-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Electrical and Electronic Engineering
p-ISSN: 2162-9455 e-ISSN: 2162-8459
2012; 2(2): 18-22
doi: 10.5923/j.eee.20120202.04
Effect of Ag-Doping on the Capacitive Behavior of Amorphous Manganese Dioxide Electrodes
Sameh Hassan 1, Masaaki Suzuki 2, Ahmed Abd El-Moneim 3
1Energy Resources and Environmental Engineering Department, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El Arab City, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt
2Department of Chemical Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 2-12-1 O-okayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, 152-8552, Japan
3Material Science and Engineering Department, Egypt- Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El Arab City, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt
Correspondence to: Sameh Hassan , Energy Resources and Environmental Engineering Department, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El Arab City, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Amorphous MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 thin films were galvanostatically deposited on a polished stainless steel substrate from 20 mM KMnO4 aqueous solutions without and with AgNO3 additions at cathodic current density of 1 mA/cm2 for the application in electrodes of electrochemical supercapacitors. The supercapacitive properties of the deposited thin films have been studied in 0.5 M Na2SO4 electrolyte by cyclic voltammetry, impedance spectroscopy, and charge-discharge measurement techniques. The Ag-free MnO2 film showed better capacitive behavior and lower charge transfer resistance compared to the Ag-doped MnO2 films. The specific capacitance and charge transfer resistance values for Ag-free MnO2 films were 160 F/g at a scan rate 10 mV/s and 3.87 Ω, respectively. Cyclic stability using charge-discharge measurement technique indicates the excellent stability of Ag-free MnO2 films and its possible use as a low cost electrode for supercapacitor applications.
Keywords: Cyclic Voltammetry, Manganese Dioxide, Power Density, Energy Density, Cyclic Stability
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Several energy storage devices, such as compressed air, hydrogen, flywheels, batteries, capacitors, and fuel cells, have been developed for various practical applications. Among these devices, high performance batteries and capacitors have presented themselves as one of the achievable, economically feasible options for meeting today’s severe energy demands. Supercapacitors have received a lot of attention as viable electrical energy storage devices owing to their ability to deliver high powers, excellent reversibility, and longer cycle life than batteries[1-3]. On the basis of the energy storage mechanism, supercapacitors can be classified into two categories[4-6], namely the electrical double-layer capacitor (EDLC) and the pseudo-capacitor. The capacitance of the former comes from the charge accumulation at the electrode/electrolyte interface (double-layer capacitance), therefore it strongly depend on the surface area of the electrode accessible to the electrolyte. The capacitance of the latter is due to the reversible faradic transfer of charge between electrode and electrolyte, such as surface functional groups and transition metal oxides. Supercapacitors fill the gap between batteries (low specific power and high specific energy) and conventional capacitors (high specific power and low specific energy), i.e. they have a specific power as high as conventional capacitors and a specific energy close to that of batteries. It is obvious that the electrode is the key in the development of supercapacitors.MnOx is a promising electrode material for electrochemical capacitors because of its the relatively low cost, excellent electrochemical performance, environmentally friendly character in comparison with the ruthenium oxides or other transition metal oxides[7-9]. Hydrous ruthenium oxide has been extensively studied[10,11] as an active electrode material for supercapacitors with capacitance as high as 720 F/g in aqueous acidic electrolytes. Although RuO2 gives high specific capacitance, its disadvantages of high cost and toxic nature limit its further commercial application. As an inexpensive alternate to RuO2, hydrous manganese oxide prepared by both chemical and electrochemical methods was found to possess capacitive characteristics with acceptable values of specific capacitance[12-16]. A specific capacitance of 130 F/g was reported[16] at a scan rate of 5 mV/s, for manganese dioxide synthesized by sol–gel method.Recent investigations showed that 1–8 wt.% Ag addition to lithium manganese dioxide electrode can significantly improve battery performance due to the increase in conductivity[17]. In another investigation the increase in conductivity of Ag-doped RuO2 compared to pure RuO2 was reported[18]. As a result, Ag-doped RuO2 showed much higher SC compared to the SC of undoped RuO2[18]. Therefore, it is important to fabricate and investigate the Ag-doped MnO2 films. MnO2 films for application in electrochemical supercapacitors (ES) can be prepared by anodic or cathodic electrodeposition from aqueous solutions. However, anodic electrolytic deposition of MnO2 on metallic current collectors presents difficulties related to the anodic oxidation and dissolution of metals. In contrast, cathodic electrodeposition can be performed on various metallic substrates. It should be noted that cathodic electrodeposition is an important industrial technique for the deposition of metals. Therefore, cathodic electrodeposition is a promising method for the co-deposition of oxides and metals and the fabrication of doped films and composites.The goal of the present study is to fabricate Ag-free MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 thin films by galvanostatically cathodic deposition on polished stainless steel substrate from KMnO4 aqueous solutions without and with AgNO3 additions for the application in electrodes of ES.
2. Experimental
- Stainless-steel (SS) sheet of grade 316 LN, thickness 0.25 mm and surface area of 6 mm × 15 mm was used as current collector and substrate for the electrodeposition of the active materials. Prior to the electrodeposition experiments, the substrate were mechanically polished with SiC papers down to 2000. MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 thin films were galvanostatically deposited from 20 mM KMnO4 solution without and with AgNO3 additions (0.5, 2, and 4 mM) at cathodic current density of 1 mA/cm2 onto SS substrate for 0.5 hour. The weight of the deposited films was measured by means of a Sartorius micro-balance (Model BP211D). The structure was characterized by means of X-ray diffractometer (Shimadzu, XRD-7000) using Cu Kα radiation.All electrochemical investigations were performed at 30±1.0C using two compartment three electrodes electrochemical cell with platinum foil as an auxiliary electrode and a saturated Ag/AgCl reference electrode. The capacitive performance of the deposited films was examined in 0.5 M Na2SO4 electrolyte using the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammtery (CV) measurement techniques, and galvanostatic charge–discharge. The CV measurements were carried out at potential ranges of 0–0.9 V vs. Ag/AgCl (sat.) at scan rates of 10–90 mV/s. The excitation amplitude for impedance measurements was 10 mV root mean square (RMS) in a frequency domain of 10-1 to 105 Hz.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure
- Figure 1 shows XRD patterns of Ag-free MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 thin films prepared by galvanostatic cathodic deposition method on polished SS substrate from 20 mM KMnO4 aqueous solutions without and with 2 mM AgNO3 addition at 1 mA/cm2. As seen, the XRD patterns show no reflection peaks typical characteristics of any crystalline or nanocrystalline MnO2–based oxide films. This indicates the formation of amorphous Ag-free MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 thin films with very high degree of structure disorder.
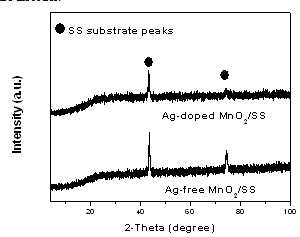 | Figure 1. XRD patterns for Ag-free MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 (2 mM AgNO3) films deposited on polished SS substrate |
3.2. Supercapacitive Properties of the Deposit Film
3.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
- Figure 2 shows the CV curves of the Ag-free MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 films in the potential range of 0–0.9 V vs. Ag/AgCl (sat.). All the curves are near-rectangular in shape and show symmetrical anodic and cathodic halves which indicate ideal capacitive behavior of the deposited films. As it can be seen in Fig. 2, the capacitive current density of Ag-free MnO2 is higher than those of Ag-doped MnO2.
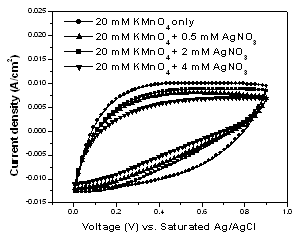 | Figure 2. Cyclic voltammetric curves of Ag-free MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 films measured in 0.5 M Na2SO4 solution at a scan rate of 90 mV/s |
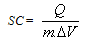 | (1) |
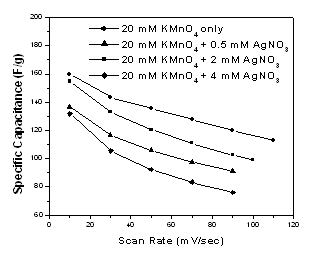 | Figure 3. Variation of the specific capacitance with the scan rate of CV measurement for MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 films |
3.2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
- In principle, the power output capability of electrochemical supercapacitor depends strongly on not only the rates of ionic mass transport[20] but also the equivalent series resistance (ESR)[21]. The ESR is the sum of two major parts, an electronic resistance and an ionic one. EIS has been widely used to study the redox (charging/discharging) processes of electrode materials and to evaluate their electronic and ionic conductivities. Figure 4 shows the measured Nyquist plots of MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 electrodes in 0.5 M Na2SO4 electrolyte. The inset of Fig. 4 represents the high frequency region of the recorded full impedance plots. In Fig. 4, two well-separated patterns are observed: an arc is obtained at frequencies high enough, which is related to interfacial processes; the low-frequency region of such plots indicated a capacitive behavior related to the film charging mechanism.
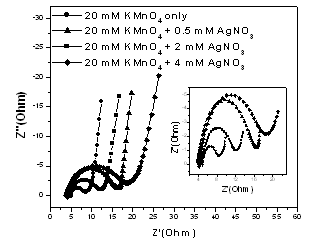 | Figure 4. The Nyquist plots of MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 electrodes investigated in 0.5 M Na2SO4 electrolyte in the frequency range of 0.1 Hz–100 kHz at 10 mV amplitude |
3.2.3. Galvanostatic Charge–Discharge
- Figure 5 presents the charge–discharge curves for the films deposited from 20 mM KMnO4 aqueous solutions with 0.0, 0.5, 2, and 4 mM AgNO3 additions. The curves were measured in the potential range between 0 and +1 V at a discharge current density of 1.1 mA/cm2. In Fig. 5, there is a linear variation of potential during charging process, indicating the capacitive behavior of MnO2 and Ag-doped MnO2 films. The discharge part of the curves consists of three segments: a resistive component from the sudden decrease of voltage (iR drop) related to the internal resistance of the deposit, the capacitance component which is related to the voltage change due to ions separation at electrode interface in the double layer region and the faradaic component which is attributed to charge transfer reaction of deposit. Detailed analysis of the results in Fig. 5 clearly shows that the Ag-free MnO2 film has longer time for charging-discharging processes and lower iR drop value than those recorded for Ag-doped MnO2 deposited films. These facts indicate the higher energy and power densities of Ag-free MnO2 than those of Ag-doped MnO2.
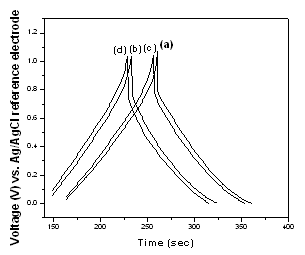 | Figure 5. Charge–discharge curves in 0.5 M Na2SO4 electrolyte for thin films deposited from 20 mM KMnO4 aqueous solutions with (a) 0.0 M AgNO3, (b) 0.5 mM AgNO3, (c) 2 mM AgNO3, and (d) 4 mM AgNO3. |
3.2.4. Cyclic Stability using Galvanostatic Charge–Discharge
- The cyclic stability test of Ag-free MnO2 film was performed at discharge current density 5.5 mA/cm2 and the results are presented in Fig. 6.
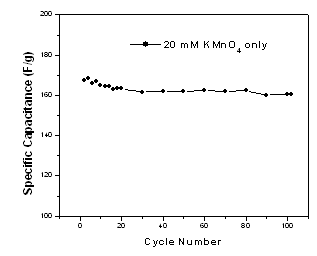 | Figure 6. Life-cycle data of the Ag-free MnO2/SS electrode at discharge current density 5.5 mA/cm2 |
4. Conclusions
- The results presented in this investigation indicated that amorphous Ag-free and Ag-doped manganese dioxide thin films were successfully prepared by galvanostatic cathodic deposition onto polished SS electrodes from KMnO4 solution without and with AgNO3 addition. The Ag-doped manganese MnO2 films showed lower capacitive behavior and higher charge transfer resistance compared with Ag-free MnO2 deposited film. The specific capacitance and charge transfer resistance values for Ag-free MnO2 films were 160 F/g at a scan rate 10 mV/s and 3.87 Ω, respectively. The Ag-free MnO2 film prepared by the cathodic electrolytic deposition on low cost stainless steel substrate can be considered as possible electrode materials for supercapacitor application.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors gratefully acknowledge the Missions Sector-Higher Education Ministry, Egypt for financial support through this work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML