-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Education
p-ISSN: 2162-9463 e-ISSN: 2162-8467
2014; 4(2): 41-51
doi:10.5923/j.edu.20140402.05
Learning Motivation of Students in Ambon Child-Friendly School, Moluccas
Marleny Leasa 1, Ronny Samallo 2
1Faculty of Teacher’s Training and Education, Pattimura University, Jln. Dr. Tamaela, PGSD Campus (Education of Primary School Teachers), Ambon, Indonesia
2Teacher, SMP Negeri 2 Salahutu (Junior High School), Maluku, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Marleny Leasa , Faculty of Teacher’s Training and Education, Pattimura University, Jln. Dr. Tamaela, PGSD Campus (Education of Primary School Teachers), Ambon, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The practices of violence increased in educational institutions life, although the local Government had been implementing the peace education and the integration of national character values in the curriculum. Post-conflict of Maluku, the presence of the NGO “Save the Children” judged to provide a positive impact for students and schools through the implementation of child-friendly school at numbers of targeted schools in the city of Ambon. This research aimed to know the influence of physical and psychological violence against the interest and attention in learning of elementary school students. Research data collected by observed learning activities in the classroom, interviewed the students, teachers and principals. Samples of the victims of violence are 100 students taken from eight elementary schools in Ambon. Data were analyzed using multiple regressions. The results showed regression equation of violence against interest is [Y=34.421 + 0.148X1 + 0.010X2], and violence against attention is [Y= 38.772 + 0.106X1 + 0.046X2]. Meanwhile, the results of the t test on hypothesis showed that the physical and psychological violence did not significantly affect the interest and attention, which is a contrast with the results of previous studies conducted in the district of West Seram.
Keywords: Children friendly school, Learning interest, Attention, Physical violence, Psychological violence
Cite this paper: Marleny Leasa , Ronny Samallo , Learning Motivation of Students in Ambon Child-Friendly School, Moluccas, Education, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 41-51. doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20140402.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
1.1. Statement of the Problem
- Schools are educational institutions that aimed to develop students through the acquisition of affections, knowledge, and skills so that they can live anywhere. Learning in the classroom is designed as good as possible, to create a harmonious relationship between fellow students, students with their teachers and including the environment. Schools are expected to be a place where students enjoy the convenience of learning, even as a learning environment which upholds the self-esteem, dignity, and rights of children [1]. Children's rights are the basic needs to ensure the child's survival, growth and development, and also protection from all forms of abuse, exploitation and children neglecting – include civil, economic, social, and cultural aspects [2]. Generally, the rights of children are include the following civil rights and freedom, family environment and alternative care, basic health and welfare, education, leisure and cultural activities, as well as special protection. The law of No. 23/2002 on Child Protection asserts the rights of the child to have optimal levels of health, education, protection and chance to participate. But in fact, current rights of the child are inadequate, because schools often become violence implementation area for students. Violence in schools is an issue that has become more prominent in recent years.Smith and Sharp [3] assessed that violence can be described as systematic abuse of power, usually occurs in specific social groups such as schools, families, and communities. Power can be abused and it really depends on the social context. Similarly, Swearer et al. [4] explained the current violence has spread widely and problem that is sometimes ignored by numbers of schools. Violence can be interpreted as angry behavior, hyperactivity, and acts of crime or other crimes, which can be done by the teacher to the students, and by fellow students. One implication of violence is the emergence of student victims of violence. Victims of violence can experience pain, low academic achievement, increased fear and anxiety, the loss of a number of positive ideas, and depression. In fact, according Alsaraireh [5] worst effects is the low emotional intelligence and self-esteem.Violence in the school seemed to be an effective culture for disciplining students, so it is claimed as unimportant matter to be resolved. Violence may be justified according the main objective to enforce discipline. The trigger factors of violence are the helplessness of the child who always used to vent anger of adults. Of course violence is not in accordance with the rules, and violating the rights of children. During the period of 2009, the National Commission for Child Protection has recorded acts of violence against students in elementary school, which numbers are pretty fantastic – 382 children for both men and women. Three types of violence included physical, sexual and psychological violence; and the most widely done is psychological violence [6].World Vision Indonesia in Sejiwa [7] reported in 2009 recorded 1891 cases of violence against children in Indonesia, and 891 of these cases occurred in school. This suggests that a significant increase in the number of child abuse from 2008 is 1626 cases. Related to that Sejiwa [7] also reported the corporal punishment is an attempt to effectively discipline students and 10% of teachers stated that they do corporal punishment. Margiyani [8] revealed that the environmental conditions in post-social conflict of Maluku influence the children's psychological condition including elementary school students. Over than 50% of teachers was practiced violence in the learning process to their students. Leasa [9] revealed that teachers in West Seram district tend to commit violence against elementary school students, although numbers of primary schools in the region are already implementing “Child-Friendly School” (CFS). As a result, violence is very significant effect on elementary school students' interest in learning. Sejiwa [7] stated teacher generally saw violence as a form of discipline, to improve student achievement. In three regions of Maluku Province including the city of Ambon, Central Maluku and West Seram District, teachers practiced violence against students, both physical and psychological violence, whereas a number of elementary schools in the intended location have implemented CFS since 2009.The previously described conditions become a reflection for us and prove that violence still occurs till this day, everywhere, especially in educational environments. According to Save the Children NGO, a few years earlier, violent practices still exist in a number of primary schools in the city of Ambon. This is a result of lack of awareness among education providers to better understand the child and the rights of their status as a child in elementary school students. In fact, this condition is believed to be the efforts of teachers in teaching students. Subtle ways, polite, and friendly which is often used by teachers judged to be success to deterrent and make students more motivated to learn. However, violence is still regarded as an effective solution for deterrence and encourages student’s motivation.We need preventive efforts, through education in schools to cope with and anticipate abuses and violence in a larger scale. People should made a realistic effort to integrate principles of “PAIKEM” positive discipline in active, innovative, creative, effective and fun learning, who dubbed their implementation with child-friendly education or Child-Friendly School (CFS). Within this framework, education is needed to assist the dimension development of appropriate intellectual, moral, psychological cognitive and psychology. Saptarini [2] proposed five phenomenon of violence in schools. First, the violence in education arising of breach is accompanied by especially physical punishment. Second, violence caused by poor education system and educational policy on curriculum aspects that rely on cognitive abilities and affective that neglect the reduction of humanization in the educational process. Third, education is affected by the violence in society and the mass media impressions that are lately increasing in showing vulgar violence. Fourth, the violence may be a reflection on society’s development that has shifted rapidly, so that obligated the emergence of instant solutions attitude or shortcuts. And fifth, the violence is influenced by socio-economic background factors.The violence that occurred in school will directly impact the learning process. The learning process can run smoothly, when students and teachers are not experiencing serious pressure which can hinder the process of learning for students and teaching assignments for teacher. Good teaching must be able to motivate exceptional student and can be cultivated to achieve good learning objectives and learning outcomes. If students live in abusive educational environment, the students will feel occupied and depressed. Consequently, the main task for the study will be disrupted. Interest, attention, and seriousness in learning will increasingly fade. Hours of study allocation will also degraded drastically, because it brings out discomfort against the teacher. In addition, the inner conditions will change into uneasy calm; the spirit of learning will be reduced. Students are always targeted for abuse of teachers, students always dogged by grief, so that students feel inferior in learning and social communities. So the violence that occurs in schools is greatly affects students' motivation. Motivation is the force or energy boost caused by circumstances such as in the unbalanced driving factors in a person who called motives. Motivation to learn is crucial for the sustainability of learning and improving student learning outcomes. Motivation is a process that gives the spirit, direction, and persistence of behavior. Behavior is motivated by full energy, focus, and long lasting [10]. In the course of learning, the motivation can be considered as the overall driving force in students that lead to learning activities, which ensures continuity of learning activities and provide direction to the learning activities, so that the desired objectives by studying a subject can be achieved. Students who do not have a strong motivation will be reluctant to take learning activities. Susanto [11] characterized motivation to learn in six types of behaviour, i.e. interest, attention, long learning, effort, rhythm feeling and appearance. Wardiyati [12] found a positive relationship between motivation and student achievement. This suggested that motivation and achievement is in positive relationship, although insignificant. So far, studies that asses the relationship of violence and student motivation are still very limited. On that basis, this study was conducted to assess the practice of school violence. The focus of this study was to determine the relationship of physical and psychological violence to the attention and interest in elementary school students and its influence in Ambon City.
1.2. Research Objectives
- The present study sought to investigate the relationship between physical and psychological violence and motivation to learn in elementary school context in which the child-friendly school exist. Motivational aspects of learning that were examined consisted of interest and attention. The relationship can be seen from the regression equation obtained.
1.3. Research Objectives
- Our study focused on the following research questions:1. Are there any relationship between physical and psychological condition of the elementary school students and their interest in learning? 2. Are there any relationship between physical and psychological condition of the elementary school students and their attention to learning?
1.4. Literature Review
- Violence in EducationIn general, violence can be defined as all the harmful activities threatening other people, either physically or psychologically. Violence is not only in the form of physical exploitation; serious emotional violence will leave a permanent trauma for the victim as well. In fact, in education context, violence can be found among juniors-seniors, even teacher-students. No matter what the reason is, still violence should not have existed at scholl. suggested that physical and psychological violence can be distinguished from each other along two dimensions: first, by whether or not the act of violence itself is physical or non physical/psychological, and second, by whether or not the consequences of the act are physical and/or non physical/psychological [13]. The rise of the shows violence in education, especially those committed by the student or by a teacher to his students, suggesting the possibility that the practice of violence happens in our school environment as well. Violence and harassment that occurs in the world of education in Indonesia lately, is not something that appears suddenly. Referring to the history of this nation, it has been firmly entrenched since before then finally explodes. For example, people who have been to high schools still remember correctly the term Student Orientation Period (SOP) or Introduction Orientation Campus/OSPEK. Both activities are always carried out every year to welcome new students. The initial goal is to introduce new students to both the school curriculum and its environment. It is considered important to help students adapt easily to the academic process as the main activities in the educational institutions.According to Amiruddin [14], violence that might exist among children include physical violence and psychological violence; they aimed at torturing or mistreating others. In contrast to physical violence, psychological violence is an act aimed at degrading the image or confidence of a person, either through words or through actions that are not preferred or desired by the victim. Violence and harassment in education, whether done consciously or not, is like planting a time-bomb that can explode at any time. The younger generation who is accustomed to violence and harassment will grow into individuals who are looking at everything from the point of view of violence as well. There are possibilities that violence becomes a life style; incorporating violence into activities every day, especially in solving problems. This is what happened recently in Indonesia. Not only the SOP and OSPEK activities, the learning activities undertaken by teachers should be a concern. Slightest harassment or excessive punishment are contributing to sow seeds of violence among the young generation. Therefore, the actions that are inconsistent with the purpose of education should be as soon as possible terminated so that a vicious cycle plagued into the world of education can be immediately disconnected. Violence is an act that is not commendable and certainly contrary to the foundation of education.Violence in education arises from the breach accompanied by particularly physical punishment, due to poor education systems and policies, since the curriculum is focused more on the achievement of the cognitive aspects and ignore education with affective and psychomotor abilities. In addition, these conditions also influenced the development of a society that has shifted rapidly, giving rise to an attitude of instant solutions, violence is influenced by socio-economic background of the perpetrator. In relation to it, the violence in education can be caused by either internal or external factors. Internal factors directly affect the behavior of the students and of the teachers. There is a gap between what the government has done in promoting education and the real conditions. On the other hand, the external factors which come from the condition of non-education take a role as an indirect factor leading to potential violence [15]. Wijayanto [16] describes some of the mechanisms of violence in education as follow: 1) The disposition of the student as a blank sheet of paper (blank paper), 2) student test scores as a determinant of everything, and 3) physical uniformity. Students as blank papers are ready to be filled with text or color as much as possible or they might be regarded as empty vessels to be poured by the water until it is full. Writing, painting, color, and water is a picture of knowledge, systematic science, formulation of concepts, theories, and certain skills as a preparation for students to continue their education to a higher level or to enter the workforce. This view was influenced by feudalistic thinking. In this case the student is always seen as the generation of immature or mature. They, thus need instructions and guidance from the older generation, who has undergone periods that have not been experienced by the younger generation.Student test scores as a determinant of everything refers to the learning process which is concerned with the empirical progress, even always based on the results of a particular measurement. Within that framework, a certain system test or written exam needs to be applied as a way to measure students' progress. This technique further facilitates and speeds up the student learning outcomes. This happens because students tend to think that the written test is the only one kind of evaluation used in the learning process; they will welcome the easy format of the written test. Such evaluation techniques increasingly distanced students from opportunity to learn from reality and the meaning of the issues studied. Here, the violence, as a result of the test mechanism result in major deterioration in the way of learning. Thus, what is produced by the education is only limited to the ability to answer test questions. The result is not the ability, intelligence, and or skills of the students in finding problems in the social environment, nor in offering solutions to it.On the other hand, education also implements the uniform presence for all things related to the learning process. This uniformity is actually intended to help teacher control the learning process. At the end, the teacher can easily detect deviant behavior of students. Unification of school outfit in terms of color, fashion, and even the time appears to have a specific purpose. Meanwhile, it is usually intended to garner a sense of equality and solidarity and reduce the gap among students. This is also done to push the students to hold these evolving norms such as neatness and propriety in their social life. However, outside the school they are educated by the general tendency of society that encourages a race or competition in many areas of life; it is about to find anyone who can exceed. The way people dress, buy school supplies, transportation, home, and even shop reflects that they have desire to reach a particular higher class than other fellows. The situation outside the school also conditions the pupil to leave the principles of the moral norms of decency implemented in schools. It shows that the regulation of wearing school uniforms might lead students to be more hypocritical and also affect the students’ way of thinking.Akhmadan [17] states that violence can be viewed from two distinguished educational foundations: cornerstone of the legal basis of education and educational psychology. Based on the legal basis of education in Indonesia , the action is contrary to claus 3 of the Law of the Republic of Indonesia Number 20 of 2003 on National Education System: “a national education functions to develop the ability and form the character and civilization of dignity in the context of the intellectual life of the nation, aimed at developing potential for students to become a man of faith and fear of God Almighty, noble, healthy, knowledgeable, skilled, creative, independent, and become citizens of a democratic and accountable”. Similarly, clause 4, paragraph 1 of the same Act states that “education held in a democratic and fair and not discriminatory uphold human rights, religious values, cultural values and national diversity.” So does clause 80 of Law No. 23 of 2002 on Child Protection.Based on the viewpoint of educational psychology, violence can be divided into physical and psychological violence. Physical abuse can be identified as the form of beatings action (using hands or tools), smack, and kicks. Such actions can cause scars or bruises on the body, even in certain cases can lead to permanent disability to be borne by the victims for the rest of their life. The psychological violence include mocking or insulting actions, intimidating, showing bad attitude or displeased expression, and action or speech that hurt others feelings. The impact of psychological violence can lead to feelings of discomfort, fear, tension, and even can cause quite a traumatic effect. In addition, since it is not physically appealing, mitigation becomes quite difficult because the victim is usually reluctant to reveal or tell. Another impact is that the student might be more quiet or loner, feel insecure and unable to socialize, do not go to school, feel stressed or nervous. As the result they have lack of concentration in learning, and in some more severe cases, they might commit suicide.Judging from developmental psychology, Havingrust in Pidarta [18] stated that the development of psychology in childhood shaped the attitudes of the students; how they get along in harmony, make the freedom of self, form conscience, morals and values, and develop attitudes towards groups and agencies social institutions. The teacher is should be able to generate a positive first impression and remain positive for the next few days. Attitudes and behavior of teachers is very important for the will and spirit of children's learning. So, the punishment carried out by teachers also might have a negative impact on children's learning process. No matter how small the effect of the violence in educational practice is, each of them should be taken into account. Schools are the perfect place for students to thrive; however, when violence occurs in schools, schools become the place in which students might find barriers to their psychological development.In elementary school, teachers generally conduct violence towards students because they are judged to be disciplined in learning and complying with a number of rules in school. Students are human beings who also have certain limitations, and seek to compensate for the limitations. Therefore, a primary school teacher plays an important role in shaping the personality of the child, including the coaching discipline. This effort was made not to rob the dignity of the child, but rather to make him understand their duties and responsibilities. In the context, it is important for teachers to properly understand disciplined approach without penalty. It is based on the assumption that education implemented in our schools has a negative effect on the meaning-oriented faults. In schools and at homes, children are involved in a series of demoralizing experience they are not prepared to deal with it. We seize the only opportunity they have which should be able to help them get to their development in the next period, the opportunity to test their own ability to be functional.Casel and Dreikurs [19] in their study of deviant behavior in children, revealed four deviant behavioral intentions. They are to attract attention, gain power, and expose the deficiencies. First intention comes when children are not given the opportunity to get a respectable status. In the classroom, they are usually trying to find a balance with the attitude of striking. Children will seek the attention of others. However, it cannot develop confidence in his own-self. Children try to be so kind that they become the center of attention. At that time, they did not intend to learn to cooperate but to get attention. When pride is not obtained, their activities will end. As the result, children can use passive methods to attract the attention of teachers and friends. Those children, thus, are known as exemplary child or teacher favorite. If the child can not master teacher sweet in a passive way, he might choose passive-destructive manner. For example, with a lazy attitude or pretending not to do anything so watch out teachers. Children whose goal in life want to get the attention of a big nuisance when they are unable to get what he wants. The boy attitude errors can not be helped with praise. Teachers help children to change the destructive method by means of constructive methods give a boost so he can perform so that he can gain recognition for what he wanted. In other words, help children to develop their social interests, do not let him isolated. Those who are shy can be active in the same way slowly.The second intention, if parents and teachers do not take action in the face of demands that concern the child would be too much, then the child seeks to expand its power. Children who are hungry for power, and wants to be ruler in on it to follow the pattern of wrong thinking. The purpose of that power looks strikingly similar to the desire of the road using passivity, only the first was clearly visible. Type active given the designation rough. This type quarrelsome, fight, lie, may also often do not obey orders, not knowing ban, did not want to do his job, being openly against. Type of passive rough look lazy, unwilling to work normally even become forgetful, stubborn, and sink into apathy. Facing power this child, teacher reaction overshadowed by the feeling that his leadership is threatened. A good way to handle this problem is to understand that the child basically has ambition. Teachers should be able to divert ambisisi it to the right path. For example, the child told her classmates to help. In the experiment, teachers provide an opportunity for the child to lead his friends. Ask for help to the child better than threatening. If the child has gained appreciation for its leadership, he will not misapplying his position. So teachers can build cooperative leadership in the classroom. More sensible way is asking for help and not the other way like threaten.The third intention if a child feels devastated that he is no longer continuing opposition to gain power, the child will attempt to retaliation. The child will become vindictive. A vindictive person who has been hit so that the feelings are trying to hurt other people. He argued that he was not liked by others and and now he wants to hurt someone else. Measures such a child would be full of sadism and brutality. He has gained a victory when labeled as evil around him. It is a pride to show its superiority. Children thus show fraud against friends, torturing animals, insulting adults, clawing, biting and lunging. If he feels excelled, he was soon making plans revenge and creating methods more violent than ever. The leader of the youth group of criminals is an example of this third intention. Behind the mask that we find individuals who have lost the spirit, there is no hope anymore. Difficult to handle children like this. Handling is better left to psychologists or psychotherapists. Emergency assistance can be done with the teacher to counter measures by using other students in the class in the sense of an integration group but will have to be careful not round up groups of children had difficult circumstances and do not let their children become good opponent. In cases where there is an offer for both children cooperate response must be avoided. The discussions in the group can help improve mutual understanding It should be consideration is in intervention anything not once group wicked son last feel invaded or harmed.The fourth intention, if a child with a passive-destructive attitude trying to attract the attention of other people so that he can gain admission. The child can become so uninspired and no longer hopes to be able to achieve something meaningful and just looking forward to failure and defeat. The child may feel hopeless because he considers everything that will come only as something that is not only fun and sass. Because children have had less self-esteem, he will retain his meager vigorously. Children will use their skills as a shield that is not how to avoid being seen as people do not need help and always avoid a situation that is not a test that uncovered shortcomings. Children suffering from low self-esteem. They rarely take part in the lesson, visible actions is limited by its inability to extreme and that he was subject to any demands and expectations. Many children who show an attitude as if they were suffering from a mental disorder. They are not children who do not have the competency, but they were not excited in such a way that the end result of his decision to give up to fate. The reaction of teachers is taking a step back. This is because the attitude of the student, so that the virus can be spread to other students. Teachers must plunge in earnest to encourage children, especially if children make mistakes. Intention children should be known by teachers with researching and getting to know the ins and outs of his attitude surrounding them.Learning MotivationMotivation can also be regarded as the driving force of the inside and on the subject to perform certain activities in order to achieve certain goals. Motivation is there in a person that makes him have the following characteristics: persevering in the face of duty, resilient in the face of adversity (not quickly discouraged, not easily satisfied with his achievements), can maintain his opinion, is not easy to let go of things that he believed, happy to locate and troubleshoot problems. If someone has the characteristics mentioned, means a person that has a strong motivation, because motivation is the driving force that causes a person to do a particular job [20]. Therefore learning is needed to determine a person's success because the higher a person's motivation to learn, the higher the success rate. Motivation contained desires, expectations, needs, goals, objectives and incentives. The three components of motivation that is the first requirement, occurs when there is an imbalance between what is owned and expected. The secod is mental power boost is oriented on expectations and achieving goals. The third, goals are to be achieved that direct the behavior of individual learning. It can be concluded that motivation as a change of energy in a person marked by the emergence of feelings and preceded with the goal. Purwanto [21] explains that the motivation contained essential elements, motivation led to a change of energy in every individual human being, the development of motivational energy would bring some changes in the existing system neurophysiological on the human organism, characterized by the emergence of a sense of motivation, affect a person. In this case the motivation is relevant to psychiatric problems, affections and emotions that can determine human behavior, and motivation will be stimulated because of the goal. So the motivation in this case is actually a response to an action that is the goal.There are two aspects in learning motivation theory proposed by Santrock [10], the first is extrinsic motivation, is to do something to get something else or how to achieve the goal. Extrinsic motivation is often influenced by external incentives such as rewards and punishments. For example, students in the exam to study hard to get good grades. There are two uses of the gift, as an incentive to want to do the work, where the objective is to control the behavior of students, and contains information about the mastery of skills. According to Ogondokun et al [22] extrinsic motivation refers to motives that are outside of and separate from behaviours they cause; the motive for the behaviour is not inherent in or essential to the behaviuor itself. If a student studies hard to do well on a test, because a good grade will result in a brand new car, then the motive behind studying is not what it is intended to do.The second is intrinsic motivation, which is an internal motivation to do something for the sake of the thing itself. Students studying for exams because she is happy in the subjects tested. Students are motivated to learn when they are given a choice, happy face challenges at their own pace, and get a reward that contain informational value but is not used to control, for example the teacher gave praise to the students. There are two types of intrinsic motivation such as intrinsic motivation based on self- determination and personal choice. In view of this, students want to believe that they are doing something because of his own accord, not because of the success or external rewards. Intrinsic interest of the students will increase if they have the choice and opportunity to take personal responsibility over their learning. The another element from intrinsic motivation is based on an optimal experience. Most optimal experience occurs when a person feels capable and fully concentrate while performing an activity. It is involved in the challenges they deem not too hard but not too easy. Slameto [23] mention factors that may influence the motivation to learn arw teacher expectations, direct instruction, feedback is appropriate, reinforcement and reward, and punishment. As a supporter of the five factors above, the shape and the way it can be used to motivate learning activities is by scoring, competition, ego involvement, giving replicates, and reward.Motivation contained two main elements interest and attention. Maulidiyah [24] described interest over three terms. First, the interest manifested in the behavior of students daily. Someone would have an interest if he could choose a credible form - fun activities themselves or manifest interest. Second, the interest derived from phrases or questions protégé. The underlying assumption is that the question someone about things that are chosen, what their likes and dislikes, is a direct illustration of the interest. Therefore, interest is nothing but a symptom of the soul in the form of questions about things that chooses or called expressed interest. Third, a person's interest in the students seem concerned individual reactions to a number of questions are organized in the form of inventory that is presented to him or inventoried interest. Interests intended as a reaction to the soul are found or arise to the questions that stimulate them. Interest and enthusiasm means a high tendency or inclination towards something great [25]. Slameto [23] states interest is a fixed tendency to notice and remember some of the activities. This activity will be considered continuous and groove. Interest is a fixed tendency to notice and remember some of the activities. Activities of a person of interest, attention is constantly accompanied by a sense of pleasure. So different from the attention, because attention is temporary and is not necessarily accompanied by feelings of pleasure and satisfaction derived from it. Interest have a great influence on learning motivation. When the lessons of materials is given not accordance with the interests of students, they will not learn as well as possible. They were reluctant to learn, they did not obtain satisfaction from the lessons learned from it. Learning materials that interest students, more easily learned and stored, as interest adds to the learning activities. Thus if there are students who are less interested in the study, it can be cultivated by way of explaining things that are interesting and useful for life as well as matters relating to the ideals and its relation to the material of the lessons learned. Based on some notion of interest that none of the above it can be concluded that the element of interest is a sense of fun, active against anything it pleases, and high curiosity about something on an individual. Thus the element of interest is more directed to the liveliness and curiosity. Attention is essential in participating in learning activities well, will also affect the students' interest in learning. Sumanto [26] argues concern is the concentration of a particular energy or life force to an objects, or the utilization of awareness to accompany an activity. Another opinion by Sarter and Lustig [27] argues that the attention describe a series of cognitive processes that act to optimize the stimulus detection, discrimination and processing, while Dayan et al [28] mentions the phenomenon of attention is a complex neurological and psychological, comes in many forms and involve various brain structures and mechanisms. Most empirical studies attention concentrated on the control, the nature and consequences selective attention. Various forms of attention has been categorized, such as sustained attention, selective, and divided. Attention is constantly subject describes the state of readiness to detect and rarely unexpected changes in the stimulus situation long time.Activities are accompanied by intensive attention will be successful, and his performance will be higher. Therefore as a teacher should always try to draw attention to their students so that they have an interest in what they learn. People who took an interest in an activity will give the most attention. He did not hesitate to sacrifice time and energy for the sake of the activity. Therefore, a student who has attention would try hard to get good grades. Thus attention is directing the activity or concentration of the soul consciousness of an object, both in and outside himself. Concern raised by the concentration of awareness of something, but not all of the same elements were subjected consciousness arises, there objects are excluded. Attention can be performed continuously associated with the three main elements include: inhibition, apperception, and adaptation. Inhibition is prohibition or exclusion of the contents of consciousness are not required. The soul must limit the field of consciousness, it is also called restriction inhibition field of consciousness. Apperception that all deliberate deployment of the contents of consciousness, including responses, understanding and so the associated with that object. The goal that we better understand the soul of the target object. Adaptation which adjustment events between subjects with the object to be targeted. However, all three of these conditions are not sufficient to prevent our attention so that no slack. There are two things that can help so that attention is not quickly loose the presence of certain feelings on an object and the presence of a strong will (needs).Lead what the student's attention, do not just keep his attention. Things that become a necessity of life will attract attention. So get yourself materials that fit their needs and bring into the activities as much as possible in accordance with their life. Seek the turn with alternating intervals, so that students do not get bored easily. The subjects relationship presented with the knowledge that he already has from materials other subjects. Perception and power adjustment is not the same child with an adult, then do not run fast demanding. Give them enough time or opportunity to make adjustments. Fatigue can loosen attention, then see that children do not get tired of doing things. The process of giving attention also greatly depends on what activities and who practice such activities. For example, someone will pay more attention to or mimic the action of rude or aggressive if he is always surrounded by such acts, than if aggressiveness rarely found in the environment. That is why, if the students growth from environment is always a fight or act rude, or if left watching scenes of violence and abuse, then it is likely that students will be easy to act rude and aggressive [29]. Observed behavior should produce effects that can be captured by the five senses. These actions have beneficial or functional value, which did not result in real results or useful for dealing with the environment, will usually be ignored. Generally, people only give little attention to what he sees every day, especially if they believe that these things have no real benefit.
2. Materials and Methods
- In accordance with the problems and objectives of the research is to analyze the relationship between variables and influences, then this type of research is exsplanatory, or studies that examine the causal relationships between variables of research, analytical approach of quantitative analysis in this study. Model of primary data collection in the study is a survey method, which is a model study using a questionnaire instrument to obtain data of the respondents opinion. Time horizon of research is the study of the stages (one-shot study) or cross-sectional, in which the data are collected only once, within a period of one month (data from one period of time) [30].
2.1. Data Collection
- The sample populations in this study were elementary school students victims of violence, scattered in 24 elementary schools that applied the principles of CFS. Purposive sampling was conducted in eight CFS elementary schools in Ambon City in September-November 2012. Total 100 students selected as the sample. Samples were abused students coming from high-grade (grade IV-VI). We used questionnaire contained statements that the truth will determine by each student by providing a choice answers; strongly agree, agree, abstain, disagree and strongly disagree. We also interviewed principals, teachers, and students to obtain data on the CFS implementation. Interviews were also conducted with the teacher that known as a teacher who openly still commit acts of violence to their students. Preparation of questionnaire and interview followed the instructions proposed by Smith and Sharp [3].
2.2. Data Analysis
- Data were analyzed quantitatively by multiple regression analysis. Sugiyono [31] explained multiple regression analysis is used by researchers to predict the state (rise and fall) of dependent variable; if two or more independent variables are predictors of manipulated factor. Additionally F and t test analysis was used to test the hypothesis. The validity of the instrument tested at the significance level of 5% of the critical value and the value of correlation (r). While the reliability test using Cronbach's coefficient approach alpha test on each indicator variable. Each physical violence and psychological questionnaires contained 12 statements and 11 items with a scale of 1-5 with options strongly disagree, disagree, abstain, agree, and strongly agree.Cronbach's Alpha coefficient resulted 0.873 and 0.749, which means physical violence and psychological questionnaires are reliable. Otherwise, the r value for physical violence was ranged between 0.700-0.865 and 0.789-0.840, thus summed as valid. Measurement of motivation which consisted of variables of attention and interest in learning is also done with the questionnaire. Cronbach's Alpha coefficient for the interest and attention are same, i.e. 0.887 which means it is reliable. While the r value of attention is ranged 0.801-0.865 and 0.709-0.851 for the interest in learning, so it is concluded valid. Before the multiple regression analysis, we started with the classic assumption test on a normality test, a non-heteroscedasticity, and non-collinearity double test.
3. Results
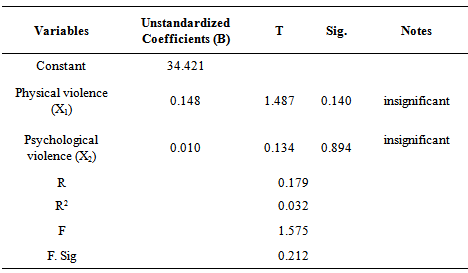
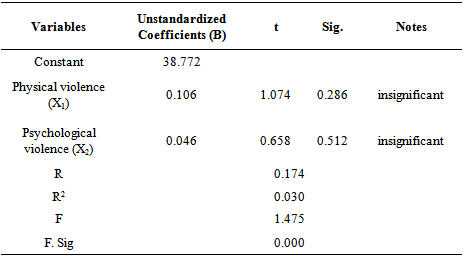
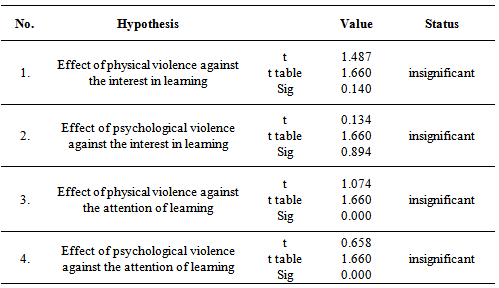
- The results of multiple regression analysis related to physical and psychological violence against the interest and attention are shown in Appendix 1 and 2. Regression model on physical violence on students' interest implied in equation: [Y=34.421 + 0.148X1 + 0.010X2]Regression coefficient β1 = 0.148 and β2 = 0.010 explained that any frequently physical violence (X1) and physiological violence (X2) resulted the increased students' interest (Y) by the value of the β1 and β2 regression coefficient.Regression model on physical violence on students' attention level implied in equation: [Y=38.772 + 0.106X1 + 0.046X2]Regression coefficient β1 = 0.106 and β2 = 0.046 explained that any frequently physical violence (X1) and physiological violence (X2) resulted increased students attention level (Y) by the value of the regression coefficient β1 and β2. T-test on hypothesis and the magnitude of t table at α = 0.05 (Appendix 3) showed that physical violence (X1) to learning interests has a value of t statistics smaller than t table (1.487 < 1.660). It implied that the physical violence is not significant towards interest in learning. Otherwise, psychological violence (X2) has a value of t statistics smaller than t table (0.134 <1.660). It is clearly found that psychological violence has no significant effect on students' interest. This means that physical violence was no empirical effect to the interest in learning.Physical violence (X1) has a value of t statistics that smaller than t table (1,074 < 1,660) to student’s attention level. These results show that physical violence is not significant to student’s attention level. Psychological violence (X2) has a value of t statistics smaller than t table (0.658 < 1.660). These results proved that psychological violence is not real or significant influence on student’s attention level.
4. Discussion
4.1. Physical Violence on the Learning Interests
- Teachers consider the occurrence of physical violence on students is due to their less discipline attitude. The student disorder occurs during and after the learning activities. Students posed impolite behavior, e.g. not doing homework, noisier and interfered learning process. These conditions made it easy to cultivate excessive emotion, so that teachers take shortcuts to soothe or reprimand the student with such practice. We even also found teachers who are extremely difficult to control their harsh and authoritarian characters. Thus, the driving force is a disorder that led students to get corporal punishment.Leasa [9] revealed that the teacher’s behavior on numbers of primary schools in the district of West Seram has effectively implemented CFS. However, most teachers still commit acts of violence on students. As a result, physical violence is negatively affecting the learning interest – increased physical violence decrease the student interest. These findings are very contradictive given the implementation of the CFS has been done in both locations. However, compared to the fact, CFS implementation on targets schools in Ambon is much better and successful than in the district of West Seram. In West Seram, violent behavior that exhibited by the teacher is very visible in any lessons. Violence is still a main culture and effort that tends to getting worse and even enjoyed by a number of senior teachers. Although teachers commonly received guidance from the principal, certain teachers are still difficult to let go such action. Otherwise Sejiwa [7] found that physically violent behavior committed by teachers is quite diverse, with a tendency of moderate frequency, i.e. beaten with cane in hand, pinched in the abdomen and arms, hit in the calf, back, and legs, squad jump, jump and hold the ears for 10 times. While the forms of physical violence in Ambon are hitting student’s hands or fingers with teacher’s bar/wood, sunbathe in the mid day, slapped in the face, ears and stomach pinched.
4.2. Psychological Violence on the Learning Interest
- The most frequent psychological violence from the teacher are some inappropriate words heard by elementary school students who still have not been able to discern any of its rational basis. Teachers sometimes mocking or provide specific designation to students who are considered naughty or academic limited. Even the facial expression of the teacher is very visible and feared by students. The teacher volume becomes stronger in the classroom during the learning. So far, this form of encountered psychological violence is still seldom. The elementary school teachers suggested that foul language is an expression of anger, though inappropriate pronounced for students. If they see a student making a mistake, teachers tend to scold and imprecate inappropriate words for the students although it is not a wise decision.Margiyani [8] stated that teachers claimed they’ve working hard to restraint their speech and behaviour to their students. Some teachers that are trained regularly by Save the Children NGO honestly stated that they really are learning and strive to become a true teacher that is expected by the students. Culturally, the character of Maluku people known as the philosophy of the sago tree – looks sturdy and hard outside, but the white (sago starch) symbolized sincerity. This character is recognized to contribute the nature and behaviour of the teacher’s communication with their students. The best way is to provide assistance for them by mentoring. It is crucial for elementary students which in the concrete operational stage of development. That is not well understood yet on the intention of expectations towards their teachers.
4.3. Physical Violence on Student’s Attention Level
- Physical violence experienced by students is highly dependent on the surface defense mechanism of increased child violence by teacher. Therefore, child acted as a boomerang to spur attention in learning. This condition is supported by the characteristics of elementary school students who are usually not vengeful to his teacher. This is consistent with previous findings that 70% students immediately forget the incidents of violence that happened, and only about 30% students remember the violence that perpetrated by the teacher. But such conditions did not last long. These students have forgotten the practices of violence committed by his teacher only about 1 week post-violence.Total of 60% students feel ordinary when dealing with teachers who practice violence, while 30% of students feel scared/tense when dealing with the teacher. They are not even recognize the teacher if encountered outside of school, and 10% still think on the violence that they get. This reinforces the reason that physical violence does not significantly improve students' attention on learning during the classroom, even though the days or hours before the teacher abused the student. Indeed, elementary students cannot do anything when treated with physical violence from teachers; they usually just keep quiet and accept. Hurt or not, they hold only in their mind, although some are moved to tears. But for innocent elementary students still love the teacher and understand that the violent behavior was for their good and future. That’s why they still show good attention during learning.Santrock [10] stated that some students bury their emotional problems. Their fear and anxiety become more severe and permanent, so that their ability to concentrate in learning will decline. Generally all children feel depressed from time to time, but most can be overcome their emotional and mood problems that are deteriorating in a few hours or days. That is why students as victims of psychological violence from teachers are not hold a grudge or anger forever. Related to this, elementary school students who have caring relationships and supportive academic typically has a positive attitude and be happy to learn. In a large-scale study, it was found that one important factor in improving students' attention during learning are toughen their perceptions about the positive/absence of their relationship with the teacher. So the quality of a good relationship between teachers and students also determine the attention should be given by the teacher to the students. It should be understood that if the teacher is in a position that tends to apply corporal punishment to students, implies that there is a rift between the two, which of course can impact on the act of attention in learning. But this condition is very dependent on the intensity or frequency of physical violence experienced by students. Teachers who show loyalty to their students and want to arouse their attention in a positive learning would behave normally, e.g. 1) ask the students if there is something wrong and distraction of learning; 2) talk to students about the problem; 3) act as a peer; 4) asked when students need help; 5) take a few minutes time to understand and call their students. Such teacher’s actions indicated social acceptance by teachers against students. Good social acceptance will impact the concentrated attention to the teacher during the lesson [23].
4.4. Psychological Violence on Student’s Attention Level
- Teachers scolding the students in scream and insults a rough warning that indirectly impact on the psychological condition of students. Surely students feel themselves worthless or inferior, ashamed, and this condition is fatal in less familiar communication or tenuous between the students with his or her teacher as well. In the end, the attention of the students in the learning process is declined. Kuswana [32] concerned to explore and move meaningful knowledge from learning resources to sustainable development. This learning process focused on the student's personal activities, learning resources and assisted media providers – ease the attention of students to focus on received new information during the learning. In the presence of psychological violence, student's attention is divided and unfocused, so that the information that received when learning is no longer meaningful.Related to classical learning theory according to behaviorist view (Pavlov), there are negative and positive experiences that can happen to elementary students. Inappropriate words spoken by the teacher, nagging and excessive anger, and uttering unpleasant child life may cause fear. Therefore, it can be seen as a conditioned fear response that affects students' attention on learning. Of course, if the frequency of psychological violence in the classroom is reduced or almost no student is not afraid to meet their teacher, neither inside nor outside or fear of the teacher during learning, thus increasing attention [10]. Thus, the learning process are also required the management of emotions that are reflected both in an effort to control anger and wrong or rude pronunciation. In the end, the relationship between teachers and students can be controlled, so that the attention of student learning will remain [29]. Teachers’ emotional violence behavior committed on the student was highly correlated with psychological conditions and the most prominent element is the students' views on themselves, known as self-esteem (self-esteem or self worth/ self-image). Alsaraireh [5] explained that each student has a self-esteem which measure people's views on him. Acceptance of teachers to students is one indication of their self-esteem is recognized or respected. Being non-acceptance is when the teacher can not consciously control their emotions and move foul, inappropriate, angry, and pierced language to their hearts. CFS environment have effectively enacted positive discipline on several targets in elementary schools in Ambon. As a result, it does look very unusual, where primary teachers almost no longer issued the obscenities, insults, or keep a deep anger toward their students. We reveal that even the circumstances ultimately force them a little scolding, it is not accompanied by a dropped or killed character of students immediately. Usually students are counselled or reprimanded in a smooth course, accompanied with jokes.
5. Conclusions
- The study revealed that violence affects elementary students' motivation, though physically and psychologically has no significant effect on the interest and attention of the students in learning. We recommend a serious and immediate treatment of all parties to the culture of violence in schools to be eliminated altogether. School strived to be open and ongoing basis socialized forms of violence, impact, and treatment on the part of teachers and students. Socialization about the impact of violence in the family or community environment also needs to be encouraged. On the other hand, a number of ornaments or accessories are Child Friendly School needs to function properly, because it is strongly supports the formation of students' character.
Appendix 1. Regression Analysis for Interest
Appendix 2. Regression Analysis for Attention
Appendix 3. Hypothesis Testing Results
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML