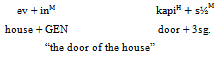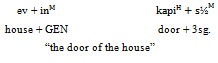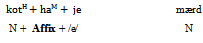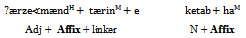A. Najibi 1, S. Olyaee 2, B. Modarresi 3
1School of e-Education, Shahid Rajaee Teacher Training University, Tehran, Lavizan, 16788-15811, Iran
2Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Shahid Rajaee Teacher Training University, Tehran, 16788-15811, Iran
3Foreign Languages Department, Islamic Azad University, Central Branch, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence to: S. Olyaee , Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Shahid Rajaee Teacher Training University, Tehran, 16788-15811, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
In this paper, different methodologies of teaching are presented including old teaching methods up to the newest one, which is e-teaching to learn second language (L2) grammar. This is important that how we can use different methodologies of teaching in the virtual environment. In this way, there is no teacher but there is an e-teacher who should use different methods to attract an e-student instead of a student. This paper will show that how the old methodologies can help this new learning with various examples. Of course computer can push us to the ways of teaching which are so novel and a student learns too many other things more than the main object. Instruction markedness grammar through this new method of learning is considered; one major point in grammar is morphological marking of grammatical relations, which may appear on either the head, or the dependent member of constituent. In this paper, different methods of teaching are support this grammar through web learning.
Keywords:
Teaching Methodology, E-Teaching, E-Learning, Virtual Environment, Markedness Grammar, Head-Marking, Dependent-Marking
Cite this paper:
A. Najibi , S. Olyaee , B. Modarresi , "Markedness Grammar Based On the Second Language Teaching Methodologies through the E-Learning", Education, Vol. 2 No. 7, 2012, pp. 356-360. doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20120207.20.
1. Introduction
Language teaching came into its own as a profession in the twentieth century and e-teaching is the newest method in 21 century[1]. This paper provides 10 methods of teaching second language specifically morphological marking of grammatical relations[2] and it will be compared with the newest method of teaching; E-teaching[3]. We want to find different techniques to use these old methods trough the newest one for learning second language. Because most of these methods are familiar, only summarize of their objectives and features are introduced here[4-7] as an example the grammatical relations to show markedness is presented. This paper is categorized as follows: in the next section different methods of teaching L2 (second language) with their objectives and features are presented. Then their advantages are discussed in section 3. A new method including the advantages of old methodologies with the newest one through web is also proposed. Markedness in Persian grammar is also discussed in section 4. The conclusions are drawn from this investigation is in the final section.
2. Teaching in Traditional Environment
2.1. Grammar-Translation Method
The Grammar-Translation Method is the oldest one, which has other different names as Church method, Classical method, and Lecture method. Teachers love it too much and students believe the teachers. Grammar is its base. L1 (first language) is a platform to understand what L2 is[3]. There are some objectives and features of this method which are listed as below: Objectives:Reading and translating are important;More understanding of L1 is possible;Develop mental discipline;Literary appreciation;Features:It is written form;Using mother tongue has not problem;Translation is important hear;There are bilingual list of words;Sentence is a unit of language;
2.2. Reading Method
Reading method is an internal skill, it is so easiest and cheapest way. Foreign culture is learned too, and the student is full of vocabulary[1].Objectives:Reading ability is tested;Knowledge about culture and history is developed;Features:Reading is based on the grammar;Vocabulary expanded;Great amount of reading is significant;Silent reading is important;
2.3. Direct Method
Direct method is completely opposite to grammar translation method (GTM). Communicate orally and more interaction is its attractiveness. It believes that direct contact can help students to learn L1[3].Objectives:Shifting from literary language to spoken communication;Features:Target language as means of instruction;Translation is forbidden;Inductive teaching of grammar;Culture + Language are instructed;Having partnership is important;Oral skills, listening and speaking is sufficient;Good pronunciation is practiced;
2.4. Audio Lingual Approach
Audio lingual approach is a scientific method. It is because of behavioristic psychology and structuralism. It is base on needs (scientific + usefulness)[3].Objectives:Natural process;It is theory- based;Oral skills are important;Features:There is no direct grammar;L1 has not placed here;There is no room for intellectual analysis;Listening and speaking are thought;Reinforcement is important;There is no room for errors;
2.5. Cognitive Methodology
Cognitive methodology is an effective method. It is highly depends on teachers and they can show if one method is good or not[4]. Objectives:This method is Controlled language in all its manifestation as a coherent and meaningful system through on acquired competence can be put in to use in real life situation;Teachers change some artificial to real things;Features:It is emphasis on communication;Language is acted as rule- formation process, not habit formation;Errors are welcome;Errors are tolerated;Meaningful learning as centre of learning;There are too many Exercises, no drills;Teachers are as facilitator;Contextualization is sufficient;Translation of L1 helps it;Bilingualism and biculturalism are happened;
2.6. Total Physical Response
Total physical response is kind of approach which deals with input and output. It is come from comprehension method and emphasizes on listening comprehension.Objectives:Teaching oral proficiency at beginning level is happened;Teaching basic speaking skill;Joyful experience is important;Features:Listening comprehension is very sufficient;Motor or physical activity helps to learn better;Sentences based on syllabus;Meaning base is the easiest approach;Stress free context is very useful;Fun is happened in learning;Oral language is useful;Readiness period is important;Teacher is a direction;Students are followers and imitators;
2.7. Natural Approach
Natural approach is a kind of direct method. It has slow rate, enough repetition and full of WH questions.Objectives:Helping students to communicate in L2 based on their needs and skills;Features:Quantity and quality of comprehensible input has been given;Vocabulary is thought by visual aides;Listening and reading are due to meaning based production;Learning is happened trough games;Topical and situational syllabuses are helped to learn better;
2.8. Community Language Learning
Community language learning is psychological learning and it is based on community. There is not teacher and upset.Objectives:Communication with native is like mastery;Oral communication is happened;Data are transferred from teacher to student;Features:Learning is facilitated in stress free condition;There is intimacy not isolation;Translation from L1 to L2 has not problem;Sitting circle in class is well come;There is counsellor- client relation;There is process- oriented relation;It is based on well fluency;Informal setting is happened;Student’s feeling is important;
2.9. Silent Way
Silent way is a method in which the class starts with no words. It is with colourful rods and charts. Teacher uses student mother tongue and only show things, then students will guess about it.Objectives:Teaching students how to learn language;Learning theory of languages is important;Features:Learning is happened trough silent way;Producing sounds is on the part of students;Colours and rods in class are used;Thinking then telling is important;There is silent period;Repetition is practice very little;Errors are important here;There is no homework;Teacher is an assistant, student is an autonomous;
2.10. Suggestopedia
Suggestopedia is a method with no pain and gain a lot. Learning is forgetting. Objectives:Advanced conversational proficiency is approached;Quick advancement and creativity is happened;Vocabulary memorization is gained;Features:Music is used;Close interaction like face to face is important;There is great authority;Natural communication is happened;There is minimal homework;Fluency and new identity are sufficient;There is no formal memorization;Fun is well come;There is no error- correction;Culture is transferred trough learning;
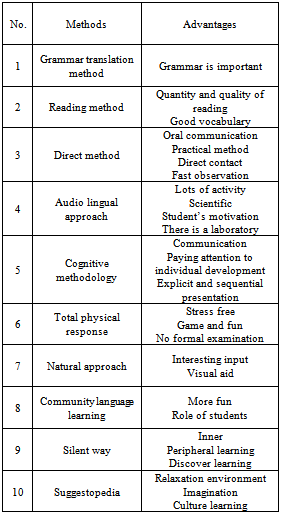
3. E-Teaching in Virtual Environment
As reviewing these methods, we can see that all of them are usable in virtual environment. For example teaching second language grammar trough web, can put different bottom for the e-student, thus he/she can choose each methods that enjoy it more. It is completely depends on the characteristics of the e-students and of course maybe only vocabulary is the reason of learning the second language for e-student. Thus, he/she can choose the oldest method of teaching which GTM was. If communication and interaction are important, the direct method or community language learning is suggested. Different methods have advantages and disadvantages. A knowledgeable e-teacher can use the advantages of these methods, to present the perfect method of learning L2 through web. Now the usable advantages of them are listed in Table 1.Therefore, an intelligence e-teacher by applying different equipments and using these advantages of ten methods and with sharing them can create a site or web log for e-students who want to learn L2 easily, deeply, and quickly.Although one of the advantages of e-learning is that there are too many instruments which we can use them in the web and trough these various devices, the e-student can learn L2 easier than before. As shown in Fig.1, there are some shared environment between old methods and new one, that here are denoted as Teacher Control and Learner Control[8].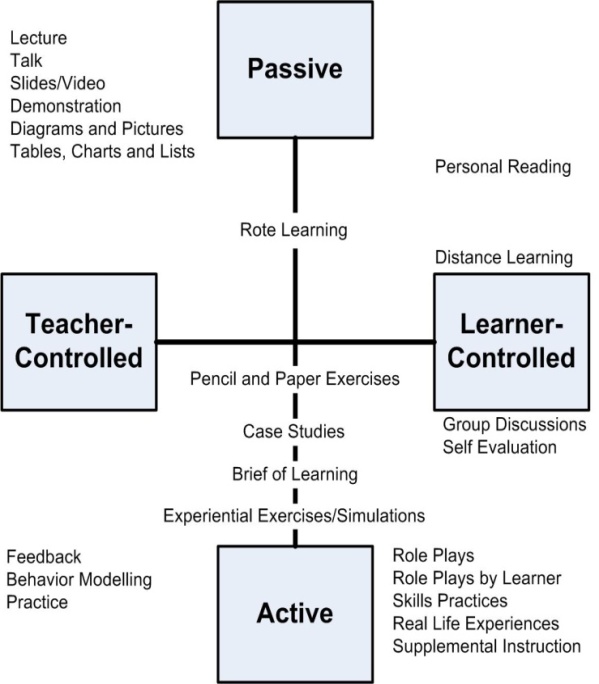 | Figure 1. Teaching Methodologies Matrix |
4. Morphological Marking of Grammatical Relations
As an example, the subject of markedness in grammatical relations in Persian language discussed here. This topic is not familiar to the students, so it can be taught trough formal class or e-environment and fined their advantages.Unfortunately, this subtitle of grammar has not been considered in Persian; this topic can be instructed very easy by these teaching methods if they add to the newest one.In all those teaching methods, grammar is taught; but they focus on learning second language for communication, not for comparison and find the relationship between languages. Two important goals are gained by the new method of teaching trough web as learning second languages for communication and finding relations.As an example, finding head and dependents in a phrase is very easy by students; if some softwares are used through web, then by practicing and playing with words in the phrase, the affixes which add to them are found. Then the possibility of its meaning and correcting of its grammar can be tested by replacement them in different words. In real classes there is not enough time and instruments to do that, but in virtual classes everything can be possible by simulation.Head or dependent are subjects, which are very familiar to students, and they have been discussed in every clauses or phrases; but the relations between these two elements are mystery use. Nichols[2] investigated about these phenomena through 90 languages in the world; she arranged eight different groups and brought different examples of separated languages, and labeled them as head-marked, dependent-marked, double-marked, neutral-marked and non-marked. Example 1 shows that an affix, /e/ is added to the Noun. /mountain/ has not affix, itself. /e/ can be said as markedness, but really it does not show any marking but shows that an NP will come after it. Example 2 illustrates the markedness briefly in Turkish.Table 1. Usable advantages of teaching methods in L2
 |
| |
|
Example 1. Affix /e/ in Persian
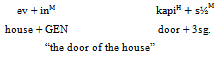 |
| |
|
As denoted in Example 2, the affix /in/ is added to the /ev/, which is the dependent and the affix /s/ is added to the /kapi/, which is the head of the phrase. So here, both head marking and dependent marking is happened at the same time, so it is called double marking. Now in Persian, there are seven groups, as Noun Phrase, Possessive phrase, Adpositional Phrase, Attributive Phrase, Adverb Phrase, Verb Phrase, and Clauses.Example 1 is for Noun Phrase. As shown, the affix /e/ is added to the head. Example 3 describes another possibility of this affix.Example 2. Double marking in Turkish
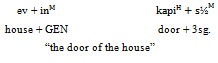 |
| |
|
Example 3. Linker in Persian
 |
| |
|
Example 4. Head-marking in Persian
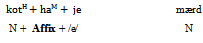 |
| |
|
Example 5. Dependent-marking in Persian
 |
| |
|
As shown, another word, /Damavænd/ is added to the phrase and the affix /e/ is added to the second word as a dependent. Therefore, /e/ can be added to the head or dependent at a same time but it cannot be named as double marking. It has no marking. In Persian this affix is called as ‘linker’.Head marking in Persian takes place in NP. The affix /ha/, /at/ and /an/ are added only to the head. In Example 4, a head-marking in Persian is displayed.Dependent marking in Persian takes place in Adjective Phrase. The clitics are added only to the dependent. Example 5 describes a dependent marking in Persian.Double marking in Persian takes place in Adjective Phrase. The affix /tær/ and /tærin/ are added to the head and at the same time the affix /ha/ is added to the dependent. In Example 6, a double marking in Persian is denoted.The makedness grammar can be analysis through all languages by preparing a web program. By composing the teaching methods with web, learning a second language is definitely easier than the old methods.Example 6. Double marking in Persian
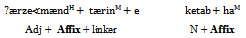 |
| |
|
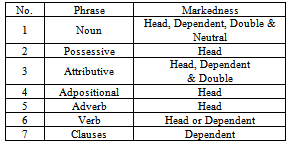
Table 2. Markedness in Persian phrases
 |
| |
|
5. Conclusions
√ Communication; √ Culture learning;√ Direct contact;√ Discover learning;√ Explicit and sequential presentation;√ Fast observation;√ Game and fun;√ Good vocabulary;√ Grammar is important;√ Imagination;√ Inner;√ Interesting input;√ Lots of activity;√ More fun;√ No formal examination;√ Oral communication;√ Paying attention to individual development;√ Peripheral learning;√ Practical method;√ Quantity and quality of reading;√ Relaxation environment;√ Role of students;√ Scientific;√ Stress free;√ Student’s motivation;√ There is a laboratory;√ Visual aid; …A skilful e-teacher can design these advantages for four skills as listening, speaking, reading, and writing. These methods can be improved by a programmer who knows L2 teaching through web and he can use some of these advantages depends on each skill.As an example, one of the absolute topics as markedness grammar has been discussed very shortly to show the advantages of this new method and this topic has been shown the variety of the Persian language. Table 2 gathers the overall view of markedness in Persian.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Dr. Motallebzadeh for his impressive aids.
References
| [1] | Richards J. C. and T. S. Rodgers, “Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching”, 2nd, Cambridge University Press, 2001. |
| [2] | Nichols J., “Head-Marking and Dependent-Marking Grammar”, JSTOR, Linguistic Society of America, Vol. 62, No. 1, (Mar1986), pp. 56-119. |
| [3] | Freeman D. Larsen, “Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching”, Oxford University Press, 1986. |
| [4] | Murcia M. Celce, “Teaching English as a Second or Foreign Language”, 3rd, Heinle Press, 2001. |
| [5] | Ellis R., “Task-Based Language Learning and Teaching”, Oxford University Press, 2003. |
| [6] | Najibi A. and S. Olyaee, “Analysis Terminologies used in Field of E-Learning with their Persian Translations”, International Conference on E-Learning & Teaching, Iran University of Science and Engineering, Tehran, Iran, pp. 1-4, December 9-10, 2009. |
| [7] | Najibi A. and S. Olyaee, “Investigation of Effectiveness Parameters on the Evaluation of the E-Content Production through Maximal Usage of Persian Words”, International Conference on E-Learning & Teaching, Iran University of Science and Engineering, Tehran, Iran, (In Persian), pp. 5-10, December 9-10, 2009. |
| [8] | http://www.londonmet.ac.uk/deliberations/seda-publications/spencer.cfm, Accessed April 2010. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML