-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Education
p-ISSN: 2162-9463 e-ISSN: 2162-8467
2016; 6(1): 17-24
doi:10.5923/j.edu.20160601.04

Culture and Education: A Study on Learning Style of Libyan College Students in Tripoli, Libya
June II A. Kibasan 1, Evangeline C. Singson 2
1Faculty of Nursing, Al Jabal Al Gharbi University, Gharyan, Libya
2Faculty of Languages, University of Tripoli, Tripoli, Libya
Correspondence to: June II A. Kibasan , Faculty of Nursing, Al Jabal Al Gharbi University, Gharyan, Libya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

People are used to learn everyday in their lives at which this learning is always an advantage to every individual. There are different ways or styles that people how to be learned. The most popular ones are visual, auditory and kinesthetic. These styles were the one utilized thus; it is seen in this study the learning style of Libyan college students and its differences according to demographic profile. Descriptive design was employed and random sampling was utilized. The VAK checklist was used in collecting data needed in the accomplishment of this endeavor. Collected data were tallied where frequency distribution and percentage was used to permit simple descriptive analysis. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences Version 20.0 (SPSS) was used to validate differences. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) or F-test and Independent samples T-test was used for the significant differences according to demographic profile. Majority of the Libyan college students were found visual learners at which there are significant differences on learning style according to their demographic profile. The result of this study can steer mentors to understand the learning styles of learners that is necessary for proper identification of a teaching strategy that fits to the need of learners and can be one of basis in curriculum and syllabi development.
Keywords: Learning style, Auditory, Visual, Kinesthetic, Libyan college students
Cite this paper: June II A. Kibasan , Evangeline C. Singson , Culture and Education: A Study on Learning Style of Libyan College Students in Tripoli, Libya, Education, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2016, pp. 17-24. doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20160601.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Culture has great influence to individuals within for it is a word "that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, art, morals, law, custom and any other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society."[1] It is "the way of life, especially the general customs and beliefs, of a particular group of people at a particular time" [2] and a series of activities or worldviews that provide humans with the illusion of being individuals of value in a world meaning-raising themselves above the merely physical aspects of existence, in order to deny the animal insignificance and death that Homo Sapiens became aware of when they acquired a larger brain. [3] While education is the process of facilitating learning, or the acquisition of knowledge, skills, values, beliefs and habits. Educational methods include storytelling, discussion, teaching, training, and directed research. Education frequently takes place under the guidance of educators, but learners may also educate themselves. [4] Literally, these are crucial for both play a vital role to learners but culture always been disregarded factor affecting learning most especially if educators are foreigners. Teachers sometimes are confused on what methods they can use for the students to learn most especially if their academic performance is low. There were times that mentors assumed that student’s achievement depend on their previous learning experiences, and this has been difficult to determine with certainty. While we use all of our senses to take in information, we seem to have preferences on how we learn best. In order to help all students learn, we need to teach as many of these preferences if possible. [5] The significance of culture in learning is becoming increasingly apparent however an important area where culture and education overlap is that of learning styles. Interest in learning styles is closely related to the idea of “learner centered” instruction as it implies a need to consider information about the learner when designing methods and content.Learning is a lifetime process, in every stage of growth and development as human being, different learning exists but to be learned has different ways. Some says that they learn not only as they see but a need for them to listen what is all about or they have to do it. With this, different authors came up with the term “learning styles” that speaks to the understanding at which every student learns differently. One of the most significant issues in learning is how an individual is taking the responsibility on how to be learned. They should know their own learning styles, its characteristics and how to behave. In this way, each can acquire the constantly changing and increasing volume of information without assistance. It is in the learner’s hand to use different ways and develop the learning styles to some extent. [6] According to Brown [7], learning style is the manner in which individuals perceive and process information in learning situations. He argues that learning style preference is one aspect of learning style, and refers to the choice of one learning situation or condition over another. Moreover, Celcia-Murcia [8] defines learning styles as the general approaches—for example, global or analytic, auditory or visual—that students use in acquiring a new language or in learning any other subject. The manner in which a learner perceives, interacts with, and responds to the learning environment. Learning style is sometimes defined as the characteristic cognitive, affective, social, and physiological behaviors that serve as relatively stable indicators of how learners perceive, interact with, and respond to the learning environment” [9]. There are three main styles of learning; first is visual to which visual learners think in pictures and learn best in visual images. They depend on the instructor’s or facilitator’s non-verbal cues such as body language to help with understanding. Sometimes, visual learners favor sitting in the front of the classroom. They also take descriptive notes over the material being presented; the second is Auditory, learners of this style discover information through listening and interpreting information by the means of pitch, emphasis and speed. These individuals gain knowledge from reading out loud in the classroom and may not have a full understanding of information that is written; and the third is Kinesthetic learner, individuals under this learn best with and active “hands-on” approach. These learners favor interaction with the physical world. Most of the time, kinesthetic learners have a difficult time staying on target and can become unfocused effortlessly. [10] Learning style is significant in many reasons, one in which it differs from one another naturally. It also offers the opportunity to teach by using a multiple strategy in an effective way and a manageable teaching-learning environment. Though we may not be perfect in terms of teaching and learning, being aware of our students’ learning styles, psychological qualities and motivational differences will help us regulate our lessons appropriately and according to the conditions. [11] [12] [6] Moreover, knowing own learning style is beneficial most especially if it will be integrated in the process of acquiring education for it lead to an individual’s fast learning and can accomplish tasks effectively leading to success. The more successful the individual is at solving the problems s/he faces, the more control s/he will take over his/her own life. [13] To be educated is a success not only the one who achieved but to entire family most especially if it is with flying colors as a result of the suitable learning style being utilized. This is one of the advantages of knowing owns learning style for it always trigger the interest to learn. With this, it is vital for mentors to understand the learners’ learning styles as basis in coming up with the implementation of best strategy into their daily activities, curriculum and assessments.The concept of the learning style has a broad meaning at which this endeavor is based on individual's preferential focus on different types of information, the different ways of perceiving the information, and the understanding of information [14] leading the authors to explore and validate the learning style of Libyan college students for better understanding. Although learning styles have been heavily researched, the intention of this study is to provide general information on learning style of Libyan college students and to find if there are significant differences on their learning style according to demographic profile. The result can be used as basis in setting up a research instruments as supportive mechanisms in higher education, development curriculums and syllabi, and identification of teaching strategy that fits to the needs of learners.
2. Methodology
- Descriptive longitudinal survey was the design of research employed in this study as it is the best choice to be used in describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied and it does not answer questions about how, when or why the characteristics occurred but rather it addresses the what are the characteristics of the population or situation being studied. [15] Random sampling was applied in the identification of respondents from the total population of students in the faculty of languages of the University of Tripoli. The data gathering tool utilized has two parts, the first is focused on the demographic profile of the respondents which are important to consider as the moderating variable and is relevant in identifying differences on learning style; and the second part is the VAK learning style questionnaire of Staffordshire University. [16] Collected data were tallied and presented in frequency count, percentage and weighted mean to permit simple descriptive analysis. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences Version 20.0 (SPSS) was used to validate differences. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) or F-test and Independent samples T-test considering the Levene's Test for Equality of Variances was used for the significant differences according to demographic profile.
3. Results
- Learning style of students can be difficult to identify but it should be known to self and mentors as it promote an effective and efficient teaching – learning environment conducive to learners. The main usefulness of learning style information is for the students and to provide vocabulary to help them define appropriate learning strategies. [6] However, recognizing that there are different styles of learning and evolving one's repertoire of learning strategies may be particularly relevant for medical students desiring careers as clinicians and health professionals to improve their academic performance and develop ways to master the lifelong professional skills. [17]
3.1. Demographic Profile of the Respondents
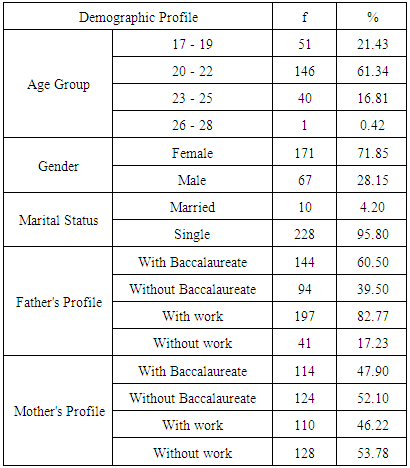
- There are 238 college students who were randomly chosen from the faculty of languages to participate in this study. Among them, majority are from age group of 20 to 22 years old with 146 or 61.34% of the respondents followed by 51(21.43%) from age group of 17 to 19 then 40 (6.81%) are from age group of 23 to 25 years old. Only 1 (0.42%) respondent is 28 year old who is happened to be the oldest. Furthermore, most of them are females with total number of 171(71.85%) while only 67 (28.15%) are males. Moreover, Single by marital status dominated with total number of 228 (95.80%) and the 10(4.20%) remaining respondents are married. On the other hand, 144 (60.50%) from the college students are sons or daughters of a father with baccalaureate degree and the remaining 94 (39.50) are with fathers who did not earned a baccalaureate degree. Most from the fathers of the respondents are working as employee with total number of 197 or 82.77% while 41 (17.23%) fathers are engaged in business. As per student’s mother profile, 124 (52.10%) mothers did not earn a baccalaureate degree in which is almost the same with those mothers who has baccalaureate degree with total number of 114 (47.97%). Finally, 128 (53.78%) of the mothers of the respondents are without work at which is again near to be the same to number of working mothers with total number of 110 or 46.22%.
3.2. Learning Style of Libyan College Students
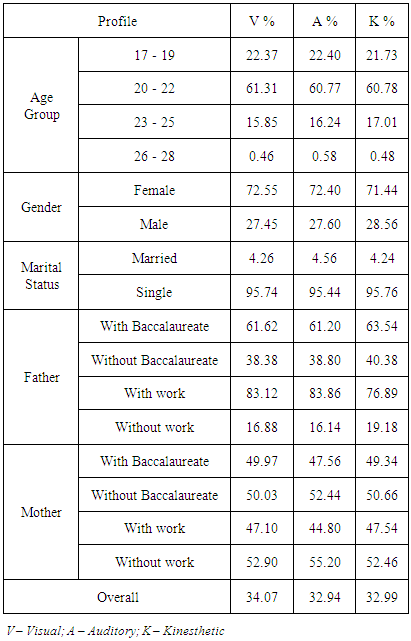
- Table 1 presented the learning style of Libyan college students of the faculty of languages at University of Tripoli, Libya. Generally, most of the college students are visual learners with score of 34.07 percent followed by kinesthetic (32.99%) then by auditory with score of 32.94%. According to their demographic profile, as to the age group, majority from the group 17 – 19 years old tend to learn with their sense of hearing with score of 22.40% then by visual at 22.37% and by kinesthetic with 21.73% while college students that belongs to 20 – 22 years of age are more on visual learning with score of 61.31% then by kinesthetic (60.78%) and by auditory with score of 60.77%. Furthermore, most from the age group 23 – 25 year old in favored kinesthetic learning style with score of 17.01% followed by auditory mode of learning(16.24%) then by visual at 15.85%. The last age group is from 26 – 28 years old. The most utilized learning style by this age group is auditory with score of 0.58% followed by kinesthetic learning (0.48%) then by visual learning at 0.46%. Additionally, the learning style of the Libyan college students according to their gender is as follows. With the female Libyan students, majority from them are visual learners with score of 72.55% followed by auditory (72.40%) then by kinesthetic with score of 71.44% while male Libyan students most are kinesthetic learners with score of 28.56 then by auditory with 27.60% and by visual with 27.45%. As to the marital status of the Libyan students, preponderance from the married Libyan students are auditory learners with score of 4.56% then by visual (4.26%) and by kinesthetic with score of 4.24% while majority from the single Libyan students kinesthetic learners (95.76%) then visual learning (95.74%) and auditory at 95.44%.
|
|
3.3. Differences on Learning Style According to Demographic Profile
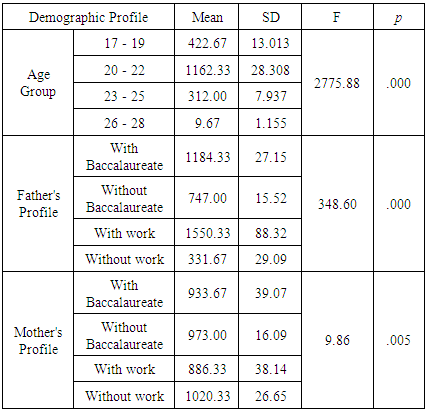
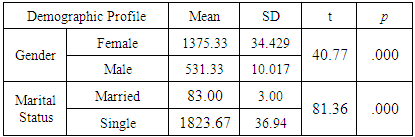
- Table 3a and 3b reflected the differences on learning style of Libyan college students according to their demographic profile. Frequency count was used as the data to be processed with the use of SPSS version 20.0 at which two inferential statistical formulas were utilized. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) or F-test for the age group, the father and mother’s profile while independent sample T-test for the gender and marital status. Presented in table 3a are the differences on learning style of Libyan students according to age group, father’s and mother’s profile. Along with the age group, the F-value is 2775.88 and the P = 0.000. The result guided the authors to conclude that there is a statistically difference between learning style of Libyan college students at 0.05 level of significance. Moreover, the study revealed that there is differences on learning style of Libyan college students related to Father’s profile (F-value=348.60; P=0.000) and mother’s profile (F-value=9.86; P=0.005) at 0.05 level of significance.On the other hand, table 3b showed differences on learning style of Libyan students according to gender and marital status. As to gender, it was found that there are significant differences on learning style of Libyan college students in terms of gender (t-value=40.77; P=0.000) and marital status (t-value=81.36; P=0.000). Maybe this is due to the effect of being a male or a female in relation to their culture and tradition and their status as married or single since married people are expected to have multiple roles as they live independently and should be responsible to their own family while singles usually depend on their parents.
|
|
4. Discussion
- All students learn, but not in the same way and it is obviously postulated that each in everyone has learning style as it goes to what we call individual differences. Discovering the learning style of learners will allow them to learn how to determine personal strengths and weaknesses that led them be learned because through learning style, educator can integrate a strategy or method corresponding to difficult tasks, strengthening weaknesses so students can easily learn. Worthwhile, it is important for students to have multiple learning opportunities at which teachers should be capable of identifying a teaching methodology that is compatible with the students' unique learning styles as it improves students' overall learning resulting to increase in motivation, efficiency and enables a positive attitude towards learning. The purpose of using learning styles is to find the best ways for both students to learn effectively and teachers to teach efficiently.This study found that most of the Libyan college students are visual learners then by kinesthetic and few are auditory. In this instance, it seems that most from the students prefer to read the concepts from their sheets or handouts. During their classes, most of them were observed staying in front to be get close where the mentor stands always. This is a proof that majority of them are visual. At first it was just an intuition of the author that students are running after the front seats to be close to the teacher is because of the classroom size which is big and the huge number of the learners but LdPride defined that visual learners are in favor of sitting in the front of the classroom. [10] Being an educator, it is important to explain the content of the lesson with visual aids and even use body language and gesture to substantiate what was expounded topic then give examples as an additional hint for the learners to understand the lesson before conducting an activity to test the level of understanding among learners. The findings is similar to the study of Dunn and Dunn [18] that only 20-30% of school age children appear to be auditory learners, 40% are visual learners, and 30-40% is tactile/kinesthetic or visual/tactile learners while Barbe and Milone [19] stated that for grade school children the most frequent modality strengths are visual (30%) followed by auditory (25%), and then by kinesthetic (15%). On the other hand, a contradicting studies at which Reid [20] reported that Chinese university students (N = 90) studying in the USA favored Kinesthetic and Tactile styles while Melton [21] found that Chinese (PRC) university students (N = 331) favored Kinesthetic, and Tactile. Moreover, Jones [22] stated that his Chinese (Taiwan) university students (N = 81) favored Kinesthetic and Tactile styles same as Rossi-Le [23] surveyed adult L2 immigrants in the US and they were in favor with Kinesthetic and Tactile styles while Hyland's Japanese learners favored Auditory and Tactile styles, and disfavored Visual and also reports that senior students favored kinesthetic styles. [24]As seen in the table, there is shifting in learning style as the age of learner advances. The shifting starts from auditory to visual to kinesthetic then by auditory. The findings proved that young people are good listeners then tries to prove what they heard by looking to it and by acting out what was learned. In the process of learning a specific task, it is important to listen to instructions and steps while watching how it will be accomplished so it can be greatly demonstrated in return. Our finding is similar with a study of Price, Dunn and Sanders [25] but different in the pattern of shifting. They found that very young children are the most tactile/kinesthetic, that there is a gradual development of visual strengths through the elementary grades, and that only in fifth or sixth grade can most youngsters learn and retain information through the auditory sense. It was also a result of this study that there is a statistically significant difference between learning styles of Libyan college students according to age group at which, in every year that their age increases, their learning style changes from one to another. Gender is one of the factors that affect learning style. However, generalizations regarding male and female learning styles are difficult to state due to conflicts in published evidences. In this study, female college students are more on visual learning which is different to males for they are more on kinesthetic learning style. The finding for female Libyan college students is similar to the study sample consisted of ethnically diverse students that included older students whose ages ranged from 23 to 45 years and it was found that female students demonstrated stronger preferences for visual and aural learning styles. [26] The result is also consistent with a study which VARK was used and found that female students in their first-year of medical studies had a greater preference for the visual learning style. [27] Furthermore, another study also used the VARK and reported that female students preferred the visual and aural learning styles more than males in the sample. [28] In contrary, a study showed that, across the four ethnic groups, female students have a higher preference for a kinesthetic learning style [29] same with a study which indicated that female learners preferred to learn using their auditory senses. [27] While the study of Saadi [30] reflected that the male students demonstrated a preference for the kinesthetic style which is similar to the finding of this study.Furthermore, it was found that there are significant differences on learning style of Libyan college students in terms of gender. The finding is just the same with the study that examined general surgery residents at the University of Cincinnati during the period of 1994 to 2006 at which the result reported significant differences in learning styles between male and female general surgery residents. [31] Another study with similar result was conducted to investigate gender differences among learning styles of 1,637 adolescents from Bermuda, Brunei, Hungary, Sweden and New Zealand. The results highlighted a significant difference for gender in general and interaction by countries. [32] Moreover, it was reported that there is significant differences in learning styles among male and female students to evaluate the effect of gender on learning styles within secondary school students in Hong Kong. [33]In contrary to our finding, a study that examined learning styles among first-year medical students to determine if there is a difference in learning style preferences in terms of gender. The researchers noted that there was no significant difference according to gender and learning styles performance. [27] Furthermore, a study conducted that investigated the individual learning of Southeast Asian students indicates no significant difference between Asian and American students’ learning style preferences in terms of gender [34] that is same as to a study conducted whose focus is on Hispanic university nursing students at which the study showed that there were no significant differences between male and female nursing students. [35] In addition, another study showed no significant difference between the learning style preferences of male and female nursing students using VARK learning styles questionnaire. [36] Similar study also reported no significant differences in learning style preferences on the basis of gender among undergraduate students in AUE. [37] When students exhibit significantly different learning styles, the instructor need to address this fact and develop appropriate learning approaches as it can enrich the learning experience. [38] But, it should be noted with caution that while sensory preferences are useful as a launching point for inquiry, they should not be used as the only source of information for creating learning improvement. [39] Indeed, the significant difference on learning style as per gender is due to factors such as biological and physiological differences between male and female students. [40] Also, this variation in sensory learning style preference between males and females could be attributed to social traditions and education systems which treat gender groups differently.In reference to the learning style of Libyan college students according to their marital status, married college students learn more by listening while single ones are more on kinesthetic that is obviously showed the significant difference. Considering what is expected to be the routine of being a single or married individual. It is common for Muslim women to be responsible in the household chores and Muslim men go out to work for the basic needs and survival of the family which is commonly similar to other countries of other religion, ethnicity and culture. Thus, this is one of the most factors affecting their learning style at which this finding is opposite with the study that is consisted of students from the medical college at King Saud University in Riyadh, KSA who were studying in their second, third, fourth, and fifth year. The learning style preferences are not related to a student’s academic achievements, marital status, residency, or study resources and at the same time, there is no relationship between marital status and the learning style and it is obviously noted that there is no significant difference on learning style of single and married medical students. [41]There is a belief that parent’s profile has influence to learning style of their child. In the Philippines, it has been observed most especially in the country side that children of professionals with work or no work or even non-professional with work or no work greatly affect how they learn. This was the experience of the authors as they begin to learn and started their education until they graduated in the university. In this study, Libyan students whose fathers either earned or not earned a baccalaureate degree and not working are more on kinesthetic learning style. Fathers found to be the role model of a family in general, no matter what kind of work or how far they’ve been in terms of education as most considered as the breadwinner or family provider and it is the main role of being a father unless there are some limitations that will intervene. Learning starts at home and the parents are the first mentors at which fathers have more time in mentoring at home than mothers for they are usually the one assigned to most of household chores. In addition, men usually talk limitedly than women. So most probably, the mentoring and learning scenario is more on actions such as body language, gestures and facial expressions that can be carried by a child while they grow up. Further, Libyan students with working fathers are more on auditory. Taking into consideration the culture of Arab people, fathers are the sole authority of the family and Libya belongs to Arab countries though it is situated in an African continent. At this point, fathers usually hand down instructions or messages to the entire family so all members tend to listen. This practice becomes a trait that they carry as they go to school. On the other way around, Libyan college students according to mother’s demographic profile has different learning style. Majority of Libyan students with mother who has baccalaureate degree are visual. In Libya, most of students are women so it is expected that more from them will be graduating from their baccalaureate degree. They were even found excelling than men but it is unusual for them to be away from their families if they would like to work or go outside the country for continuing education in post graduate if they are single. In the end, most of them were found taking care of their children at home. Being a mother at home, it is one of their responsibilities or functions is to educate their children on basics of education at which there are times that due to other responsibilities that needs to be accomplished, she will write down instructions and other activities to be done that initiates a child to learn visually and this trait can be carried until they will go to school. Moreover, college students whose mother did not earn baccalaureate and whose mother who are not working are more on auditory learning style. Mothers are still considered a dependent of the breadwinner and the father as the head is the breadwinner that nurtures his family which is a general practice worldwide that was observed in Libya. It was said earlier that father is the sole of authority who passes instruction to all members of the family, tendencies here is that the children with the mother listen to what the father’s instruction at which if instructions not clear with the children, clarification be done through the mother so they need to listen to what their mother told them. This practice may be one of the factors that influence an individual to be an auditory learner. Furthermore, college students whose mother is working are more on kinesthetic learning style. In Arab countries, fewer opportunities were given to mothers to work outside their home but some urban place like Tripoli allowed them to land in a job outside their house as permitted by the head of the family. A working Libyan mother is just like any working mothers in the world has to train her children to do things as she is not always around for help. Therefore, the mother tries to demonstrate and or illustrate how things are done at the same allows her child to do the same. In this manner, the child can benefit though experiencing and the child learns through familiarization with action. This practice will initiate a child to learn kinesthetically and it can be carried to school. Finally, the study found out that there are significant differences on learning style of Libyan college students according to their demographic profile. This really proves that learning is individualized and each individual is different from one to another. Similarity sometime may occur but that is due to influence. Moreover, culture plays a vital role in learning as it can influence an individual how will learn thing things to make them be educated.
5. Conclusions
- Knowledge and understanding on learning styles is vital as classroom sizes increase and the technology advances to promote learning and for the mentors to easily come up with the best strategy in teaching and learning for the betterment of education that is of great help and beneficial to the students leading to success. While there are many theories, models, and instruments that purport to measure learning styles, conclusions were made by the authors based on the research conducted to date. Generally, Majority of the Libyan college students are visual learners at which there is shifting of learning style as their age increases. Moreover, most female Libyan college students are visual learner while males are more on kinesthetic. Furthermore, majority of married Libyan students are auditory learners while kinesthetic is the commonest learning style among singles. In addition, Libyan students whose fathers either earned or not earned a baccalaureate degree and not working are more on kinesthetic learning style while those with working fathers are more on auditory. On the other way around, majority of Libyan students with mother who has baccalaureate degree are visual while college students whose mother did not earn baccalaureate and whose mother who are not working are more on auditory learning style and college students whose mother is working are more on kinesthetic learning style. Lastly, there are significant differences on learning style of Libyan college students according to their demographic profile.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML