| [1] | Costa, D.L. (2001). Air pollution. In Casarett and Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons, sixth edition (Ed) Klaassen, C.D., Mcgraw-Hill, N.Y. USA. pp.979-1012 |
| [2] | United Nation (1998). Prospect of world urbanization (Population Study No.112), New York |
| [3] | Schwela, D (2000).Air pollution and health in urban areas. Reviews on Environmental Health, 15(12):13-14. |
| [4] | Autrup, S.E(2006). Survey of air pollution in Cotonou, Benin-air monitoring and biomarkers, Science of Total Environment, 358(1-1):85-96 |
| [5] | Bolund, P and Hunhammers, S (1999). Ecosystem services in urban areas. Ecological Economics, 29:293-301 |
| [6] | Ulrich, R.S (1984). View through a window may influence recovery from surgery. Science, 224:420-421 |
| [7] | Kuo, F.E and Sullivan, W.C (2001). Environment and crime in the inner city-does vegetation reduce crime? Environment and Behaviour, 33:343-367 |
| [8] | Fuller, R.A. Irvine, K.N, Devine-Wright, P, Warren, P.H and Gaston, K.J(2007). Psychological benefits of green space increase with biodiversity. Biology letters, 3:390-394 |
| [9] | McDowell, C.R, Low, A.B and Mckenzie, B (1991). National remnants and corridors in Greater Cape Town: their role in threatened plant conservation. In the role of corridors (eds) D.A Saunders and R. J. Hobbs, Survey Beatty and sons, chipping Norton, NSW. |
| [10] | Schwartz, M. W. Jurjavice, N. L. and O’ Brien, J. M(2002).Conservation’s disenfranchised urban poor. Bioscience, 52: 601-606. |
| [11] | Lawson, D. M. Lamar, C. K and Schwartz, M.W (2008). Quantifying plant population persistence in human - dominated landscapes. Conservation Biology, 22:922-928 |
| [12] | Pickett, S.T.A. Cadenasso, M.L (2008). Linking ecological and built components of urban mosaics and open cycle of ecological design. Journal of Ecology, 96:8-12 |
| [13] | Landsberge, H. E (1981). The Urban Climate. National Academy press, New York, p.275. |
| [14] | Oke, T.R (1982). The energetic basis of urban heat Island. Quarterly Journal of the Royal meteorological society, 108 (455):1-24 |
| [15] | Voogt, J.A. (2002). Urban heat Island. In Munn, T. (ed), Encyclopedia of Global Change. Wiley, New York, pp. 660-666. |
| [16] | Makhelouf, A (2009). The effect of green spaces on urban climate and pollution. Iran journal of Environmental Health Sciences and Engineering, 6(1):35-40. |
| [17] | Liu, Y.J. Mu, Y. J and Zhu, Y.G (2007). Which ornamental plants species effectively remove benzene from indoor air? Atmosphere environment, 51:650-654. |
| [18] | Jayashnee, N(2012) ‘Air Controll’ The Times of India, October, 28 |
| [19] | Lakshmi, P.S. Sravanti, K.L and Srinivas, N (2008). Air pollution tolerance index of various plant species growing in industrial areas. The Ecoscan, 2(2). 203-206. |
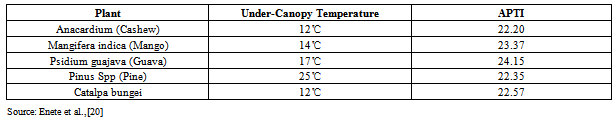
| [20] | Enete, I.C. Alabi, M.O and Chukwudelunzu, V.U (2012a). Tree Canopy Variation effects on urban heat Island in Enugu City, Nigerian. Developing Country Studies, 2(6):12-18. |
| [21] | Agbaire, P.O (2009). Air pollution tolerance indices of some plants around Erhoike-kokori oil exploration site of Delta state, Nigeria. International journal of physical sciences, 4: 366-368. |
| [22] | Singh, S. N and Verma, A (2007). Phytoremediation of Air Pollutants: A Review. In: Environmental Bioremediation technology, Singh, S. N. and Tripathi, R.D (eds). Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 293-314. |
| [23] | Arora, A Sairam, R.K and sirvastava, G.C (2002). Oxidative stress and antioxidative system in plants. Current Science, 82:1227-1238. |
| [24] | Joshni, P. C and Swami, A (2007). Physiological Responses of some tree species under roadside automobile pollution stress around city of Haridwar, India. Environmentalist, 27:365-374 |
| [25] | Escobedo, F.J. Wagner, J.E. Nowak, D. J. Dele Maza, C. L. Rodriguez, M and Crane, D.E (2008). Analyzing the cost effectiveness of Santiago, Chiles Policy of using Urban forests to improve air quality. Journal of Environmental Management, 86: 148-157. |
| [26] | Pasqualini, S. Batini, P. Ederli, L (2001). Effects of short-term ozone fumigation on tobacco plants: response of the scavenging system and expression of the glutathione reductase, Plant cell environment, 24:245-252 |
| [27] | Conkin, P. (2001). Recent advance in the role and biosynthesis of ascorbic acid in plants. Plant cell Environment, 24: 383-394 |
| [28] | Liu, Y. J and Ding, H (2008). Variation in air pollution tolerance index of plants near a steel factory: Implication for landscape-plant species selection for industrial areas. Environmental development, 4:24-32 |
| [29] | Williams, N.S. Schwartz M.W. Vesk, P.A. Mclarthy, M.A. Hahs, Ak> Clemants, S.E Courlett, R.T. Duncan, RP. (2009). A Conceptual Framework for predicting the effects of urban environments on floras. Journal of Ecology, 97:4-9 |
| [30] | Cheptou, P.O., Carrue, O.Rouifed, S and Cantarel, A (2008). Rapid evolution of seed dispersal in urban environment in the weed crepts sancta. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105:3796-3799. |
| [31] | Rao, C.S. (2006). Environmental pollution controlEngineering. New Age International publishers, Revised second edition. |
| [32] | Bhatia, S.C. (2006). Environmental Chemisty. CBSPublishers and Distributors, India. |
| [33] | Steubing, L. Fangmier, A Both, R (1989). Effects of SO2, NO2 and O3 on population Development and morphological and physiological parameters of native herb layer species in a Beech Forest. Environmental pollution, 58:281-302. |
| [34] | Dohman, G. P. Loppers, A, Langebartels, (1990). Biochemical Response of Norway Spruce (Picea Abies (L) karst) Toward 14-months exposure to ozone and Acid mist, effect on amino acid, Glutathione and polyamine titers. Environmental pollution, 64; 375-383. |
| [35] | Singh, A. (1977): Practical Plant physiology. KalyariPublishers. New Dehli. |
| [36] | Agbaire, P.O and Esiefarinrhe, E(2009). Air Pollution tolerance indices of some plants around Otorogum gas plants in Delta State, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences, and Environmental Management, 13:11-14. |
| [37] | Bajaj, K. L and Kaur, G(1981). Spectrophotometric Determination of ascorbic acid in vegetables and fruits. Analyst, 106:117-120. |
| [38] | Singh, S.K and Rao, D.N (1983). Evaluation of plants for their tolerance to air pollution, proceedings of the symposium on air pollution control, pp.218-224. |
| [39] | Katiyar,V and Dubey, P.S (2001).Sulphur dioxide Sensitivity on two stage of leaf development in a few tropical tree species. Journal of Environmental Sciences, Toxicology, 11:78-81 |
| [40] | Beg, M.U., Farooq, M.H., Bhargava, S.K., Kidwai, M.U and Lal, M.M(1990). Performance of trees around a thermal power station. Envirnomental Ecology, 8:791-797. |
| [41] | Jyothi, J.S and Jaya, D.S(2010). Evaluation of air pollution tolerance index of selected plant species along roadsides in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. Journal of Environmental Biology, 31:379-386 |
| [42] | Raza,S.H and Murthy, M.S.R (1988).Air pollution tolerance index of certain plants of Nacharam Industrial Area, Hyderabed, Indian. Journal of Botony,11(1):91-95 |
| [43] | Lewis, S (1976). Vitamin C: Its molecular biology and medical potential, Academic press, London. |
| [44] | Chaudhary, C.S and Rao, D.N(1977). A Study of some factors in plants controlling their susceptibility to SO2 pollution. Proceedings of Indian National Science Academy, 43:236-241 |
| [45] | Varshney, S.R.K and Varshney, C.K(1984). Effects of SO2 on ascorbic acid in crop plants. Environmental Pollution (Serial A), 35:285-290 |
| [46] | Swami, A., Bhatt, D and Joshi, P.C(2004). Effects of automobile pollution on Sal (Shore robusta) and rohini (Mallotus phillipinensis) at Asarori, Dehradun. Himalayan Journal of Environment and ZOOLOGY,18(1):57-61 |
| [47] | Larcher, W (1995). Physiological Plant Ecology. Berlin: Springer |
| [48] | Agrawal, L and Tiwari, S.L(1997). Susceptibility level of few plants on the basis of air pollution tolerance index. Indian Forester,1(2):319-322 |
| [49] | Karthiyayini, R., Ponnammal, N.R and Joseph, R(2005). Air pollution tolerance index of certain plants of coimbatoreooty highways, near I.T.I Area, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu. Pollution Research, 24:363-365 |
| [50] | Tripathi, A.K., Tiwari, P.B., Mahima, S and Singh, D(2009). Assessment of air pollution tolerance index of some trees in Moradabad City, India.Journal of Environmental Biology, 30(4):545-550 |
| [51] | Chauhan, R.G(2010). Tree as bio-indicator of automobile pollution in Dehradum City. A Case Study. Journal of New York Science, 3(6):88-95 |
| [52] | Abida, B and Harikrishna, S(2010). Evaluation of some tree species to absorb air pollutants in three in dustrial locations of South Bengaluru, India. E-Journal of Chemistry, 7(S1):51-56 |
| [53] | Sirajuddin, M and Ravichandran, M(2010).Ambient air quality in an urban area and its effects on plants and human beings: A case study of Tiruchiraalli, India. Kathmandu University Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology, 6(2):13-19 |
| [54] | Enete, I.C.,Ogbonna, C.E and Officha, M.C(2012b).Using trees as urban heat island reduction tool in Enugu City, Nigeria based on their air pollution tolerance index. Ethopian Journal of Environmental Studies and Management, 5(4-1):484-488. |
| [55] | Enete, I.C and Ogbonna, C.E(2012).Evaluation of air pollution tolerance index of some selected Ornamental Shrubs in Enugu City, Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology, 1(2):22-25. |
| [56] | Yan-Ju, L and Hui, D (2008). Variation in air pollution tolerance index of plants near steel factory. Implication for landscape-plant species selection for industrial areas. Environmental Development, 1 (4): 24-30 |
| [57] | Nugrahani, P. Prasetyawati, E. T. Sugijanto, O and Pumobasuki, H (2012). Asian Journal of Biological Sciences, 3(2): 298-302. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML