-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Education
p-ISSN: 2162-9463 e-ISSN: 2162-8467
2017; 7(2): 17-21
doi:10.5923/j.edu.20170702.01

Assessment of Undergraduate Long Vocation Training (LVT) Students’ Research Projects
1Department of Education Foundations, Faculty of Technology Education, Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University, Bauchi, Nigeria
2School of Technical Education, Federal College of Education, Technical, Bichi, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Aminu Yusuf, Department of Education Foundations, Faculty of Technology Education, Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University, Bauchi, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Content analysis of research projects submitted by undergraduate LVT students was made based on conceptual analysis on check list of six concepts: research objectives, research questions/hypotheses, research design, data collection instruments, and procedures for data analysis and presentation. The population of the study consisted of 115(75 from the department of Vocational and Technology Education, VTE and 40 from the department of Science Education, Sci. Edu.) final year 2009/2010 academic session undergraduate LVT students’ research projects. A total of 86(56 VTE and 30 Sc.Edu) research projects were proportionate randomly selected and analyzed. The study revealed that only 37.20% of undergraduate LVT students used correct data analysis technique on the research project to Faculty of technology Education (FTE), Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University, (ATBU) Bauchi-Nigeria. Orientation lecturers on research proposal; similar study to be carryout to justify the findings or otherwise of this study were among the recommendations made from the study.
Keywords: Assessment, Long Vocation Training Students, Research projects
Cite this paper: Aminu Yusuf, Sule Musa, Assessment of Undergraduate Long Vocation Training (LVT) Students’ Research Projects, Education, Vol. 7 No. 2, 2017, pp. 17-21. doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20170702.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Assessment as used in this context refers to direction for action based on the outcomes and recommendations of this study. Long Vocation Training (LVT) or Sandwich is a program designed for members of the public especially school teachers who could not join regular degree program run by universities to pursue degree program on vocation periods. Depending on the institution the LVT program leading to the award of degree certificate last for 6- 7 years. The LVT students like regular students are expected to carry research project work popularly known as Undergraduate Research Project (URP). URP as inquiry or investigation conducted by an undergraduate student that makes an original intellectual or creative contribution to the discipline (area of student specialization) [4]. A research project is an essential aspect of many undergraduate degree programs [10]. It provides experience of writing in the discipline and given chance to be creative [2]. URP accords undergraduate students with experience that allows the students to better understand published works learn to balance collaborative and individual work [11]. For the student to conduct research work which is free of research misconduct (fabrication, falsification or plagiarism in proposing, performing or reviewing research results [14]) supervisor is appointed by the departmental URP coordinator. Undergraduate Research Project Supervision (URPS) refers to a series of collaborative interaction between the supervisor and the student in which the student is intellectually engaged in the scholarly research problem or program [4]. It is one-to- one interaction between a supervisor and a student [15], and for supervision to be effective, its require supervisor to be knowledgeable, and skilled in the research field [1]. Poor supervision can have a significant impact on students, not only limiting the quality of their work, but also their motivation [15]. Despite the fact that, student work with the supervisor, the URP associated with problems. The URP is associated with problems of relying too much on Google, Wikipedia and information from non scholarly websites, not making careful use of scholarly sources available in library and failing to distinguish between effective sources and in appropriate ones [7]. Other problems include questionable data; grammatical errors; and misconception of research concepts as used in URP ([5]; [8]; [16]). These were acknowledged. However, there is there is need to research further into the content of URP.In view of this, the study aims for assessing through analyzing the contents of research projects submitted by undergraduate 2009/2010 academic session LVT students from Faculty of Technology Education (FTE), Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University, (ATBU) Bauchi. Specifically, the study assed by determine from the LVT research projects submitted to the FTE, the appropriateness or otherwise of i. objectives of the study ii. Research question /hypotheses usediii. Data collection instruments usediv. Research design usedv. Data analysis techniques usedvi. Procedures for data analysis and presentation used.
2. Methods
- Content analysis was used for the study. The purpose of content analysis is to organize and elicit meaning from the data collected and to draw realistic conclusion from it [3]. The population of the study consisted of 115(75 from the department of Vocational and Technology Education, VTE and 40 from the department of Science Education, Sci. Edu.) final year 2009/2010 academic session undergraduate LVT students’ research projects. Sample of 86(56 VTE and 30 Sc.Edu) were proportionate randomly selected. [3] observed that, there are no established criteria when using content analysis for the size of a unit of analysis, neither the number of subjects of study.Check list of six concepts, research question, research hypotheses, research objectives, research design, data collection instruments, procedure for data analysis and presentation was used. For meaning recording and interpretation of information obtained from the data coding process was used, where identified meaning unit is labeled with a code (1= correct; 2= not correct) in relation to the context been asses. To ensure accurate data was obtained and recorded, it takes 4 1/2 weeks (4 copies per day for 2 hours, Mondays through Fridays) for the researchers to studies, recorded and summarized the obtained information. And to ensure the validity of the data collected, both researchers performed the analysis separately and later discussed the results and obtained consensus which is in line with [3].Conceptual analysis based on the check list of the six concepts under study was used. In quantitative content analysis, facts from the text are presented in the form of frequency expressed as a percentage or actual number of key categories, Berelson, Krippendorify and Neuendory as cited in [3]. As such Tables, Frequency, percentages and Figures were used for the data analysis. The data was analyzed using percentages, charts and 2 written summaries examples as evidence obtained for the variables under study. The outcomes from the study hoped to provide useful information and recommendations to the LVT program coordinator, course lecturers (Research methods and Educational Statistics) and researchers embarking on similar study.
3. Analysis and Interpretation
- Data analysis is a practice in which raw data is ordered and organized so that useful information can be extracted from it [12]. For this study, the results from data collected were generated in tables, frequencies, percentages and figures in accordance with the objectives of the study.
|
|
|
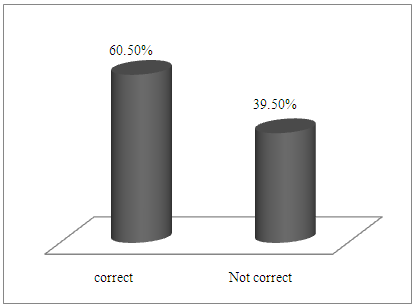 | Figure 1. Research design used |
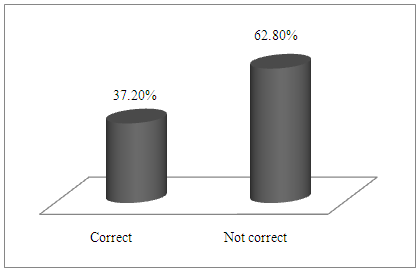 | Figure 2. Data analysis technique used |
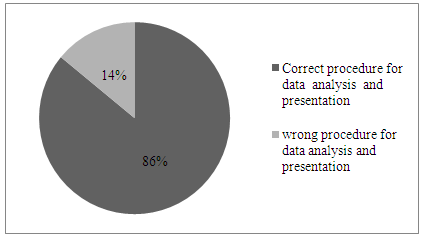 | Figure 3. Procedure for data analysis and presentation |
4. Findings
- • 34.9% of the objectives of the study were not clearly stated. • 37.2%, of the undergraduate LVT students used research question /Hypotheses were not clearly stated.• 58/.1% of the undergraduate LVT students used correct instruments for data collection.• 60.50% of the undergraduate LVT students used correct research design.• 37.20% of undergraduate LVT students used correct data analysis technique.• 86% of the undergraduate LVT students used correct procedures for data analysis and presentation.
5. Discussion
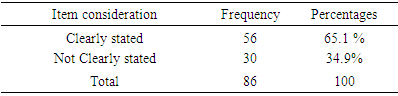
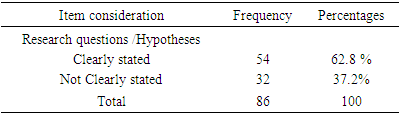
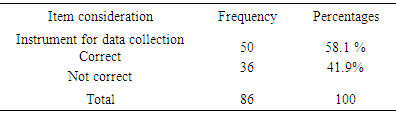
- In discussion the results from the study, limitation such as gender difference on the extent of appropriateness or otherwise with the objectives outlined on the assessment of undergraduate LVT students’ research projects; qualification /experience of the project supervisors’; grammatical errors associated with LVT research project must be acknowledged. To achieve objective i from the study, result on Table 1 was used. From the result, 65.1% of the LVT students stated clearly correct objectives of the study. While 34.9% did not clearly stated corrected objectives of the study. Findings from this revealed that 34.9% of the undergraduate LVT students’ research project objectives of the study were not clearly stated. Extracted from two randomly sample topics and objectives from undergraduate LVT student’s research project work reads-;1. Topic:- Comparison of academic performance of students in Junior Secondary School Certificate Examination (JSCE) 2012-2014 between private and public schools in Bauchi metropolis.Objectives:- i. Determine whether Junior Secondary School Students obtained specific skills to per sue a chosen trade or career.ii. Provide training that enables students to acquire specialized crafts man skills.2. Topic: - Influence of gender on students’ academic achievement in accounting subjects in public and private schools in Gombe metropolis, Gombe State.Objectives:- i. To determine the availability of qualified teachers teaching accounting subjects in Senior Secondary Schools.ii. Determine the accounting students’ performance in National Examination Council in the last 3 years. Result on Table 2, shows that 62.8% of the undergraduate LVT students stated clearly correct research questions or hypotheses. While 37.2% were not. Finding from this, revealed that 37.2%, undergraduate LVT students did not clearly stated correct research question s or hypotheses. Examples extracted from this reads-: 1. Objective of the study: Determine stock taking skills required by business education graduates for sustainable entrepreneurship in Bauchi State.Hypothesis: There is no significance difference in mean responses of Business education lecturers in stock taking skills required by Business education graduates for sustainable entrepreneurship in Bauchi State. 2. Objective of the study: Identify the causes of girl child drop out from schools in Bauchi metropolis.Hypothesis: there is no significance relationship between factors responsible for girl child drop out and causes of girl child drop out in Bauchi metropolis.Result from Table 3 shows the proportion of undergraduate LVT students who used correct instruments for data collection. Finding from the result, revealed that 58/.1% of the of the undergraduate LVT students used correct instruments for data collection while 49.9% used wrong instruments for data collection. Examples extracted from this reads-: 1. Topic: Comparison of academic performance of students in Business education in Junior Secondary Certificate Examination 2012-2014 between public and private schools in Bauchi metropolis.Instrument for data collection: Questionnaire.2. Topic: Effects of instructional facilities in teaching and learning Business Studies in Gombe Local Government Area.Instrument for data collection: Questionnaire.The finding is in agreement with [6] who observed that most of the instruments for data collection had not produced the type of information the students required. It was cautioned that researchers should selects instrument for data collection taking into consideration of the nature of the investigation and objectives of the study [9].Result from Figure 1, revealed that 60.50% of the undergraduate LVT students used correct research design while 39.50% used wrong research design. Examples extracted reads-:1. Topic: Effects of instructional facilities in teaching and learning of Business Studies in Gombe Local Government Area.Research design: Survey2. Topic: Effects of class size on Junior Secondary School students performance in Business Studies. . . . .Research design: SurveyFinding from this revealed that the undergraduate LVT students used research design without taking into consideration of the topic and objectives of the study. The finding is in agreement with previous finding, that achieving the goal of research design depends mainly on the research purpose or objectives of the study [9]. Data analysis technique used by the undergraduate LVT students was shown on Figure 3. From the result as shown on Figure 2, only 37.20 % of undergraduate LVT students used correct data analysis technique. Examples extracted from the 62.8 % of the students who used in correct data analysis technique reads:- 1. Topic: Attitude of teachers towards teaching and learning financial accounting in senior secondary schools in Ningi.Data analysis technique: Mean and Standard deviation.2. Topic: Teachers’ perception towards the role of quality secondary schools supervision in Bauchi Local Government Ares. Data analysis technique: MeanFinding from this revealed the students had misconception on the differences between the two branches of statistics (descriptive and Inferential) as such the data analyzed lost it meaning. The uses of correct data analysis technique make the raw data meaningful and assist the researcher in testing the null hypotheses so as to obtain significant results and draw sound inferences [13]. Result from Figure 3, shows 86% of the undergraduate LVT students used correct procedures for data analysis and presentation while 14% used wrong procedure for data analysis and presentation. Finding from this, revealed that higher proportion (865) of LVT research project used correct procedures for data analysis and presentation of result.
6. Conclusions
- The study assessed the final year 2009/2010 undergraduate LVT students’ research project quality from Faculty of Technology Education, ATBU, and Bauchi. The assessment was based on the conceptual analysis of six concepts stated in the objectives of the study. Tables and Figures were used to summarize the results, findings were summarized; examples from results obtained were extracted and discussed too. Lecturers, supervisors and project coordinators are hoped to benefits from the findings and recommendations from this study.
7. Recommendations
- Orientation lecturers could be organized by the departments (VTE and Sci. Edu) for students with emphases on relationship and difference between research questions, hypotheses and research objectives; difference between descriptive and inferential statistics; survey and experimental; research at least a week before research project supervisors are appointed. Emphasis to be made by supervisor’s on student to state objectives of the (proposed) study from which the research topic could be derived. Similar study could be carryout to justify the findings or otherwise of this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML