-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Education
p-ISSN: 2162-9463 e-ISSN: 2162-8467
2013; 3(6): 348-361
doi:10.5923/j.edu.20130306.11
Epitomizing Teacher Educators’ Conception of Teaching from Student Teachers’ Reflection
Giuseppe Tacconi, Adula Bekele Hunde
Department of Philosophy, Psychology and Pedagogy, University of Verona, Verona, L.ge Porta Vittoria, 17, 37129, Verona, Italia
Correspondence to: Giuseppe Tacconi, Department of Philosophy, Psychology and Pedagogy, University of Verona, Verona, L.ge Porta Vittoria, 17, 37129, Verona, Italia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Teaching practices of teachers strongly influence students’ learning. In turn, teachers’ practices shaped by the teaching conception they hold. Hence, this study explores the teaching conceptions held by teacher educators from the angle of their teaching practices using student teachers’ learning as a lens. In addition, refining the dimensional variations of teaching conception and figuring out teaching practices that work across the different conceptual categories were the intention of the study. To this end, reflection of 54 student teachers on what and how their professors have been doing and in what way did that assist them develop as a new teacher was considered. This came in three hierarchically related teaching conceptions: transmitting teachers’ understanding of the discipline, developing students’ understanding and challenging students’ understanding. These conceptions appeared to be varied across: contents, student role, interplay, motivation and evaluation. Coming to teaching practices, availing learning resources, modeling of teaching practices and using of video films were used differently across the conceptual categories.
Keywords: Teaching Conception, Teaching Practice, Teacher Educator, Student Teacher, Italy
Cite this paper: Giuseppe Tacconi, Adula Bekele Hunde, Epitomizing Teacher Educators’ Conception of Teaching from Student Teachers’ Reflection, Education, Vol. 3 No. 6, 2013, pp. 348-361. doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20130306.11.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the Study
- Higher education is expected to provide a high level intellectual challenge and this can be seen from the depth of approach students take in their learning[1]. Students normally take either of surface or deep approach to learning where in the first case they remained memorizing compartmentalized facts while in the latter point they go to the depth of the meaning, relationship, relevance and application of the learned concepts[2]. Thus, if meaningful and long lasting learning is required, transforming students’ learning to the deep approach is unquestionable. Students are not born to be neither deep nor surface learner rather it is the context in which they are learning that lead them to take either of the directions[1]. In general, as teacher quality is the single most school related factors that greatly influence students’ learning[3], teaching approach utilized by the teacher has an influence on the approach students take in their learning. More specifically, it is what a teacher does in the teaching and learning process that determines the level of student engagement. As further elaborated in[4], university teachers who focus on themselves and what they are doing tend to have students who focus on memorizing of facts. On the contrary, others who focus on students and their learning tend to have students who are focusing on meaning and understanding of their learning.Conversely, previous research in higher education has proven that lecturers teaching approach correlates with their teaching conception[5]. Teaching conception embeds beliefs teachers hold about teaching that guide their perceptions of situations and will shape the actions[6]. Accordingly, in a situation where lecturers assume teaching as transmitting basic information, they tend to focus on delivering facts they think worth important to be learned by students. In response, the task of students turned out to be attending lectures, reading notes and textbooks. On the contrary, when lecturers conceive teaching as a process of facilitating students’ construction of knowledge on their own, they are focusing on inspiring students to take responsibility for their development.Coming to teacher education, the issue has paramount effect as it is the first scene where students begin learning about teaching profession. They may learn about teaching profession not only from the content the teacher educators are teaching but also from what and how they are doing in the process of teaching. This imprints solid foundation in the mind of student teachers regarding the how of teaching students. However, teacher educators’ practice is in turn influenced by the conception they have held about teaching. As a result, teaching conception of teacher educators worth the study if laying firm foundation about the proper teaching conception in the mind of the future teachers is needed. For the same reason, this article intended to explore the teaching conception of teacher educators from the view of student teachers’ reflection.
1.2. Theoretical Framework
- It has been long since teaching conception becomes the focus of research in higher education[see 7 & 8]. As any phenomenographic study, a core assumption of studies in conception of teaching focuses on its referential (the meaning) and structural (approach) aspects. For example, as used in the study of[8], the referential aspect stands for the ranges of meanings teaching bears as experienced by university teachers while structural aspects refers to the intentional aspects with which they approach their teaching. In line with this, studies have been consistently showing commonalities in depicting the meaning teaching hold for university teachers as transmitting information to students with great focus on the role of teacher and teaching strategies (teaching-focused approach) or facilitating development of conceptual understanding in students where focus of action is on students and their learning (learning-focused approach). Thus, these two qualitative categories of teaching conception remained consistent across studies but diversification and a new way of understanding comes as one goes further into examining if these conceptions are consistent across contexts (stable or relational), hierarchically related or independent) and the quest for coming up with new way of understanding teaching conception by expanding its dimensional variations[6, 7, 8, 9, 10 & 11]. Studies focusing on the stable or relational aspect of teaching conception focus on exploring if teachers conception of teaching is influenced by the situational factors. In response, the study of relationship between teaching conception and teaching practices on 18 teachers in Hong Kong revealed that, in a situation where there is high contextual influence like external examination syllabi, teachers’ conception of teaching and teaching practices in secondary schools divorce each other[6]. In addition, the study conducted on 20 Helsinki university teachers, who were working in five academic units that won the national awards of quality education, shows that contextual factors are not only divorcing the teaching conception and practices but it also shapes the teaching conception of teachers[10]. They found out that teachers’ conception of good teaching coincides with the characteristics of good teaching mentioned by the university; which is also in line with selection criteria used in national quality education award. Provision of support to teaching staff along the externally driven criteria has implication in transforming their teaching conception and practices to the desired level. Review of eight international studies done by[12] and empirical studies by[13 & 14] confirm this notion by showing the positive impact the instructional development initiative has in facilitating the development of student-focused conception of teaching. In general, the aforementioned analyses indicate the influence of situational factors on teaching conception teachers may hold. On the other hand, in the situation where there is no strict contextual factor that demands university teachers to do in a specific way, their teaching conception and practice coincide.Coming to the independence or related aspects of teaching conceptions, phenomenographical studies in general agree that teaching conceptions are hierarchically related where conception at the higher and more complex level becomes conscious of lower level dimensions. In this manner, teacher who hold of teaching conception as changing students’ understanding (learning-focused approach) have been seen of talking about teaching episodes related to transmitting the discipline information (teaching-focused approach) but difficult to find higher level elements in the explanation of teachers falls in the category of lower level conception[8 & 9].Coming to teaching conceptual categories and their dimensional variation, there are five conceptual categories of teaching synthesized from the review of thirteen studies on teaching conception of university teachers[7]. These are: • Imparting information, • Transmitting structured knowledge, • Interacting with students, • Facilitating understanding, and • Changing conception. While the first two categories are included under teaching-focused conception, the last two go for learning-focused. However, interacting with students remained at the middle ground of teacher-focused and student-focused orientation. The subsequent study spoke against the intermediate conceptual category quoting Samuelowicz and Bain (2001) who suggested that all conceptions of teaching are primarily teacher-focused or student-focused; hence, there is no justification for having the middle ground[8]. The aforementioned study investigated teaching conception of university teachers based on their experience as being a teacher, which resulted in four conceptual categories: transmission, relation, engagement and learning focused experience. Thus, in contrary to findings in[7], the study labeled the student - teacher relation focused experience as teacher-focused approach. The decision was rationalized in such a way that even if the aim of developing good relationship with students is to motivate them and help them develop problem solving abilities and practical skills, more focus is on teachers’ activities during the attempt of establishing relationship. For instance, interviewees in the study were more talking about the roles they have in establishing relationship than that of students[8].Gonzalez has taken further the study of the hierarchical relation and dimensional variation of teaching conception[9]. As this study is more inclusive and recent as well compared to the previous studies on teaching conception, we used it as framework for the study from which we produced this article. Gonzalez interviewed 18 Australian university teachers who were drawn from various disciplines and synthesized four teaching conceptual categories with four dimensional variations:• Transmitting the basic information of the discipline,• Transmitting teacher’s understanding of the discipline,• Developing student understanding, • Changing students’ understanding.Structurally, the first two categories belong to teaching-focused conception while the last embraced under learning-focused conception of teaching. Four dimensions of variation identified based on which one level of conception differs from the other: content, teacher role, student role and motivation. At the lowest level of the conceptual category, transmitting the basic information of the discipline, teaching content is bounded to the course syllabi; teachers are active organizers and transmitters of the lesson while learners’ task is passive receipt. What is more, inspiring and engaging students in the learning process (motivation) is not the very nature of this category. On the topic of teaching conception as transmitting teacher understanding of the discipline, content of the teaching can go beyond the limit of syllabus as long as a teacher has new insights on the points students need to learn. However, the role of the teacher and students as well as focuses on motivation remained as before. The role of the teacher transformed to facilitators while that of students become active constructor of knowledge where contents can be either provided by the teacher or picked by students in a situation teaching conceived as developing students’ understanding. Here, teachers realize that student’s construction of understanding is difficult merely by supplying information unless students become conscious of the relevance of their learning and actively involved in the process and develop own understanding out of what is taught. Thus, motivation gets emphasis from teachers with this category of teaching conception. Changing students’ understanding is the last and advanced level of teaching conception according to Gonzalez. Teachers who hold this conception don’t consider teaching as letting students repeat what has been taught unlike the first two categories. At the same time, engaging students in understanding their personal understanding of the subject alone is not adequate. Rather they intend that students need to get the deeper understanding of the world, able to use a learned concept in different way depending on the demands from the real world. To this end, teachers with this conception are seen engaging themselves in challenging students’ thinking: provoking dialogue, life-related task and pushing them to go beyond the immediate scene. Student are also playing active role in the process of learning. Moreover, content of the lesson is flexible and can be generated through interaction between teachers and students. These teachers understand that these all is impossible unless students have a motive for their learning. Hence, being able to motivate student is characteristic of good teaching.These conceptual categories are hierarchically related in which the lower levels are stepping stone for subsequent higher level conceptions. In this manner, teachers who hold conception of teaching at the higher level are normally addressing lower level conceptions as a means to reach their destination[15].As can be understood from this analysis, the ongoing explanatory studies result in better understanding of the different facets of teaching conception. For the same reason, Gonzalez has pleaded for further investigation on the same area. Studies so far mentioned were conducted on university teachers except[6], which was done on secondary school teachers. However, we believe that as teacher education is starting place for learning of teaching profession, teaching conceptions hold by teacher educators deserves study. In addition, each conceptual categories of teaching and the corresponding dimensional variations manifested through teachers’ practices[16]. Put it differently, it is what the teacher is doing that influence the shape and nature of learning content, either the content is to be picked by students or decided on by the teacher; students’ motivation for learning also depends on the relationship teachers established with students as well as the degree to which the teacher relates his teaching to the life of students. Besides, it is teaching practices of teachers that put their role in the teaching and learning process as active transmitter of the knowledge, or facilitators and challengers of the learning process. Likewise, teachers’ plan and teaching strategies used have a direct relationship with the role students have to take in their learning. It is what the teacher is doing that lets student passively listen to the lecture, or be in a position of indentifying gaps in their own personal and professional development and strive hard to fill in the gap than merely reproducing lecture notes. Therefore, exploring further the conception of teaching from practices of teachers as experienced by students in the course of facilitating their learning will have a significant contribution not only for expanding conceptions of teaching but also for pinning desirable teaching practices in the context of initial teacher preparation. Alternatively, this shows the possibility of tracing back to the teaching conceptions of teachers from their practices. Therefore, analyzing teaching conceptions from the view of end users (student teachers), based on practical experiences they have encountered as being a student, is a good sieve for filtering teaching practices of teacher educators and their teaching conception behind the practices.
1.3. Purpose of the Study
- The purpose of this study was to explore the teaching conception of teacher educators from the angle of their teaching practices using student teachers’ learning as a lens. More specifically, it intended to: • Examine teaching conception of teacher educators from the view of student teachers,• Extend dimensional variation of teaching conceptions from the experiences of student teachers,• Explore cross-cutting teaching practices across different level of conceptual categories.
1.4. Context of the Study
- Initial teachers’ preparation for secondary school has short story in Italy. The first University-based teacher education in the country has stipulated by law 341/1990, which led to the establishment of two-year Specialization degree for Teaching in Secondary Schools (Scuola di Specializzazione per I’Insegnamento Secondario), hereafter referred as SSIS [17]. Thus, the program was conducted in a form of serial model where trainees recruited from four-year degree graduates or from three-year and two-year General and Specialist degree in relevant discipline for secondary school contents. The admission to the program was on a competitive base where entrance examination set at the national level and selection was done taking into consideration the available position at schools[17 & 18]. Albeit the proclamation was set in 1990, SSIS had been under operation only from 1998/99 to 2009/10.After ten years of service, SSIS has been dissolved and instead one year initial teacher preparation program (Tirocinio Formativo Attivo), hereafter referred as TFA, has launched by law 249/2010[19]. Like that of SSIS, access to the TFA is in a programmed number; hence admission is based on competition where one needs to stand for national examination in order to get the place. Accordingly, the first batch of TFA, which is the target of this study, commenced, at the University of Verona, in November 2012 and concluded in July 2013. The program has three phases: common areas (18 ECTS), discipline didactics (18 ECTS) and school practicum (tirocinio) with 19 ECTS, which is concluded with production of a written work (5 ECTS) based on the practicum experiences. The program is designed in such a way that the first phase composing of general and special Pedagogy courses covered by professors from the Pedagogy Unit, then didactic discipline followed with relevant experts from corresponding departments then student teachers deployed to schools for practicum under the guidance informed tutors.
2. Research Methodology
- The study was guided by the phenomenographic approach. Phenomenography uses to describe holistically the meanings people create for phenomenon around them[20]. Phenomenon has two interwoven aspects, namely referential and structural[21]. The referential aspect stands for the meaning people attach to the phenomena (What?) while the structural aspect represents the way of approaching it (How?). Thus, phenomenon in this study is conception of teaching. Hence, the referential aspect is the teaching conception hold by teachers as perceived by student teachers while the structural aspect is teaching practices of teacher educators as experienced by student teacher.Classical phenomenographic studies focus on the direct meaning people create to the phenomenon a researcher is interested in[14]. However, this study went step further to see the teaching conception and practices of teacher educators, not directly by asking teacher educators what it means for them teaching student teachers is and how they are doing of it, but using student teachers’ learning experiences as a lens in order to screen teaching practice they conceived as important for their preparation as a future teacher, then examining the teaching conception laying behind the practices. Consequently, the study made use of the lived experiences of student teachers who were taking part in the new teacher preparation program for upper secondary school at University of Verona, Italy, in 2012-2013 academic year.Accordingly, 85 student teachers who have been on the verge of finishing the last course of the first phase (common areas) were invited to participate in the study. Eventually, 54 student teachers submitted their reflections. They were clearly informed both in written on the e-learning’s workspace designed for the program and orally in class that they were required to reflect on professors’ practices that assisted them learn as a future teacher. We also provided them feedback in between looking at the general responses particularly those who couldn’t make clear distinction between teaching practices and how or in what way it assisted them change. The analysis of participants’s reflection was also done following basic principle of phenomenographic study: revealing understanding of the phenomenon from participants’ point of view than the researchers’ understanding[18], analyzing particular experiences of participants in the way ranges of conceptions that provide complete explanation of the phenomenon emerge[ 9 & 14]. In addition, grounded theory was used in coding the texts along the existing categories, dimensional variations and labeling of teaching practices. In a situation where the analyst has several categories, coding can be done by relating the major points in the paragraph or sentences with these categories[22]. Thus, as the goal of the research is to refine teaching conceptions of teacher educators from the view of student teachers using teaching conceptual categories synthesized by Gonzalez, we analyzed each part of the text in the individual student reflection by asking what major idea brought in the sentence or paragraph in terms of learning of student teachers, then to which conceptual categories does the claimed change belong: transmission of content discipline, transmission of teacher’s understandings, developing of understanding or changing of students’ understanding? Similarly, as the aim is to find out practices of teacher educators that facilitate student teachers’ learning, the reflection was considered if reflector indicated teachers’ action behind the change. Then, coding across dimensional variations within a conceptual category was done by asking a question: to which dimensional variation does the claimed change belong: content, teacher role, student role, motivation or any dimension out of these? Thus, the coding across the dimensional variation was done along taking explanatory notes as why of such text classified under the corresponding dimensional variations. Using the previous annotations and re-analyzing the part of text categorized under each conceptual categories, and the corresponding dimensional variations, code provided to the underlying teaching practice. Unlike conceptual categories and dimensional variations, we didn’t use predefined categories for teaching practices. Rather we coded practices from what teacher educators have mentioned in their reflection, then we used comparative analysis in order to give similar code for similar practices across different categories[23].In general, coding of student teachers’ reflection was done at three levels with the possibilities of going forth and back: coding against the conceptual categories, dimensional variations and then in terms of the underlining teaching practices. In sum, the followings are details of procedure we went through:1. Clearing and giving code for reflection of each individual from 1-54 as a case and then entering these into Nvivo 10 version. Similarly, each of the four teaching conception categories defined and entered into the software along the four dimensional variation under each of them.2. Each text from individual student critically read, and the part that corresponding to either of the conceptual category selected and coded. In doing so, explanatory notes were given for each as per why it was coded under the corresponding category (in terms of what student teachers have gained out of it and the underlining practices of the teacher educator). In this manner, we have undergone first coding for 54 cases where three participants were excluded as they simply evaluated the teaching of professors without indicating the lesson they gained or specific practices behind the change.3. Then, parts of texts coded under each conceptual category further coded in terms of the dimensional variations indicated above. These processes even allow us to reconsider the previous coding, and annotations. Right at this point, using our annotations, we coded the text under the corresponding dimensional variation into teaching practices used by teacher educators. Thus, we generated list of teaching practices under conceptual categories/dimensional variations.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Teaching Conception
- Three categorical assumption of teaching emerged from the analysis of student teachers’ reflections:• Teaching as transmitting teacher’s understanding of the discipline, • Teaching as developing students’ understanding,• Teaching as changing students’ understanding.Analysis of teaching conception of teacher educators from student teachers’ reflection maintained the aforementioned conceptual categories founded recently in the exploration of teaching conception by Gonzalez. However, there was no evidence for the persistent of conception of teaching as transmitting discipline’s basic information. Teachers who hold teaching conception as transmitting discipline’s information are bounding their teaching to the course syllabus[8 & 9]. However, in this study we didn’t come across any reflection that acknowledged any of professors’ teaching practices with reference to the content transmission based on predesigned syllabus. Moreover, the remaining conceptual categories appeared as hierarchically related where conception of teaching as transmitting teachers’ understanding of the discipline (Conceptual category one/C1) appeared as a base for students to process so as to develop their own understanding of what is being taught (Conceptual category two/C2). Then, students’ understanding of what is being taught assists them as a vehicle in dealing with the reality of the school teaching, which is complex and dynamic in nature for which challenging students’ understanding (Conceptual category three/C3) in the way they can continuously shape skills and abilities they have developed so far in response to ever existing dynamisms is required. What is more, structurally C1 falls under teaching-focused approach, while the remaining two belong to learning-focused approach.Dimensional variations of teaching conception refined further including previously unrecognized dimension: interplay and evaluation but with the omission of teacher role as separate dimensional variation. Thus, five dimensional variations of teaching conceptions: content, student role, interplay, motivation and evaluation were characteristics identified as a frame of references for categorizing teaching practices of teacher educators into three hierarchically related conceptual categories. In the previous studies by Gonzalez and Akerlind, teacher role was identified as a separate dimensional variation[8 & 9]. However, in this case it didn’t appear as independent dimension as all other dimensional variations depend on what the teacher educators supposed to do. For examples, letting students to be passive receipts of information from teacher’s preaching in C1, putting students in a position of taking responsibility for their personal definition of concepts taught in the class in C2 and teachers and students co-agent of knowledge construction in C3 are depending on what the teacher educator does. Therefore, teacher educators’ role is important determinant factor but embedded in all dimensional variation of teaching conception.In general, all what teacher educators are doing in relation to facilitating learning of content, student role, motivation, interplay and evaluation that are targeting transmission of teacher educators’ understanding classified as C1 while those focusing on assisting student teachers develop personal understanding of the concept taught and challenging the solid understanding of students are respectively come into C2 and C3. Next, dimensional variations of teaching conceptions are presented along with teaching practices of teacher educators which is accompanied by sample excerpts taken from student teachers’ reflection. At the end of each excerpts, either of C1, C2, or C3 used to indicate the conceptual categories it represents, which is also an indication for the possibilities of using single teaching practice under the same dimensional variation but addressing the three ladders of conceptual categories.
3.2. Dimensional Variations of Teaching Conception Content
- It is clear that we talk about teaching practices because there is content: be it in a form of concept, value or skill that has to be learned by student teachers. However, the way the teacher educators present contents for learning depends on the way they conceive teaching. Hence, content appears in the study as one of the dimensional variations. Availing learning resources Analysis of student teachers’ reflection showed availing learning resources as the sole relevant practice of teacher educators in relation to facilitating the learning of the content. However, the way teacher educators’ facilitate the availability of learning resources differ qualitatively across conceptual categories. In the first instance, student teachers considered educators’ attempt of providing well-organized materials with harmonized definition as useful practices for facilitating their learning. To illustrate:I found professor’s provision of pantry or the book of the course as excellent practice. Having all materials organized in a consistent and timely manner allows students to save time. It also avoids both the problem of finding more sources in which splitting up of the content proposed may occur with the possibility of having inconsistency of definitions or notations, given that they have been harmonized by the teacher (C1).Thus, the above quote implies the existence of educators who engaged in determining and organizing the learning materials for student teachers which they belief that may save time for student teachers as well as inhibit misinterpretation by the student teachers. In this case, the intention of teaching can be considered as transmission of the discipline content. At the same time, organizing contents and providing harmonized definitions and notations take into consideration the importance of educators’ understanding of the discipline. Apart from this, there is evidence that shows educators’ attempt of availing learning resources, not to be memorized but to let student teachers get deeper understanding of the content: Professors provide details of a collection of websites or specific references and retrieval tools, a practice that can also be understood as an invitation to seek direct contact with the sources, and personal exploration of the documents (C2).Understanding develops when students’ got opportunity to learn by doing[24] and that is possible when they obtained learning materials and activities which are relevant to their need. The above mentioned quote testifies the existence of teacher educators with similar notion and as a result who are organizing learning resources in the way student teachers may pick and learn the one appeal to their need. Therefore, as the attempt is more on assisting student to get understanding of the concept to be taught, it is considered as C2. Moreover, respondents acknowledged teacher educators’ attempt of putting students in a position of learning through the book than the book itself as a fruitful practice for student teachers’ learning. To illustrate:…the philosophical flavor: the teacher teaches through books, not the textbook. For the teacher, the book is only a facade of a much broader background.[…] From this perspective every effort to add useful material or to delete the obsolete material combined with practical activities based on the book show that the professor is no longer needs to stop us at the textbook adopted[…] he also didn’t want us to study books for examination but to use concepts in the books in preparing projects, criticizing cases and reviewing of books or articles that we get interested in[...] (C3).According to this idea, teacher educators’ effort in providing practical activities based on updated and relevant learning materials allow student teachers to use the basic principles and concepts in the book as a tool in the process of their learning. Using learning concepts and skills as a tool in the process of learning enable the users to realize the contextual applicability concepts learned. This is advantageous to trainees as real world of work is complex and as a result it is difficult to have one to one kind of relationship with skills. Therefore, letting them learn using the concept and skills already developed is giving them opportunity to go on refining learned skills and concepts as per the demand. In sum, useful practices of teacher educators that student teacher has identified in relation to content of their learning ranges from availing well structured learning materials to be memorized to availing learning resources for the purpose of allowing students to study through the book than the book itself.Student role Students are normally expected to take the lion share in the process of their learning. However, the role they expected to play depends on the teaching practices of their teacher educators, which is influenced by the conception they hold about teaching. In view of this, ranges of teaching practices used by teacher educators that student teachers considered as relevant for their learning were identified. Some of these practices seem to put students in a position of a mere receiver of information (C1) while the others engaged them in activities that let them get the personal meaning of the learning object (C2) and those that challenge student to use the learning concepts as a tool in their subsequent learning and realize the contextual meaning and use of concepts (C3). In a nutshell, hereunder are educators’ practices in relation to facilitation of student’s role.Using of video or filmTeacher educators have been using video in their teaching for different purpose. One among these is to address sheer volume of information that they couldn’t achieve using lecture method. To illustrate: …the use of short documentaries, have made me understand many things, which I think, through a lecture, could not be passed in the same way ( C1).I found professors’ use of film clips very useful in enabling me even now to recall some concepts or some nuances (C1). The above reflections show the positive elements in educators’ use of video as it assisted educators to cover the large portion of the discipline’s information as well as assisted students to recall concepts important for their practices. However, it is impossible to be sure if this practice would assist students to understand concepts taught. The task of students perceived in this case as receiving and recalling of facts. A collection of films for teaching purpose is from the experience and understanding of the teacher educators. As a result, the practice of using video for teaching purpose can be taken as C1.There were also some who claimed that educators’ use of video assisted them to focus quickly on the lesson of the day and internalize the basic concept as a result. To illustrate: [...] by watching film clips[which are] more or less famous, I came to focus quickly on the topic of the day,[…] then immediately internalize the basic concept much more than what I could do with hours and hours of individual study on a manual.[…] I also found useful the subsequent analysis we were making on individual films and documentaries on specific issues being addressed in the class[…] (C2). As can be seen from the above, using of video attract and sustain students’ attention towards the lesson, then analyzing the video film from the point of the day’s lesson facilitates students’ understanding of the lesson. Another step further, using of film allows student teachers to visualize the simulated life of school teachers and analyze possibilities for making teaching practice better from their own view points. To illustrate:[…] I found professors’ use of videos inspiring particularly those involving teachers struggling for success in their teaching.[…] I was particularly impressed with the figure of Professor Katherine Watson[character in the film], which I think is revolutionary in the teaching profession. These clips have given me the opportunity to analyze certain teaching episodes[…] and reflect on the fact that there could be a different way to deal with them, a way I have not yet had the opportunity to discover before (C3) Using documentary films as a teaching method allowed student teachers to reflect on teaching episodes in a different way than they have been thinking of. This put student teachers in a position of reconstructing the teaching episodes shown and argued on possibilities of doing it in a better way if they were given the opportunity.Providing opportunity to learn in group This is another teaching practice that student teachers repeatedly reported as vibrating their roles in the process of teaching and learning. So, even if we didn’t come across students commenting on the relevance of teachers use of group work that goes to C1, more witness come in favor of the practice in facilitating student construction of knowledge (C2) and development of critical thinking skills (C3). The following excerpts were taken from students’ reflections:[…] group work to me[...] is digging into the school experience of my colleagues who have already taught at school.[..] The practical knowledge that often emerges from narratives of classmates about significant events is helping me to have a concrete background to have clear understanding of what teaching at schools looks like (C2).The aspect that I found most useful and stimulating was undoubtedly the constant comparison with my "Fellow travellers":to hear their stories, their experiences, and difficulties in which they are or have been. As a new teacher, for me this is the most important source from which to draw material alive for my teaching practices, much more than I could make a theoretical manual. Confront with them, especially in times when we were given the opportunity to work in small groups, this gave me an opportunity to reconsider my act, think back to some details that I didn’t consider.[…] It is interesting to see that my problems are theirs, I can find the difficulties I have met in their words, listen to how they managed to overcome such difficulties[…] (C3). The first quote indicates that letting students learn in group benefits learners with less experiences to learn from the accounts of their colleagues with more teaching experiences in school. In this case, the reflector stressed that such opportunity assisted learners to correlate learning of specific concepts and skills with actual practices in schools, which made the lesson more immediate, concrete and understandable. Put it differently, learning in group in this case where student teachers encouraged to share their school experiences in relation to the lesson at hand is contextualizing learning on concrete ground that let them understand easily the school reality and the corresponding lesson in a better way. The second extract shows that learning in group go beyond understanding of new skills to reconsidering one’s own teaching practices.Bringing school experiences into classroom discussion Teacher educators who were able to relate classroom discussion to issues happenings at school including inviting student teachers to bring their experiences of working at a school into discussion considered as a vital practice for facilitating learning. As can be seen from the following excerpts, bringing school experiences into classroom discussion is useful for all students disregarding the duration of experiences they have at school:I joined teaching very recently[…]. For me, it is important when professors engaged us in the real moment of schools and teachers life in that context. Particularly, I liked when colleagues talk about their school experiences and we analyzed the cases they bring in the light word of the topics in the classroom (C2).[…] the aspect that I find most important and that helps me in teaching practice is the lesson I gained from colleagues: their relationship with children, subject matter and the practical situations they are facing at school, which it seems to me that the texts of pedagogy and didactics sometimes disregard perhaps more than they should.[...]. I believe that this aspect is fundamental in terms of effectiveness of teaching, but also the expansion of the perspective with which you look pupils and our own teaching (C3).Therefore, letting student teachers discuss about live problems and everyday activities at school would lead them to have concrete understanding of the school reality and skills they need in order to cope up with pressures laying in front of them. Furthermore, bringing trainees experiences into discussion enable them to have broad understanding of didactic at secondary school. Thus, educators attempt of letting student teachers to work in team, discuss openly their current experiences in relation to topics of study is assisting them to consider single phenomena from different perspectives as what works in certain school may not work in other as well as the same problem in different context may require different approach. Therefore, teacher educators’ attempt of bringing school experiences into classroom discussion, like group work indicated above, aligned with C2 and C3. Modeling teaching practicesStudent teachers witnessed that they were learning about teaching not only from the contents that their teacher educators have brought to the classroom but also from what and how the teacher educators taught them in the course of teaching and learning process. In this regard, it is up to student teachers to figure out teaching activities relevant for them from what their teacher educators are orchestrating in their teaching. One of the respondents put this idea bluntly as follow: [...] all techniques so far put in place by several teachers completely new for me and they are absolutely effective not only for the content of the knowledge presented in class, but also for the acquisition of teaching practices they are demonstrating that we may in turn use in the future. (C2) This shows that modeling of teaching practices by teacher educators enable student teachers to acquire specific teaching techniques. More importantly, student teachers reported the possibilities of learning the situation in which the use of specific teaching technique overweigh the others by comparing the effect on their own learning as a student. To illustrate:I learned not so much from the contents conveyed by professors rather from observing the techniques and methods they have used during the lesson. During the course we were able to compare the various types of lesson (exhibition, narratives, and heuristics) and tested directly on ourselves the strengths and weaknesses of these approaches (C3).The forerunning reflections in general show the possibility for student teachers to learn new skills and practices from the way teacher educators were doing than what actually they were teaching (C2); evaluating the effectiveness of different teaching methods and techniques using their own learning as a litmus paper (C3).Inviting for reflectionEncouraging students to make deep reflection on why and how they are doing what they are doing in relation to their professional practices is another point that student teachers acknowledged as useful practice. As one of student teacher strongly commented such opportunity assist them to elevate their teaching skills to the higher level:I think that a reflection on the experience of learning that we had as a student and as a student teacher has a double benefit. In the first instance, it provides opportunity to internalize techniques and knowledge studied. Secondly, personally I find myself thinking about my practices in class as a teacher, and think about how I can improve my teaching action not only in the light of contents studied, but by observing the way contents were put into practice on us as a student (C3). Thus, getting opportunity of reflecting on their learning as a student and linking that to how they could be implemented in their classroom teaching would result in changing their teaching practice. InterplayInterplay, interaction between teachers and students is among dimensional variation of teaching conception identified in the study. It is different from motivation as it is more prone to be condition for motivation. Motivation is the desire to engage in learning activity while having sound student-teacher interplay is the prerequisite for the state of motivation. Hence, interplay appears in this study as a dimensional variation of conceptual category. The followings are teaching practices reported as vehicle for establishing interplay. Closing the gap Narrowing down the physical and psychological gap between student and educators is one of strategies teacher educators used as a means to lay down foundation for sound interplay. Teacher educators who are close to students, moving among students during classroom instruction and those who are perceived by students as supportive, attentive, and facilitators than as somebody who is the master of everything that cannot be reached off are effective in building sound relationship with student teachers. To illustrate:[…] professors have tried to reduce the physical distance they had with us. They tried to move inside the classroom; avoid sitting behind the desk except for brief moments dictated by conditional needs. This situation makes us understand that they have an interest in teaching and has taken learners into account (C1). Teaching practice that I have already started to experiment in the classroom is to teach the pupils moving among them.[…] The teacher "falls" among the students mingle with them, urging their interventions, assisting them in case of difficulty, or simply making their presence felt natural to give more thickness and density to the content of the lesson (C2). In this context, teacher educators’ movement in class during delivery of lesson is important in keeping the attention of students even in the moment the lesson is hard or difficult to comprehend. As a result, the intention could be to transmit knowledge as there is no evidence for the development of understanding. In the later excerpt, the student teacher went beyond recognizing the value of minimizing the gap to applying it in their teaching. This shows that the responder came to understand and apply new teaching technique, hence, the practice fall in C2. Moreover, closing the gap is not only for teachers and students relationship, rather it concerns interaction among learners themselves. As a result, student teachers were praising the attempt of some of their teacher’s educators for letting them know one another’s background, as depicted hereunder:Prof X planned his lesson in such a way that students present themselves centering on their personal story, educational background and experiences. All students have received the demand positively and that has improved the classroom climate, which in my opinion are the foundation for effective students’ learning (C2).At the beginning of each lesson the professor has left us a space for our presentations giving the opportunity to everyone to explain its current situation and educational background. He also used the group work that allowed us to meet with colleagues teaching similar subjects but in different schools (C2).As can be understood from above extracts, teacher educators closed the psychological gap (understanding) among students by letting them know who about of each other from the start. Thus, understanding each other better will assist the co-construction of knowledge (C2).Sharing worries Other method student teachers claimed their educators used to maintain positive interplay with them is listening actively to their worries and personal questions even during classroom instruction and signify them that at least they understood their concern. The following extracts were taken to illustrate the case: Technique of listening that many have adopted in certain situations, especially in times of disappointment from student side regarding the onerous of the course and the program in general was stunning. That is, at a time they felt our discomfort, they stopped the usual lesson to give space to hear our worries and complaints. In my understanding losing of a few minutes to listen to students’ problem will earn positive relationship, which will give best result later on (C1).[…] during first day of class, I explained to Prof X the difficulties I have with the train time, then immediately he answered saying: "I know what it means to have something to do with trains, I used to commute”. Do not worry, I understand”. “I always remember these words, because it really made me realize something very important: teachers should know how to reach out to those who want to learn or who are in trouble.[...] As a result, I begin to create a proper environment in my classroom with my students: propose topics to children in a way close to them, more understandable and engaging (C2).In the first quote, student teacher acknowledged that some teacher educators gave space during instruction for student teachers to speak out their mind regarding the pressing issue they have. Thus, giving brief time for students to express their worries and clarifying the concern to the level best, then proceeding to the lesson at hand is perceived as a good bridge for student-teacher relationship. This action is more gear toward getting the attention of student in the mid of the lecture, hence we put it as C1. The second quote speaks for the educators’ action in communicating back to student teachers that they understood their concern. And this regarded by the reflector as relevant for teaching profession and even went to applying the same thing in his/her teaching. As a result, this action of teacher educator even went beyond recognizing the value of having sound relationship to applying it, hence the reflector’s remark put as C2.Actively listening to students’ ideaHaving habit of actively listening to student teachers’ idea is the other way of managing relationship. As one of student teacher put straight forward, listening actively to the ideas of student teachers would enable teacher educators to win trust and respect from student teacher that can service as a vehicle for transmission of knowledge. First of all, I really enjoyed the listening start up business that has been proposed in the first module.[…] Being able to listen to our students is essential in order to win their trust and build a relationship based on respect and esteem, serve as a vehicle for better transmission of knowledge (C1). Furthermore, other student teacher commented that they have understood the need for sincerely listening to student idea while they are sharing their viewpoints, personal experiences and achievement as well as consistently valuing their contribution as palpable way of having sound relationship. To illustrate:…one of the good features that I have learned from these professors: the ability to listen on the part of teachers, the "creation" of an atmosphere of non-judgment during the lessons, especially in moments of greatest intensity on a personal level narration of experiences (C2). […] the goodness of a lesson depends on the type of relationship that the teacher is able to weave with her students, and in this regard I have to admit that all professors that I have met during the various modules[…] were paying great attention to our needs, giving us pause frequently, often asking us how we were going through the lesson, if we had any questions, if we wanted to add something by listening all the interventions with respect and thanking at the end of each intervention emphasizing consistency or another aspect of positive, encouraging and valuing words (C2). When one looks closely at the rationale behind teacher educators’ use of active listening in the above quotes, the first is to communicate knowledge effectively (C1) while the other is to encourage development of understanding by student teachers through sharing thought, and feeling where student teachers put in a position of knowledge construction (C2).Motivation Motivation appeared as one of the dimensional variations of teaching conceptual categories as witnessed from the analysis of student teachers’ reflections. Thus, teacher educators’ attempt of inspiring and engaging student teachers in learning process qualitatively varies along the conceptual categories of teaching where at the lower level of the conception educators’ action targeting on getting the attention of learners, then eventually progressing to action that put student teacher in learning for the sake of learning. The followings are educators’ practices orchestrated across the range of the conceptual categories.Teaching with passionTeacher educators who approach their teaching with strong passion for teaching can easily win the attention and interest of student teachers that in turn will inspire them to perform to the level best in their learning. To illustrate:Some of professors, despite approaching the lessons in a more lecture way, their actions imply the love and respect they have for their course and the profession. The mode of explanation, attention given to terms, and the tone of their voice signify their intention and keep the class alerted.[…] I think without this we cannot teach well, and inspires students for study (C1).Thus, student teachers considered teacher educators’ ability of communicating their passion for teaching profession using different strategies such as changing their voice depending on the message they wanted to pass and stressing key concepts of the lesson in their lecture. These mechanisms assisted them to maintain attention of student teachers as well as passing the passion they have for teaching to their trainees. In these scenario, it seems that the target of the teacher educators focus on how of transmitting the interest and knowledge they have to learners than letting learners develop understanding of the things taught through personal effort. As a result, teaching with passion as a means of getting students motivated for learning fall under C1.Modeling practicesHearing and watching practices of educators assist student teachers to recognize the role and responsibilities of teachers. For example, as shown below, educators’ mastery of the subject, preparation for teaching and effort they are making to participate students in their lesson deliver similar message to student teachers for their later teaching:Thinking back to the teachers who have come and gone so far in the course I noticed first of all a common denominator: a remarkable expertise in their disciplines flanked by a careful and timely preparation of lessons and a palpable desire to make us partakers of the lesson (C1).Moreover, participants have indicated that teacher educators use of certain teaching tools assist them to understand the value of using such approach in their later teaching. Here are some of the things they have said:The use of diagrams and mind maps to help students to follow the thread of the conversation was used in some cases and is, in my opinion, essential to teach in the secondary school (C2). Certainly I gained a lot[…] not only from books and articles, which I have also found it very interesting, but also from the way professors teach. They never said, "Do so," but we were shown, with spontaneity and ease, what we should do (C2).These two immediate quotes indicate that student teachers clearly identified the roles and responsibility of teachers as well as specific practice which can be also used successfully in teaching secondary school. Put it differently, they have developed basic understanding of specific teaching techniques as a result of observing teaching of their teacher educators, which can go for C2.Paying attention to the clarity of the passages in the course Teacher educators who are making the overall goals and structure of their course transparent from the outset were perceived by student teachers as effective in promoting learning. In view of that, provision of course syllabus with details of its components has the power of influencing student teacher to monitor the progress of their learning as they know what, when and how they are going to learn and what would be their roles and responsibilities in the process:[…] he provided us the structure of the module in advance[…] and this allowed me to effectively organize the activities of study in advance, read resources, and make in-depth analysis of articles.[…] having course syllabus, the term I came to know very recently, is just like having the beginning and the end of the course in advance. I know what will happen in the classroom, which is useful in reducing anxiety and elevate my performance (C2).Teacher educators reported of making the structure of their course transparent including assessment methods and procedures reported as plausible way of inspiring learners. Here is the sample extract from student teachers’ reflection:[…] some professors have made clear from the start what would be the evaluation methods and evidences to be considered in determining success of performance. Knowing the final assessment and grids to be used as for evaluation is the most significant phases for a student. This allows each student to organize their work and not to be weary. Above all, no surprises that we all tried to give the best of us in course where the professor made us aware of all the paths we need to follow (C2).However, it seemed that a mere provision of detail course syllabus is not adequate in inspiring student teachers’ learning. Rather, student indicated that these professors were also smart in taking time and communicating orally the overall structure, assessment methods, procedures and criteria as of the start of the course: […] I noticed in all the teachers pay special attention to clarity of the course: they devoted more than a few minutes to explain the objectives of the modules, contents, study materials and explaining how to deal with the examination and how it would be structured (C2).In general, the professors who uncovered the overall structure of a module from the beginning are effective in letting student teachers inspired for their learning learners as learners easily recognize what they expect to do including when and how to do it. So, this is providing a cognitive map for students so that they will engage in activities that would allow them to hit the target required of them. In this case, the direction is gearing of student teachers to take a responsibility for their own learning which at least lead towards mastery of the concepts and skills to be taught (C2).Evaluation Evaluation is another new dimensional variation of teaching conception noticed in the reflection of student teachers on the teaching practices of their teacher educators, which they considered as valuable enough to facilitate their learning that in turn indicate the conception about teaching teacher educators hold. In view of that, practices related to student evaluation indicate the intention of teaching as a mere replication of what has been taught (C1) to at least leading student teachers to show optimal effort to learn for understanding on their own (C2).Wise use of PPT slidesStudent teachers indicated that educators’ use of PowerPoint assisted them in getting prepared for examination provided that such slides would inform specific areas where they need to focus on while preparing for examination.I found that provision of PowerPoint slides used during lesson was useful in preparing for examination. However, its usefulness is much more depending on the quality of the transparencies. Good transparencies are those that, although in the synthesis, have a fair degree of detail,[...] highlighting the most relevant content of the material and that can be used as a tool for revision in preparation for the final examination or tests (C1).However, educators’ provision of transparency paper with details of important key notes-usually underlined or written in different styles is assisting students to identify where to focus during their preparation for examination. In this process, the intention of the teacher is more on what he/she knows and expects students to master in the process of learning. This in turn tells student what they need to focus on and reproduce to pass the examination. For this reason, this teaching practice came under C1.Promoting ongoing self-evaluation Some teacher educators integrate student learning with assessment where students get opportunity to check their progress and reflect more in their learning process as a result of weekly deliveries provided for them. To illustrate:The weekly deliveries, reviews, comments given have opened a gap in your understanding and this gap made you to push further until you felt that you filled in. These deliveries assisted me to mark those activities I can perform easily and for those I need to refer further. In this way I am always ticking those areas I mastered well and other that I still need to do more (C2).Therefore, using weekly delivery for reflection assist learners to see deep into their learning in relation to activities they can perform and for which they still need to work hard. This definitely led to the personal understanding of the learning regarding the concepts and skills that have been taught (C2). However, it is difficult to determine if such activities result in challenging students’ learning (C3) as long as we are not sure if student have developed critical thinking abilities.Making evaluation criteria transparent Teacher educators who made their evaluation criteria and its procedure clear to student teachers from the start is reported by student teachers as effective in transforming their learning. Here is an example:[...] I understood how important it is to define precisely in advance the criteria for evaluation.[...] final assessment is a significant moment for the student and must be managed with care: I understand the importance of defining the criteria for evaluation, formulate clear criteria for the mark. As a student, I had never noticed while here, especially thanks to a teacher, I discovered the profound value of this moment as it assisted me to dig into to the detail until I realize that I can hit the goal set (C2). Therefore, as mentioned in the above quote, making evaluation criteria transparent to students is letting them take their learning seriously as they know what is expected of them.
3.3. Teacher Educators’ Practices in Relation to Teaching Conceptual Categories
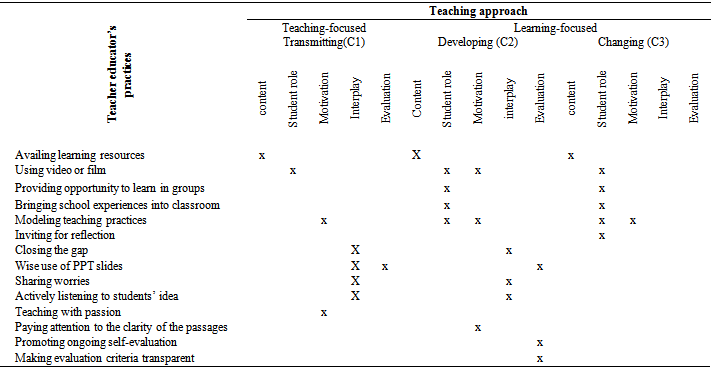
- As it is already indicated, exploration of teacher educators’ conception of teaching in the study was based on the teaching practices they have been exercising among which student teachers experienced as relevant for their learning as future teachers. Accordingly, fourteen different teaching practices have been identified (see table 1).
|
4. Conclusions and Implications
4.1. Conclusions
- Teaching practice that doesn’t transform student teachers learning is like planting a tree on a stone. It is obvious that a tree planted on a stone will dry soon as there is no way of getting nutrients that can sustain its life. In the same way, if student teachers don’t consider teaching of teacher educators as relevant for their current learning and later teaching, they won’t try it in their later teaching, hence, the practice will evaporate soon like that of the seedling planted on a stone. In line with this, we didn’t come up with any evidence from the analysis of lived experiences of student teachers that indicate the relevance of teaching conceptions of teacher educators as transmitting discipline’s basic information, which was identified in the previous studies as one of the conceptual categories of teaching. Apart from these, the study confirms the existence of the following conceptual categories in hierarchically related manner:• Teaching as transmitting teacher’s understanding of the discipline, • Teaching as developing students’ understanding,• Teaching as changing students’ understanding.In a similar way to the previous phenomenographic studies, the first teaching conception as transmitting teachers’ understanding of the discipline structurally belongs to teacher-focused approach while the remaining two go for learning-centered approach. They also appeared in hierarchical order in which the conceptual category found at the lower level is a prerequisite for the successful application of the subsequent category. In this case, realizing high level learning-focused teaching (challenging students’ understanding) by nature demands climbing up through the bottom ladders of conceptual categories though the turnaround doesn’t work[15]. Similarly, in the analysis of teaching strategies informed by the three instructional theories,[24] show that different teaching strategies required depending on the prior knowledge of the learners about the task and the nature of the learning task. In this case, learning by doing real activities in a real context (constructivist principles) demands students’ understanding of the concepts (cognitivist principle), which in turn is in need of first getting information from experts (behaviorist principle). Therefore, three levels of conceptual strategies seem essential for facilitating student teachers’ learning and application of the upper level demands the knowledge of the lower one, hence focusing on the top level is means of addressing the remaining conceptual categories.Coming to the dimensional variations, five have been identified as important characteristics based on which the three teaching conceptual categories distinguished from each other: student role, interplay, motivation, content and evaluation. Among these, the first three aforementioned points seemed more of the focus for teacher educators’ practice.Fourteen teaching practices have been identified as relevant strategies in facilitating learning of student teachers. Among these: modeling teaching practices, using video or film clips and availing learning resources used qualitatively in a different way across the three conceptual categories. Therefore, having of the same teaching practice implemented in a different way across the different level of conceptual categories witnessed not only the hierarchical relationship of conceptual category but also the relevance of all conceptual categories for the betterment of students’ learning.
4.2. Implications
- Student teachers’ reflections used for the study was based on teaching of professors facilitated common area courses: General pedagogies and special education, who have handled 25% of the overall programs. Therefore, for better understanding of teaching conceptions, dimensional variations and teaching practices entertained in teacher education program for the betterment of student teachers’ learning, conducting study based on student teachers experiences under instruction of subject didactic professors deem important.In this study, list of teaching practices useful for facilitating preparation of future teachers was identified. Thus, readers may draw generalization to their own context from descriptions provided for each practice. Moreover, integration of such practices into teacher education curriculum as well as professional development initiative for teacher educators seems relevant for the successful preparation of future teachers.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML