-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
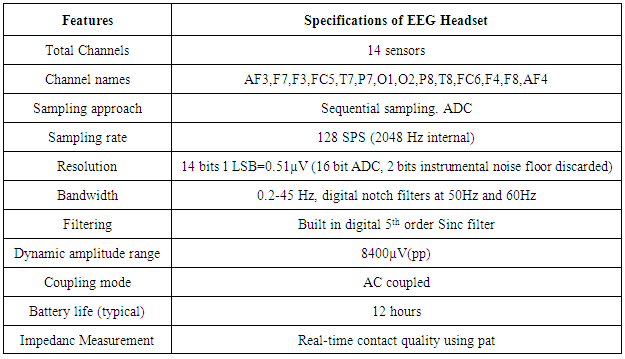
Electrical and Electronic Engineering
p-ISSN: 2162-9455 e-ISSN: 2162-8459
2017; 7(3): 69-76
doi:10.5923/j.eee.20170703.01

Evaluation of P300 based Lie Detection Algorithm
Syed Kamran Haider1, Malik Imran Daud2, Aimin Jiang1, Zubair Khan1
1Department of Internet of Things, Hohai University, Changzhou, China
2Department of Electrical Engineering, Foundation University, Rawalpindi, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Syed Kamran Haider, Department of Internet of Things, Hohai University, Changzhou, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Lie detection mechanism is used to evaluate the ethical and moral values of people. In general, these moral and ethical values are difficult to determine. Earlier technique like polygraph does not provide accuracy in determining mental behaviour. Lately, it is possible to study psychological response of a person using electroencephalogram (EEG). Based on this, we develop a standalone solution that can detect brain signals using EEG. To this end, we extract the desired features from the brain signals acquired through sixteen electrodes using various extraction techniques. Then, we implement linear discriminant analysis (LDA) classification technique to differentiate the positive and negative samples from the signals obtained from sensors in order to achieve a decision for either guilty subject or innocent subject accordingly. The whole work is designed with the help of MATLAB and Xilinx tool. For efficiency, the whole system is implemented on FPGA. The amount of correct deception detection in guilty and innocent subjects are 85%. It is easy and more convenient approach than other previously used methods.
Keywords: Event Related Potential, Linear Discriminant Analysis, P300 Features Extraction
Cite this paper: Syed Kamran Haider, Malik Imran Daud, Aimin Jiang, Zubair Khan, Evaluation of P300 based Lie Detection Algorithm, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 69-76. doi: 10.5923/j.eee.20170703.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Deception detection has drawn much value from scientific society in the past decades. It has found many applications related to psychological implications. In present, the older technique polygraph are widely used for the justification of deceptive and truthful behavior of subject [1]. A researchable analysis gives us an idea that, with the help of EEG signals we can easily monitor the psychological variations, brain activities and deception detection related features [2, 3].In decision making situation where scientific study gives us best solution which is relevant to the measurement of P300 event related potentials (ERP). The reason is to do so far is that cognitive disability is often associated with variations in the P300 potentials, the waveform can be helpful in treatments of cognitive task. There is a variety of uses for the P300 potential in scientific study, leading from study of depression and drug infatuation to anxiety dis-orders.Currently designed Brain Computer Interface (BCI) systems and prototypes are facing problems in slow communication channel. The transfer rate (ITR) between human brain and BCI prototypes are lower than 100 bits per minute [4]. A systematic framework for hardware BCI is implemented using FPGA [5]. The system utilizes a BCI hardware modular architecture based on FPGA and allows integrating the complete BCI on a single FPGA device. Our research aims to explore the possibilities of the high-speed recognition from EEG signals, and a standalone system that can be used as a lie detector with less processing time without any software involvement. But this achievement is reached at a price of implementing the whole work process on MATLAB and as well as on FGPA chip.In this research a system is designed to prove the feasibility of the whole concept of lie detector. The implementation of lie detector algorithm on FPGA and its interfacing with blue tooth module is the most critical step in our work. To reduce the development time that takes place at feature extraction and signal classification stage, high level synthesis approach is used. This approach is much better than the Register Transfer Language (RTL) flow, which can generate small enough design, such that it can fit the complete BCI pipeline into one FPGA device. Usage of LDA classifier synthesis speeds up the design process and allows us to work on a fairly high level of abstraction during the development of new algorithms. Further, high available computational power of FPGA device will allow us to integrate progressive non-linear signal processing algorithms like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Independent Component Analysis (ICA) for feature extraction. Compared to other known solutions of Transmit (Tx) part, Bluetooth Low Energy radio interface is proposed to keep the system power consumption as low as possible.The remaining paper is arranged as follows. In Section II, the methodology of proposed approach is discussed. Section III focuses on implementing results and some discussions are made. In the end, the conclusion is given in Section IV.
2. Test Based for Implementation using FPGA
2.1. Participants
- Twenty subjects (15 males and 5 females, ages between 20-25 years) that were generally universities students (undergraduate and postgraduate) and all had good health with stable psychological behavior participated in this study. Fig.1 shows the step-wise methods for the understanding of lie detector we have developed with some overview of the methodological analysis of this research.
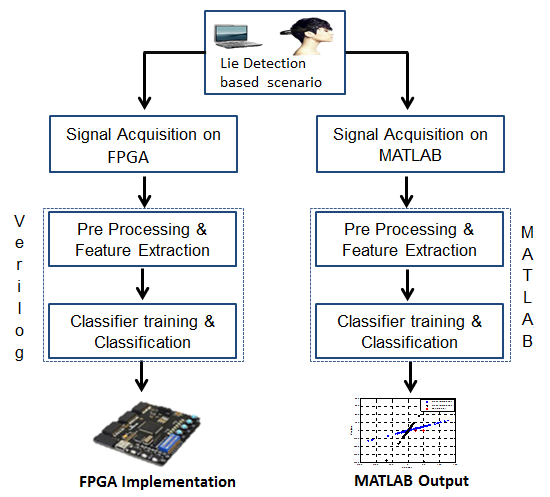 | Figure 1. Lie Detector Implementation flow chart |
2.2. Lie Detection Based Scenario
- We have recorded data of over 15 to 20 subjects. In one scenario, some precious items (e.g., jewelry, cash, smart phones, etc.) were placed in front of some subjects. Those subjects were not informed about the scenario and the subject can be any random person. Another person called as Subject-2 intended to perform this test come and stole that item that was placed in front of person called as Subject-1. It can be any person but suggestively that can be his/her close friend. As this test was performed in university, university authorities would handle the case of that stolen item [6]. This was done only to put our subject under pressure for lie and truth response. While conducting test in the presence of authorities our subject wore Emotiv EPOC headset. Some training data was collected to define the correct lie and truth classes. Training slides were prepared on MATLAB with defined time period (in our case 5 to 6 seconds for each question) of each image and questionnaire set. First some obvious questions were asked that everybody would answer the obvious answers, i.e., the true answer [7]. The instructions was also given to the subjects during the process to count the total number of questions asked by the investigator. This was essential to keep a record that our subject was mentally attentive and fluctuating thoughts did not come during the data acquisition process. Authenticity of data was achieved through counting. At the end, the subject was asked to inform about the total number of questions displayed [8].
2.3. Desired Signal Acquisition
- The brain signals were recorded with the sample rate of 128 samples per second. The recorded signals which were digitized and amplified can be monitored offline with the help of MATLAB software. Pass band filter were used with the range of 0.3-30 Hz prior to data analysis. For P300-based study about Guilty Knowledge Test (GKT) the previous mentioned pass band filter range were used [9]. The EEG signals from EPOC headset are itself digitized because headset contains the built-in analog to digital converter (ADC). The data can be received through the headset using Bluetooth receiver at reception end.The electroencephalogram (EEG) signals were recorded using 16 channels Emotiv EPOC headset. The position of the sensors is shown in Fig.2.
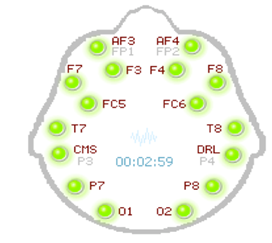 | Figure 2. Placement of electrodes |
|
2.4. Pre-Processing
- After applying pass band filter on EEG signals, each continuous subject record is divided into single sweep as per the times known by stimulus presentation [10]. The total length of each single sweep is 1000ms, and contains 128 samples. Then the signal pattern recognition technique includes special features extraction and features selection. After that apply classification method on the signals to assess the detection rate. It should be noticed that, in all cases related to P300 ERP the Pz is the prime location where P300 can be monitored maximal and therefore visual related experiments were performed only on Pz data [11].
2.5. Optimal Features Extraction
- The original recorded EEG signal is in time domain and the whole signal energy distribution is dispersed. The optimal features are suppressed with the noise. In order to dig out the features, EEG signal is observed under the signal energy in the form of time domain or frequency domain. The frequency domain analysis is the best for those features utilized in the mental task related to EEG signals [12].Two types of features were observed in this evaluation. These extracted features were also involved in similar studies and shown good performance and it is also useful for our application too.
2.5.1. Morphological Features
- Several morphological features (based on shape) were extracted and evaluated. It has; Latency time, Maximum Peak value of signal, Positive value in the signal, Total Area and some others as discussed in [14]. These optimal features were previously used in to identify depressive subjects by using P600 ERP of the signal [13].
2.5.2. Frequency Features
- This group of features has the frequency related characteristic of the signal [14]. It contains the features; mode, median and mean of the frequency.
2.6. Features Abstraction
- To determine the guilty and innocent response of the subject all the defined features from the probe sweeps were save in European data format (.edf) file. Then the analysis was applied to find out the most related features for the guilty subjects (G-Probes) and innocent subjects (I-Probes) at signal classification stage [15].
2.7. Signal Classification
- Extracted features were referred towards the LDA [16, 17]. This method has less computational requirement and it is more appropriate method for many pattern recognition related problems. In addition, LDA classifier is very simple to use and provides better results. The popularity of this classifier has been involved EEG processing, ERP related researches such as motor imagery based BCI systems, P300 speller and P300 component detection. This classification technique is more perfect and best practical processing method on data collected for P300 speller paradigm. Moreover, same like other classifier, LDA also share some drawbacks. Before applying P300 classifier on EEG signals, LDA needs to take the average of several trials to de-noise the background noise and increase the magnitude of P300 response for better results. Taking average of several trials is a time consuming step which greatly slows down the classification process and therefore it is not appropriate for real time P300 classification with single trial. It becomes our interest to implement algorithms for the detection of P300 in lie detection scenario [18].In our research we are following class depend approach. The mathematical model of the class depend transformation we adopted as follow:For better understanding of two-class problem, this concept is applied on 2-D data points. Mathematical interpretation of this classification method in cooperate with the MATLAB implementation allied with this work. The representation of 2-D data sets in the matrix containing features [19]:
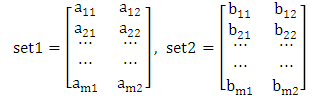 | (1) |
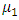 represents mean of data set1 and
represents mean of data set1 and 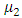 represents be the mean of data set2, respectively, and
represents be the mean of data set2, respectively, and 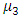 represents the entire data mean, which is calculated by inclusion of set1 and set2:
represents the entire data mean, which is calculated by inclusion of set1 and set2: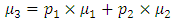 | (2) |
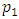 and
and 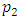 shows the two-class a prior probabilities. In our scenario of deception detection, the probability index is consider to be 0.5.(2) All the covariance matrices hold the symmetric property. Let cov1 represents the covariance of data set1 and cov2 represents the covariance of data set2. Covariance matrix is calculated with the help of following equation.
shows the two-class a prior probabilities. In our scenario of deception detection, the probability index is consider to be 0.5.(2) All the covariance matrices hold the symmetric property. Let cov1 represents the covariance of data set1 and cov2 represents the covariance of data set2. Covariance matrix is calculated with the help of following equation.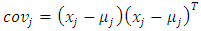 | (3) |
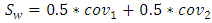 | (4) |
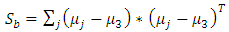 | (5) |
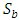 can be represented as the covariance of data sets whose elements belongs to mean vector of each class. As defined before, formulation of optimization criterion in classification of LDA is the proportion of between-class distribution to within-class distribution. The solution achieved by maximizing this criterion represent the axes of new transformed space. Moreover in class-dependent case the optimizing criterion is calculated by using mention above equations. It should be verified that in class dependent LDA type, for L-class type L separate optimizing criterion are needed for each single class as calculated in Eq (6).(5) The optimizing index in case of class dependent type are computed as:
can be represented as the covariance of data sets whose elements belongs to mean vector of each class. As defined before, formulation of optimization criterion in classification of LDA is the proportion of between-class distribution to within-class distribution. The solution achieved by maximizing this criterion represent the axes of new transformed space. Moreover in class-dependent case the optimizing criterion is calculated by using mention above equations. It should be verified that in class dependent LDA type, for L-class type L separate optimizing criterion are needed for each single class as calculated in Eq (6).(5) The optimizing index in case of class dependent type are computed as: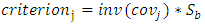 | (6) |
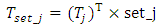 | (7) |
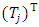 is the transpose of the Eigen vector which is obtained from the
is the transpose of the Eigen vector which is obtained from the 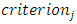 of each sets and set_j are the data set 1 and data set 2. (7) Once the transformation are concluded using LDA transformation, then Euclidean distance or Root mean square (RMS) distance is used for the classification of data points.
of each sets and set_j are the data set 1 and data set 2. (7) Once the transformation are concluded using LDA transformation, then Euclidean distance or Root mean square (RMS) distance is used for the classification of data points. 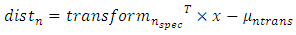 | (8) |
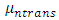 is the mean of the transformed data set, n is the class index and x is the test vector. For n classes n, Euclidean distances are obtained for each test point. The smallest Euclidean distance among the distances classifies the test vector as belonging to class n.
is the mean of the transformed data set, n is the class index and x is the test vector. For n classes n, Euclidean distances are obtained for each test point. The smallest Euclidean distance among the distances classifies the test vector as belonging to class n.2.8. FPGA Implementation
- The contribution presents a novel high performance, low power BCI architecture allowing a single-chip implementation of a BCI device. FPGA platform is used to reach high performance and low power consumption; to speed up the classification process, high-level synthesis of signal processing algorithms is employed by research scientists. FPGA architecture has many advantages i.e. configurability, possibility of independent development, topological compatibility, scalability, and high computational power as proposed for P300 based lie detector implementation [20].Usage of developing the whole system on FPGA synthesis speed up the design process and allows us to work on a fairly high level of abstraction during development of new algorithms. Further, high available computational power of the FPGA device will allow us to integrate progressive non-linear signal processing algorithms like PCA and ICA for feature extraction. Compared to other known solution of the Transmit (Tx) part, Bluetooth Low Energy radio interface is proposed to keep the system power consumption as low as possible.Hardware descriptive language (HDL) model needs to be transformed into binary stream before it can be coded to FPGA. ELBERT series related chips can only accepts binary (.bin) data bit stream created by XILINX software tool kit. Once HDL model is synthesized, it is more easy and convenient to produce a binary data bit stream out of it. The Papilio Pro board uses the FT2232 dual channel interface USD chip that helps for the easy reprogramming of SPI flash [21]. The .mat extension file load from the host application (MATLAB) and program it in to SPI Flash memory and then lets the FPGA boot from the flash.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MATLAB Simulation Results
- As given in first scenario, the training data sets of two classes i.e. the lie & truth data sets are plotted corresponding to one another. Set1 is the truth data set class whereas set2 belongs to lie data sets.Data sets are transformed through LDA classifier. Mean, variances, co-variances are calculated. Increase of separability criterion by the calculation of between and within class variances. In this project, class dependent transformation is applied because the objective is to maximize adequate class separability measure. Test vector is the target data, which need to be calculated that to which class it belongs. In the following figure it is clearly shown that vector set lies at minimum distance to the transformed set1 which is data set of truth class. This shows honest behavior of subject. On the other hand if the test vector lies at minimum distance to the transformed set2 i.e. lie data set, the subject is lying.The Figure 3. indicates the data sets of lie and truth classes. The data sets of two classes are scattered randomly which would not provide the required information needed to separate the classes. The values are also normalized in feature vector set to remove the noise content of EEG signal.LDA maximizes the separability measure of the two classes, which are shown in the next figure.
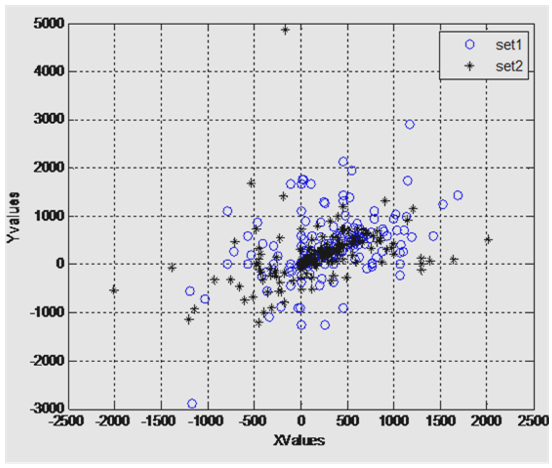 | Figure 3. Training data of truth & lie sets (subject 1) |
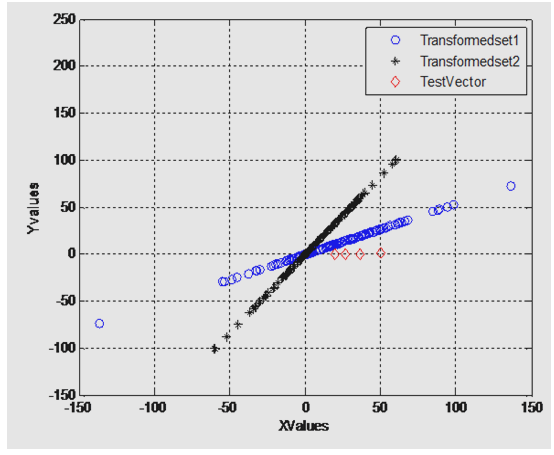 | Figure 4. Target data indicating it belongs to transformed set 1 (the truth response) |
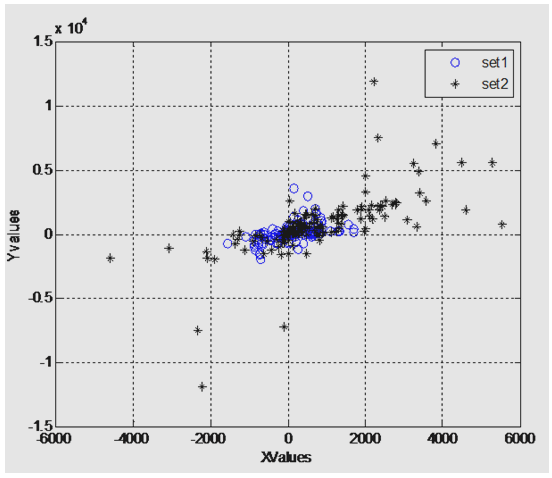 | Figure 5. Training data of truth & lie sets (subject 2) |
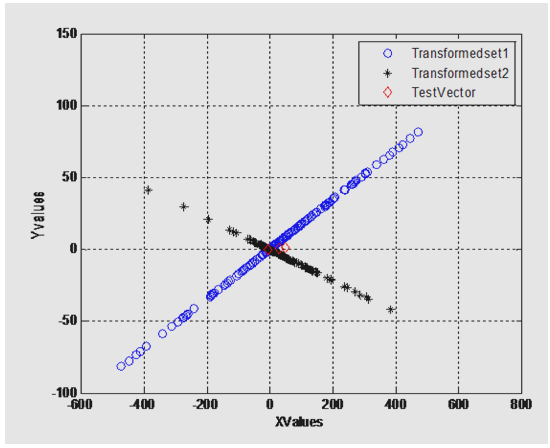 | Figure 6. Target data indicating it belongs to transformed set 2 (the Lie response) |
3.2. FPGA Implementation Results
- After the implementation of algorithm on MATLAB the next step is move towards the FPGA. The main theme is to implement the algorithm on FPGA to make a standalone system for lie detector. Software based implementation needs much time to execute the code based on complex equation. The processing speed of FPGA is faster due to data flow programming and even we can perform all of those steps simultaneously and control the specific timing for each step. Moreover, because FPGA prototypes run faster, larger data sets can be used, potentially exposing bugs that would not be uncovered by a simulation model. Model-Based Design using HDL code generation enables teams to produce the first prototype faster than a manual workflow. That’s the reason behind the evaluation of lie detector on FPGA chip. If we connect headset with the FPGA using Bluetooth then there is no need for the intermediate device to monitor the signals. We can display the result on output port of FPGA using red and green light using with the help of screen display. In this section using Verilog coding the lie detection algorithm were implemented after verifying the MATLAB results. The FPGA kit is of Xilinx Company (Papilio Pro) is used. We used ISE 14.2 suit of Xilinx for writing the Verilog Coding.The first case is about the innocent person and the below results shows the execution of first case. In the same manner like MATLAB after extracting the desired features from training data and testing data all values were stored on (.mat) file.
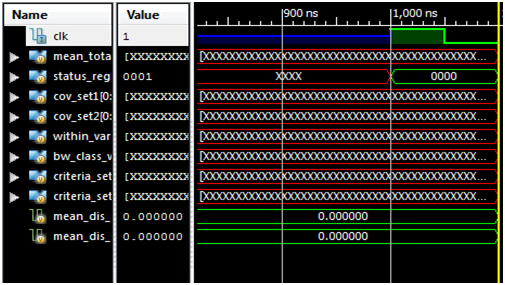 | Figure 7. FPGA reset state |
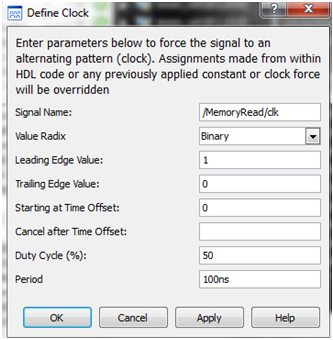 | Figure 8. FPGA clock frequency adjustment |
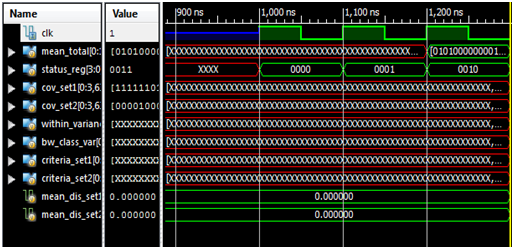 | Figure 9. Reading the Test vector, set1 & set2 data on the next leading edge of clock |
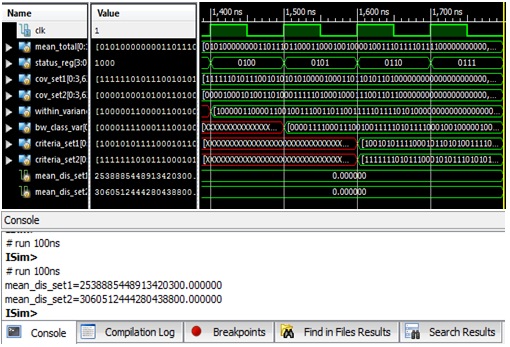 | Figure 10. Calculate Euclidean distance for both set1 & set2 |
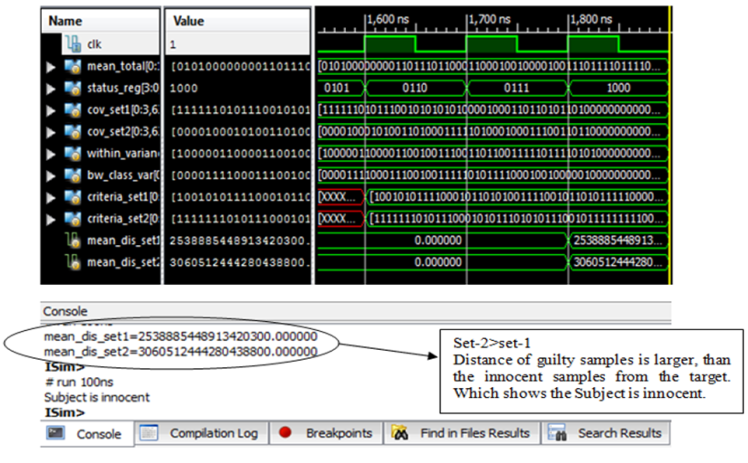 | Figure 11. Output of FPGA (Innocent response of subject) |
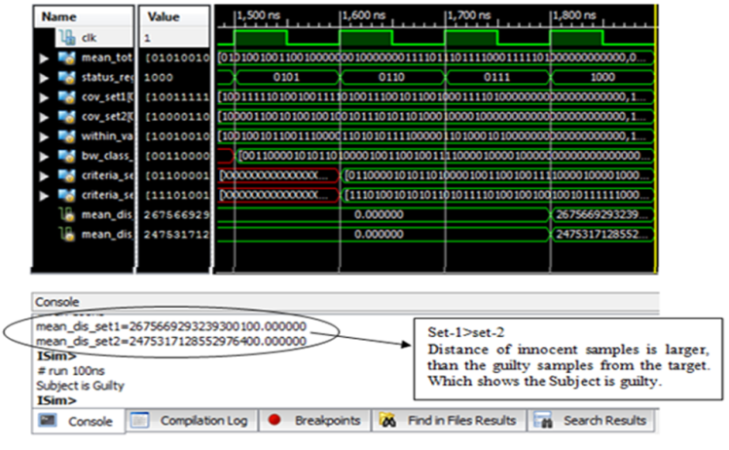 | Figure 12. Output of FPGA (Guilty response of subject) |
4. Conclusions
- In this research, it becomes the determination and motivation to hardware (FPGA) implementation of the algorithm; P300 component analysis based on LDA classification technique with P300 peak values corresponding to each channel of electrode. We have achieved 85% accuracy in detecting lie and truth subjects. Simulation results on MATLAB is achieved by acquiring signals on Emotiv headset whereas on FPGA simulation is attained by converting the .edf format into .mat format and loaded it into the Papilio pro. Emotiv headset is the latest device that can map the EEG signal more accurately and with good signal to noise ratio. The filters that are used in headset digitized the signal and send to the Bluetooth receiver and we can monitor the signals on our systems. Our research is targeted to the evaluation of the high processing speed recognition from the EEG signals and makes a standalone system, which can be used as a lie detector. However, this achievement was reached at a price of implementing the whole algorithm on MATLAB and FPGA.In terms of cost analysis the FPGA device is cheaper than the super computers to execute the heavy programs and the execution time of hardware is better than the software simulation of code. In the old methodology like polygraph to detect lie heavy machines were used to generate the reports. This new system eliminates the cost of heavy machines and gives the idea to build a standalone system using a small hardware device with good performance ability. However, with the emerging technology of latest products new methods are still under consideration to give the better output.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This work was supported in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under grants 61101158, 61471157, and 61401148, and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China under grants BK20130238, BK20141159 and BK20141157, and Science &Technology Program of Changzhou, China under Grant CJ20159039.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML