-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
World Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-1573 e-ISSN: 2163-1581
2014; 4(3): 101-110
doi:10.5923/j.env.20140403.02
Effects of Rhizobacteria on the Growth and Uptake of Lead by Wheat (Tritium aestivum L.)
Miriam Ighoavodha , Maria Begonia , Gregorio Begonia , Gloria Miller , Jennifer Ntoni , Halima Stringer
Plant Physiology/Microbiology Laboratory, Department of Biology, P.O. Box 18540, College of Science, Engineering, and Technology, Jackson State University, 100 Lynch Street, Jackson, Mississippi 39217, USA
Correspondence to: Gloria Miller , Plant Physiology/Microbiology Laboratory, Department of Biology, P.O. Box 18540, College of Science, Engineering, and Technology, Jackson State University, 100 Lynch Street, Jackson, Mississippi 39217, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of bacteria and ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) on the growth and lead (Pb) accumulation of wheat (Triticum aestivum, L.) grown in sterile and non-sterile soils. Wheat seeds were inoculated with two strains of commercial bacteria; Pseudomonas monteilii (B1) and Wautersia metallidurans (B2). Inoculated seeds were planted in plastic tubes containing sterile or non-sterile soil mixture consisting of topsoil and peat (2:1, v: v) that had been spiked with various amounts (0, 500, 1000, 2000 mg Pb/Kg dry soil) of lead nitrate. The plants were allowed to grow for six weeks in a naturally lit greenhouse. Our results showed that there were higher Pb concentrations in shoots of plants treated with EDTA + B1 and EDTA + B2 that were grown in non-sterile soils as compared to treatments in sterile soils. These results indicated that EDTA + bacteria may have synergized to mobilize Pb in the soil for plant uptake and translocation. In general, EDTA, bacteria, and a combination of both, increased the shoot and root Pb uptake and dry biomass in wheat.
Keywords: Rhizobacteria, Wheat, Lead, Pseudomonas monteilii, Wautersia metallidurans, Phytoremediation
Cite this paper: Miriam Ighoavodha , Maria Begonia , Gregorio Begonia , Gloria Miller , Jennifer Ntoni , Halima Stringer , Effects of Rhizobacteria on the Growth and Uptake of Lead by Wheat (Tritium aestivum L.), World Environment, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 101-110. doi: 10.5923/j.env.20140403.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Lead (Pb) is one of the most commonly identified environmental contaminants and is difficult to remediate because of its limited solubility in soils and its limited bioavailability for plant uptake due to complexation with organic matter and precipitation as carbonates [1]. It is widespread naturally in air and soil, and is a cumulative poison in humans especially in children. In spite of the health effects of Pb that have been recognized for centuries, lead continues to be one of the most useful and most widely used metals primarily because of its beneficial properties. Lead mixes well with other metals, makes long-lasting paint pigments, resists corrosion, and is strong and durable [2].While there has been a substantial reduction in the use of Pb in gasoline, solder, water pipes, and lead-based residential paints, Pb from their use is still in the environment and constitutes an important source of lead in the atmosphere, water, and soil [2, 3].Phytoextraction is a branch of phytoremediation that is emerging as a potential strategy for cost-effective and environmentally sound cleanup of metal-contaminated soils. This trend is due in part because the costs of growing a crop are minimal compared to those of soil removal and replacement [4, 5]. Additionally, the disturbance to the environment is marginal and the secondary waste is eliminated. There are basically two challenges to phytoextraction of lead-contaminated soils: 1) among the major soil contaminating metals, Pb appears to have no naturally evolved hyperaccumulating plant species, and 2) the lack of bioavailability of the metal due to the tight binding characteristic of Pb to soils and plant materials that makes a significant portion of Pb unavailable for root uptake by plants.Microorganisms are fundamental components in the biogeochemical cycles and mineral formation in terrestrial environments. Metal cycles are driven by microorganisms, because some metal ions are essential for microbial nutrition, while others are oxidized or reduced to obtain metabolic energy. In particular, heavy metals such as Pb and Cd, can cause toxic effects. To counter these effects, microorganisms have developed genetic responses or strategies to enable the cell to detoxify them [6]. Rhizosphere bacteria have been shown to be resistant to many heavy metals, and to enhance the accumulation of Se, Hg, and Cd in the roots of non- accumulator plants [7], and may be important for increasing the availability of water-soluble Zn for hyperaccumulation from soils with a high proportion of non-labile Zn [7].Plant-microbe interactions are considered to be important processes in determining the efficiency of phytoremediation. Inoculation of pollutant-degrading bacteria can be a valuable additive to improve the efficiency of phytomediation or bioaugmentation. The combination of the two approaches, phytoremediation and bioaugmentation, results in a process known as rhizoremediation. During rhizoremediation, exudates derived from the plant can help to stimulate the survival and action of bacteria, subsequently resulting in a more efficient degradation of pollutants. The bacteria are spread through the soil via the root system of plants penetrating otherwise impermeable soil layers [8]. In previous studies using a modified hydroponics system and Cd-amended sand, wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. TAM-109) was identified as a suitable phytoextraction species because of its high biomass yield under elevated metal levels, and its ability to accumulate high amounts of metal into its shoots [9-11]. In addition, wheat can be grown during the colder months of a year-round cropping scheme, thus ensuring ground cover for an otherwise barren, contaminated soil.The two bacteria used in this study were Pseudomonas monteilii (ATCC 700476) and Wautersia metallidurans (ATCC 43123). Pseudomonas monteilii is a gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is nonhemolytic on blood agar and was isolated from clinical sources. Various rhizosphere bacteria are potential (micro) biological pesticides which are able to protect plants against disease and improve plant yield [12]. The beneficial pseudomonas are particularly suitable for application as agricultural biocontrol agents since they can use many exudate compounds as a nutrient source, are abundantly present in natural soils, in particular on plant root systems, have a high growth rate relative to many other rhizosphere bacteria, and are easy to grow in vitro [12].Wautersia metallidurans is thought to be resistant to zinc, cobalt, nickel, mercury, cadmium, and produces a zinc-binding protein. In broth, the cells may appear as short to long rods (ATCC, 2007). These soil-borne bacteria with plant-growth promoting effects are generally termed plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) [12, 13].
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
- Lead nitrate [(Pb(NO3)2], and other chemicals were purchased from Sigma Chemical (St. Louis, MO), and Fisher Scientific (Houston, TX). Delta top soil and humus peat were purchased from Hutto's Garden Supply (Jackson, MS). Wheat seeds were obtained from a local store in Jackson, MS. Deepot D40 656 mL planting tubes (referred to hereafter as planting tubes or tubes) and support trays were purchased from Stuewe and Sons, Inc. (Corvallis, OR). Delta top soil and peat were weighed on a Brainweight 1500 scale, Model B1500 (Ohaus Scale corp.).Dry tissue biomass was determined using a Metler AE260 analytical balance. Reagents were weighed with a Wards Electronic top loading balance (Model 15 W6201). Plant tissue samples were dried in a Precision Thelco Model 18 convection oven at 75C for approximately 48 hours. Lead concentration of plant tissues were analyzed with a Perkin Elmer Optima 3300 DV Inductively Coupled Plasma -Optical Emission Spectrometer (ICP-OES) and were expressed as µg Pb/g dry weight (ppm). Modified Hoagland's nutrient solution containing buffers and trace elements were prepared in the laboratory.
2.2. Soil and Growth Medium Preparation
- Appropriate amounts of lead nitrate [Pb(NO3)2] were mixed with delta top soil and humus peat. Delta top soil is a silt loam soil, a member of the fine, kaolinitic, thermic typic kandiudult soils [14]. Representative samples of the prepared soil mixture were sent to Mississippi State University Soil Testing Laboratory, Mississippi State, MS for determination of its physical and chemical characteristics.Approximately 550 g of the dry, sieved delta topsoil, peat mixture (2:1 v/v) were placed in a plastic zip lock bag and amended with either 0, 500, 1000, or 2000 mg Pb/kg dry soil mixture using lead nitrate. Deionized distilled water (DDW) was added to the bags to adjust the soil moisture content to approximately 30% field capacity. The bags of soil were left to equilibrate (age) on a laboratory bench in the greenhouse for six months. The bags were occasionally turned and mixed during the incubation period to ensure thorough mixing.Sterile soils were prepared by placing 550g of each soil mixture with the appropriate metal concentration into separate brown paper bags and autoclaved at 121℃, 15 psi, for one hour on three consecutive days. The autoclaved soil in each bag was dispensed into each sterile 660 mL black plastic planting tubes, and pre-treated, bacterial-inoculated wheat seeds were planted. All treatments were carried out in three replicates.
2.3. Preparation of Axenic Seeds
- Wheat seeds were surface-sterilized by shaking in 70% ethanol for one minute then rinsed five times with sterile water. A germination test was conducted for axenic seeds and non-sterile seeds to determine their viability.
2.4. Bacterial Inoculation
- Two strains of commercial bacteria were used: Pseudomonas monteilii (B1 [Bacteria 1]) and Wautersia metallidurans (B2 [Bacteria 2]) based from a viability study previously conducted in our laboratory (data not presented). Following the procedure of Whiting and his colleagues [7], a mixed inoculum of these two bacterial strains was prepared for seed inocculation. One loopful of each bacterial strain was added to 5 mL of sterile 0.85% saline (NaCl) solution in a sterile plastic 15 mL BD Falcon tube and vortexed to suspend the bacteria. One mL of this suspension was added to 4 mL of sterile 0.5% methylcellulose solution prepared with 0.85% sterile saline solution to provide a bacterial suspension for seed inoculation.To estimate the number of bacteria in the culture, serial dilutions of each of the bacterial solutions were spread on 1.5% trypticase soy agar (TSA) plates and incubated at 25℃ for 7 days. The live bacterial suspension contained a total of 2.52 x 108 colony-forming units (CFU) per milliliter. One set of sterile wheat seeds were soaked in the bacterial solution containing B1 (Pseudomonas monteilii). A second set of sterile wheat seeds were soaked in a bacterial solution containing B2 (Wautersia metallidurans). A third set of sterile wheat seeds were soaked in bacterial solution containing both B1 and B2. After 20 minutes of soaking, all seeds were removed from the bacterial solutions and dried on sterile filter papers in a laminar-flow cabinet. All subsequent seed transfers from the filter papers to the growth media were performed using flamed, autoclaved forceps in a laminar-flow cabinet.
2.5. Planting, Plant Establishment and Maintenance, and Harvesting
- After the seeds were inoculated with Pseudomonas monteilii and Wautersia metallidurans, they were planted in sterile plastic D40 planting tubes containing sterile or non-sterile metal-contaminated soil. Each sterile planting tube was filled with 550g of the appropriate sterile Pb-spiked soil mixture (0, 500, 1000, 2000 mg Pb/kg dry soil) previously prepared. Eight of the pre-treated seeds were sown in each of the planting tubes and watered with 10 mL autoclaved water.Emerged seedlings were thinned out to a desired population density of four plants per tube at 5 days after emergence. In this experiment, each treatment replicate consisted of one tube containing four plants. Any symptoms of metal toxicity (e.g. discoloration, pigmentation, yellowing, stunting) exhibited by plants were noted during the experimental period. Additionally, the position of each D40 tray was rotated one position clockwise each week to prevent any growth discrepancies that may occur due to shading by another plant. Plants were maintained at the naturally lit Jackson State University greenhouse throughout the experimental period. Each planting tube was watered with 10 mL of autoclaved water as needed. After 15 days, the plants were watered with modified Hoagland’s nutrient solution on alternating days. The chelating agent ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) was applied to the soil as an aqueous solution, one week before harvest. The plants were allowed to grow for six weeks. After harvesting, the root and shoot lengths were measured, roots and shoots were separated and roots were washed with DDW to remove any adhering soil particle and debris. The roots and shoots were placed separately in brown paper bags and oven dried at 75℃ for 48 hours. The dry weight of roots and shoots were determined using a Metler AE260 analytical balance.
2.6. Lead Extraction and Analyses
- Lead was extracted from all root and shoot samples using a nitric acid-hydrogen peroxide procedures with slight modifications [15]. In general, this study was arranged in a randomized complete block design (RCBD) and consisted of three replicates. Data were analysed using SAS V9. Statistical analysis of variance was performed on all data sets. Least significant difference (Fisher's LSD) was used for multiple comparisons between different treatments and control groups. Results of the statistical data were summarized in figures and tables. In this study, a probability of 0.05 or less was considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Characterization
- The delta top soil used in this study was classified as a silt loam soil, belonging to the family of fine, Kaolinitic, thermic typic Kandiudult soils [14]. The soil had a sandy loam texture with a cation exchange capacity (CEC) of 17.6 and a pH of 6.3. The extractable magnesium was considered to be very high at 815 kg/ha.
3.2. Wheat Responses to Bacteria and/or Chelate Amendments
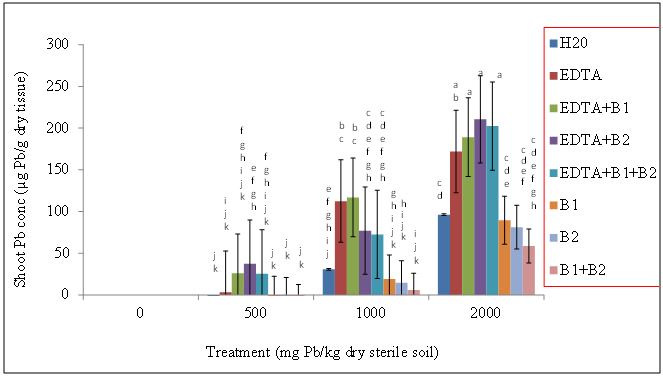
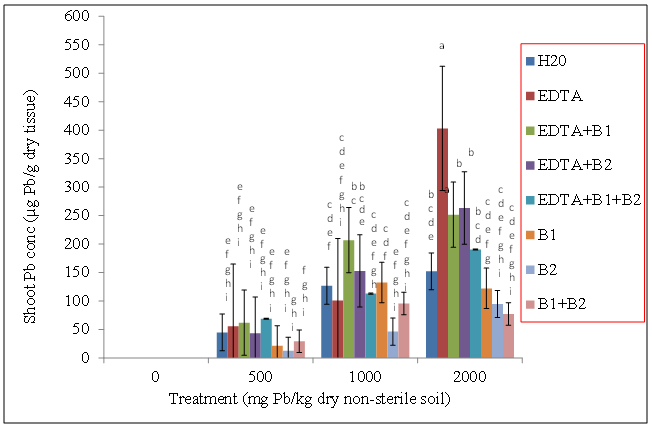
- Wheat plants were grown in sterile (autoclaved) Pb-contaminated soils (0, 500, 1000, and 2000 mg Pb/kg dry sterile soil) with the following treatments: sterile DDW, EDTA alone, EDTA + Pseudomonas monteilii (B1 [bacteria 1]), EDTA + Wautersia metallidurans (B2 [bacteria 2]), EDTA + a combination of B1 and B2, and bacteria alone (no EDTA).Our results showed that regardless of bacteria and EDTA amendments, shoot Pb concentrations (µg Pb/g dry tissue) increased with increasing soil Pb treatments (Figure 1). The highest shoot lead concentrations were observed in plants exposed to 2000 mg Pb/kg dry sterile soil with the addition of EDTA and bacteria (Figure 1). Lead concentrations (µg Pb/g dry tissue) were in the range of 171.87, 189.04, 210.49, and 202.38 for plants exposed to EDTA alone (no bacteria), EDTA + B1, EDTA + B2 and EDTA + B1 + B2, respectively, compared to the control plants with 96.18 µg Pb/g dry tissue. Treatments with bacteria alone (without EDTA) had the lowest shoot Pb tissue concentrations (µg Pb/g dry tissue) of 308.12, 257.21 and 254.64 for wheat plants treated with B1, B2, or a combination of B1 + B2, respectively (Figure 1). Shoot lead concentrations (µg Pb/g dry tissue) of wheat plants that had been grown in non-sterile Pb-contaminated soil followed the same trend as those wheat plants that had been grown in sterile soil with bacterial and/or chelate amendments. There was an increase in shoot Pb concentrations with increasing soil Pb treatment with the highest shoot tissue concentrations observed in wheat plants exposed to EDTA plus bacteria. The lowest shoot Pb concentrations were exhibited by plants treated with bacteria alone (Figure 2).
3.3. Translocation Index
- Translocation index of wheat in sterile soil was highest in each Pb soil treatment (500, 1000, and 2000 mg Pb/kg dry soil) wherein EDTA was added. The highest translocation indices were observed in wheat plants exposed to 2000 mg Pb/kg dry soil with values of 13.11, and 14.47 corresponding to EDTA+B2 and EDTA+B1+B2 treatments, respectively (Data not shown). Translocation indices of wheat grown in non-sterile soil spiked with 500 mg Pb/kg dry soil was also higher with the addition of EDTA.
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Characterization
- The soil used in this study was classified as delta top soil, a silt loam soil which belongs to a family of fine, Kaolinitic, thermic typic Kandiudult soils. These soils have a low, but not extremely low cation-exchange capacity (CEC) [14]. Soil pH is one of the most influential parameters controlling the mobility and availability of metals in the soils. In our greenhouse study, soil pH before planting was 6.3 and decreased with increasing amounts of soil-applied Pb. After chelate application, the soil pH remained in the range of 5.5 - 6.5 (data not shown), a range not unusual in chelate-assisted phytoextraction [16]. Unlike nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA), another strong complexing agent, which exhibits a significant pH dependency, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), the chelating agent used in this study, is generally pH insensitive and can remain relatively constant over a broad pH range (4.9 - 11.3) as demonstrated by Peters and Shem [16].In general, the chemistry of metal interaction with soil matrix is central to the phytoremediation concept. While the soil used in this study was high in phosphorus, potassium and zinc; and very high in magnesium, these were, nonetheless, essential plant nutrients. Overall, the parameters of the soil used in this study were well within limits for our objectives. Although the total Pb concentration in many contaminated soils may be high, the bioavailable Pb fraction (water soluble and exchangeable) is usually very low due to the strong association of Pb with organic matter, Fe-Mn oxides, and clays, and precipitation as carbonates, hydroxides, and phosphates [1]. In order to determine Pb mobility in Kandiudult delta top soil, Miller [17] performed a sequential extraction procedure [19] on a laboratory prepared Pb-spiked soil that had been prepared using the same method that were used in this study. The results of Miller's sequential extraction revealed that approximately 17% of the Pb is expected to be bioavailable for plant root uptake [17]. The greater percentage of Pb was concentrated in the residual and exchangeable fractions of this soil type [17, 19]. The residual fraction (fraction 5) can be thought of as what is left over after the first four fractions have been removed. It contains primary and secondary minerals which may hold trace metals within their crystal structure [18]. These metals are not expected to be released under normal environmental conditions and therefore, not bioavailable for plant uptake.
4.2. Wheat Tolerance, Growth, and Uptake of Lead
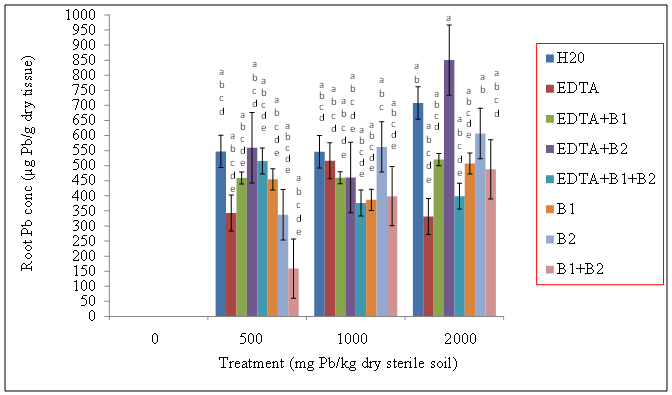
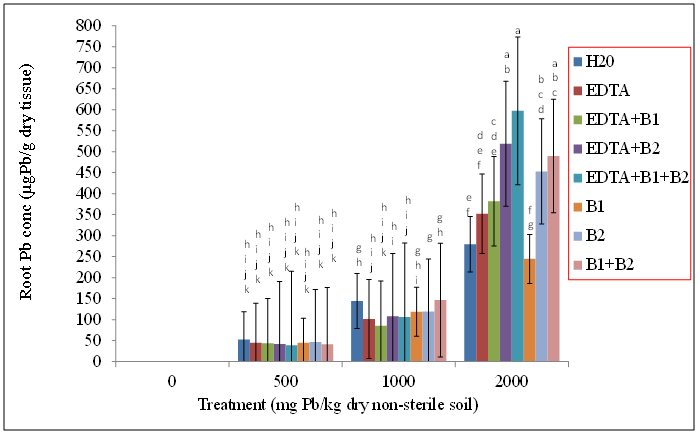
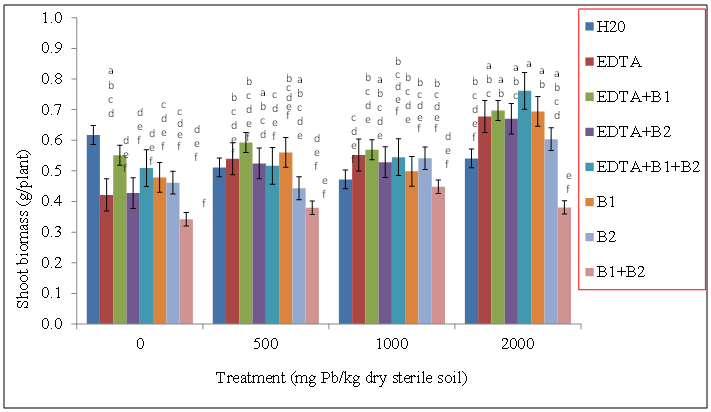
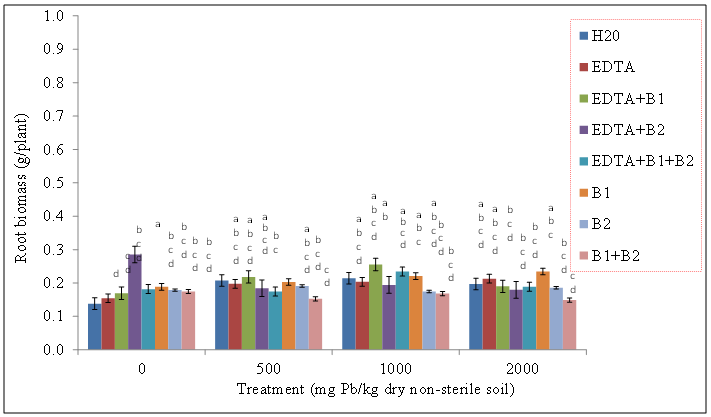
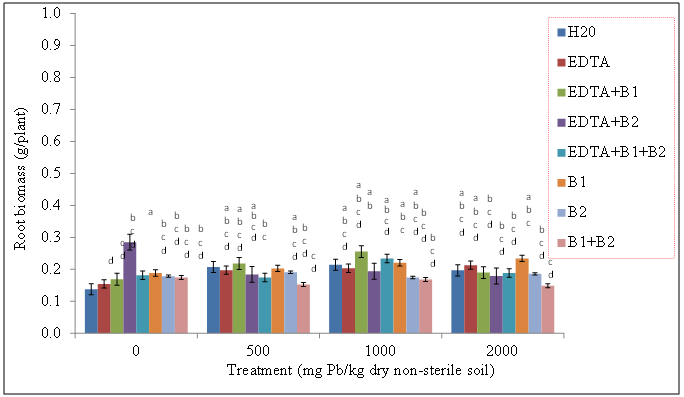
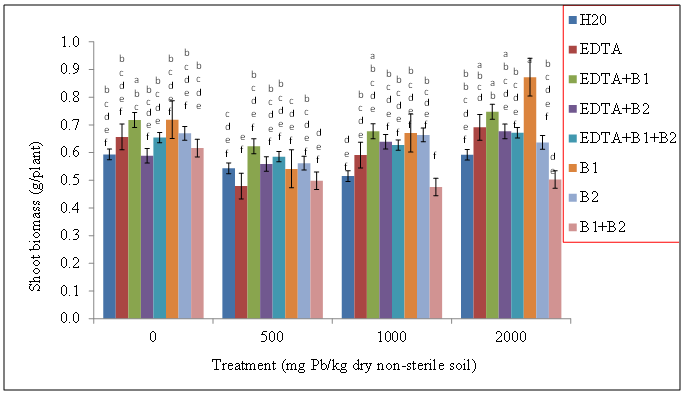
- Our data revealed that wheat was tolerant to Pb soil concentrations and was able to sequester Pb in its shoot tissue (Figures 1, and 2), We also found the same trend for wheat root tissues (Figures 3 and 4). Our findings are consistent with the findings of Ntoni [11]. Wherein she reported that wheat (T. aestivum) displayed classical metal toxicity symptoms such as stunted growth, but was nonetheless tolerant to high concentrations of cadmium (Cd). We found that wheat was able to survive high levels of Pb, though the mechanism of wheat tolerance is still largely unknown.Enhancing metal accumulation in high-yielding crop plants without diminishing their yield is fundamental to successful phytoremediation [20]. Compared with control treatments, inoculation with rhizobacteria did not greatly influence the metal concentrations in plant tissues, but achieved a much larger aboveground biomass thus resulting in a much higher metal removal. We believe that Pb soil concentrations of 2000 mg Pb/kg dry soil may have surpassed the threshold of metal tolerance for the plants as well as for the soil rhizobacteria, Wautersia metallidurans ATCC 43123 and Pseudomonas monteilii ATCC 700476. An increasing body of evidence suggests that microorganisms are far more sensitive to heavy metal stress than soil animals or plants growing on the same soils [21]. Results from the literature suggest that heavy metals may be removed from contaminated soils using plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. These are particularly useful in highly contaminated soils where the heavy metal content exceeds the limit of plant tolerance [21].Our results indicate that Wautersia metallidurans ATCC 43123 and Pseudomonas monteilii ATCC 700476 may have facilitated the growth and Pb tissue uptake of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants and therefore may increase the phytoremediation efficiency especially at Pb soil concentrations less than 2000 mg Pb/kg dry soil.Soil rhizobacteria may have also directly influenced metal solubility by changing heavy metal speciation in the rhizosphere of wheat, similar to what has been reported earlier by [22]. Study of the roles of mycorrhiza in metal speciation in the rhizosphere and the impact on increasing host plant tolerance against excessive heavy metals in soil showed that speciations of Cu, Zn, and Pb changed significantly in the rhizosphere of arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) of infected and non-infected maize in comparison to bulk soil [22]. Jing and his colleagues [22] further reported that the greatest change was exchangeable Cu that increased by 26% and 43% in non-infected and AM-infected rhizosphere, respectively, than in bulk soil.Wheat plants survived the Pb soil treatments of 500, 1000, and 2000 mg Pb/kg dry soil but displayed stunted growth and lower biomass especially at the highest level of soil Pb treatments. This apparently indicated that Wautersia metallidurans and Pseudomonas monteilii could protect their host plants from the phytotoxicity of excessive Pb. A similar finding was reported by Jing [22] and his colleagues who found that mycorrhiza may have played a part in protecting plants from copper, zinc and lead by changing the speciation from bioavailable to the non-bioavailable form. They further reported that copper and zinc accumulation in the roots and shoots of mycorrhiza-infected plants were significantly lower than those in the non-infected plants, which might also suggest that mycorrhiza efficiently restrict excessive copper and zinc absorptions into the host plants [22].Chelates such as EDTA bring more ions into solution, and properly selected plants provide enhanced surface area for absorption of Pb ions and their chelated forms [23]. Radish has been reported to tolerate Pb concentrations as high as 240 ppm and accumulates significant levels of the metal in its shoots especially in conjunction with EDTA [24].The translocation index (TI) of Pb in wheat can be used to evaluate the capacity of a plant to transfer a metal from the roots to the shoots. It is usually > 1 in the hyperaccumulators and < 1 in excluders [25, 26]. Results of our research showed that the roots of wheat plants were capable of translocating significant amounts of the metal to the aboveground parts; an attractive feature for phytoextraction efficiency.The success of phytoextraction process depends upon both shoot biomass and shoot metal concentration. Therefore, the potential effectiveness of each plant for phytoremediation was evaluated through calculating the metal accumulation inside the plant (metal concentration x plant dry weight). The heavy metal removal by plant shoots is an important index which is useful for the practical application of treatments. Our results showed that there were significant differences in the uptake of the heavy metals exhibited by plants exposed to various treatments. The first requisite in phytoextraction is the production of high plant biomass at the contaminated site. Metal phytotoxicity causes stress to the plant, resulting in a reduction in biomass and in some cases eventually death. Generally, T. aestivum (wheat) produced a high biomass and was tolerant to elevated levels of Pb/EDTA in the soil. Our results showed that the amounts of heavy metal absorbed by wheat was higher in the roots. It is generally agreed that chelating agents can form strong complexes with some metals. The efficacy of the chelate to remobilize these heavy metals from a contaminated soil depends on the association of the metal with the soil matrix, as well as the chemistry of the metal. In this context, the total concentration of the metal present in the polluted soil provides little insight into the solubility and/or extractability of the metal. Rather, it is the knowledge of metal speciation in the soil that is essential in predicting the outcome of the phytoextractive process.We found no indication that the two bacteria species used in this study, Pseudomonas monteilii and Wautersia metallidurans, had an effect on the growth of wheat plant. Shoot biomass of wheat plants grown in sterile (Figure 5) and non-sterile soils (Figure 6) were rather similar across all treatments. The same was true for wheat root biomass (Figures 7 and 8).While it was generally observed that the highest amounts of Pb uptake was evident in plants treated with a combination of EDTA and rhizobacteria, more research is needed to elucidate the combined effects of rhizobacteria and EDTA on uptake and growth of plants grown especially in soils contaminated with elevated levels of Pb.
5. Conclusions
- The selection of phytoremediating species is possibly the single most important factor affecting the extent of metal removal. Although, the potential for metal extraction is of primary importance, other criteria, such as ecosystem protection must also be considered when selecting remediating plants. As a general rule, native species are preferred since exotic plants can be invasive and can endanger the harmony of the ecosystem [27].Plants respond to metal toxicity through ligands, which are naturally occurring metal binding ligands known as phytochelatins and metallothiones. These ligands make the metal less toxic to the plant, but at this stage, we are not certain whether the same tolerance mechanism exists in wheat.Complex interactions such as soil pH, location, and extent of contamination, that take place under site-specific conditions require that metal phytoextraction must be approached as a multi-disciplinary research effort incorporating the expertise of plant biologist, soil microbiologists, agronomists, and environmental engineers to identify and solve issues such as 1) how to best enhance Pb bioavailability for uptake while avoiding groundwater contamination , 2) means of optimizing the plant's ability to take up and store Pb, and 3) ways to incorporate soil amendments including synthetic chelates, as well as when and how to harvest. These and other creative research tools may provide a means of cleaning up metal contaminated soils that far supersede the possibilities of phytoextraction. It is therefore likely that further technical refinements are needed on the use of rhizobacteria in phytoextraction.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Support for this research was provided by the Title III Program: Strengthening the Environmental Science Ph.D. Program in Research, a grant funded by the U.S. Department of Education – Grant No. P031B090210. Also, this publication was made possible through support provided by NASA through the University of Mississippi under the terms of grant No. NNX10AJ79H. The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of NASA or the University of Mississippi.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML