-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Education
p-ISSN: 2162-9463 e-ISSN: 2162-8467
2012; 2(7): 220-226
doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20120207.01
The Balance Score Card for the Design and Validation Instrumens to Measure the Academic Teachers´s Achievement and Performance
Alexis Tejedor De León 1, José Manuel Huertas 2
1Department of Materials and Metallurgy, Centro Regional de Veraguas, Universidad Tecnologica de Panama, Santiago de Veraguas, P.O. Box 00923-0074, Panama
2Department of Agricultural Education, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences, University of Puerto Rico, Mayagüez Campus
Correspondence to: Alexis Tejedor De León , Department of Materials and Metallurgy, Centro Regional de Veraguas, Universidad Tecnologica de Panama, Santiago de Veraguas, P.O. Box 00923-0074, Panama.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The evaluation of faculty work is critical for the university accreditation. Moreover, particularly sensitive to this related tendency of faculty work evaluation; it is necessary to go beyond the knowledge factor and concentrating more in the degree of satisfaction of the stakeholders included in the process of university education. In this context, this research aims to design and validate the instruments directed to explore the internal academic environment of the faculty at the Centro Regional de Veraguas, Universidad Tecnologica de Panama; considered as dimensional axes to the organization, development, and the psycho-pedagogic properties of academic work. For the present research, the BSC methodology was used in different stages of strategic planning and program evaluation. The Delphi technique was used to validate the content and the construction of the instruments. The validation of the reliability value was established by the Cronbach's alpha value by using the SPSS for analysing the data.
Keywords: Balanced Score Card, Delphi Technique, Reliability, Validation, Cronbach´s Alpha
Cite this paper: Alexis Tejedor De León , José Manuel Huertas , "The Balance Score Card for the Design and Validation Instrumens to Measure the Academic Teachers´s Achievement and Performance", Education, Vol. 2 No. 7, 2012, pp. 220-226. doi: 10.5923/j.edu.20120207.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In general terms, the University can be defined as an integrated structure, formed by different units, able to contribute to the generation of human resources in quantitative and qualitative terms, necessary for life and progress of society as a whole. Thus, institution of higher learning can be defined as the structure formed by formal teaching, non formal (dissemination or divulgation) and research. The desired outcome is to improve the quality of life of graduates and society as a whole, and to generate human beings able to sustain themselves, who can excel in life and participate fully in the society‘s progress.Likewise, Faculty activities must be performed under complete academic freedom. In that context, each student will benefit to the maximum extent of the academia.Universidad Tecnologica de Panama was founded in 1981, and the National Center of Veraguas, located in the Pan-American road, whose location has coastline on both the Pacific and Caribbean oceans, was established in 1991.Since 2004, the Campus is offering a total of 99 careers, including one Doctoral and 20 Master Degree programs, and this institution has a population of over 14,000 students, including locals and foreigners. In 2004, the University began adopting the College Standard International Admission Policy, which is based on the Puerto Rico’ College Board. From the view of the community and society in general, the education offered by the University seems like the most powerful tool for achieving individual and collective capabilities. By the same token, the institution is also open to innovations, critical thinking, progress and the search for the truth.At the same time, the University is also conservative in regard to preserving their academic styles[1].Nowadays, Faculty members perform not only the traditional practice of adoption and management of analytical tools by the students, but also a new conception of the academic formative process that focus in the student’s learning process[2].There is not doubt that the accelerated transformations that are currently taking place in the world, are putting pressure in higher learning institutions to have more flexibility in their structures, processes and activities, like it is happening in different service’s organizations[3].Although one of the most researched aspects of the academia was the faculty evaluation, until recently, the outcome of the university teaching-learning process was attributed as one of the aspects to be defined[4].Therefore, it is imperative for Higher Learning Institutions to count with an integrated and accurate evaluation system that can measure results of the academic process. At the administrative level, as the recognition of the importance and the necessity of incorporating an evaluation and assessment system into the university teaching-learning process grow, provisions must me made to include professional improvement, and development of the evaluated faculty integrated into the evaluation system. The process should include elements for the process of reflection, decision making, and the achievement of the objectives. Diverse models and methodologies have been proposed to respond to such challenges.The topic of design and validation of instruments have been the object of scientific studies of certain in-depth and relevance.However, one of the greatest dilemmas of Latin American universities is the availability of instruments that reflect with a high degree of accuracy the result of the academic performance as a tool for decision making.Despite the fact that the application of structured methods of strategic support at the entrepreneur level has been widely disseminated, such as the BSC–The Balance Scorecard–[5], with all characteristics as a tool to provide direction to the managerial tasks[6],[7], its use in the academic environment have been scarce and divergent with the diagnostics of the educational process that shows a great need of improvement in the university processes[8].As opposed from previous approaches, Reference[9], suggests a progressive development of the strategic planning in the context of the academic process based in the organizational learning and decision making[10].Currently, due to the wide use of scales, following the directions of the “Cuadro del Mando Integral” by the Spanish anachronism of CMI, the objective of this article is to apply and review in a simple way, the concept of internal consistency and the interpretation of the coefficient of Crobach’s Alpha, based on the design and validation of instruments for exploring the internal environment of the Faculty members at Centro Regional de Veraguas, of Universidad Tecnologica de Panama. The mentioned approach is focusing in the Planning, Development and the Faculty Activities inherent to their academic duties.
2. Materials and Method
- The present research presents three (3) phases: (i) elaboration of the BSC - CMI, (ii) instruments design and (iii) procedures for validation of instruments.
2.1. Elaboration of BSC - CMI
- The methodology suggested by Reference[11], was followed for implementing the Initial Faculty Evaluation Program for the Academic Achievement or “Programa Inicial de la Evaluación del Desempeño Académico Docente” by the Spanish anachronism of (PIEDAD) at Centro Regional de Veraguas, of Universidad Tecnologica de Panama.At this stage of the research, a set of strategic indicators were defined. A system of information was designed in order to analyze the links among research, mission, long-term vision, intermediate term and short term of PIEDAD. The same author’s citated, point out the definitions of three matrixes: strategic, evaluation of external factors -MSEF, and evaluation of internal factors-MSIF.
2.2. Instruments Design
- The stage of design was developed to satisfy the need for the availability of simple instruments than can be standardized. Instruments must contain the academic environment of the Faculty members in their academic endeavours. They should consider the three (3) main focus of the evaluation process: Evaluation, Self-evaluation and Co- evaluation.The inventory for collecting the information for the instrument’s design was based on the existing documents available at Universidad Tecnológica de Panamá and other universities. The aspects relevant to the academic dimensions to be evaluated were selected. The dimensions considered for the construction of the instruments were identified in several reference sources and were three (3). From the available inventory, a number of items were written according to the corresponding standards.Additionally, stakeholders were included in the process. From both sources, a list of questions was prepared, related to the academic responsabilities of the Faculty personnel.The instruments were written in past tense, in the first or third person singular, with analogies pertinent to the academia. The listing of dimensions was as follows: Planning Dimension: Includes the statements related to the academia planning tasks, including course plan and the communication with students. Development Dimension: Includes situations related to the subject matter during the academic, derived from the organization and classes’ preparation until thecommunication to students.Activity Dimension: Includes activities related to the teaching and learning process used by Faculty to achieve their academic goals and objectives, including references utilized, evaluation methods proposed, and the utilization of alternative teaching methods and pedagogical resources.
2.3. Validation Procedure
- This stage had two steps: (i) Conceptual and Construct Validation and (ii) the Validation of Consistency or Reliability. Table 1 presents different stages of the validation process, which contain different tools in the design of instruments to evaluate the academic achievement of faculty members. SPSS package for the PC was used to generate the consistency or reliability of the instruments.
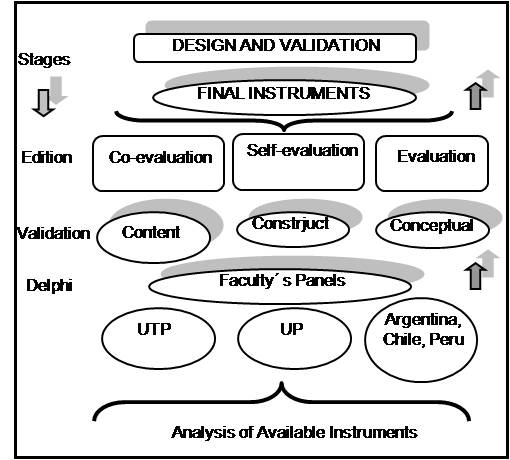 | Figure 1. Summary of the methodology utilized for the design and validation of instruments regarding the academic achievement of faculty members |
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Development of SBC - CMI
- The first stage in the construction of integral control was the revision or construction of the Strategic Frame, which was the analysis and definition of the Mission and Vision of PIEDAD.In the next stage, stakeholders were defined to include academic departments, Faculty members and students, and the responsible for the implementation of the evaluation, Co-Evaluation and Self-evaluation of the academic roles performed by the Faculty personnel at Universidad Tecnologica de Panama, Centro Regional de Veraguas.Based on the information collected in the diagnostics of SOWT (Strengths, Opportunities, Weakness and Threats), and considering the importance of the external environment for its implementation, the matrix was elaborated.The methodology of CMI recommends comparing the value obtained in the MSEF with an average value of (2.5) after analyzing the results. In this research, the value obtained in the MSEF matrix was of 1.37, which was below the desirable value. Thus, the value for the external environment was not appropriate for the PIEDAD implementation.The mentioned output allowed determining the minimum needs required to implement PIEDAD; -needed resources –infrastructure, humans and financial resources for its implementation, and the availability of Evaluation, Co-evaluation and Self-evaluation instruments scientifically designed and validated.The value for the internal environment was also included in the matrix –MSIF-, which allowed determining the internal capacity of the organization to confront the external environment and allowed the achievement of the mission and the survival of the organization.Likewise, following the methodology, it is recommended to determine the value of the Matrix to be included in the MSIF and comparing with the average (2.5). The calculated value for the internal environment was 2.65. Thus, internally, the organization and their stakeholders are ready to implement PIEDAD with very good possibilities of success
3.2. Content and Construct Validation
- Universidad Tecnologica de Panama–UTP–has been using the traditional evaluation model of assessing the faculty achievement, based only on students input. The evaluation form is collected on line.The analysis of the existing instruments from internal records, from others in-country universities and from additional Latin American countries, were utilized as background information for the design of instruments. Nevertheless, only instruments related to academic achievement of faculty were considered. Extension, Administration and Research related instruments were not considered.For the content and construct validation, a consensus technique was used to reach a consensus in six (6) sessions. Sessions were used to revise the proposed instruments. Faculty participated in the sessions.In each session, recommended modifications were incorporated, including the inclusion of new sentences or the allocation of the different dimensions of the academia. Out of 110 sentences originated, 78 propositions were approved.Finally, for the three structural components included in the content and construct validation, the number of statements for each component were as follow: 33 statements for the instrument of Evaluation; 33 for the instrument of Co-evaluation and 12 statements for the instrument of Self-evaluation.
3.3. Reliability Evaluation
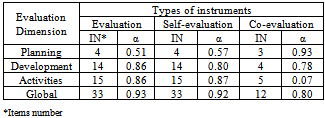
- For obtaining the reliability index, a total of 218 subjects participated. A total of 165 faculty members (75.7%) answered self administered instruments, and those were included in the data analysis process. The global internal consistency of the three instruments was satisfactory, with a Cronbach’s Alpha coefficient ranging from 0.926 to 0.917 for the instruments of Evaluation and Self-evaluation respectively. Likewise, the instrument of Co-evaluation obtained a Cronbach Alpha index of 0.804. Table 2 summarized the reliability coefficient index obtained for the instruments self –administered and their respective dimensions (Planning, Development, Educational activities, and type of instrument (Evaluation,Co-evaluation and Self-evaluation).
|
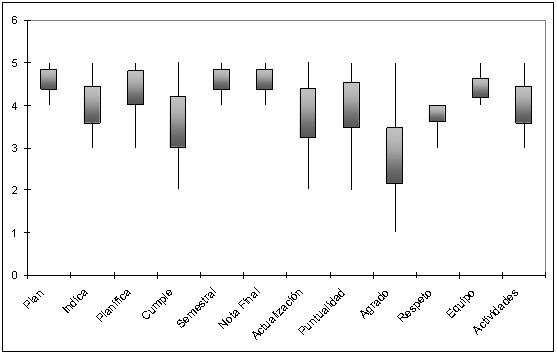 | Figure 2. Box & Wisker Plot Graph, for the items of the instrument of Co-evaluation |
3.4. Implementation: Lead Scale
- In order to implement the institutional level PIEDAD conducted a pilot study involving 65 teachers, with their students and their academic coordinators respectively. Teachers were randomly selected as the subject for bids in the corresponding semester of implementation. In this case, it was First Semester 2011.After applying the three instruments, we proceeded to analyze the results, to know, for example, which of the three dimensions, the teacher is "weaker" and how it was assessed both by his students, for their respective coordinator.Data were graphed and for one of the teachers, the results are presented in the figures below.
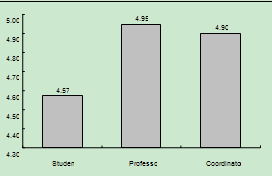 | Figure 3. Column Graph, overall weighting for the estate |
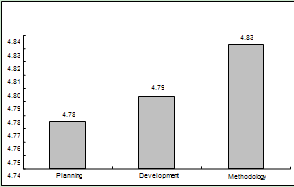 | Figure 4. Column Graph, for final Academic average for axle |
4. Conclusions
- The present study had the following outcomes:• During all the research process for validating evaluation’s instruments, the Management of the process was done with a great deal of rigor, in reference to the techniques (CMI, Delphy technique, and the determination of Alpha Value), during the different situations presented during the research’s development• Three evaluation instruments were designed in order to collect information with a high degree of accuracy, to measure the academic achievement of faculty personnel at Universidad Tecnológica de Panamá, at Centro Regional de Veraguas. The compiled information was very relevant, due to the scarcity of valid and reliable instruments in the area, not only in Panama, but also in many higher education institutions in Latin-American countries, and in universities corresponding to industrialized societies. Presently, very few instruments addressed the three main areas of faculty assessment: Evaluation, Self evaluation and Co-evaluation.• The main goal of the research was to achieve: the generation of useful instruments designed to evaluate the academic achievement of the faculty at Universidad Tecnológica de Panamá, Centro Regional de Veraguas. • The advantage of the availability of scientifically validated instruments make possible to detect the strong and weak points of the university teaching process and the availability of the tools to improve them.• Findings will allow more evidence to the discussion of the strengths and weakness of the planning, development and the methodology strategy used by faculty personnel.• One of the strength’ of the evaluation process was the utilization of the strategic planning based on the information collected in the diagnostics of SOWT(Strengths, Opportunities, weakness and threats) and the importance of considering the internal and external environment. • In this study, Stakeholders were defined to include academic departments, Faculty members and students, and the responsible for the implementation of the evaluation, Co-evaluation and Self-evaluation of the academic roles performed by the Faculty personnel at Universidad Tecnológica de Panamá, Centro Regional de Veraguas • Cronbach’s Alpha scales were used for evaluating reliability and consistency index of the three dimensions: Planning, Development and Academic Activities; and for the three types of instruments: Evaluation, Self-evaluation and Co-evaluation ; and the definitions of three matrixes: strategic, evaluation of external factors -MSEF, and evaluation of internal factors-MSIF.
References
| [1] | M. MARTÍNEZ, M. R. BUXARRAIS, F. F. BARRA La Universidad como espacio de aprendizaje ético. Organization of Iberoamerican States for Education, Science and Culture (OEI), Revista Iberoamericana de Educación, vol. 29, pp. 17 – 42, 2002 |
| [2] | M. A. PEREYRA, A. L. TRUJILLO, D. S. MERINO. Las universidades europeas y el proceso de construcción del espacio europeo de educación superior: limitaciones y perspectivas de cambio. Spanish Society of Comparative Education, Revista Española de Educación Comparada, vol. 12, pp. 113 – 143, 2006. |
| [3] | M. CHAUI. A universidade pública sob nova perspective. National Association of Post Graduate Studies and Research in Education – Brazil-, Revista Brasileira de Educação, vol, 244, pp.5 -15, 2003 |
| [4] | P. PÁRAMO. Factores psicosociales asociados a la evaluación del docente. Faculty of Education at the University of La Sabana – Colombia-, Educación y Educadores, vol, 11, n° 1 pp. 11 – 30, 2008. |
| [5] | R. KAPLAN, R., D. NORTON, D. The Balanced Scorecard: measures that drive performance. Harvard Business Scholl Publishing, Harvard Business Review, pp.71 – 79, 1992. |
| [6] | M. MARTINSONS, R. DAVISON, D. SE. The balanced scorecard: a foundation for the strategic management of information systems. Elsevier Publising, Decision Support Systems, vol. 25, pp. 71 – 88, 1999 |
| [7] | G. LAWRIE, I. COBBOLD. Development of the 3rd generation balanced scorecard: evolution of the balanced scorecard into an effective strategic performance management tool. Berkshire, Active Management, vol. 1, n° 1, pp. 1 – 15, 2002 |
| [8] | J. BUSTOS, M. ZAPATA, M. T. RAMÍREZ-VALDIVIA. Más allá de la gestión estratégica en educación superior: aplicación del Cuadro de Mando Integral. School of Management and Economics of the Catholic University Cardenal Raul Silva Hernández – Chile-, Revista OIKOS, vol. 12, n° 26, pp. 98 – 114, 2008 |
| [9] | M. J. DOORIS. Two decades of strategic planning. Is strategic planning a useful tool or a counterproductive management fad?. Society for College and University Planning, Planning for Higher Education, vol. 31, n° 2, pp. 26 -32, 2003 |
| [10] | BASTIDAS, Z. MORENO. “El Cuadro de Mando Integral en la gestión de las organizaciones del sector público: el caso Universidad Centroccidental Lisandro Alvarado”, Accounting Post Graduate Program at the Universidade Regional de Blumenau (PPGCC / FURB), Brazil, Revista Universo Contábil vol 2, n° 3, pp. 104 – 118, 2006 |
| [11] | J. T. NEGRE, C. V. URIETA. El cuadro de mando integral en la administración pública: el caso del Ayuntamiento de Sant Cugat del Vallès. In: INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF CLAD, 8, 2003, Panamá. La Reforma del Estado y de la Administración Pública. pp. 1 – 13, 2003 |
| [12] | G. A. CABRERA-ARANA, J. L. LONDOÑO-PIMIENTA, L. D. BELLO-PARÍAS. Validación de un instrumento para medir calidad percibida por usuarios de hospitales de Colombia. Faculty of Medicine, Universidad Nacional de Colomiba – Colombia -, Revista de Salud Pública, vol. 10, n° 3, pp. 443 – 451, 2008 |
| [13] | J. A. PIÑA-LÓPEZ (2003).Validación de un instrumento para medir competencias conductuales en personas VIH positivas. Nacional Public Health Insitote – Mexico -, Salud Pública de México, vol. 45, n° 4, pp. 293 – 297, 2003 |
| [14] | F. DE LA PEÑA, M. PATIÑO, A. MENDIZABAL, J. CORTÉS, E. CRUZ. La entrevista semiestructurada para adolescentes (ESA): características del instrumento y estudio de confiabilidad interevaluador y temporal. National Institute of Psychiatry Ramón de la Fuente Muñiz – Mexico -, Salud Mental, vol. 21, n° 6, pp. 11 -18, 1998 |
| [15] | J. M. CORTINA. What is coefficient aplha? An examination of theory and applications. American Psychological Association, Journal of Applied Psychology, vol. 18, n° 1, pp. 98 – 104, 1991 |
| [16] | N. SCHMITT. Uses and abuses of coefficient alpha. American Psychological Association, Psychological Assessment, vol. 8, n° 4, pp. 350 – 353, 1998 |
| [17] | NUVIALA, A.; TAMAYO, J.A.; IRANZO, J., & FALCÓN, D. (2008).Creación, diseño, validación y puesta en práctica de un instrumento de medición de la satisfacción de usuarios de organizaciones que prestan servicios deportivos. Revista Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación., (14), 10 – 16. |
| [18] | R. BROCKMANN, S. CAUSSADEL, N. L. HOLMGREN, F. PRADO, B. REYES, P. VIVIANI, P. BERTRAND, P. “Actividad física y obesidad en niños con asma”, Revista Chilena de Pediatría, Journal of the Chilean Society of Pediatrics, vol. 78, n° 5, pp. 482 – 488, 2007. |
| [19] | CHIA-CHINE, H., & BRIAN, A. (2007) The Delphi Technique: making sense of consensus. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 12 (10), 1 – 8. |
| [20] | MARTÍN MORENO, C. (2007). Metodología de investigación en estudios de usuarios. Revista General de Información y Documentación, 17 (2), 129 – 149 |
| [21] | DOBBIE, A.; RHODES, M.; TYSINGER, J.W., & FREEMAN, J. (2004). Using a modified nominal group technique as a curriculum evaluation tool. Family Medicine, 36 (6), 402 – 406. |
| [22] | POTTER, M.; GORDON, S., & HAMER, P. (2004). The nominal group technique: a useful consensus methodology in physiotherapy research. NZ Journal of Physiotherapy, 32 (3), 126 – 130. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML