atmos Res 2008; 89: 382–90. |



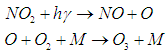
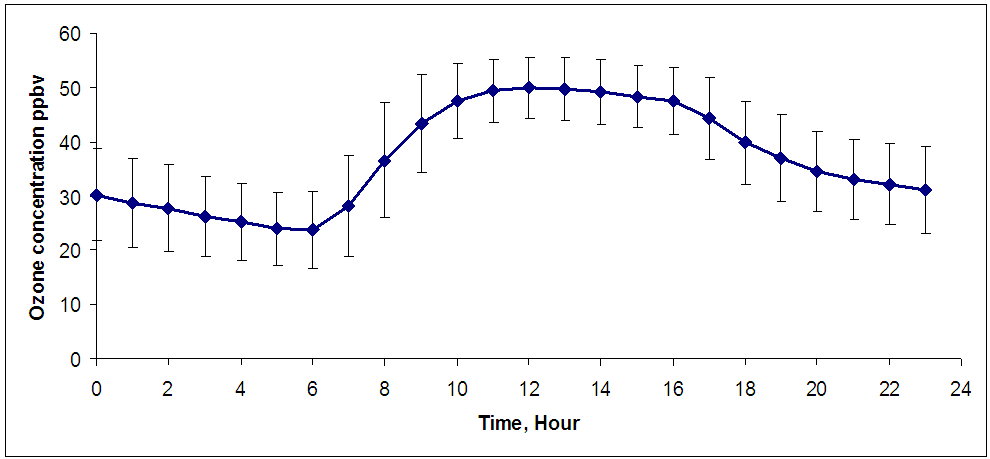
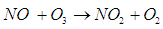
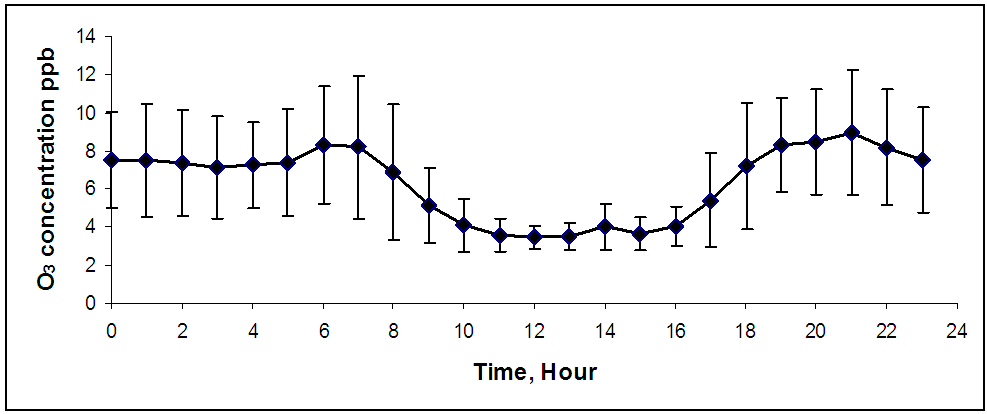
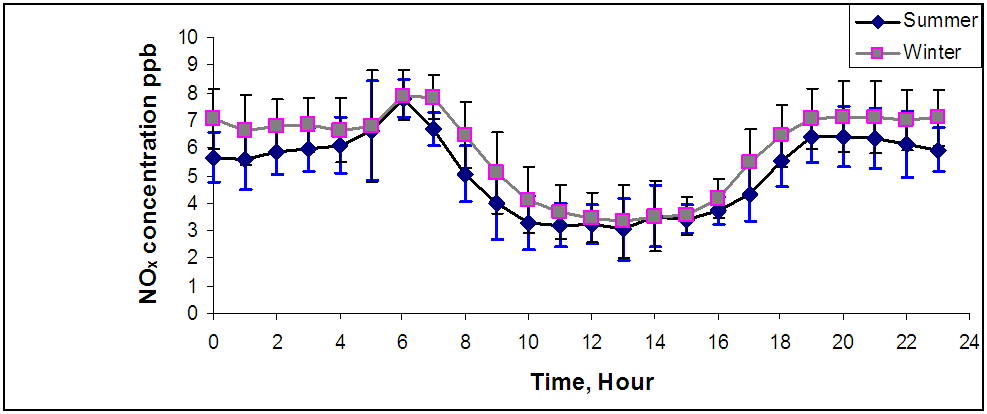
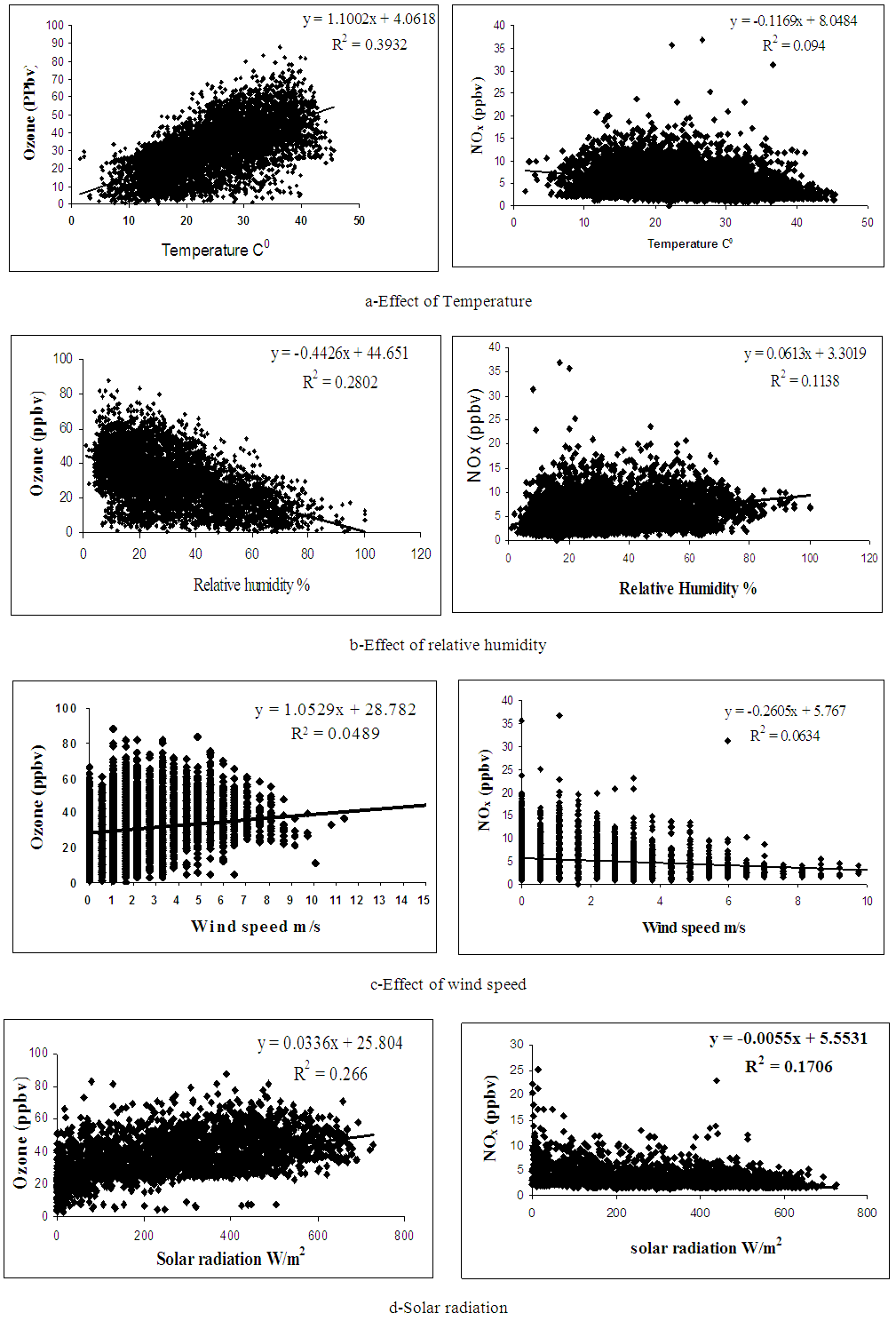
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML