-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
World Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-1573 e-ISSN: 2163-1581
2012; 2(4): 76-80
doi: 10.5923/j.env.20120204.04
Characterization of Vibrio Alginolyticus Trh Positive From Mediterranean Environment of Tamouda Bay (Morocco)
Sabir Mustapha 1, 2, 3, Ennaji Moulay Mustapha 4, Bouchrif Brahim 1, Cohen Nozha 1
1Laboratory of Microbiology and Food Hygiene and Environment, Institut Pasteur Morocco , Casablanca , Morocco
2Laboratory of Virology and Microbiology &
3Hygiene, Faculty of Science and Technology , Mohammedia , Morocco
4Laboratory of Virology and Microbiology & Hygiene, Faculty of Science and Technology , Mohammedia , Morocco
Correspondence to: Sabir Mustapha , Laboratory of Microbiology and Food Hygiene and Environment, Institut Pasteur Morocco , Casablanca , Morocco.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Vibrio alginolyticus is a halophilic Vibrio and is considered the most frequent species living freely in water and sediment and can survive in seawater even under starvation conditions while maintaining its virulence. Our objective in this study is to investigate the existence of virulence genes in Vibrio alginolyticus in Tamouda bay (Morocco). A total of 588 samples were collected during the study and analyzed. The study of cultural biochemical and molecular characteristics of strains showed an incidence of 70.2% of Vibrio alginolyticus. Among 412 strains of Vibrio alginolyticus identified eleven (2.7%) were urease and Kanagawa Phenomenon (KP) positive. To study the presence of the gene for virulence genes in ten strains of Vibrio alginolyticus urease positive and KP positive, we used the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The results revealed that 70% of the strains have the trh gene (250 bp) but all strains are tdh negative. This is the first report who demonstrated the presence of V. alginolyticus KP positive and trh gene in Morocco. These findings indicate the potential sanitary risk associated with the presence of Vibrio alginolyticus KP positive and the implications of the trh gene in plankton, sediment, sea water and shellfish as a pathogen of food poisonning.
Keywords: Vibrio Alginolyticus , Virulence Genes , Urease , Kanagawa Phenomenon , Haemolysin , PCR , Trh , Tdh, Mediterranean Sea , Morocco
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Vibrio (V.) is a genus of bacteria indigenous to the aquatic environment. Some bacterial species of this genus are now considered as emerging pathogens, involved in food-borne infections in humans[6], which poses a public health risk. Several studies have been conducted on the prevalence of Vibrio in seafood in Morocco[4,5,7,8].V. alginolyticus is considered one of the most frequent species living freely in water and sediment[10] and can survive in sea water even in famine conditions while maintaining their virulence[3].The first reports identifying V. alginolyticus as possessing the trh gene occurred in Alaska[19] and in Tunisia[2]. In addition, it has been shown that strains of V. alginolyticus carry the trh gene and the pathogenic V.alginolyticus strains is recognised as a potential reservoir of many known virulence genes of other Vibrio species in the aquatic environment which have been demonstrated to contributes to the onset of wound infections, enteric pathologies, septicaemia and peritonitis in humans by exposure to seawater[17,26]. The same studies have underlined the virulence of Vibrio. Another study in Australia reported a case of V. alginolyticusin China[28] confirming reports from other countries in Europe and America[1,11,18,21,25].This study is a follow-up investigation to the prevalence and environmental impact factor of V. alginolyticus in one of the Mediterranean coasts of Morocco[23], it will look more specifically at the virulence factors of V. alginolyticus urease positive strains isolated from the Tamouda Bay in Morocco.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
- Tamouda Bay is located in the Mediterranean coast of Morocco, between Sebta at the North (35°54’N, 5°17’10”W) and Cap Negron at the South (35°40’N, 5°16’40”W) where the climate is typically Mediterranean. The average annual temperature is about 18℃, while the annual rainfall average ranges between 800 and 1000 mm.
2.2. Environmental Sampling
- A total of four hundred and twelve (412) (142 sea water, 90 plankton, 73 shellfish and 107 sediment) samples were collected in three sampling sites at Tamouda Bay. One of the three coastal sites, located at the mouth of the Smir's river (site 2), is described high risk while the two others (sites 1 and 3) are considered low risk. All samples were analyzed for the monitoring of physicochemical parameters of seawater taken from the as well as identification of Vibrio alginolyticus in water samples, plankton, shellfish and sediment. Bimonthly samples were made over a period of two years (January 2007- December 2008).
2.3. Phenotypic Identification of Bacteria
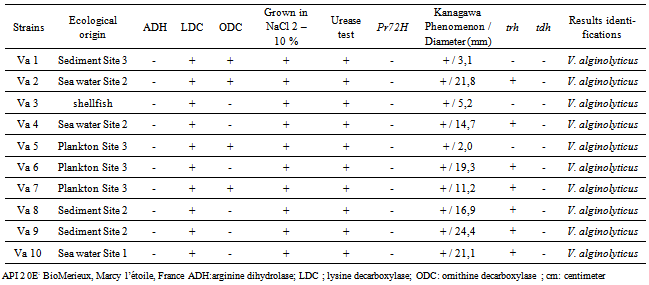
- Presumptive identification was performed on the 412 strains of V. alginolyticus isolated by the search for oxidase, arginine dihydrolase (ADH), lysine decarboxylase (LDC) and ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) assays, and a serial growth in salt consists of a series tube of alkaline peptone water containing 2 to 10% NaCl. The identification was then continued only with oxidase positive strains, negative ADH and positive LDC by performing seeding on the API 20E commercial Kit (Biomerieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France).
2.4. Molecular Identification
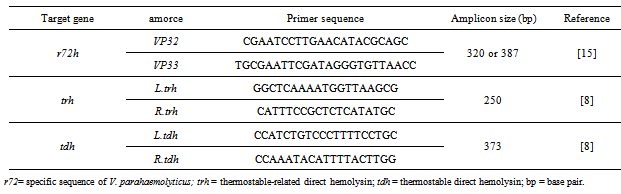
- Robert-Pillot and al.[22] demonstrated that amplification of the R72H fragment, for amplicons of 320 bp or 387 bp, is a powerful tool for reliable identification of V. parahaemolyticus. Consequently, for this study, the biochemical identification of V. alginolyticus strains was confirmed by the absence the sequence of r72h as described by Lee [15]. The application of this molecular study of strains biochemically identified as V. alginolyticus eliminates any strains of V. parahaemolyticus atypical for sucrose[22].Bacterial DNA was extracted following the protocol designed for the extraction of DNA from gram positive and gram negative bacteria in the commercial kit Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega, France). The oligonucleotide primers relating to r72h and size of the amplicons are displayed in table 1. The PCR mixture contained 1x PCR amplification buffer (50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, 0.1% Triton X-100), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 200 mM (each) deoxynucleoside triphosphates, 1 mM (each) primers, 1.25 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen), 5 ml (40 ng) of template DNA or lysed bacterial broth, and double-distilled water treated with 0.1% diethylpyrocarbonate to make a final volume of 50 ml and was then subjected to 35 PCR cycles in a programmable temperature cycler (Bio-Rad, DyadDisciple). The parameters for the amplification cycles were denaturation for 1 min at 94℃, annealing of primers for 1 min at 60℃, and primer extension for 1 min at 72℃. After the last cycle, the PCR mixtures were incubated for 10 min at 72℃.PCR-amplified DNA was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis in 2% agarose gels (invitrogen). Ten µl each of the amplification mixtures was subjected to electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. The specific amplified DNA fragments were visualized by UV illumination.
2.5. Detection of Kanagawa Phenomenon
- In order to detect the power haemolysin strains of V. alginolyticus, the Kanagawa phenomenon (K.P.) was studied on Wagatsuma blood agar[9]. All urease positive strains of V. alginolyticus (10 strains) were examined by culturing overnight in tryptic soy broth supplemented with 7% NaCl on Wagatsuma agar which contained 5% washed rabbit erythrocytes, 0.5% yeast extract, 1% peptone, 7% NaCl, 0.0001% crystal violet, and 1.5% agar (pH 7,5).
2.6. Detection of Virulence Genes
- Purification of plasmid DNAIn order to confirm the presence of structural trh and tdh genes in V. alginolyticus strains, we used V. parahaemolyticus strains as a positive control for both of these genes. Bacterial DNA was extracted following the protocol designed for the extraction of DNA from gram positive and gram negative bacteria in the commercial kit Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega, France).Oligonucleotide primersThe oligonucleotide primers specific for the trh and tdh genes and size of the amplicons following PCR amplification are described in table 1.
|
- Amplification of trh and tdh gene for PCRThe amplification was optimized in a 50 µl reaction consisting of 0.5 µg of purified genomic DNA of V. alginolyticus strains, 1 µM of each of the oligonucleotide primers for trh (1.2µl of each of the primers from a 20 µM stock suspension)(Sigma), 5 µl of a 10 X PCR reaction buffer (10 X buffer consisted of 500 µM Tris-Cl, pH 8.9, 500 mM KCl) and 4 µl MgCl2 (4 mM) (Invitrogen); final concentration of 1x), 200 µM of each of the dNTPs (4 µl from a 10 mM stock dNTP) (Promega-Madison wi USA), 0.6 units AmpliTaq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen) and an appropriate volume of sterile MilliQ water (Millipore).The PCR amplification was performed in a DNA thermal cycler (Bio-Rad, DyadDisciple) using the following temperature-cycling parameters: initial denaturation at 94℃ for 5 min followed by 30 cycles of amplification; each cycle consisted of denaturation at 94℃ for 1 min, primer annealing at 54℃ for 1 min, and primer extension at 72℃ for 1 min. Following the amplification cycles, samples were kept at 72℃ for 10 min to allow final extension of the incompletely synthesized DNA.PCR products (10 µl each) were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis in a 2% agarose gel (Invitrogen) run at 75V for 1.5h in 1xTris-acetate-EDTA. Amplification products were visualized by ethidium bromide staining and visualized and photographed using a UV transilluminator (Vilber Lourmat, Germany).
3. Results and Discussion
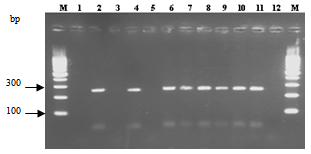
- A total of 588 samples were collected during the study, of which 70.24% were found to be positive for the incidence of V. alginolyticus. The highest incidence was found in water (34%) followed by sediment (26%), plankton (22%) and shellfish (18%).Furthermore, our study showed a prevalence of V. alginolyticus from 70% in shellfish analyzed, a prevalence highly superior to the 50%[5] and 8.2%[8] reported for this species for shellfish marketed in Morocco Among 412 strains of Vibrio alginolyticus identified, eleven (2.7%) were urease and KP positive. Moreover, all ten strains assumed to be V. alginolyticus were confirmed by the absence of the gene r72h.PCR analyses revealed 70% of the samples positive for trh (250 bp). Figure 1 shows that only strains Va2, Va4, Va6, Va7, Va8, Va9 and Va10 were trh positive, while strains Va1, Va3 and Va5 were trh negative. However, all strains are tdh negative.Moreover, trh positive strains showed a zone of haemolysis with a diameter greater than 11,2 mm. While trh negative strains have a diameter between 2 and 5.2 mm (table 2).Being an autochthonous marine bacterium, V. alginolyticus is probably subjected to a high level of recombination with the diverse, closely related bacterial strains populating marine environments. Marine environments provide a habitat where Vibrio can be exposed to high levels of gene transfer by transduction[14], and consequently, putative transfers of virulence factor genes like trh and tdh can occur between marine bacteria.
|
- The presence of a trh gene actively expressed in a V. alginolyticus strain supports the hypothesis that this gene is transferred among Vibrio and this shows that V. alginolyticus often possessed homologues of virulence genes of V. parahaemolyticus and V. cholerae, suggesting that V. alginolyticus can be a reservoir for these genes in the aquatic environment[28]. The practical implications of these results are that detection of the trh gene in mixed cultures, such as broth enrichments or nucleic acid extracts of seafood or environmental samples, does not always imply that pathogenic V. parahaemolyticus is present.Many Vibrio species are pathogenic for humans and/or marine vertebrates and invertebrates, with the virulence mechanisms reflecting the presence of enterotoxin haemolysin, cytotoxin, protease, lipase, phospholipase, siderophore, adhesive factor and/or haemagglutinins.Haemolysin is an exotoxin that attacks blood cell membranes and causes cell rupture. Haemolysis, which results from the lyses of erythrocyte membranes with the liberation of haemoglobin, consists of β-haemolysis, i.e. the complete degradation of haemoglobin, and α-haemolysis, i.e. the incomplete degradation of haemoglobin. Haemolysins are produced by many different species of bacteria including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and vibrios. In most cases, epidemiological and experimental evidence suggests that haemolysins are involved in disease pathogenesis[16,24,27].In fact, studies have shown that the trh gene had significant nucleotide sequence homology with the tdh gene. The amino acid sequences of the haemolysin subunits deduced from the nucleotide sequences of the trh gene and tdh gene were homologous and contained the two cysteine residues to form an intrachain bond at the same positions[20]. Moreover, they have similar biological, immunological and physicochemical characteristics[12], which explains that the genes tdh and trh may have had a common ancestor and may have evolved by a single base change so they can maintain the basic architecture of the molecules.
4. Conclusions
- This study pioneers the demonstration of the presence of KP positive and trh V. alginolyticus in Morocco. The presence of pathogenic V. alginolyticus strains in seawater, plankton, sediment, and shellfish represent a risk of infection following exposure and indicates the potential sanitary risk associated with the presence of V. alginolyticus KP positive strains and those carrying the trh gene as pathogens implicated in cases of food poisoning[13].To conclude, our results suggest that a long-term monitoring program should be initiated to detect pathogenic V. alginolyticus KP positive strains and those carrying the trh gene in the aquatic environment during the warm summer months, when concentrations of this bacterium in Tamouda Bay are thought to be at their highest[23].
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- We thank all members of Royal Mounted Police brigade of M 'diq city for their help in carrying out the sampling as well as the The VibrioSea Consortium: Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), France, MEDIAS-France, Toulouse, France, Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS), Toulouse, France, Institut Pasteur (IP) Paris-France; IP Maroc; IP Algerie; IP Tunisie, Institut Agronomique et Vétérinaire Hassan II de Rabat, Morocco, Istituto di Scienze del Mare- ISMAR-CNR, Venezia, Italy, Institut Français de Recherche pour L'exploitation de la Mer (IFREMER), Brest, France, Department of Biology, University of Genova, Italy and Department of Pathology, University of Verona, Italy.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML