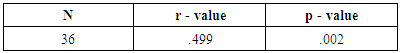-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Education
p-ISSN: 2162-9463 e-ISSN: 2162-8467
2017; 7(3): 53-57
doi:10.5923/j.edu.20170703.03

Academic Achievement as Influenced by Sports Participation in Selected Universities in the Philippines
Rona C. Montecalbo-Ignacio1, Rodolfo A. Ignacio III2, Merites M. Buot1
1Department of Human Kinetics, College of Arts and Sciences, University of the Philippines Los Baños, Philippines
2Department of Physical Education, College of Arts and Sciences, Laguna State Polytechnic University, Los Baños Campus, Philippines
Correspondence to: Rona C. Montecalbo-Ignacio, Department of Human Kinetics, College of Arts and Sciences, University of the Philippines Los Baños, Philippines.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Issues and deliberations concerning sports participation and academic achievement have been heard for decades. Sports enthusiasts were claiming that participation in any sports help the student-athletes to have “a sound mind and a sound body” individual. However, some people in the academe believed that sports participation hindered students’ ability to excel in their academic courses because most of their times were allotted into sports commitments such as training and competitions than studying alone. Some critics further believed that there was no possibility that the student-athletes achieve excellence in sports as well as in academics at the same time. The present study examined the relationship between sports participation and academic achievement of thirty-six (36) randomly selected collegiate athletes who participated in the National State Colleges and Universities Athletic Association Competition. They were taking up different academic courses. While in the university academic achievement was measured based on their general weighted average (GWA). Secondary data on 1st and 2nd semesters of AY 2014-2016 GWA were used in the analysis. The results of the study revealed that there was a significant relationship between sports participation and academic success of the student-athletes. Sports participation improved athletes’ perceptions on academic excellence, mental processes and becoming more logical and patient. A significant improvement regarding class attendance of the student-athletes was also noticed.
Keywords: Philippines, Collegiate athletes, Sports participation, Academic achievement
Cite this paper: Rona C. Montecalbo-Ignacio, Rodolfo A. Ignacio III, Merites M. Buot, Academic Achievement as Influenced by Sports Participation in Selected Universities in the Philippines, Education, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 53-57. doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20170703.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Sports involvement and academic success of student-athletes had been a topic of discussion long time ago. Critics observed that participation in sports may reduce the time available for studying and learning [17], since students-athletes were having difficulties in managing their time between hectic schedules of sports training and requirements of academic subjects [14]. However, sports enthusiasts claimed that sports participation can motivate student-athletes to achieve harder, raise scholastic ambition, can keep them attending school, can improve students’ academic grades [7], develop awareness the benefits of good health, fitness and exercise, and understanding the spirit of team work, sportsmanship and camaraderie [16]. In addition, researches showed pieces of evidence that student participating in sports and physical activities lead to developed mental and physical alertness [9], mentally and physically alert students always improved their performances, accomplished more, and likely to continue attending classes in school [22]. Majority of the previous researches were conducted with high school student-athletes participants, their academic achievement were measured based on their GWA (general weighted average) on general subjects such as English, math, and science. The present study examined the relationship between sports participation and academic achievement of collegiate student-athletes. Participants were from engineering, education, criminology, information technology, hotel restaurant management, food technology, agriculture, fishery, and forestry courses in the different universities. Their academic achievements were measured and compared in terms of gender based on their GWA (general weighted average) on major subjects acquired on the 1st and 2nd semester of academic year 2014-2016. Student-athletes were also asked regarding their perceptions on their improvement regarding academic excellence, mental processes, logic, patience, and class attendance. Results of the study will generally help the student-athletes to get the support they need from their parents, relatives, friends, teachers and professors. It is also an eye opener for school administrator and other critics that participation in sports are not just for fun, leisure, nor hindrance to the future academic success of the student-athletes, hence, it will be a great help for them to push harder, become more active in school, more positive in life, to develop self-discipline, promote fitness and wellness, friendship and camaraderie. In addition, coaches and trainers of various universities should have a closer monitoring on both athletic and academic performances of the student-athletes all through out the school year not just prior to competition.
2. Materials and Method
- A total of thirty-six randomly selected student-athletes (16 females and 20 males) aged 16-24 participated in this study. They were taking up different major courses in two different Universities; from the University of the Philippines Los Baños: Engineering, Agriculture, and Forestry while from Laguna State Polytechnic University – Los Baños Campus: Education, Information Technology, Criminology, Hotel and Restaurant Management, Food Technology, and Fisheries. Student-athletes were those who participated in the National State Colleges and Universities Athletic Association representing Region IV-A from Los Baños area. The National SCUAA tournament was the highest level of Regional competition in the Philippines. Structured questionnaire following the 5 point Likert scales ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree was prepared. Transcripts of records of the student-athletes were also collected for the basis of their general weighted average from academic year 2004-2016.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Perceived Academic Improvement of Student-Athletes in Terms of Gender
- Student-athletes participants were asked on their perception regarding improvement on their academic excellence, mental processes, logic, patience, and class attendance. Figures 1 and 2 show the perceived academic improvement of male and female student-athletes. In the statement “my idea about academic excellence improves” majority of the male (30%) strongly agreed compared to 13% from female student-athletes. Result of this study validates the study of Prasad [15] that male students who participated in sports demonstrated higher level of academic achievement than female student-athletes. In the statement of “my mental processes improves” majority of the student-athletes (50%) males and (38%) females strongly agreed. This result supported Bailey [1], Coe and colleagues [4], Mahar colleagues [11], Taras [22], Miller and colleagues [12], and Darling and colleagues [6] that participation in sports and physical activities increase the blood flows to the brain increases individual’s mental alertness, improves learning and memory, self-esteem, self-confidence, social development, and reduces feeling of boredom and depression. On the other hand, the statement “I am more logical” 55% male while 13% female student-athletes strongly agreed. Result indicated that male athletes perceived more logical than female, this was due to the fact that male were less emotional than female. In relation to sports, male tend to easily accept why he or his team lost a game and be able to recover in a short period of time, while female were more emotional, most of the time blamed herself or themselves why she or her team lost a game, cannot easily recover and sometimes withdrew from the sports she/they participated in. On the statement “I have more patience” 40% male and 44% female strongly agreed. Result of this study confirmed the study of Rasmussen [16] that sports participation promoted discipline and developed friendship to every athletes. However, a deeper analysis of data indicated that 5% male while none of the female student-athletes strongly disagreed. This result proved that in general men were more impatient than women. In relation to sports, male athletes became impatient particularly when it comes to officials decisions, bias calls from referees and umpires, and body contact from opponents. These might cause unsportsmanlike conduct that will lead the athletes to be thrown out from the game or disbanded permanently from any sports competition. From the statement “I want to attend classes regularly” 35% male and 56% female strongly agreed. Result of this study supported previous findings that sports participation and physical activities help students concentrate better in class [25] and like to continue attending classes in school [22]. However, a further analysis of data showed that 10% of the male student-athletes disagreed. This result clearly showed the fact that male and female was different when it came to their priorities. In relation to sports, some of male athletes knew what they wanted and prioritized their performances in sports rather than performances in school. The male athletes displayed focus on what they really enjoyed on what they really wanted and loved to do rather than what they needed to do while female athletes were the opposite. Female athletes prioritized their school performances among others. Based on interviews with former female athletes who are professionals now, they revealed that they gave up their sports career before and prioritized their study and became who they are now.
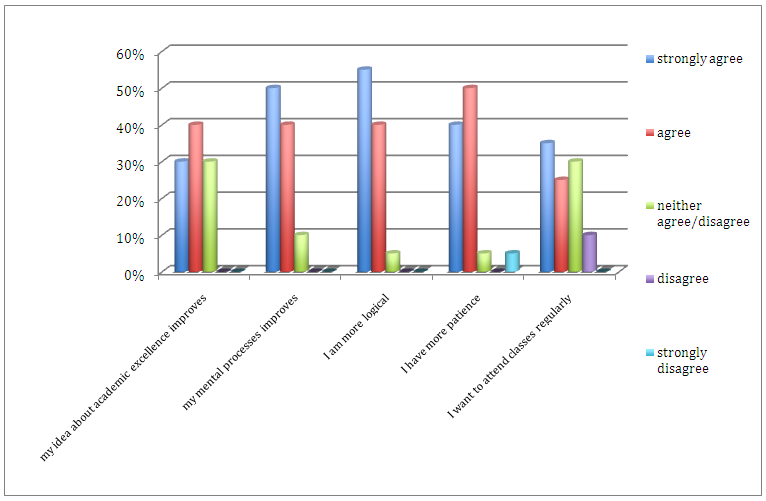 | Figure 1. Perceived academic improvement (%) of male student-athletes |
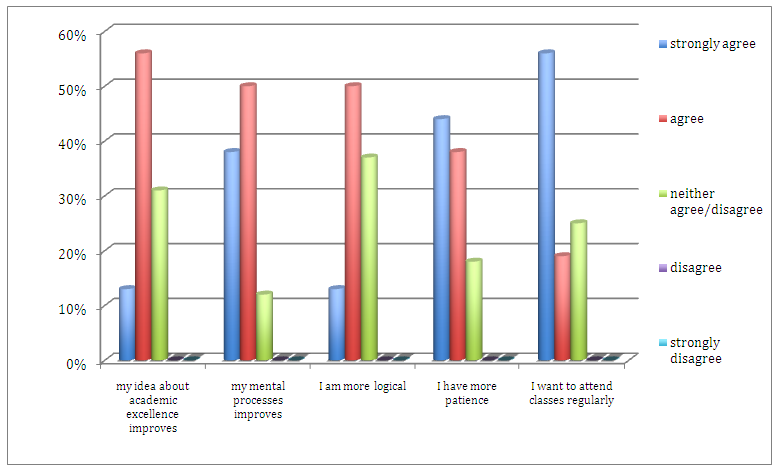 | Figure 2. Perceived academic improvement (%) of female student-athletes |
3.2. Comparison of General Weighted Average of Student-Athletes in Terms of Gender
- Figure 3 shows the general weighted average of male and female student-athletes from AY 2014-2016. General weighted average of male and female student-athletes were consistently changing and becoming better every semester. Results of this study validated the previous findings that learning efficiency increased with sports participation [24], increased development and a higher degree of academic achievement [3] and through sports participation student-athletes attained higher school grades more successfully [5, 7]. This strongly indicated that participation in sports and physical activities did not harm students academically [18]. However, in comparison of the general weighted average of the male and female student-athletes who participated in this study, it showed that female athletes (2.16) got consistent higher grades from AY 2014-2016 respectively than their male (2.49) counterpart. Results of this study contradicted the findings of previous study that sports participation was positively associated with higher academic grades for male athletes participants [8, 10, 15], and that female athletes recorded to have a much poorer academic grades [13]. Though, it confirmed the results of study of Stephen and colleague [21], Schlesser [19], and Sitkowski [20] that female athletes significantly got higher and better grade than male athletes.
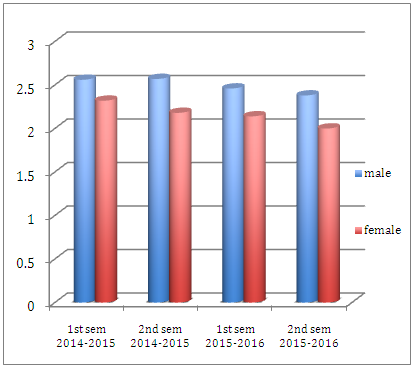 | Figure 3. General Weighted Average of male and female student-athletes from AY 2014-2016 |
3.3. Relationship between Sports Participation and Academic Achievement
- Sports participation of the respondents were measured based on the number of years the student-athletes participated in their respective sports while the academic achievement measured based on their general weighted average (GWA) from academic year 2014-2016. Table 1 shows that almost 25% of the variance of the number of years the student-athletes participated in sports was predictable from the variance of the general weighted average the student got in four semesters (2014-2016). Thus, the number of years the student-athletes participated in their respective sports and their general weighted average were strongly positively correlated r (36) = .499, p = .002. Result of this study indicated that the longer the student-athletes involved in sports the better the academic grades. This result validates the study of Tower [22] and Buot and colleagues (2) that if the student-athletes spent majority of their lives participating in sports were considered themselves as naturally competitive individual not just in sports but also in academic grades as well.
|
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
- This particular study showed that there was really a link between sports participation and academic achievement of the student-athletes. Sports participations developed and enhanced academic excellence, self-discipline, mental/cognitive development and class participation of student-athletes. Sports involvement have positive influence on memory, students’ concentration in education, increased learning efficiency, attained higher degree of academic achievement, and obtained higher school grades.Looking at the relationship presented in the data analysis, this is a good point for the parents, school administrator, teachers, and professors to support the students who want to pursue their passion in sports. Since sports involvement not just develop the physical appearances and physical fitness of the student-athletes but also enhance and mold their attitude towards positive behaviors, self-discipline, mental alertness, and help them grow into a more confident individual.School policy makers should give consideration on the academic and training schedules of the student-athletes by giving them a priority on the enlistment process for the student-athletes to find academic schedule that suits to their time for them to have enough preparation and recovery after long and tiring day of training schedule and competitions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to acknowledge the student-athletes participants from the University of the Philippines Los Baños and Laguna State Polytechnic University – Los Baños Campus for the time they spent completing the questionnaires and Dr. Marcial M. Bandoy for the statistical analysis of this study. No grant money or other financial support was received during the conduct of this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML