-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
World Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-1573 e-ISSN: 2163-1581
2015; 5(3): 101-111
doi:10.5923/j.env.20150503.02
Suitability Analysis of Resettlement Sites for Flood Disaster Victims in Lokoja and Environs
Isa Ibrahim1, Kolawole H. Muibi1, Abayomi T. Alaga1, Oyekanmi Babatimehin2, Olusola Ige-Olumide3, Oloko-Oba O. Mustapha1, Sedenu A. Hafeez1
1Cooperative Information Network, National Space Research and Development Agency, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria
2Department of Geography, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria
3Institute of Ecology Obafemi Awolowo Universty, Ile-ife, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Isa Ibrahim, Cooperative Information Network, National Space Research and Development Agency, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
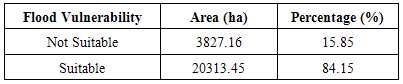
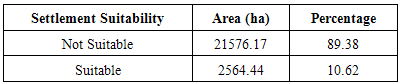
The purpose of this study is to identify suitable sites for resettlement of flood disaster victims in Lokoja environs using Remote Sensing and GIS. The bio-physical and socio-economic factors used for evaluation of environmental suitability of the resettlement site are land use/land cover, slope, elevation and nearness to road. Land use/land cover information were extracted from NigeriaSat1 image of 2007, contours and drainage information were extracted from Sheet 246 & 247 of the Nigeria Topographic Map Series of 1963 while road networks were extracted from the Geo-Eye images. By analyzing the information extracted, weights were assigned to the information based on their suitability for human settlement. Weighted overlay techniques were then applied to derive a flood resettlement suitability map. The individual analysis of these factors indicated that 82.78% of the study area has a gentle slope (lowland) while 17.22% of the area is found to be highland which is hilly and steepy. In terms of land use/land cover, 75.15% of the study area is suitable such as forest and rock outcrop while 24.85% representing built-up, water body, sand deposits and wetland are not suitable and cannot be recommended for settlement. The result showed that about ¾ of the study area is not suitable for human resettlement while a minimal 10.62% is suitable having an area of 2564.44ha with 5 locations (4.14%) out of the suitable sites having a continuous area of more than 100ha. Therefore before planning and implementing any resettlement program, environmental suitability, ecological carrying capacity and sustainability of the area has to be analyzed thoroughly.
Keywords: Resettlement, Flood Disaster, GIS and Remote Sensing, Weighted Overlay
Cite this paper: Isa Ibrahim, Kolawole H. Muibi, Abayomi T. Alaga, Oyekanmi Babatimehin, Olusola Ige-Olumide, Oloko-Oba O. Mustapha, Sedenu A. Hafeez, Suitability Analysis of Resettlement Sites for Flood Disaster Victims in Lokoja and Environs, World Environment, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 101-111. doi: 10.5923/j.env.20150503.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Resettlement is a process whereby a community’s housing, assets, and public infrastructure are rebuilt in another location [1]. Relocation of settlement is sometimes perceived to be the best option after a disaster for one or more of the following reasons: first, people have already been displaced by the disaster, second, their current location is judged to be uninhabitable, and third, it may be considered the best option to reduce vulnerability to the risk of future disasters. Settlement relocation may be appropriate when the vulnerability of the disaster is site-specific. Informal settlements in urban areas, for instance, are often located on sites where topography makes the site’s vulnerabilities impossible to mitigate. Not all risks are site-specific and relocation itself entails numerous risks. Assessing adequate sites for relocating disaster-affected communities can be an enormous challenge. Unsuitable new sites can lead to loss of livelihoods, one’s own community, cultural alienation and create further poverty which makes many people to abandon the new sites and return to the location of their original community. The economic, social, and environmental costs of relocation should be carefully assessed before the decision to relocate is finalized, and other mitigation options should be considered. Human settlements are foci for many economic, social, and governmental processes. The government has taken resettlement program as the best strategy to address the multi-faceted socio-economic and food security problems in areas where there is high population density and severe ecological degradation. In a country like Nigeria, where the majority of the people are agrarian and directly depend on the natural environment for their livelihood, environmental suitability analysis is necessary for settling people in a new resettlement site. In kogi state, Lokoja environs is one of the areas resettled by people originated from the neighborhood states like Niger, Nasarawa and Benue states. Currently, the area is inhabited by 150,000 residents. The criteria used by Nigeria Government to identify site for resettlement was simply based on the existence of vacant space with productive virgin agricultural land. In rural areas, settlements in flood zones have vulnerabilities that may also be impossible to address [1]. Studies show that, the worst floods in over 50 years hit south and central Mozambique in early 2000. The enormous amount of rainfall, dumped by three consecutive cyclones, affected around 4.5 million people, which is one-quarter of the country’s population. The floods displaced 400,000 people, and caused at least 700 fatalities [7]. In 2001, the central provinces faced flooding again, this time, affecting 554,000 people (including 220,000 displaced persons), and resulting in 113 deaths as reported by Government of Mozambique in 2001. Two years later, in early 2003, the country faced both a drought and a flood: while struggling with a severe drought in the central and southern parts of the country, the northern provinces of Zambezia and Nampula had 100,000 flood-affected people [24].However, Nigeria also has her share of flood events which has taken a toll on lives and properties. A lot of research has been carried out to ascertain the causes of flooding and different reasons have been identified, such include: dumping of refuse over the years which has led to the filling up of ponds and blockages of other natural water ways or drainages; high intensity rainfall coupled with a gentle slope for water accumulation; dam failure coupled with almost bare surface; rapid rate of unplanned settlement leading to poor drainage system among many others. The spatial distribution of risks as well as the benefits of flood mitigation measures is rarely considered. Therefore, it is often unknown which area benefit most from a measure and which areas do not. In August 2011 and July 2013 flooding in Ibadan has claimed lives and properties. A close look at this historical update shows that flooding and flood management has become one of the issues to contend with in this ancient city. This underscores the need for this study so as to find a reasonable solution, prevention and mitigation strategy for this menace. The multi-criteria flood risk/vulnerability mapping approach will show the spatial distribution of the different risk criteria. However, a holistic view of the contributing factors to flood will be desirable, in as much as flood cannot be eradicated but the impact can be minimized.In northern India, Bangladesh and Nepal, almost 20 million people have been displaced from some of the worst floods that have hit a wide swath of these areas in 2007. Roads were washed away and hundreds of villages were cut off by swollen rivers. In Bangladesh thousands of families are on the move in search of higher ground. Hundreds of thousands of people across the affected area are at risk from hunger and disease. In India, 125 people were killed and 12 million stranded, mostly in Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Assam [5].In Nigeria, the pattern is similar with the rest of the world. Flooding in various parts of Nigeria have forced millions of people from their homes, destroyed businesses, polluted water resources and increased the risk of diseases [11]. Settlements along the river course are prone to flooding due to increase in the river discharge. In the last three decades in Nigeria, the impacts of flooding have increasingly assumed from significant to threatening proportions, resulting in loss of lives and properties. Flash floods from torrential rains washed away thousands of hectares of farmland. Dam bursts are common following such flood. In August 1988 for instance, 142 people died, 18,000 houses were destroyed and 14,000 farms were swept away when the Bagauda Dam in kano collapsed following a flash flood. Urban flooding such as the Ogunpa disaster which claimed over 200 lives and damaged property worth millions of Naira in Ibadan, is also one popular flood event in Nigeria. Though detailed statistics are not available regarding the losses sustained by the urban dwellers and flood victims, it is obvious from the available records that irreparable havocs were sustained by the citizen of Nigeria due to what has become perennial natural disaster in our cities. Apart from residential houses that collapsed as a result of flooding, schools, buildings and bridges sometimes collapse as well. Markets places and farmlands were submerged for weeks and sometimes washed away [11].However, resettlement remains one of the major solutions to areas with persistent flood disaster. This resettlement otherwise known as settlement relocation is laden with some benefits and challenges. The benefits include undertaking of job that are difficult to fill, adding of diversity to the community, job creation through refugee-owned businesses and public services developed to assist refugees, such as transit programmes etc. The challenges include communication barriers due to cultural and language difference, poverty and ignorance of the social norms and laws of the new location. Also resettlement is highly complex, because it requires rigorous application of social, agricultural as well as physical planning principles.In assessing the suitability of sites put forward for housing purposes, it is important to ensure that each site is assessed in a consistent manner, using a clear and robust methodology. In order to achieve this all sites put forward for consideration were systematically evaluated using the scoring system. The assessment criteria measured the suitability of sites across four key characteristics. Firstly, how well the site fitted the spatial strategy, secondly site the suitability of its location, landscape sensitivity, and finally site use [17].A growing emphasis on environmental quality has prompted many counties to adopt legislation and guidelines that will ensure the consideration of the natural environment in land-use planning and site selection processes. This has resulted in considerable research and development of models that can support the location planning and decision-making processes. In most cases these models are based on the analysis of interaction between three sets of mutually related factors, namely, locations, development actions and environmental effects. This approach usually considers a comprehensive set of factors in determining vulnerability of flood for various development activities and vice versa. Therefore, its effective use requires not only a flexible system capable of storing, manipulating and transforming a large volume of spatially oriented data into usable information, but also a mechanism for analyzing relations and applying criteria related to environmental quality in land use planning and site selection process [33].
1.1. Statement of the Research Problem
- Lokoja is located at the confluence of the main Niger River and the Benue River in central Nigeria. The communities along the banks of the river cultivate in the floodplain and surrounding land and also do some fishing. The farmers in Lokoja and environs are affected by regular floods, which in some years caused considerable damage to their crops and houses. Erosion of the river banks is also a significant problem to these communities. Predictive Modelling of Floods in Nigeria using Cellular Automaton Evolutionary Slope and River Model (CAESAR) has also been carried out; a predictive model was applied to predict flood inundation extents in three different zones (Adamawa, Ibadan and Kogi State) in Nigeria [27]. The results were validated with actual flood extent measurements to determine if the natural floodplain was actually exceeded. Another study was carried out on vulnerability mapping and resettlement for Baratang Island, Andaman, India [3]. They considered seven parameters such as elevation, geology, geomorphology, sea level trends, horizontal shoreline displacement, tidal ranges and wave heights to demarcate the vulnerability line all along the coast. They observed that the tsunami affected areas were within the 0-20 m contour region and suggested that settlements within this region should be moved away. They integrated thematic layers such as land use / land cover, transport, Slope and Disaster prone areas in ArcGIS to suggest sites for resettlement.Application of flood makes management system to establish rehabilitation plan of reducing natural disaster in South Korea. They utilized the height and true elevation of the flood to create flood mark map and flood hazard map to establish rehabilitation plan of reducing natural disaster [14]. Geospatial analysis of flood disaster with a view to determining the flood disaster impacts (physical and economic) on the life and property of the residents of the affected areas in Lokoja was also carried out, but they did not look at settlement relocation for flood victims. Research into resettlement of any type has focused on the direct economic costs and benefits expected from the projects and, to a lesser extent, their environmental and social ramifications [33]. There has been comparatively limited research undertaken on the potentially far-reaching and long-term social impacts of the resettlement processes. In this study area, however, no research work was conducted regarding the suitability of the environment for human settlement. Therefore, there is serious need to determine suitable sites for relocation in case of further severe flood disaster.
1.2. AIM and Objectives
- AIMThe aim of this study is to explore suitable sites for resettlement of flood disaster victims using geospatial techniquesOBJECTIVESBased on the aim, the specific objectives are to:1. Delineate the flood vulnerable zone of the study area;2. Carry out terrain analysis for Lokoja environs; and3. Determine sites suitable for relocation of flood victims.
1.3. Study Area
- The study area, Lokoja lies between latitudes 7°45΄27.56΄΄ and 7°51΄04.34΄΄ N of the equator and longitude 6o41΄55.64΄΄ and 6o45΄36.58΄΄E of the Greenwich Meridian. Lokoja is the administrative headquarters of Kogi State in Nigeria. It is well connected and accessible through state and federal highways. It is also located close to confluence of the River Niger and Benue; the area is sandwiched between a water body and a hill i.e. River Niger and Mount Patti respectively which had streamlined the settlement to a linear one and has a modifying effect on the climate. The annual rainfall in the area is between 1016 mm and 1524 mm with its mean annual temperature not falling below 27°C. The rainy season lasts from April to October when the dry season lasts from November to March. The land rises from about 300 metres along the Niger-Benue confluence, to the heights of between 300 and 600 metres above the sea level in the uplands [23].Lokoja is drained by Niger and Benue rivers and their tributaries. The confluence of the Niger and Benue rivers which could be viewed from the top of Mount Patti is located within the study area.The general relief is undulating and characterized by high hills. The Niger-Benue trough is a Y-shaped lowland area which divides the sub-humid zone into three parts. It has been deeply dissected by erosion into tabular hills separated by river valleys. The flood plains of the Niger and Benue river valleys in Lokoja have the hydromorphic soils which contain a mixture of coarse alluvial and colluvial deposits [3]. The alluvial soils along the valleys of the rivers are sandy, while the adjoining laterite soils are deeply weathered and grey or reddish in colour, sticky and permeable. The soils are generally characterized by a sandy surface horizon overlying a weakly structured clay accumulation.The main vegetation type in Lokoja is Guinea savanna or parkland savanna with tall grasses and some trees. These are green in the rainy season with fresh leaves and tall grasses. The different types of vegetation are not in their natural luxuriant state owing to the careless human use of the forest and the resultant derived deciduous and savanna vegetation. Agriculture serves as the main occupation of the people. However, the status of the Lokoja as an administrative headquarters brought some institutions into the area, which put many people in the public institutions like the Kogi State Polytechnic, Specialist Hospital and other governmental offices.
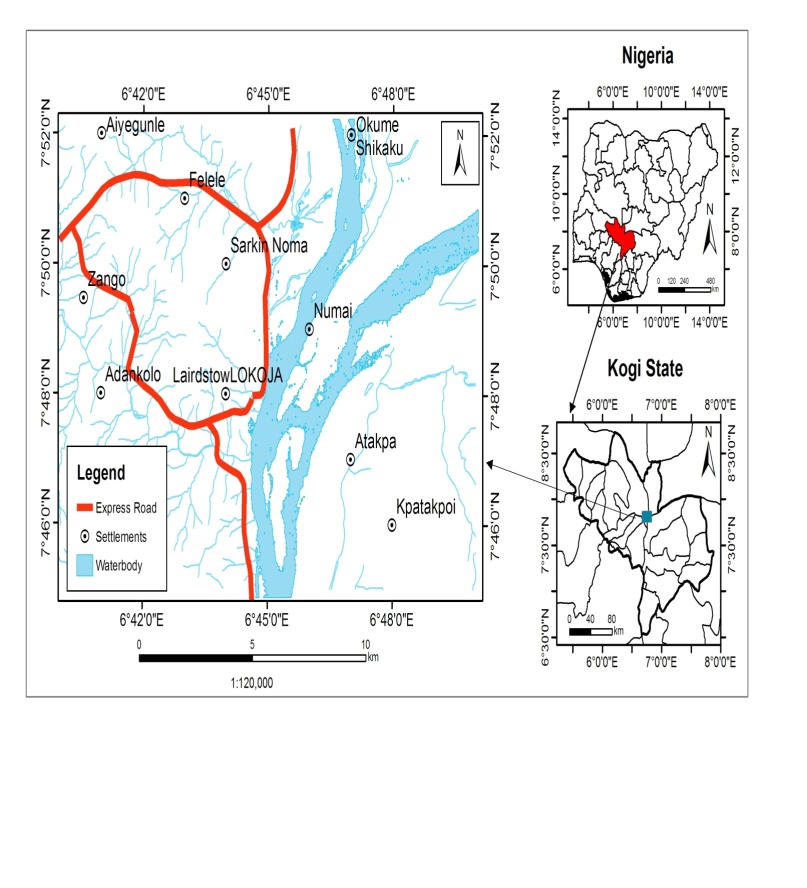 | Figure 1. The Study Area |
2. Materials and Methods
- Geospatial data acquired from both primary and secondary sources were used for the study. The data used include Ground Control Point (GCP), Topographic maps of sheets 246 and 247 of 1963 at scale of 1:50,000, Nigersat-1 satellite image and Geo-Eye satellite image. Lokoja Topographical sheets 246 and 247 of 1963 were imported into the GIS environment for geo-referencing and digitizing to extract the contour and drainages. Roads and building layers were digitized from the Geo-Eye satellite image while the land use/land cover was derived from NigeriaSat_x image by supervised classification technique using maximum likelihood into six land cover types namely built-up, waterbody, rock outcrop, forest, wetland and sand deposit.From the digitized layers, the following thematic maps were derived; Drainage network, Slope, Settlement, Road and Digital Elevation Model. Weighted Overlay Analysis was used to generate flood vulnerability model. In a GIS‐based environmental suitability analysis, there is a need to standardize the data in order to integrate the data measured in different units and mapped in different scale of measurement, such as nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio scales [28]. Therefore, there is need to reclassify the layers of data for suitability factor to common evaluating scale. This process will eventually assure appropriate correlation of suitability factors.There are a number of approaches that can be applied to compare and standardize the attribute of all the layers of spatially referenced data used in this analysis. All the data formats were converted to raster at 30m resolution for criteria standardization and the Reclass Tool in GIS tool box was used to assign codes to the classification. Accordingly, all the factors used for weighted overlay analysis were reclassified into common evaluating scale with the values 1 and 2, where the value of 1 was taken as the suitable while that of 1 was not suitable for all factors considered.However, it is important to note that there were some variables that did not fulfill the whole range of the criteria.The purpose of weighting in environmental suitability analysis in human resettlement site is to express the importance of each suitability factor relative to the other variables. In the procedure for MCE, it is necessary that the weights sum to 1. Accordingly, AHP (Analytical hierarchy process) Script, in GIS environment was used. It applies the pair wise comparison technique to help develop a set of factor weights that will sum to 1.In a pair wise comparison matrix, two factors are compared at a time in terms of their importance related to the stated objective. Weights will finally develop after every possible pairs are compared with each other and the ratings are entered into a pair wise comparison matrix or ratio matrix. The system also calculates a consistency ratio to indicate any inconsistencies that may have been arising during the pairwise comparison process. As the matrix is symmetrical, only the lower triangle actually needs to be filled in. The remaining cells are then simply the reciprocals of the lower triangle. For this purpose discussion was held with experts and careful analysis of evaluation criteria was carried out and a pairwise comparison was made based on the result obtained from the AHP Script. Apart from its capability to generate maps, one of the most important advantages of GIS is its capacity for integration and analysis of spatially referenced multisource datasets [20]. The Weighted Overlay Tool was used to perform the weighted overlay analysis using the results of the AHP Scripts to generate suitability map for resettlement sites.
3. Result and Discussion
- The result of the various parameters examined for flood vulnerability area and suitable sites for resettlement are presented below;
3.1. Flood Vulnerability Assessment
3.1.1. Flood Plain (based on elevation)
- The topography of the area ranges from 100m to 1350m above mean sea level. The area was calculated using the Tabulate Area Tool in GIS Spatial Analyst Toolbox. Flood plains occur in areas less than 150 metres above mean sea level and this area represent 51.52% of the study area, an indication that Lokoja is very prone to flooding while the remaining 48.48% land based on proximity to river channels area is not on flood plains. Figure 2 shows the spatial analysis of areas vulnerable to flood in Lokoja based on elevation.
 | Figure 2. Flood Vulnerability based on elevation |
|
3.1.2. Flood Prone Areas (based on proximity to river channels)
- According to space standard for urban development, second flood plain was classified by creating a 70metres buffer zone around the drainages and classified as Not Suitable. The area was calculated using the Tabulate Area Tool in the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst Toolbox. This classification is about 16% of the total land area.
|
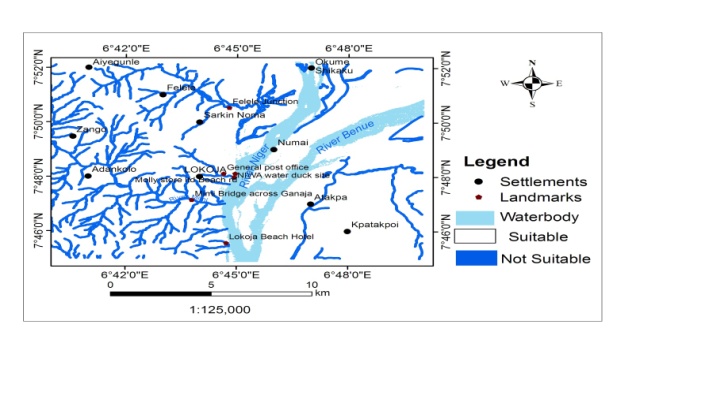 | Figure 3. Suitability based on flood vulnerability (based on proximity to river) |
 | Figure 4. Composite Flood Vulnerability of the Study area |
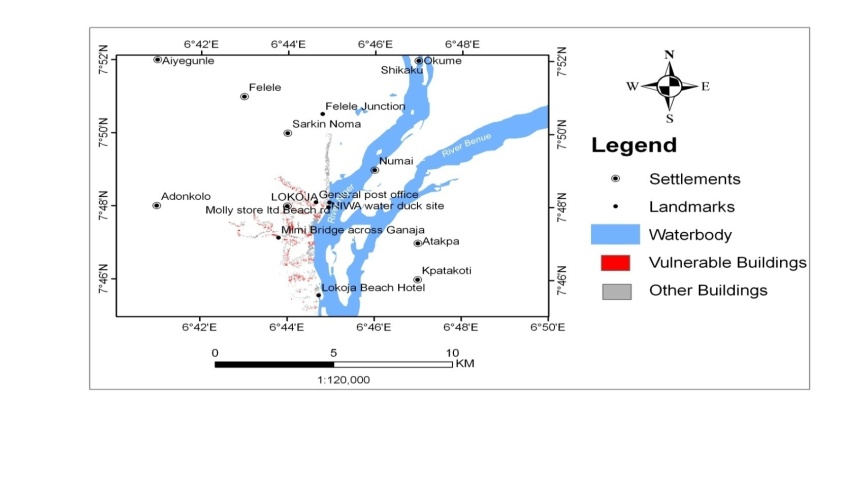 | Figure 5. Number of buildings vulnerable to flood |
3.2. Biophysical Suitability of Lokoja Resettlement Site
- Considering land-use land-cover suitability, it is observed that 75.15% of the area is suitable such as forest and rock outcrop. However, 24.85% representing built-up, waterbody, sand deposits and wetland are not suitable as shown in table 3.
|
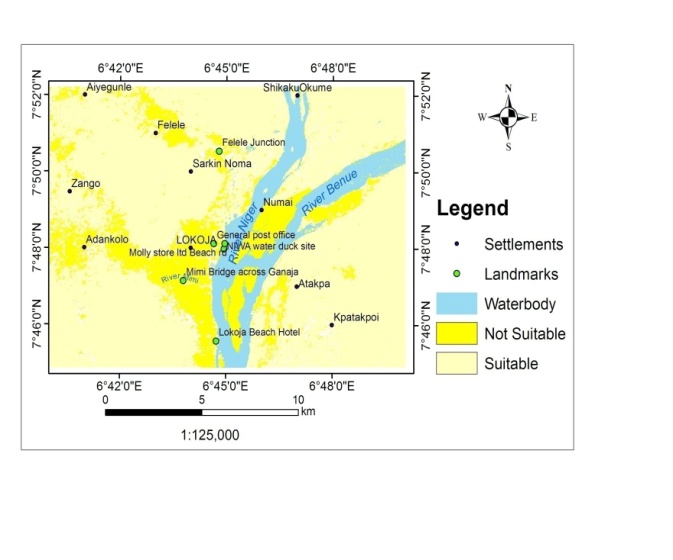 | Figure 6. Land Use Land Cover suitability map |
3.3. Topographic Suitability
3.3.1. Slope
- Result of independent analysis of the topographic factors; indicate that the area has 82.78% suitable slope representing low land while the remaining 17.22% of the area is found to have unsuitable slope. The unsuitable slope is highland, hilly and steepy area of Lokoja.
|
3.3.2. Elevation
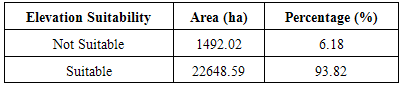
- The elevation suitability shows that 93.82% of the study area is less than 750m above mean sea level and is suitable for human settlement as Lokoja is majorly on lowland. However, just 6.18% covering about 1492ha land area is on the hills.
|
3.4. Nearness to Infrastructure (Road)
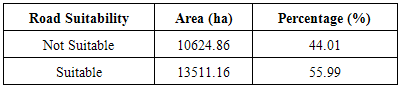
- A total land area of 55.99% is accessible by major roads and within 2.5km which is an indication that accessibility to major facilities like road, transport, electricity etc. is good in Lokoja while the remaining 44.01% of total land area is outside 2.5km from major roads.
|
3.5. Most Suitable Resettlement Location
- Each of the suitability parameters (Land-use, land-cover, Elevation, Slope and Nearness to road) were compared against each other, weighted and overlaid based on their relative importance for the purpose of human resettlement. As it can be observed, land cover suitability factor was assigned 33.14% influence, followed by flood plain delineation in terms of elevation as 30.87%. These two factors are more important than slope which was assigned 16.89%, 15.10% for access to infrastructure (road) and elevation at 4%. The overall weighted overlay of the suitability factors (Figures 7, 8 and 9) revealed that 89.38% is not suitable for human resettlement while only 10.62% is suitable having an area of 2564.44ha. (Table 7).
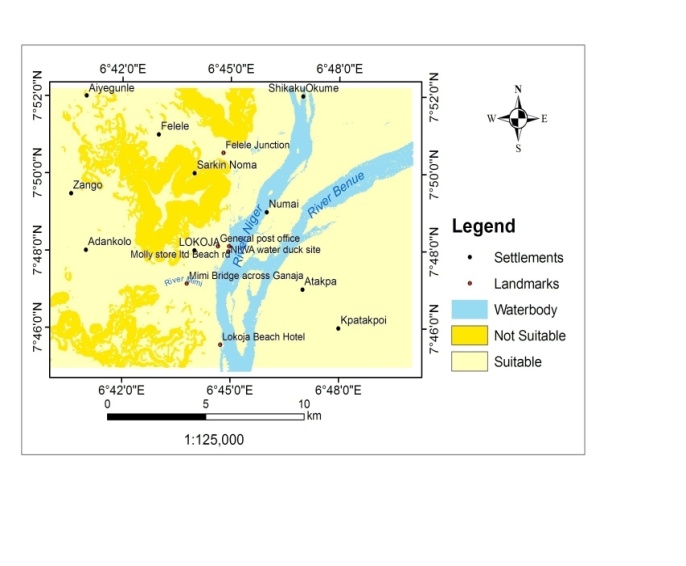 | Figure 7. Slope Suitability Map |
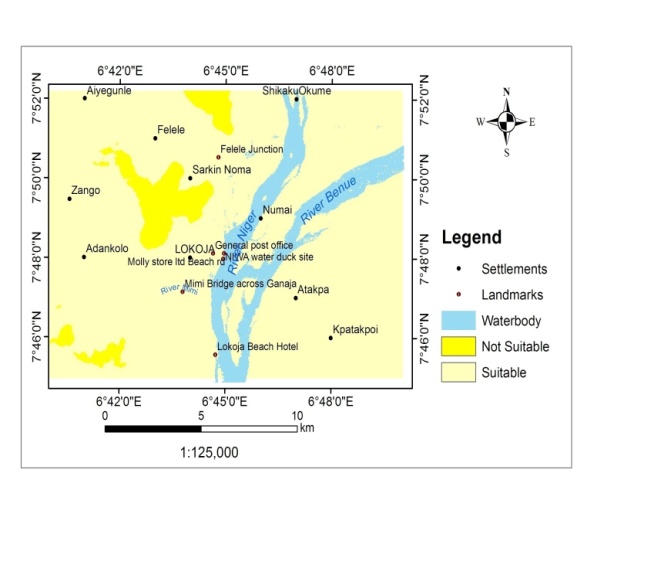 | Figure 8. Elevation Suitability |
 | Figure 9. Suitability based on closeness to infrastructure |
|
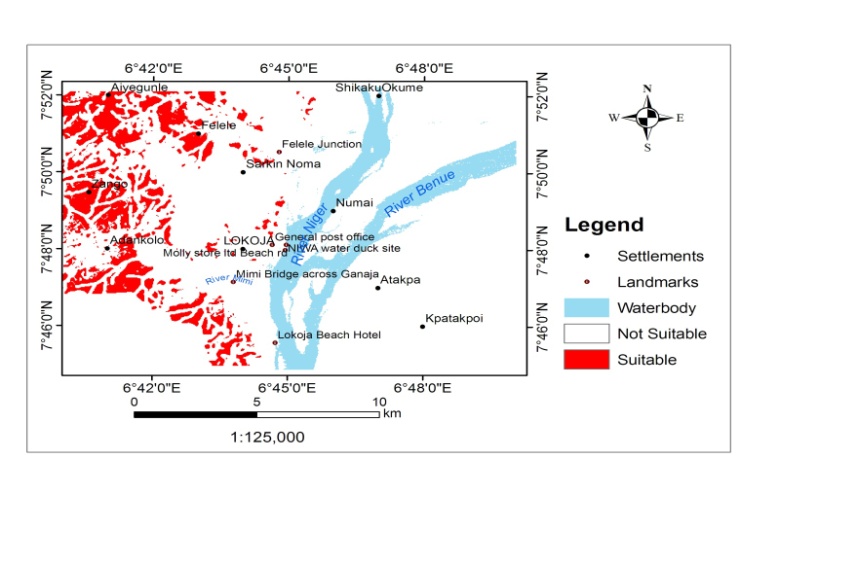 | Figure 10. Overall suitability map for resettlement |
 | Figure 11. Overall suitability map for resettlement based on land exceeding 100ha space |
4. Conclusions
4.1. Summary
- The factors used in this study are inevitable in the analysis of environmental suitability for human resettlement. They have a crucial role to play in determining the suitability of the resettlement site. These include topography, land use/land cover and infrastructure. The individual analysis of these factors indicated that 82.78% of the study area is suitable for settlement in terms of slope while 17.22% of the area is found to have unsuitable slope and the elevation suitability shows that 93.82% is suitable meaning the area has very suitable topographic set up. In terms of land use/land cover, the largest proportion in 75.15% of the study area is suitable such as forest and Rock outcrop. However, 24.85% representing built-up, water body, sand deposits and wetland are not suitable and cannot be recommended for settlement.The factors of accessibility to major roads are important socio-economic factor that is unavoidable in the analysis of environmental suitability for human resettlement. In terms of this, the town has a linear settlement along the waterbody making distance from one location to another not far.The combined suitability assessment shows that more than ¾ of the study area is not suitable for human resettlement while a minimal 10.62% is suitable having an area of 2564.44ha. However only 5(4.14%) of the suitable sites have a continuous area of more than 100ha.
4.2. Conclusions
- Environment is one of the issues composed of the interaction of complicated variables. It is difficult to consider only one variable separately for the analysis of its suitability for human resettlement. This is particularly because they are naturally interwoven in a complicated system. Paradoxically, it is equally difficult to evaluate all environmental factors at a time. However, GIS and remote sensing is an ideal platform that provides adequate facilities for the systematic integration and due consideration of the most important environmental factors. For this purpose, environmental suitability of Lokoja resettlement site has been analyzed in this study in terms of bio-physical and socio-economic environmental factors. What could be done to reduce the effect of flooding in the vulnerable areas include: construction of drainages in the urban areas, dredging of the river to reduce overbank flow. The individual analysis of these factors indicated that 82.78% of the study area is suitable for settlement in terms of slope while 17.22% of the area is found to have unsuitable slope and the elevation suitability shows that 93.82% is suitable meaning the area has very suitable topographic set up. In terms of land use/land cover, the largest proportion in 75.15% of the study area is suitable such as forest and Rock outcrop. However, 24.85% representing built-up, water body, sand deposits and wetland are not suitable and cannot be recommended for settlement.In conclusion a large proportion of the area is suitable for the land cover factor. The factors of accessibility to major roads are important socio-economic factor that is unavoidable in the analysis of environmental suitability for human resettlement. In terms of this, the town has a linear settlement along the waterbody making distance from one location to another not far.The combined suitability assessment shows that more than ¾ of the study area is not suitable for human resettlement while a minimal 10.62% is suitable having an area of 2564.44ha. However only 5(4.14%) of the suitable sites have a continuous area of more than 100ha.
4.3. Recommendations
- Being unsettled for a certain land does not guaranty its environmental suitability and sustainability for a resettlement site. Apart from the virginity of a land, other environmental factors like climate, soil, slope, geology, accessibility, infrastructural development and other socio economic factors has to be considered in evaluating the suitability of resettlement site.Therefore before planning and implementing any resettlement program environmental suitability, ecological carrying capacity and sustainability of the area has to be analyzed thoroughly.■ To avoid the allocation of unsuitable areas for resettlement and to overcome the misuse and degradation of the land and other natural resources, land suitability of new resettlement sites has to be identified by well-trained and qualified experts applying GIS and remote sensing techniques, putting into consideration the various factors like biophysical, topographical and socio-economic of the study area.■ For maintaining the sustainability of the land suitability it is important to relocate the people who settled in marginally suitable areas into moderate and high suitability areas based on the carrying capacity.■ Strengthen community-based environmental resource protection practices in the resettlement sites through efficient land registration systems and creating community awareness. Providing an alternative energy source, like rural electrification for the settlers so that natural forest clearance for firewood can be minimized.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML